Cross Sectional anatomy Quiz 1
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Two major cavities of the body
Ventral and Dorsal cavity
The dorsal cavity includes
cranial cavity and spinal cavity
cranial cavity
Cavity that contains the brain and cerebellum
Spinal cavity
Cavity that contains the spinal cord, CSF
The ventral cavity includes
thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
What is the thoracic cavity?
The cavity that is enclosed by the rib cage.
What is another name for the thoracic cavity?
Pleural cavity.
What covers the thoracic cavity?
Pleural lining.
What separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity?
The diaphragm.
The abdominopelvic cavity is from the
diaphragm to the pubic bone
The abdominopelvic cavity is divided into
abdominal( superior)l cavity and pelvic(inferior) cavity
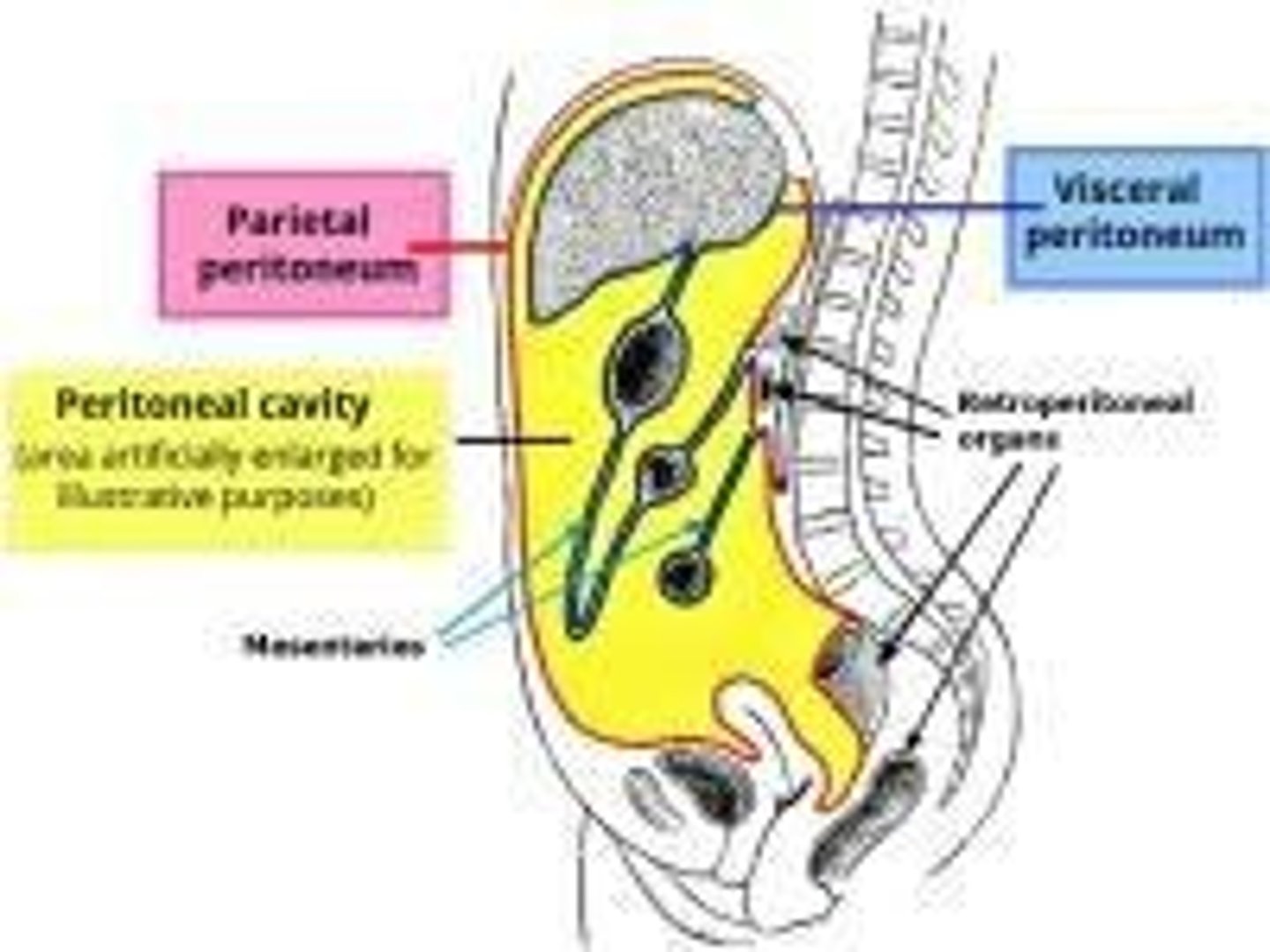
Peritoneal cavity
The anterior area of the abdominopelvic cavity that is covered by the peritoneal lining
Retroperitoneal cavity
The posterior area of the abdominopelvic cavity, posterior to the peritoneal lining
What is the peritoneum?
A thin, serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers the abdominal organs.
What is the parietal peritoneum?
The layer of the peritoneum that lines the inner surface of the abdominal wall.
What is the visceral peritoneum?
The layer of the peritoneum that covers the abdominal organs.
Abdominal portion of the peritoneal cavity
Greater sac, lesser sca, and foramen winslow( Epiploic foramen)
What does the greater sac enclose?
Most of the abdominal organs
What are the organs enclosed by the greater sac called?
Intraperitoneal organs
From where to where does the greater sac extend?
From the diaphragm to the pelvis
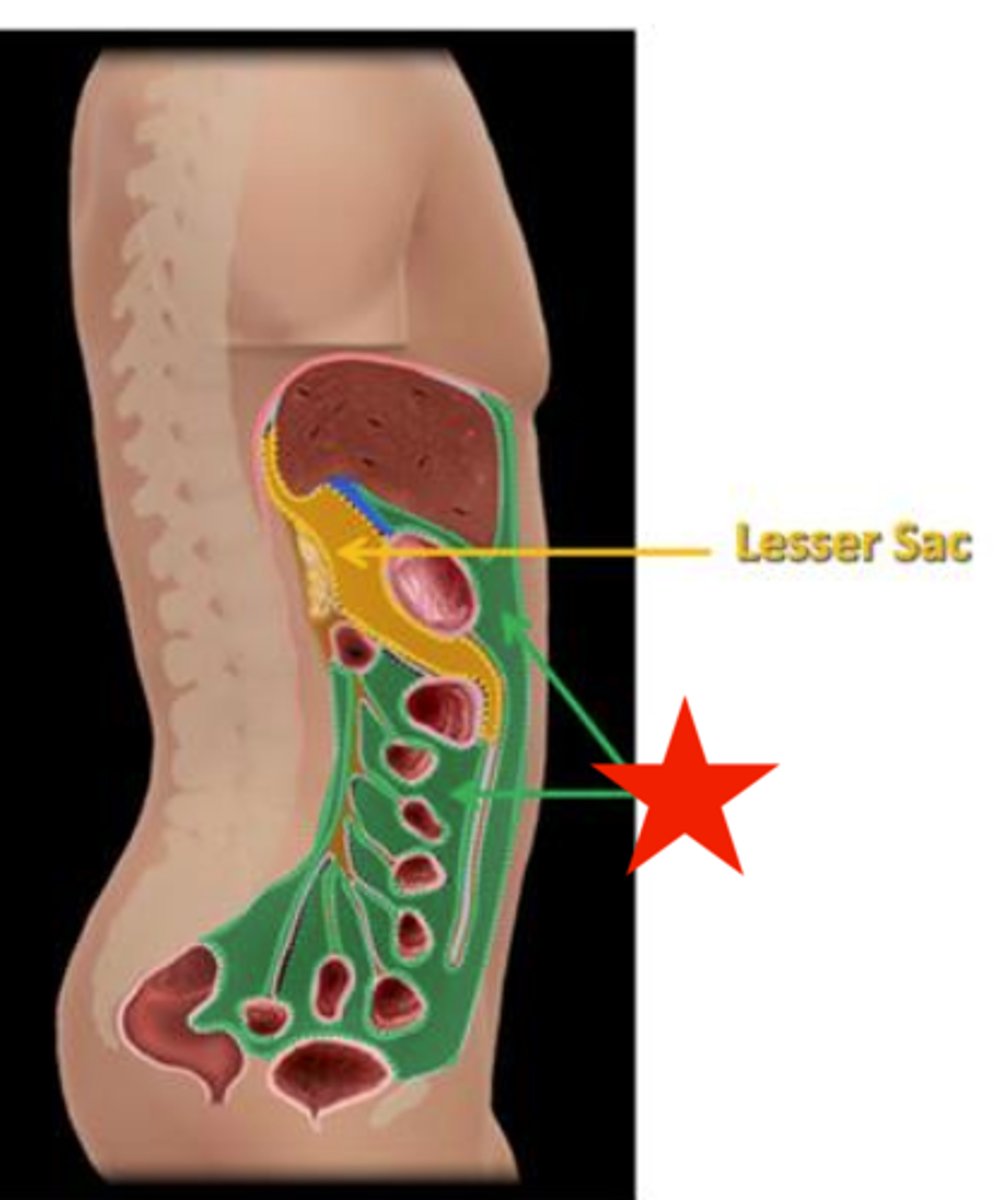
lesser sac
It is a diverticulum or extension of the greater sac and is located posterior to the stomach and anterior to the pancreas, and is part of the transverse colon
Epiplioc Foramen or Foramen of Winslow
The passageway between the greater and lesser sacs is just inferior to the liver
Omentum
A double layer of peritoneum folding
greater omentum
double fold of the peritoneum that extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, hangs down like an apron over the small intestines, and then attaches to the transverse colon.
Lesser omentum
folding of the peritoneum that extends/connects from the liver(porta hepatis area) to the lesser curvature of the stomach and the first part of the duodenum
Organs in the peritoneal( intraperitoneal) cavity
liver, gallbladder, ovaries, stomach, spleen, transverse colon, most of the small intestines( except the mid portion of the duodenum)
Retroperitoneal cavity
Posterior area of the abdominopelvic cavity, posterior to the peritoneal lining
- Pararenal space
- Anterior pararenal space
- Great vessels region
- Diaphragmatic crura
organs in the retroperitoneal cavity
kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, ascending colon, descending colon, part of the duodenum, pancreas, prostate gland, aorta, ivc
Major vessels in the retroperitoneal cavity
Aorta and IVC
Supracolic compartment
An abdominal space above the transverse colon
Right subhepatic space
space underneath the liver; between the right liver and the right kidney, also known as Morrison's pouch
Morrison's pouch
The most dependent part of the abdominal cavity. It acts as a drainage pathway for fluid from the liver and kidney and it provides a space for the accumulation of fluid, such as ascites or blood
Left subhepatic space
behind the left lobe of the liver, lesser sac
Right and Left Subphrenic spaces
spaces between the diaphragm and the anterior right and left lobes of the liver
Infracolic Compartments
Areas inferior to the transverse colon( right paracolic gutter, left paracolic gutters, and right and left mesentric gutters)
Right paracolic gutter
between the ascending colon and the right abdominal wall
Left paracolic gutter
Between the descending colon and the left abdominal wall
4 quadrants of the abdomen
RUQ, LUQ, RLQ, LLQ
Anatomical position
Standing erect, arms at the sides, face, and palms, direct forward
What are the three anatomical divisions
Sagittal, coronal, and transverse
Sagittal plane
divides the body into right and left
Coronal plane
divides the body into anterior and posterior planes
Transverse Plane
divides the body into superior and inferior sections
The light or notch on the transducer is
the left side of the screen or sector
When scanning transverse turn
90 degrees counterclockwise
Sections of the aorta
1. Root of the aorta
- left ventricular outflow tract
2. Ascending Aorta
- supply upper/ jhead and neck
3. Descending aorta
4. Abdominal aorta
5. Bifurcation- Iliac arteries
Iliac arteries divide into
internal and external iliac arteries
Internal iliac artery supply
the pelvis
External iliac artery supply
extremeties
Ascending aorta
arches superior on the aortic arch
What are the branches of the Ascending Aorta?
-Right innominate artery(brachiocephalic)
-Left common carotid artery
- Left subclavian artery
What does the Right innominate artery branch into?
Right subclavian artery and right common carotid artery
What does the Right innominate artery supply blood to?
The right side of the head, neck, and arm
What does the Left common carotid artery supply blood to?
The brain and neck
What does the Left subclavian artery supply blood to?
The left side of the head, neck, and left arm
The abdominal aorta characteristics
-Anterior and slightly to the left of the vertebral column
-A retroperitoneal structure
- The aorta is posterior to the left lobe of the liver, the body of the pancreas, the pylorus of the stomach, the splenic vein, the superior mesenteric artery, and the left renal vein
Aorta size
Diameter is 2-3 cm and tapers inferiorly
- the more inferiorly the aorta gets more superficial it becomes
- the prox aorta is deeper
What are the three layers of the aorta?
Tunica Intima, Tunica Media, Tunica Adventitia
What is the Tunica Media?
The middle layer of the aortic wall, which is the thickest layer made up of elastic fibers, smooth muscle cells, and collagen.
What is the Tunica Adventitia?
The outer layer of the aorta, composed of elastic and collagen fibers.
Why are arteries less compressible than veins?
Arteries are thicker and contain more smooth muscle fibers than cells.
Abdominal Aorta Branches
-Celiac Trunk: Most superior branch( about 2 cm from the diaphragm)
-Superior Mesenteric Artery: Anterior branch
-Right& Left Renal arteries: lateral branches
-Inferior Mesenteric Artery: anterior branch
- Some patients have suprarenal Arteries that branch off horizontally and supply adrenal glands. They are usually between celiac and SMA
Celiac trunk branches into
Left gastric artery, splenic artery, and common hepatic artery
Left Gastric Artery
A branch of the celiac trunk. Courses superiorly to the left along the left side of the lesser curvature of the stomach( supplies it with blood) and then back toward the right to eventually anastomose (join) with the right hepatic artery.
Splenic Artery
A branch of the celiac trunk. Courses to the left horizontally along the superior border of the pancreas and supply the spleen
Common Hepatic Artery Branches
Proper hepatic artery and Gastroduodenal artery
Common hepatic artery
A branch of the celiac trunk. Branches horizontally to the right into the proper hepatic artery and the gastroduodenal artery
Proper hepatic artery
A branch of the common hepatic artery. Course right lateral and superiorly, supplying the liver via the right, middle, and left hepatic arteries
Cystic artery
Branches from the right hepatic artery and feeds the gallbladder
The Left Hepatic artery supplies
The left lobe of the liver and the caudate lobe of the liver
Gastroduodenal artery
A branch of the Common hepatic artery. Courses inferior to the anterior lateral border of the head of the pancreas
Superior Mesenteric Artery( SMA)
Supply the ascending colon and part of the transverse colon
Inferior Mesenteric artery
Supply parts of the transverse colon, descending colon, and parts of the rectum
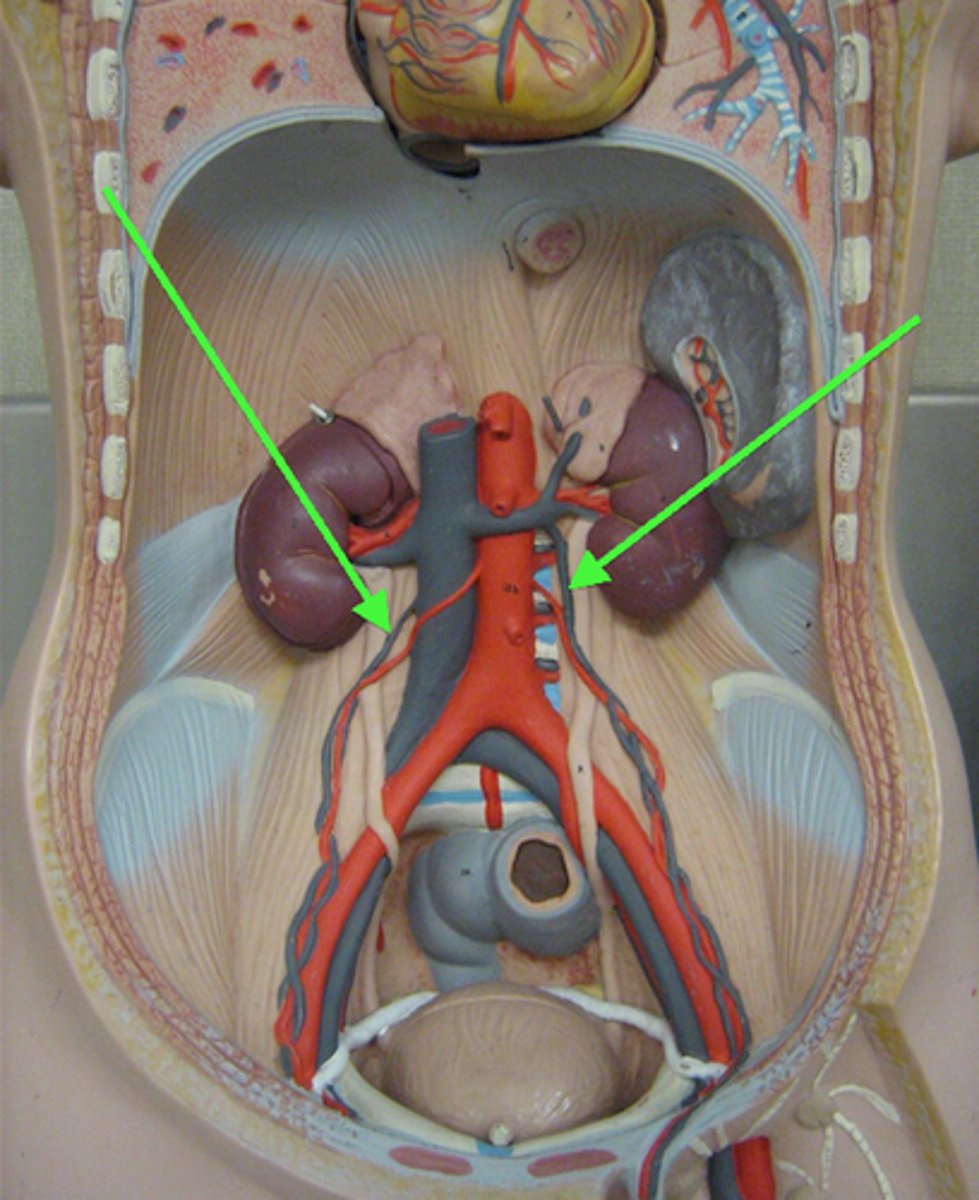
Renal arteries
-Within a few cm of the SMA
- branches off in a lateral aspect and courses horizontally to supply the kidneys
Right renal artery
It is longer than the left renal artery and is posterior to the IVC
Left renal artery
Is posterior to the left renal vein. It usually originates slightly superior to the right renal artery
Inferior Vena Cava (IVC)
-Runs upward in the retroperitoneal cavity
- returns deoxygenated blood to the heart
- low-pressure system
- collapsible, larger diameter with inspiration
The IVC is located
To the right and anterior to the vertebral bodies. It travels through the diaphragm and empties into the right atrium
Bifurcation of iVC happens
At level L-4, into the right and left iliac veins
Major tributaries of the IVC
-right and left renal veins
-Before it enters the thoracic cavity ( caval hiatus) the IVC receives the three hepatic veins.
Left renal vein is
longer than the right renal vein
The lesser sac is located:
posterior to the stomach
The peritoneum that surrounds the abdominal organs is referred to as?
Visceral peritoneum
Ascites typically collects in all the following potential spaces
Morrison's pouch, paracolic gutter, and mesenteric gutters
Before it enters the thoracic cavity, the IVC receives blood from the:
Hepatic veins
Which vessels lie posterior to the IVC?
A. Right renal artery
B.Right renal vein
C.Left renal vein
D.Left renal artery
Right renal artery
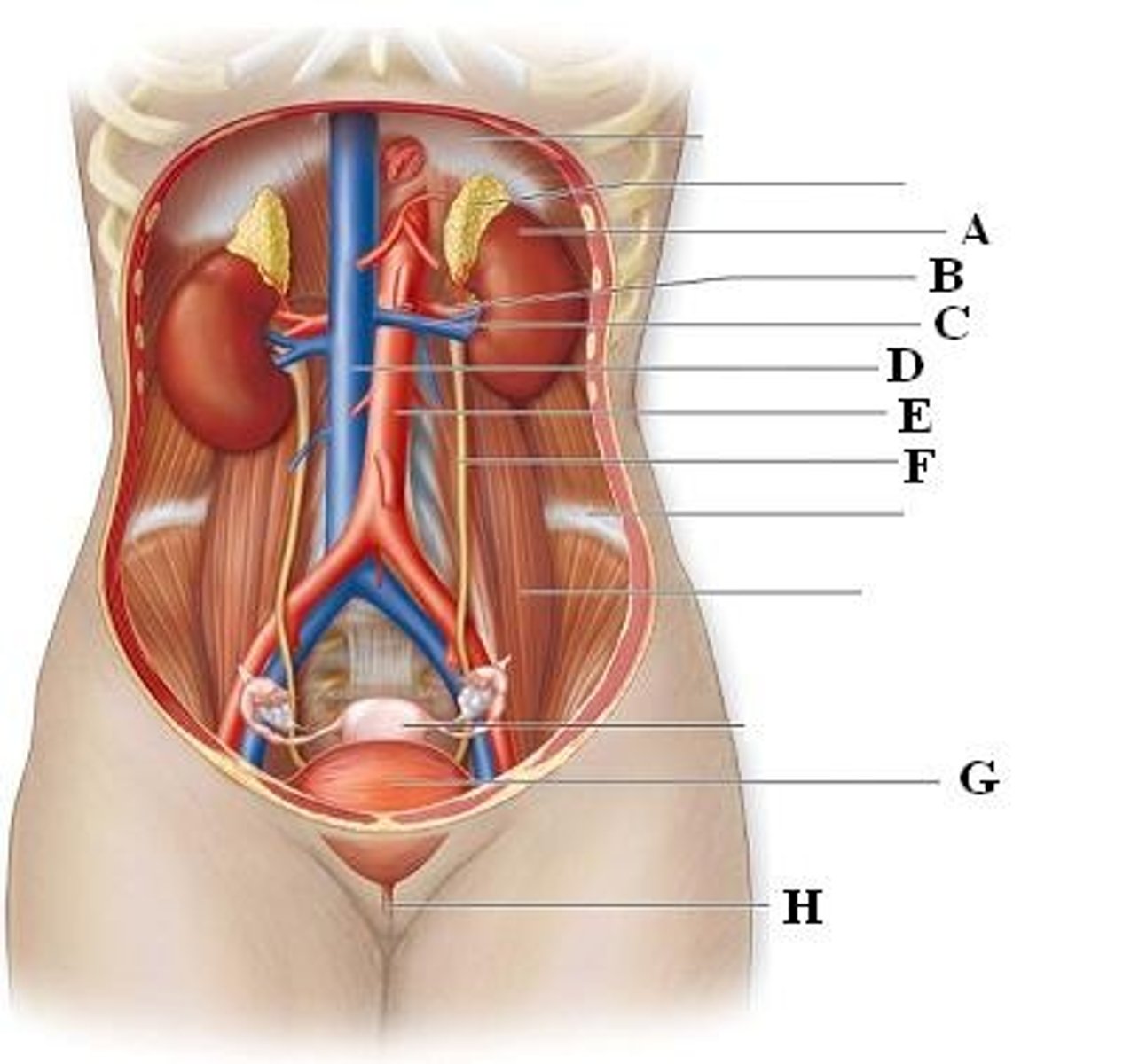
Which vessel courses posterior to the SMA and anterior to the aorta?
A. Superior mesenteric vein
B. Splenic vein
C. Left renal vein
D. Left gastric vein
left renal vein
All the following are IVC tributaries
Hepatic veins and renal veins
Two potential spaces located in the supracolic compartment are?
Subhepatic and Subphrenic spaces
the right renal vein runs anterior to
the right renal artery
The pancreas extends from the _____ to the _____
epigastrium to the left hypochondriac region
The head lies more _____ than the body and tail
inferior
The pancreas is posterior to the
stomach
What duct courses through the pancreas
The main pancreatic duct
What structures are anterior to the pancreas?
Stomach, first part of the duodenum, transverse colon,
What structures are posterior to the pancreas?
splenic vein, SMA, SMV, Aorta, IVC, prevertebral connective tissue, and spine
What structures are lateral to the pancreas
spleen and kidney
What structures are medial to the pancreas?
C-loop of the duodenum
which vessel courses posterior to the SMA and anterior to the aorta
Left renal vein
What is the gateway to the liver referencing?
The porta hepatic