AQA A Level Biology - Respiration
1/45
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is the purpose of respiration ?
To release energy from glucose
To produce ATP
What is the general equation for aerobic respiration ?
6O2 + C6H1206 --> 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy
What do plants need energy for ? (name 5)
1. Photosynthesis
2. Active transport of minerals via roots
3. DNA replication,
4. Cell division,
5. Protein synthesis
What do animals need energy for ? (name 6)
1. Muscle contraction
2. Maintaining a constant body temperature
3. Active transport
4. DNA replication
5. Cell division
6. Protein synthesis
What is the chemical name for ATP?
Adenosine triphosphate
What are the 3 components of ATP?
1 molecule of adenine
1 molecule of ribose
3 molecules of phosphate ions
How is ATP formed?
Condensation reaction between adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi)
Catalysed by ATP synthase
Which enzyme catalyses the condensation reaction between ADP and Pi ?
ATP synthase
What is phosphorylation ?
Adding phosphate to a molecule
How does ATP move through the cell ?
Diffusion
Which enzyme catalyses the hydrolysis of ATP ?
ATP hydrolase
What are the 6 properties of ATP ?
1. Stores and releases small amount of energy so none wasted as heat
2. Small, soluble molecule so easily transported
3. Easily hydrolysed so energy releases instantly
4. Quickly resynthesised
5. Make other molecules more reactive (phosphorylation)
6. Can't pass out of cell so immediate energy supply
What is the compensation point ?
The level of light intensity (in plants) where the rate of respiration and photosynthesis are the same
How could you find a plant's compensation point ?
Plot a graph of light intensity against net oxygen production
Find the light intensity when net oxygen production =0
What are 3 differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration ?
1. Aerobic uses oxygen, anaerobic doesn't
2. Aerobic has 4 stages, anaerobic just has glycolysis
3. Aerobic produces CO2 and H2O, anaerobic produced lactic acid (animals) and ethanol (yeast)
Where does glycolysis occur ?
Cell cytoplasm
Which 3 coenzymes are used in (aerobic) respiration ?
NAD, FAD, coenzyme A
Which stage of respiration is an anaerobic process and why ?
Glycolysis
Uses no O2
What are the 2 stages of glycolysis ?
1. Phosphorylation of glucose
2. Oxidation of triose phosphate
What is the purpose of glycolysis ?
To produce pyruvate from glucose
Describe what happens when glucose is phosphorylated (3 stages)
1. ATP donates Pi to glucose to form glucose phosphate (and ADP)
2. ATP donates Pi to glucose phosphate to form hexose bisphosphate (and ADP)
3. Hexose bisphosphate split to form 2 molecules of triose phosphate
Describe what happens when 2 molecules of triose phosphate is oxidised
2 molecules of triose phosphate are oxidised to 2 molecules of pyruvate
2 molecules of NAD are reduced to reduced NAD
4 molecules of ATP are produced from 4 molecules of ADP/Pi
What is the net production of ATP in glycolysis ?
2 ATP
2 used and 4 produced
What is the reduced NAD produced in glycolysis used for ?
Oxidative phosphorylation
What is the pyruvate produced in glycolysis used for ?
Actively transported into the mitochondrial matrix
Link reaction
Why does glycolysis take place in the cytoplasm ?
Glucose can't cross the mitochondrial membrane
It's too big
Describe the process after glycolysis in yeast/plants (2 stages)
1. Pyruvate loses CO2 to form ethanal
2. Ethanal reduced to ethanol and reduced NAD oxidised to NAD
What is the purpose of anaerobic respiration ?
To produce ATP by glycolysis
Oxidises reduced NAD from glycolysis to NAD to allow glycolysis to continue
Describe the process of lactate fermentation
Pyruvate reduced to lactate (lactic acid)
Reduced NAD oxidised to form NAD
Where does the link reaction occur ?
Matrix of the mitochondria
What is the purpose of the link reaction ?
To convert pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A
Describe what happens during the link reaction
1. Pyruvate is decarboxylated to form acetate
2a. Pyruvate is oxidised to acetate
2b. NAD is reduced to reduced NAD
3. Coenzyme A combines with acetate to form acetyl coenzyme A
Where is the acetyl coenzyme A used ?
Krebs Cycle
Where is the reduced NAD used ?
Oxidative phosphorylation
What happens to the CO2 produced in the link reaction ?
Lost as a waste product
What happens in the Krebs Cycle ?
ATP and reduced coenzymes are produced in a series of redox reactions
CO2 is lost as a waste product
Where does the Krebs Cycle take place ?
Matrix of the mitochondria
Describe what happens in the Krebs Cycle
1. Aceyl CoA reacts with a 4 carbon compound to form a 6 carbon compound and coenzyme A
2. The 6 carbon compound forms a 5 carbon compound
3. The 5 carbon compound reforms the 4 carbon compound
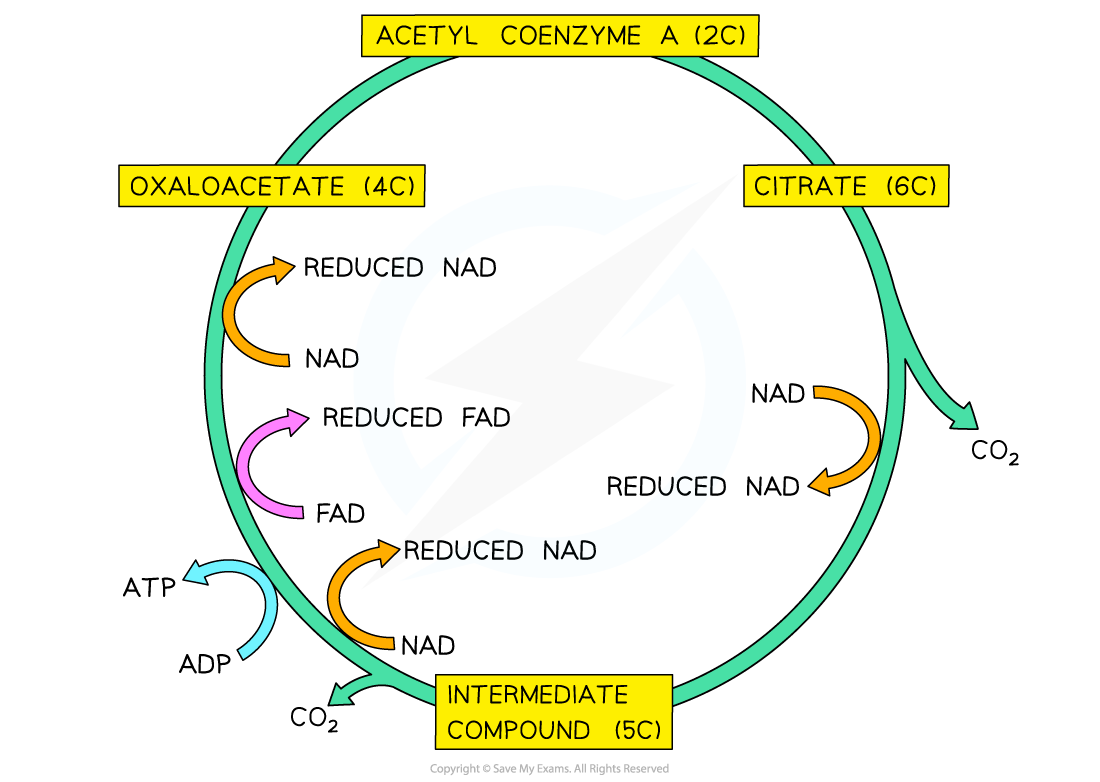
What is substrate level phosphorylation ?
When a phosphate group is directly transferred from one molecule to another
e.g. the production of ATP in the Krebs Cycle
What is the CoA produced in the Krebs Cycle used for ?
The Link Reaction
What are the reduced enzymes produced in the Krebs Cycle used for ?
Oxidative phosphorylation
What is oxidative phosphorylation ?
The process where energy from electrons from reduced coenzymes is used to synthesise ATP
Describe the stages of oxidative phosphorylation
1. NAD/FAD release H atoms (split to H+ and e-)
2. Electrons move down electron transport chain and lose energy at each electron carreir
3. Energy used to actively transport protons into intermembrane space from mitochondrial matrix (forms electrochemical gradient)
4. Protons move down electrochemical gradient into matrix via ATP synthase
5. The protons and electrons combine with oxygen to form water
What is the importance of oxygen in aerobic respiration?
FINAL ELECTRON ACCEPTOR
in oxidative phosphorylation
If there is no glucose, what substances can enter the Krebs Cycle ?
Breakdown products of lipids
Amino acids
REQUIRED PRACTICAL