Nervous System: Brain, Spinal Cord, and Pathways Overview
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
What are the seven structures that compose the limbic system?
Cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, hippocampus, amygdaloid body, olfactory bulbs, fornix, and various nuclei.
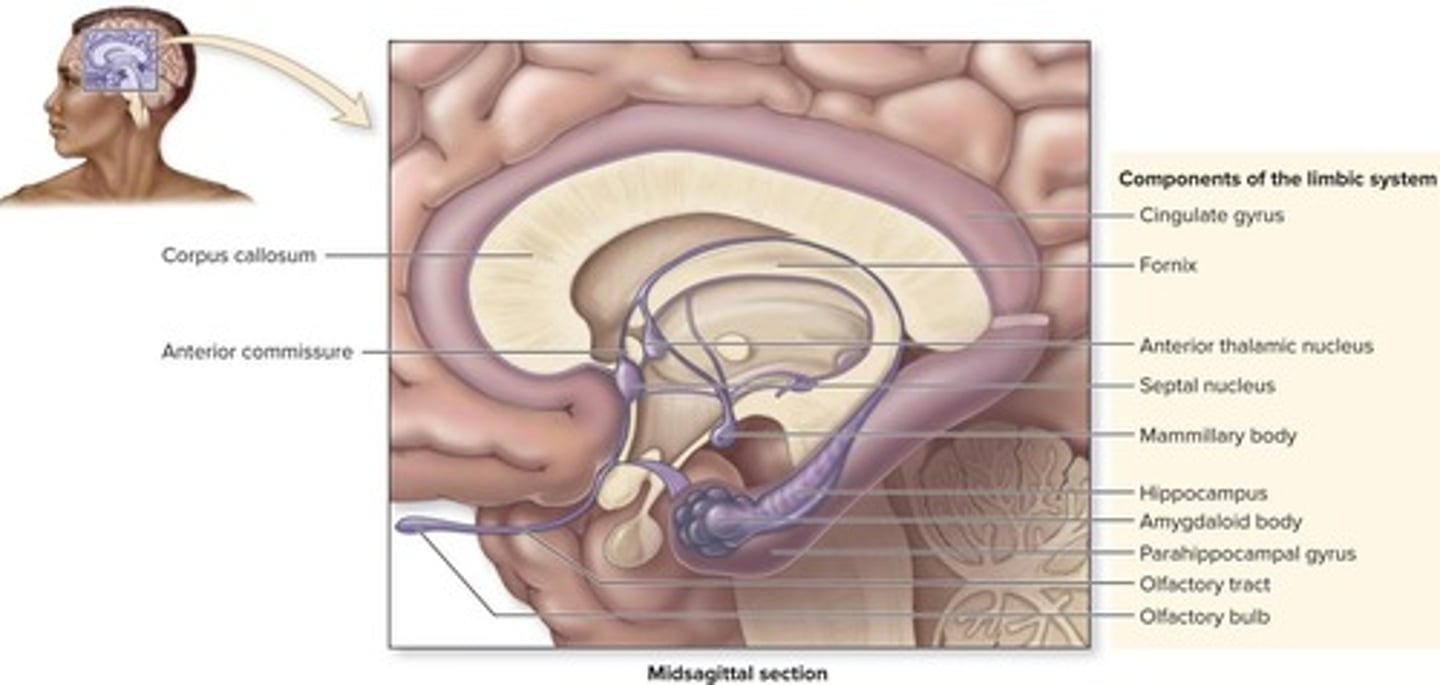
What is the main function of the limbic system?
It processes and experiences emotions.
What is the role of the reticular formation?
It regulates muscle tone and autonomic functions, and processes sensory information for alertness.
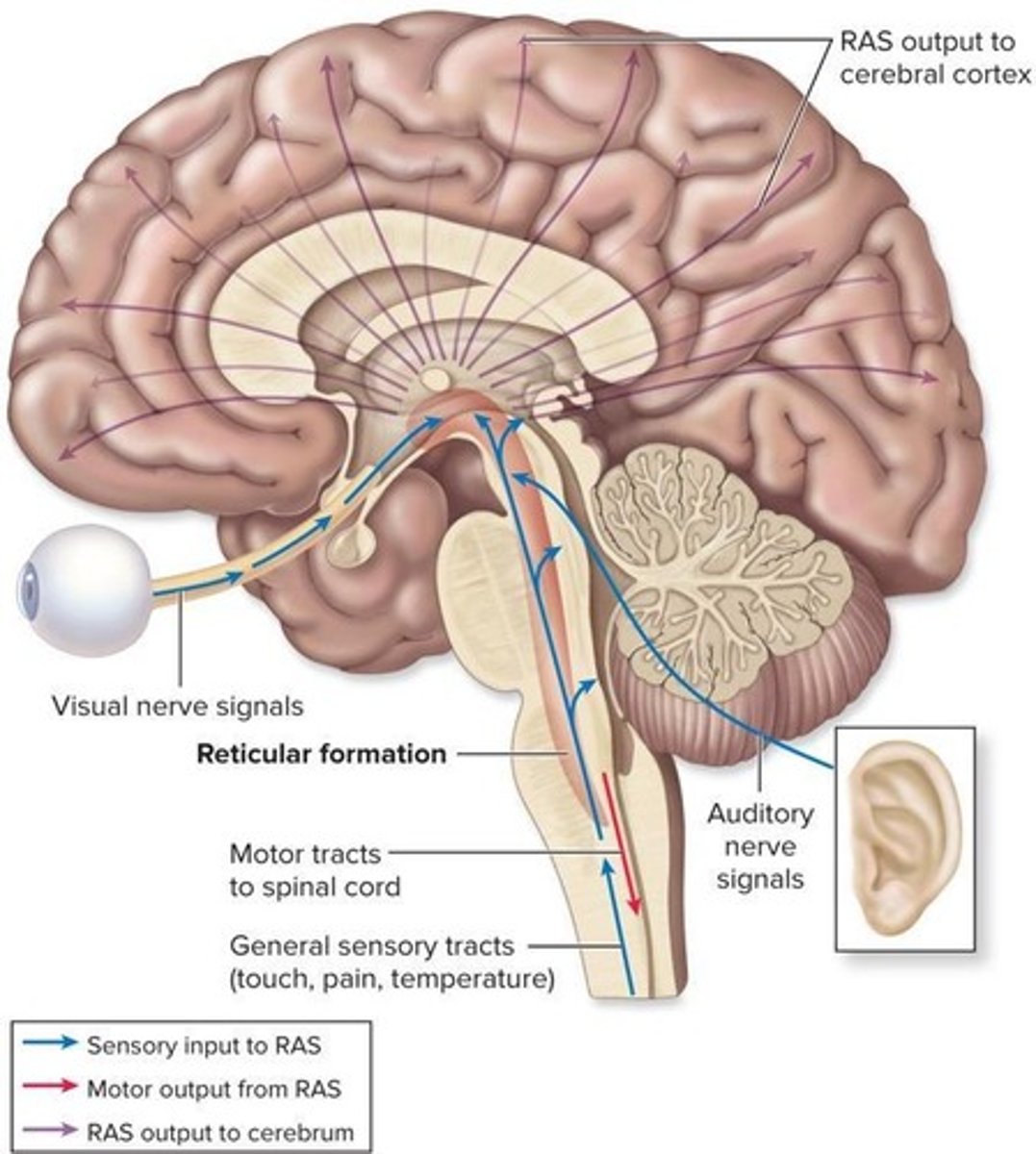
What is the reticular activating system (RAS)?
A sensory component of the reticular formation that processes sensory information and promotes alertness.
What is the relationship between age and higher-order brain functioning?
Higher-order brain functioning can decline with age.
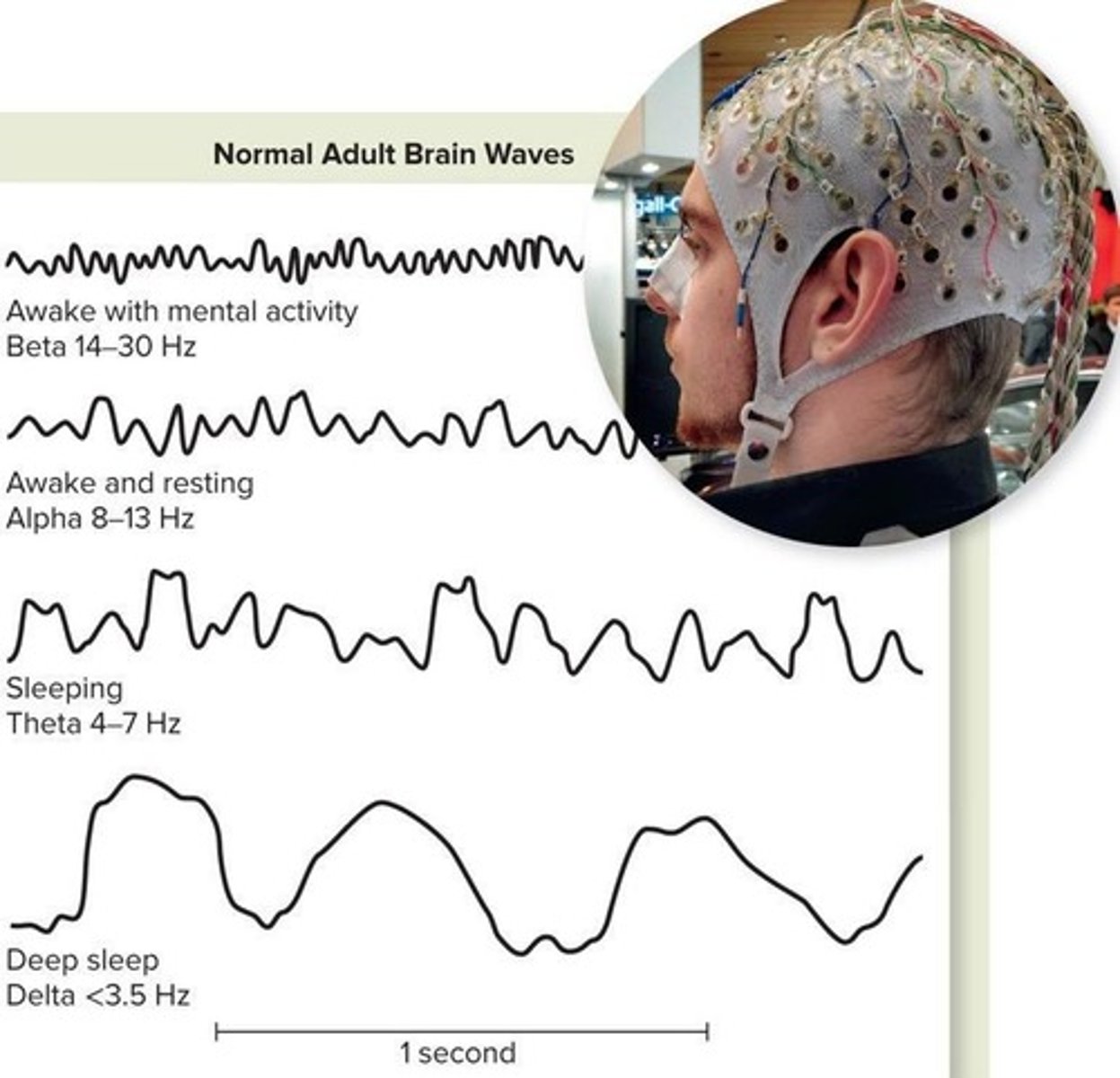
How does an electroencephalogram (EEG) examine brain activity?
It records electrical activity of the brain.
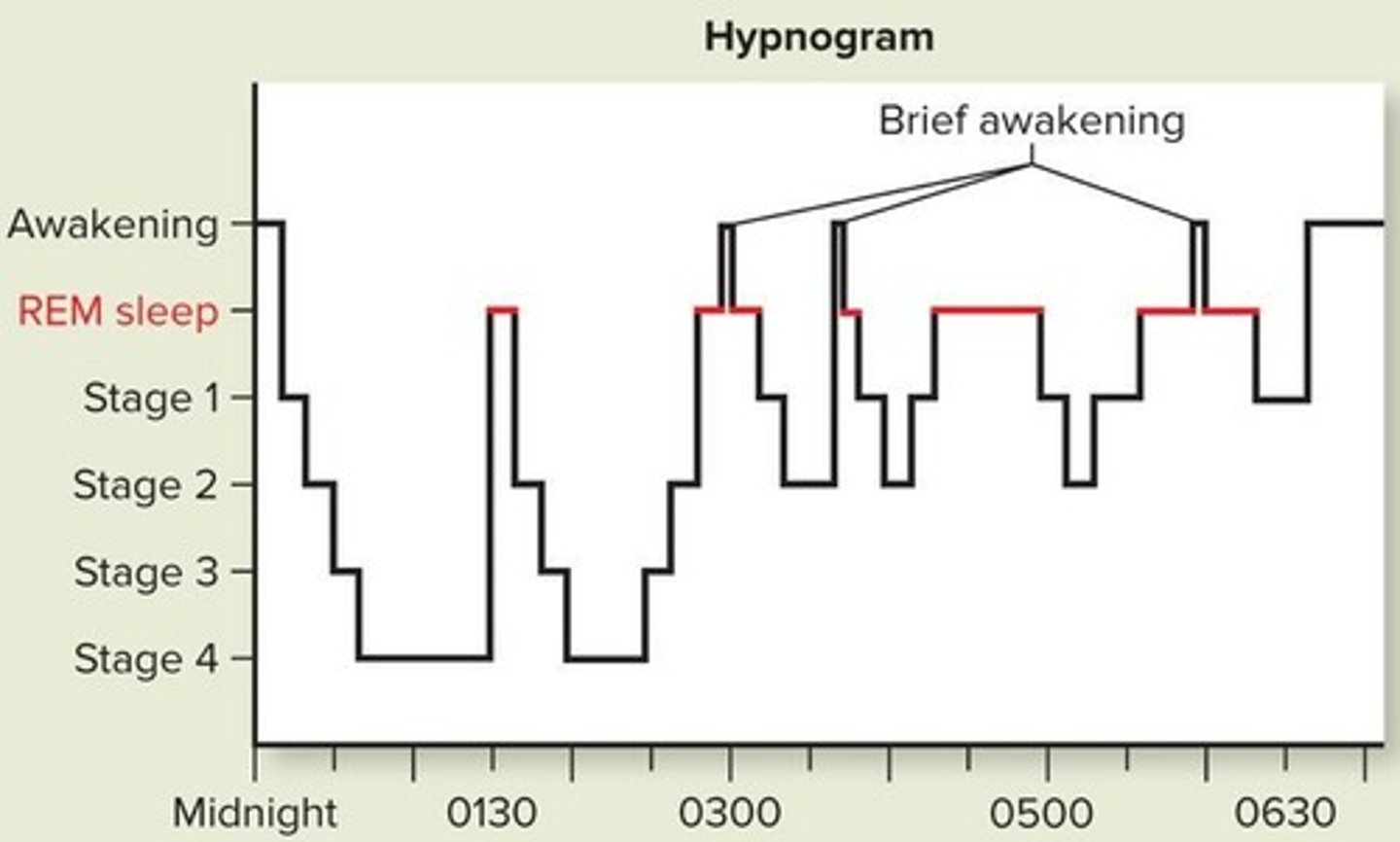
What are the main characteristics of sleep?
Includes non-REM and REM sleep, with distinct physiological changes.
What is cognition?
The mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding.
How do lesions in different regions of the cortex affect cognition?
They can impair specific cognitive functions depending on the affected area.
What are short-term and long-term memory?
Short-term memory holds information temporarily, while long-term memory stores information for extended periods.
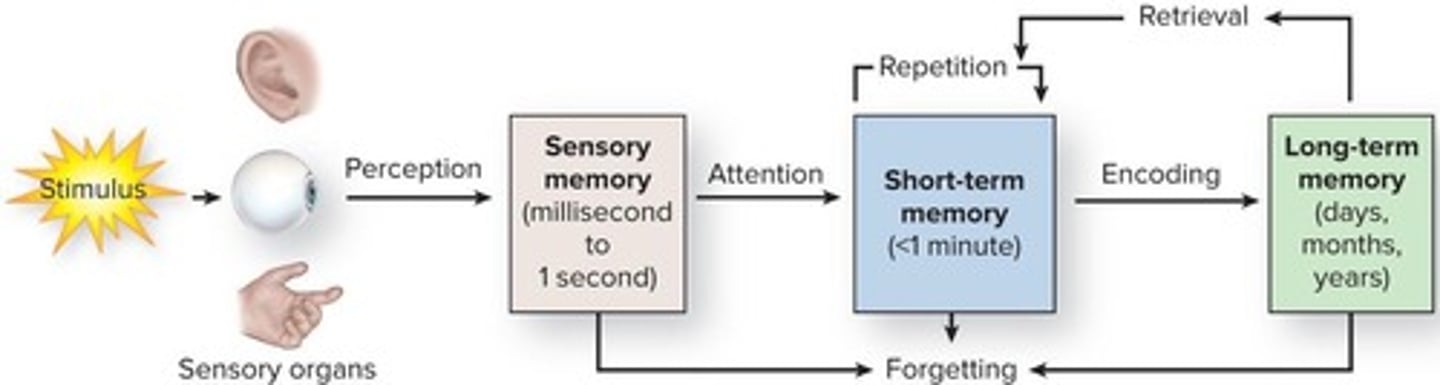
Which parts of the brain are involved in short-term memory?
Primarily the prefrontal cortex.
Which parts of the brain are involved in long-term memory?
Primarily the hippocampus and related structures.
How do the prefrontal cortex and limbic system interact in the expression of emotions?
The prefrontal cortex regulates emotional responses initiated by the limbic system.
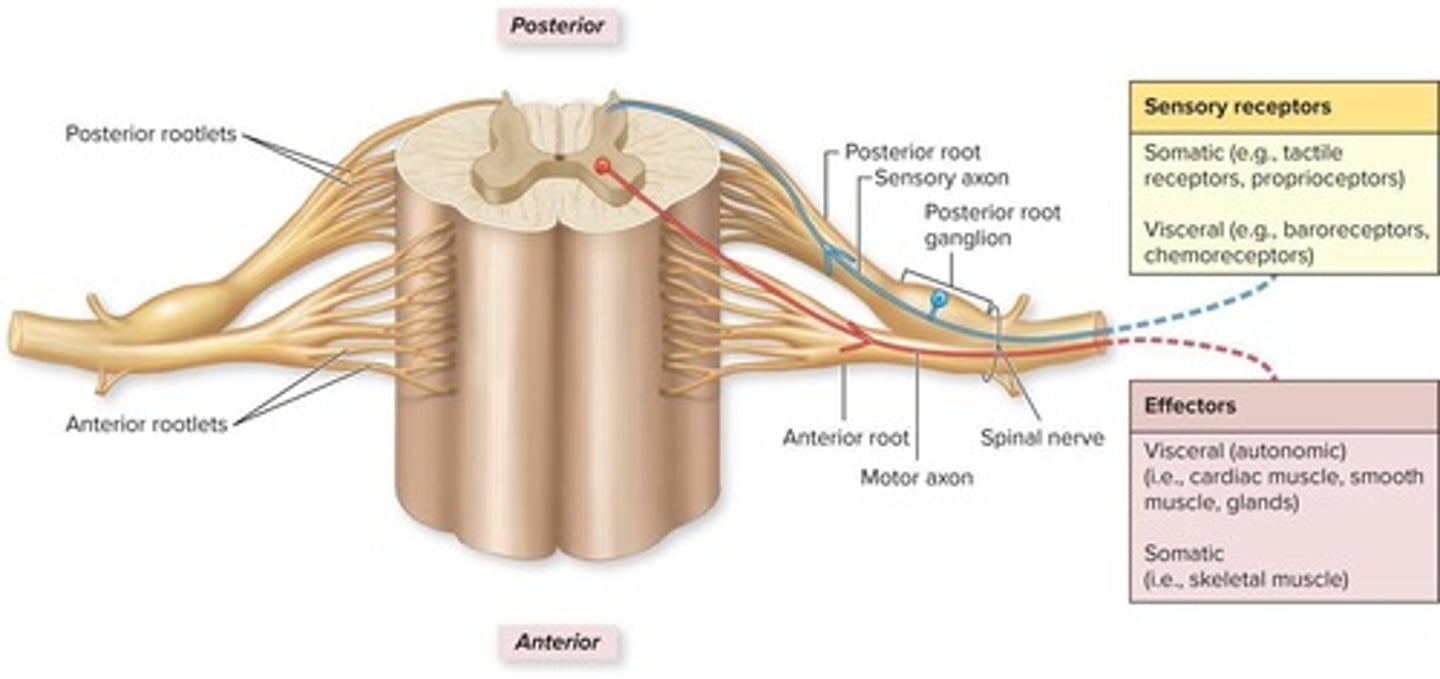
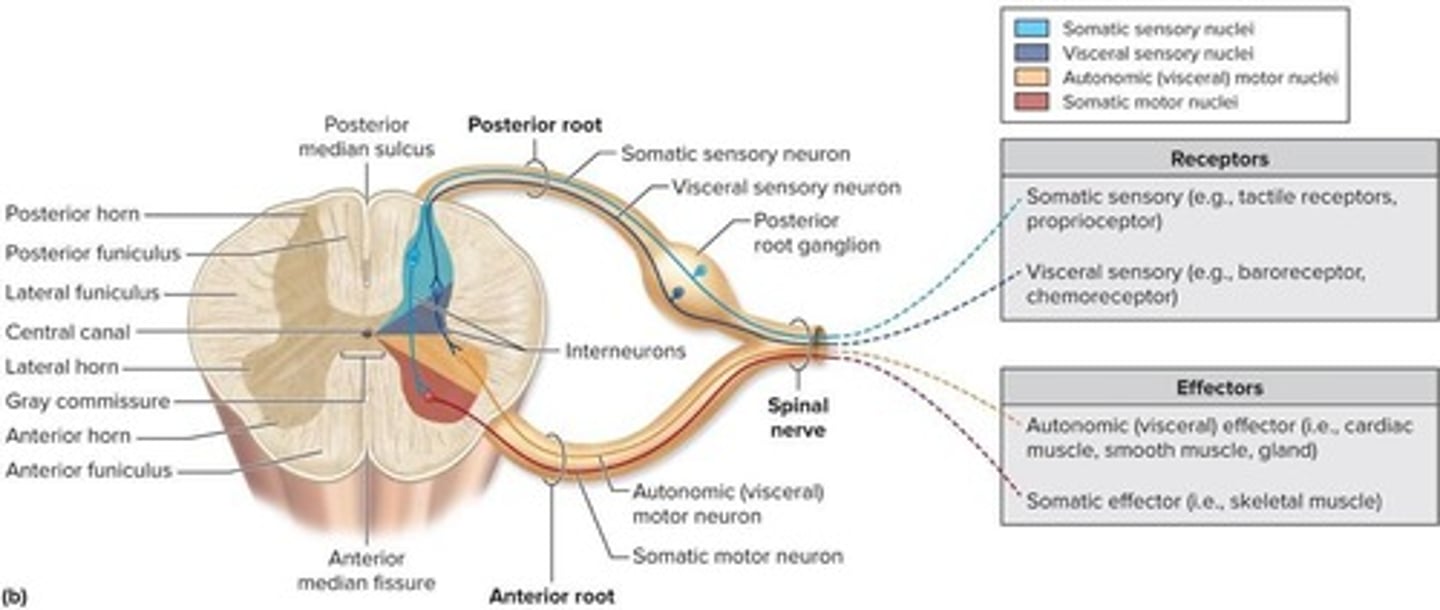
What is a spinal nerve?
A nerve that emerges from the spinal cord and carries sensory and motor information.
What are the three types of neurons used in a sensory pathway?
First-order, second-order, and third-order neurons.
What is a dermatome?
An area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve root.
What is a nerve plexus?
A network of intersecting nerves.
What are the properties of a reflex?
Involuntary responses to stimuli that involve a reflex arc.
What structures are involved in a reflex arc?
Sensory receptor, sensory neuron, integration center, motor neuron, and effector.
How does the neural tube form the gray matter structures in the spinal cord?
The neural tube develops into the central nervous system, including gray matter.
What is fainting?
A brief loss of consciousness often due to inadequate cerebral blood flow.
What is stupor?
A state of reduced responsiveness, arousable only to extreme stimuli.
What is a coma?
A deep and profound unconsciousness with no response to stimuli.
What is a persistent vegetative state?
A condition of unresponsiveness with preserved noncognitive brain functions.
What are higher-order mental functions?
They include learning, memory, and reasoning.
Where do higher-order mental functions occur?
Within the cortex of the cerebrum.
What is the significance of CNS development in relation to processing abilities?
Processing abilities become complex with maturation.
When is brain growth most rapid?
In early childhood, reaching 95% completion by age 5.
What is an EEG used for?
To record brain activity and evaluate conditions like sleep, brain lesions, and epilepsy.
What are the common EEG frequency waves during wakefulness?
Alpha (α) and beta (β) waves.
What characterizes non-REM sleep?
Slower frequency brain waves and takes up about 75% of total sleep time.
What is REM sleep important for?
Consolidation of memories and memorable dreaming.
How many hours of sleep do infants need?
17 to 18 hours.
What is insomnia?
Difficulty in falling asleep or staying asleep.
What is sleep apnea?
Breathing interruptions during sleep that lead to frequent awakenings.
What are the mental processes involved in cognition?
Awareness, knowledge, memory, perception, and thinking.
What brain areas are responsible for memory encoding?
Amygdala and hippocampus.
What is Alzheimer's disease?
A leading cause of dementia characterized by slow, progressive loss of higher intellectual function.
What is amnesia?
Partial or complete loss of memory, usually temporary.
Which brain regions are involved in emotion?
The limbic system interprets emotions; expression is controlled by the prefrontal cortex.
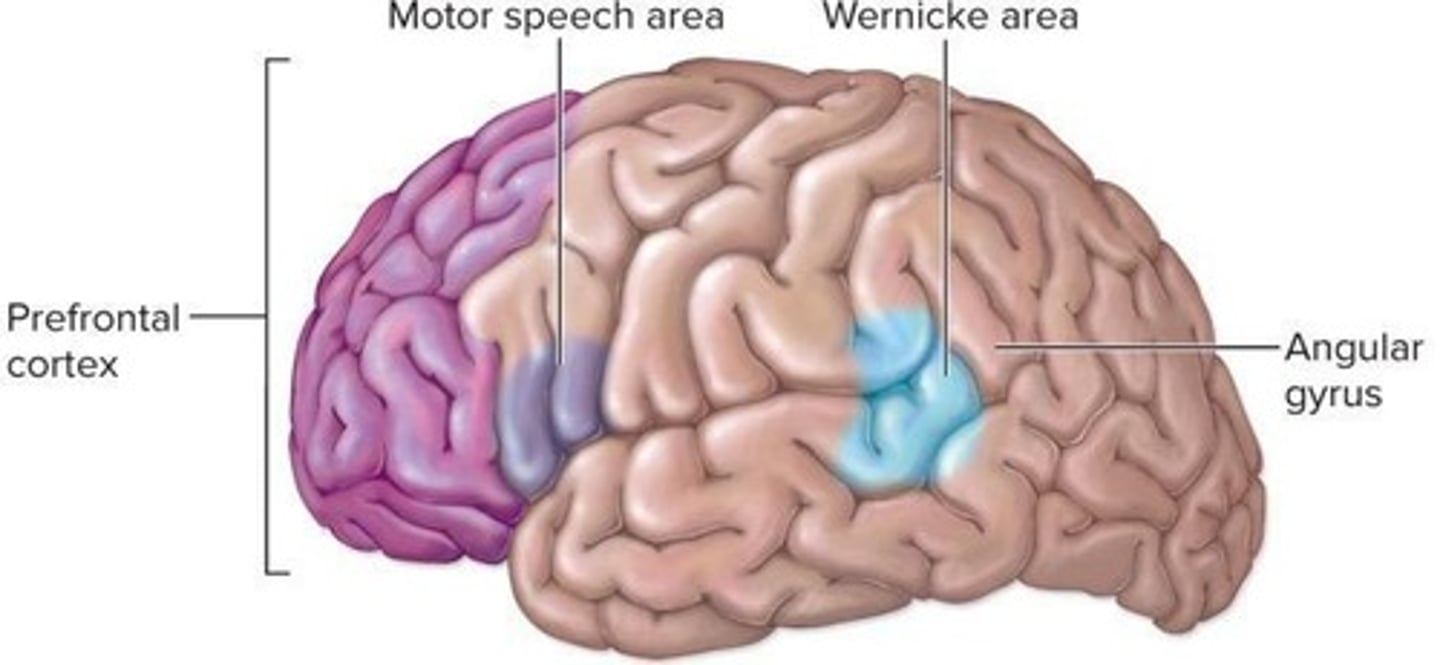
What is the role of the Wernicke area?
It interprets language.
What is dyslexia?
An inherited learning disability affecting reading, writing, and spelling.
What is apraxia of speech?
A motor disorder where a person knows what they want to say but cannot speak properly.
What is aphasia?
Difficulty understanding or producing speech, often due to head injury or stroke.
What is the difference between short-term and long-term memory?
Short-term memory has limited capacity and brief duration; long-term memory can exist indefinitely.
What are the implications of the brain's anatomic development not being complete until after the early 20s?
It affects cognitive and emotional development.
What are the main differences between non-REM and REM sleep?
Non-REM sleep has slower brain waves and takes up 75% of sleep, while REM sleep is active and involves dreaming, taking up 25%.
What is the effect of damage to the primary somatosensory cortex?
It causes loss of body awareness on the opposite side.
What is agnosia?
Inability to recognize or understand the meaning of stimuli.
What is the role of the primary motor cortex in speech?
It signals motor neurons to produce speech.
What happens to memory if the hippocampus is damaged?
Formation of new memories is disrupted or prevented.
What are the types of memory?
Sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory.
What is the significance of beta amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease?
Their significance as an underlying cause is debated.
What is the typical sleep requirement for adults?
7 to 8 hours.
What is the role of the categorical hemisphere in language?
It analyzes the literal meaning of speech.
What is the role of the representational hemisphere in language?
It analyzes the emotional content of speech.
What forms the cerebrum?
The telencephalon
What structures are formed by the diencephalon?
Thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus
What does the mesencephalon form?
The rostral end of the brainstem
What does the metencephalon form?
The pons and cerebellum
What does the myelencephalon form?
The medulla oblongata
Where is gray matter located in the cerebrum?
In the outer cerebral cortex and deeper cerebral nuclei
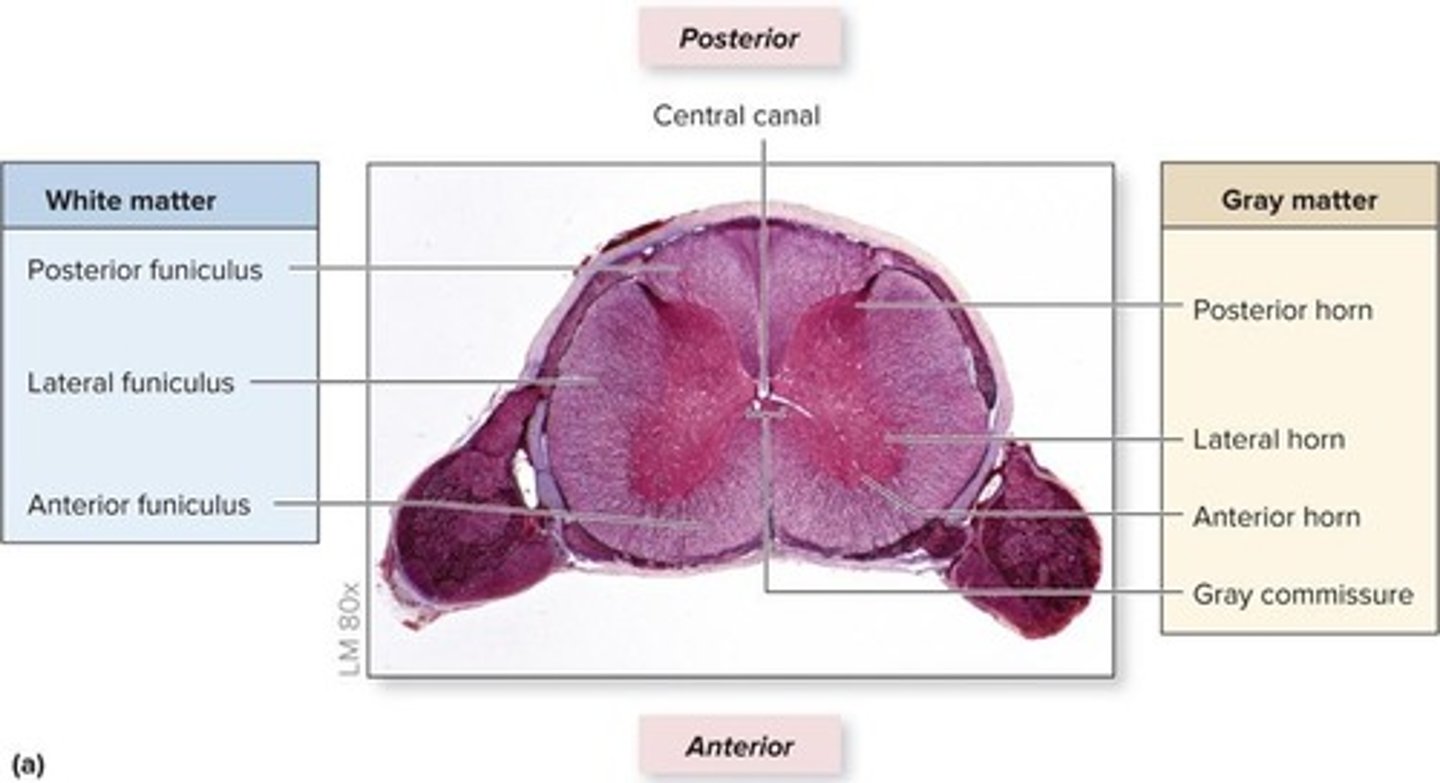
What surrounds the central portion of gray matter in the spinal cord?
Columns of white matter
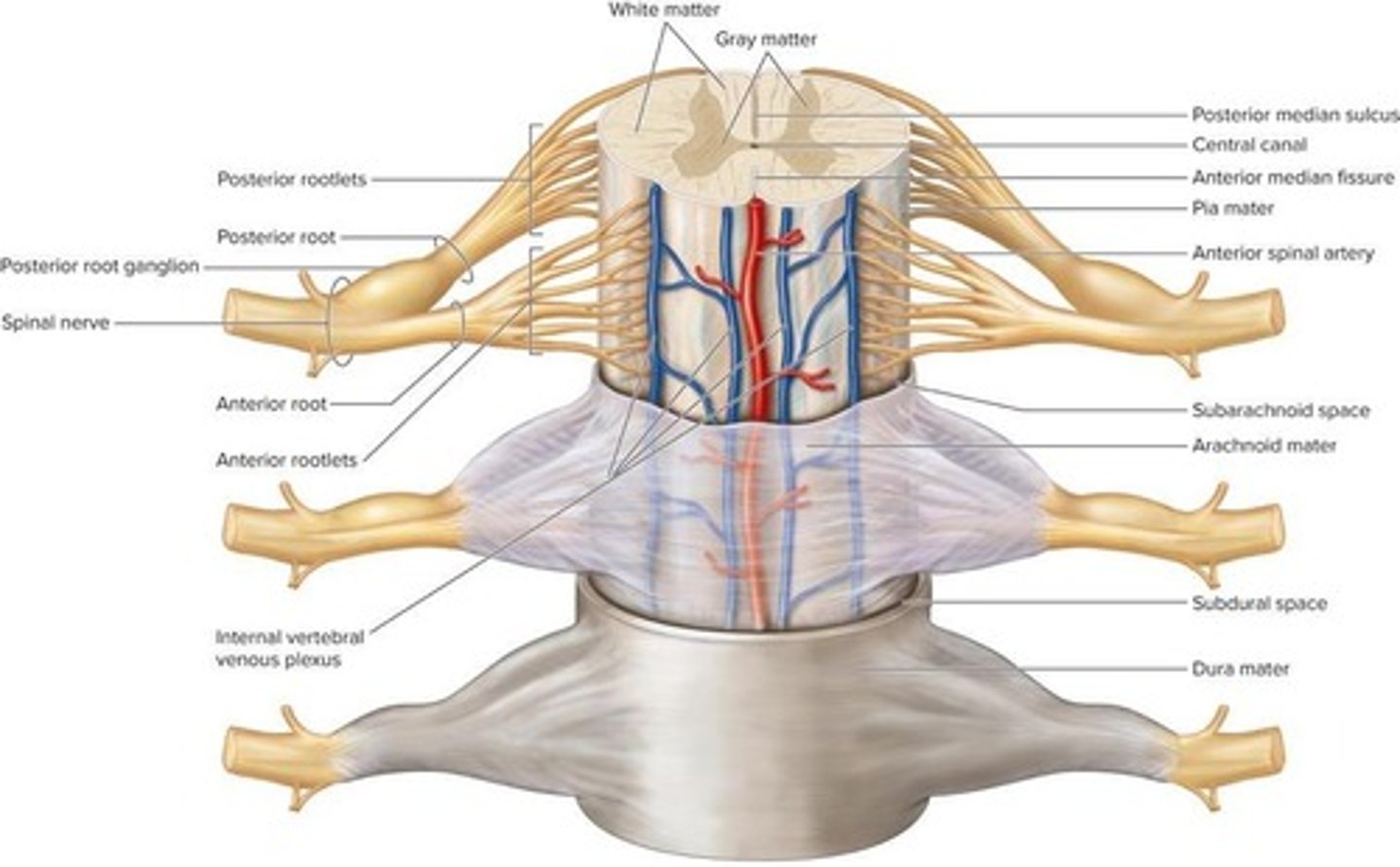
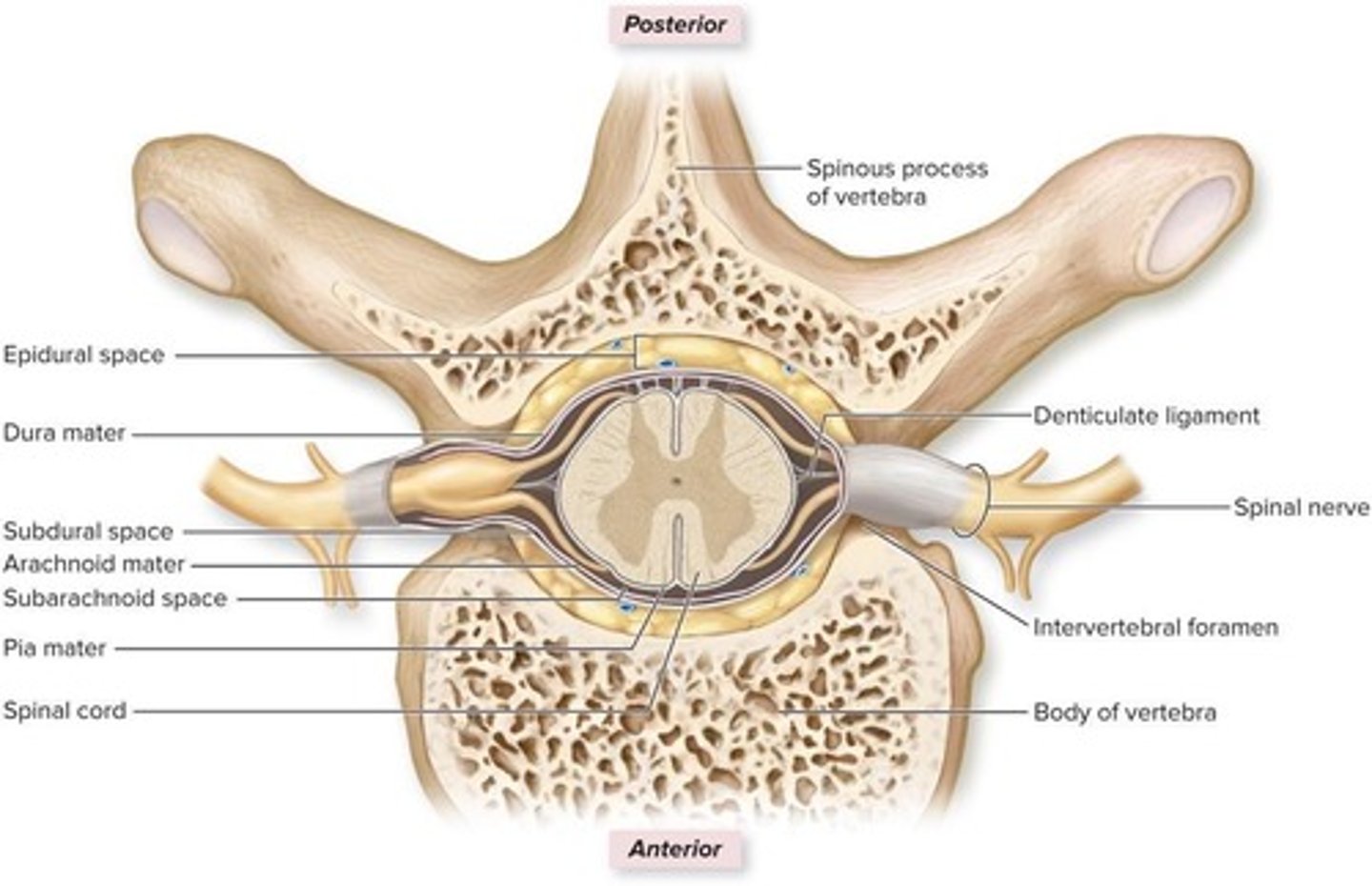
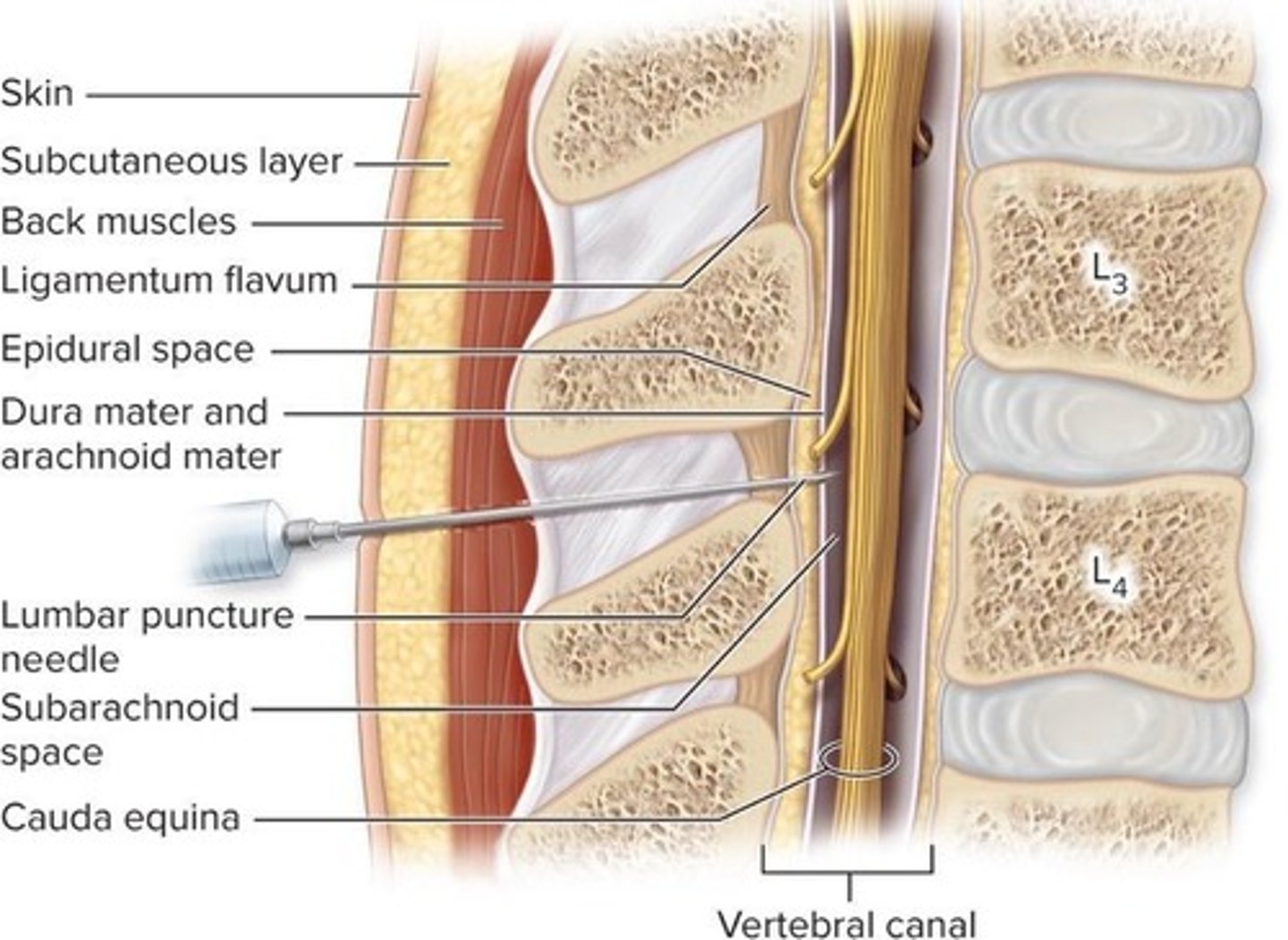
What are the layers of the meninges?
Pia mater, subarachnoid space, arachnoid mater, subdural space, inner meningeal layer of dura mater, outer periosteal layer of dura mater
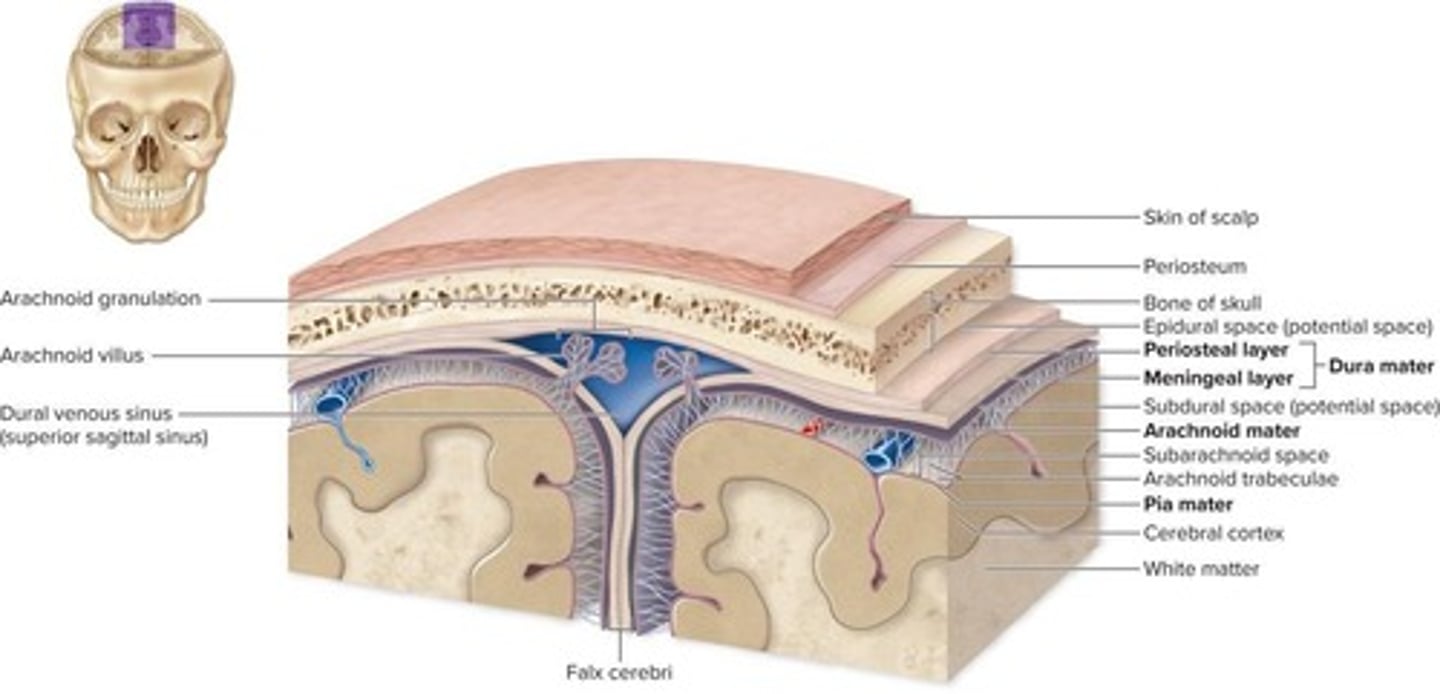
Where are dural venous sinuses located?
Between the inner meningeal and outer periosteal layers of dura mater
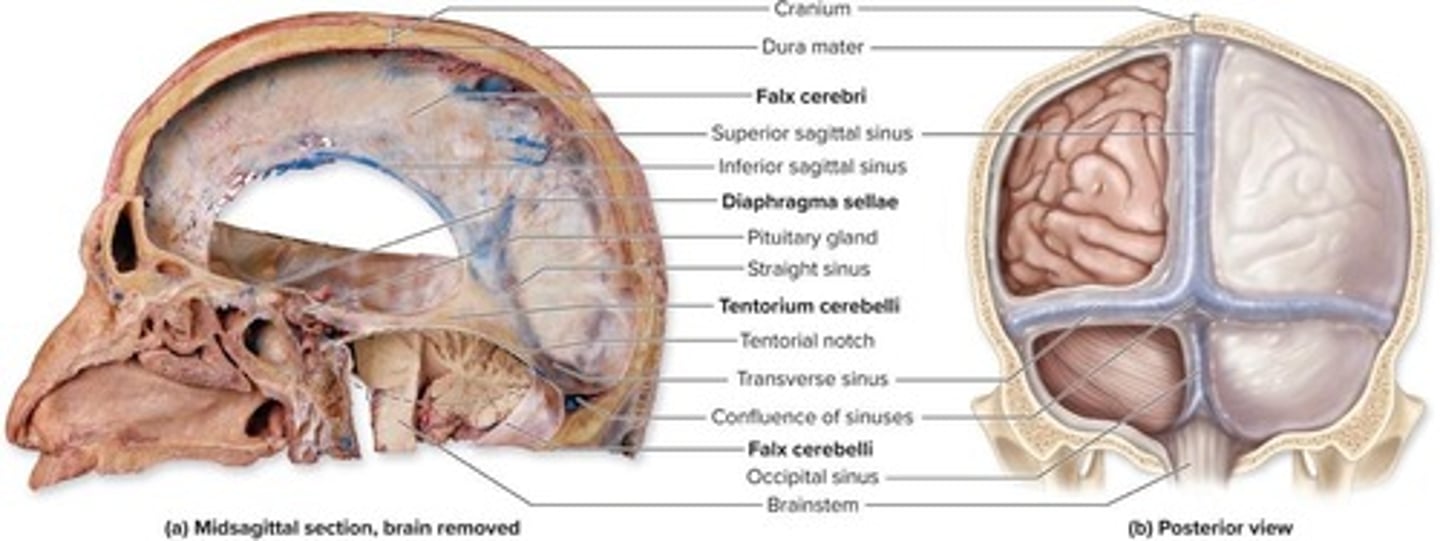
What is the falx cerebri?
A large fold of dura mater separating the left and right hemispheres of the brain
Where is the fourth ventricle located?
Between the pons and cerebellum
What is the function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
Provides buoyancy, protects the brain, and transports nutrients and waste
What is the flow of CSF production and circulation?
Lateral ventricles → interventricular foramina → 3rd ventricle → cerebral aqueduct → 4th ventricle → median and lateral apertures → subarachnoid space → arachnoid villi → dural venous sinuses
What does the blood-brain barrier do?
Regulates substances entering the brain from capillaries

What is the function of the cerebrum?
Location of conscious thought processes and complex intellectual functions
What does the corpus callosum do?
Provides communication between the hemispheres of the brain

What is the function of the primary motor cortex?
Controls skeletal muscle activity

What is the function of the premotor cortex?
Coordinates learned, skilled motor activities
What is the function of the motor speech area?
Controls muscular movements necessary for vocalization
What is the function of the primary somatosensory cortex?
Receives, processes, and stores somatic sensory information
What is the function of the Wernicke Area?
Understanding written and spoken language
What is the role of association areas in the brain?
Integrate current sensory or motor information with previous experiences
What is cerebral lateralization?
Specialization of the two cerebral hemispheres
What is the function of the substantia nigra?
Produces dopamine, affecting movement and emotional response
What are the main autonomic centers in the medulla oblongata?
Cardiac center, vasoconstriction center, medullary respiratory center
What does the tectal plate process?
Auditory stimuli (inferior colliculi) and visual stimuli (superior colliculi)
What regulates respiration in the pons?
Pontine respiratory center
What are the two hemispheres of the cerebellum?
Discrete hemispheres
What does the cerebellum consist of?
Two discrete hemispheres, each separated into anterior and posterior lobes by the primary fissure.
What are folia in the cerebellum?
Folds of the cerebellar cortex consisting of gray matter with underlying white matter called the arbor vitae.
What connects the cerebellum to the pons?
The middle cerebellar peduncles.
What is the function of the cerebellum?
To integrate somatic motor output from the cerebrum with proprioception and sensory stimuli to coordinate and fine-tune skeletal muscle movements.
What is the role of the limbic system?
To process and experience emotions.
Which structures are involved in long-term memory formation?
The hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus.
What is the function of the amygdaloid body?
Involvement in emotions such as fear.
What does RAC stand for?
Reticular Activating Component, associated with states of consciousness.
What does an EEG evaluate?
Sleep disorders, epilepsy, seizure disorders, and stages of unconsciousness.
What percentage of sleep is Non-REM sleep?
About 75%.
What are optimum study methods for forming long-term memories?
Methods involving multiple repetitions and assessments of knowledge.
Which cranial nerves carry only sensory information?
Olfactory, optic, and vestibulocochlear nerves.
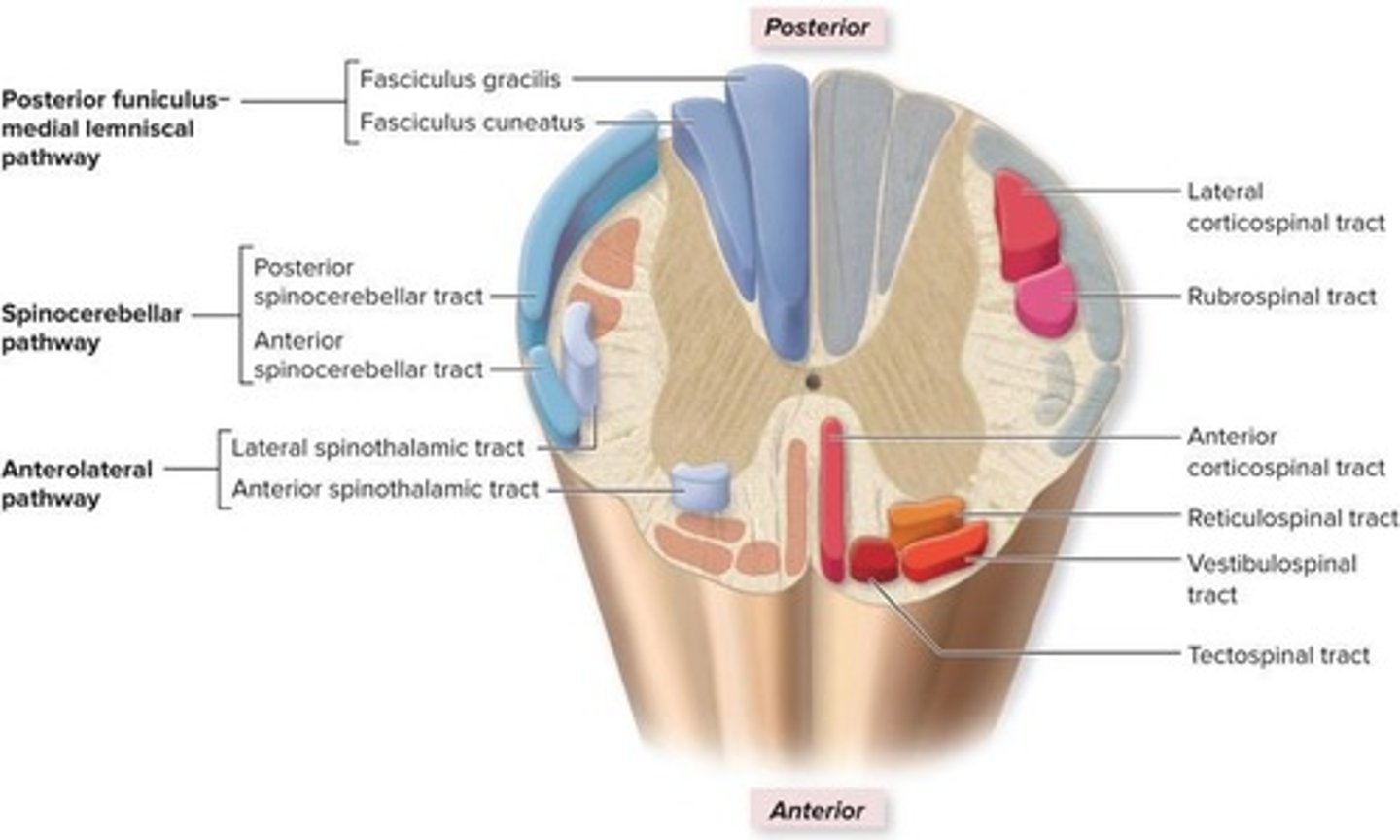
What are the major functions of the spinal cord?
To serve as a structural and functional link between the brain and the rest of the body and to facilitate spinal reflexes.
What is the typical length of an adult spinal cord?
16-18 inches.
What are the two widened regions of the spinal cord?
Cervical enlargement and lumbar enlargement.
What is the cauda equina?
A structure formed by lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal spinal nerves extending from the conus medullaris.