1st Bio exam for Appstate Professor Chialvo
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:23 AM on 9/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
1
New cards
(How is something considered living through the cell theory.) What is the thing made up off
all living things are made up off cells
2
New cards
(How is something considered living through the cell theory.) can't be man made
Those cells came from preexisting cells
3
New cards
(How is something considered living through the cell theory.) the cells must be able to have...
energy flow in the cell (metabolism)
4
New cards
(How is something considered living through the cell theory.) Must have what stored in cell that can be passed down
genetic info stored in the cell that can be passed down to other cells
5
New cards
(Function of eukaryotic structures) Nucleus
regulates all activity/behavior of the cell
6
New cards
(Function of eukaryotic structures) ER
local transport of materials
7
New cards
(Function of eukaryotic structures) Golgi body
packaging/tagging/transporting of materials out of the cell
8
New cards
(Function of eukaryotic structures) Mitochondrion
supplies chemical energy (ATP) to the cell
9
New cards
(Function of eukaryotic structures) Lysosomes
recycle old cellular material and also destroys pathogens
10
New cards
(Function of eukaryotic structures) Peroxisomes
digest and breaks down cellular material; neutralize reactive oxygen compounds
11
New cards
(Function of eukaryotic structures) ribosomes
manufacture proteins
12
New cards
(What properties does the cell membrane have?) selective permeable
can decide what comes in and out of a cell
13
New cards
How is the cell membrane put together? phospholipid bilayer
the O likes to
water the tail doesn't. put two together and it makes a phospholipid bilayer
water the tail doesn't. put two together and it makes a phospholipid bilayer
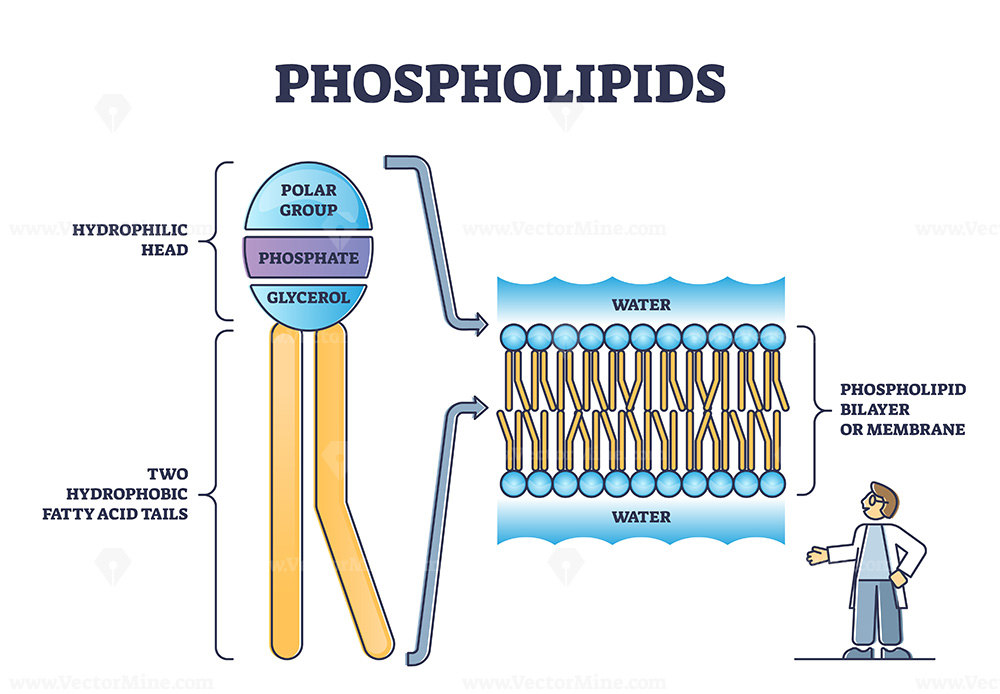
14
New cards
(What properties does the cell membrane have?) transport/transmembrane proteins
helps with movement of materials
15
New cards
What is concentration gradients
there is an area of high concentration and low concentration; as a result, the molecules will move from high to low (moving down)
16
New cards
(Cellular transport) passive transport/diffusion
small molecules are going to move across the membrane without transport or energy (moving down)
17
New cards
(Cellular transport) facilitated transport
large molecules are going to move across the membrane with the assistance of transport proteins but without the need for energy (ATP) (moving down)
18
New cards
(Cellular transport) active transport
large molecules are going to move across the membrane with the assistance of transport proteins and the use of energy (ATP) (moving Up)
19
New cards
(Predict the movement of water based on tonicity) hypotonic
the outside of the cell has a lower concentration of solute than inside the cell (water is going to enter the cell)
20
New cards
(Predict the movement of water based on tonicity) hypertonic
the outside environment has a higher concentration of solute than the inside of the cell (water is going to leave the cell)
21
New cards
(Predict the movement of water based on tonicity) isotonic
same inside the cell as the outside (water is going to flow back and forth at an even rate)
22
New cards
step one of cellular signaling
signaling ( carries by a ligand)
23
New cards
step two of cellular signaling
reception (bind to a receptor)
24
New cards
step three of cellular signaling
transduction (relaying of the message via chemical messengers)
25
New cards
step four of cellular signaling
response (cell performs the action given by the ligand)
26
New cards
positive feedback loops
trying to increase the frequency or intensity of stimulus
27
New cards
negative feedback loop
trying to decrease the frequency or intensity of stimulus
28
New cards
stimulus
the environmental factor that is felt or sensed
29
New cards
sensors
the cellular components which detect/sense the stimulus
30
New cards
integrator
the body part that takes in sensory info and cause a response
31
New cards
effector
the things that have an effect on the stimulus
32
New cards
Cellular division- chromatin
loose form of DNA present during cellular division
33
New cards
Cellular division- Chromosomes
highly condensed form of chromatin
34
New cards
Cellular division- Sister chromatid
identical, copied chromosomes that are connected in the middle
35
New cards
Cell Cycle- G1
Absorbs all things necessary for division and then checks inside and outside the cell if it is appropriate for the division
36
New cards
Cell Cycle- S
Duplicate our DNA
37
New cards
Cell Cycle- G2
Duplicates the organelles and checks for DNA copying errors
38
New cards
Cell Cycle- Mitotic
The cell then divides into two daughter cells, each receiving one copy of the doubled material. The mitotic cycle is complete when each daughter cell is surrounded by its own outer membrane.
39
New cards
What is the importance of checkpoints in the cell cycle.
to insure the division process runs smoothly
40
New cards
what is the impact of cancerous tumors on the human body?
-cells within the tumor do not function properly
-cancer leech nutrients from other cells
-cancer leech nutrients from other cells
41
New cards
(What genes are responsible for preventing cancer? What are their functions?) proto-oncogenes
regulates the speed of division. If mutated, the cell will divide as fast as they can
42
New cards
(What genes are responsible for preventing cancer? What are their functions?) tumor suppressors
enforce checkpoints. If mutated, the cell does not stop at any checkpoints
43
New cards
(What genes are responsible for preventing cancer? What are their functions?) DNA repair genes
fixes mutations. If mutated, mutations do not get fixed
44
New cards
(treatments for cancer) surgery
the surgeon removes cancer, usually along with some healthy tissue around it. Removing this healthy tissue helps improve the chances that all cancer has been removed.
45
New cards
(treatments for cancer) radiation
works by making small breaks in the DNA inside cells
46
New cards
(treatments for cancer) chemotherapy
damages the genes inside the nucleus of cells.
47
New cards
(treatments for cancer) targeted therapy
blocking cancer cells from copying themselves.
48
New cards
(treatments for cancer) immunotherapy
stimulating the immune system