Chapter 7: Product management
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Consumer products vs intermediate products
Consumer products | Intermediate products |
|
|
Product strategy - related concepts
1) Product positioning : see STP
2) Product mix
Product mix Width
Line Depth
Product mix Length
3) Product life cycle - PLC
4) Product innovation
5) The broader P of product
Product strategy: Product mix (2)
Dimensions
Width = number of product lines
Depth = number of items in a product line
Length = assortment of models, sizes, colors
Consistency = degree of relatedness of product lines
Possible expansion paths
Add new product lines = increase width of product mix
Add variations in line = deepen product lines
Add items = lengthen product mix

Product strategy: Product Life Cycle (3)
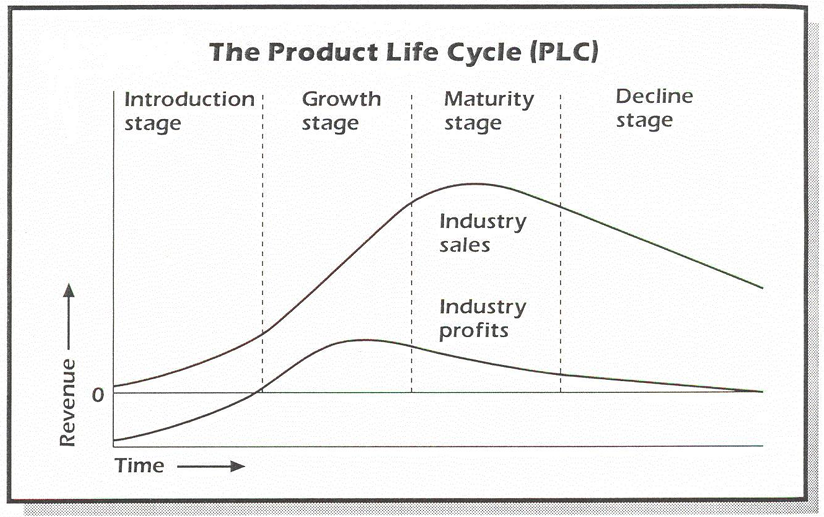
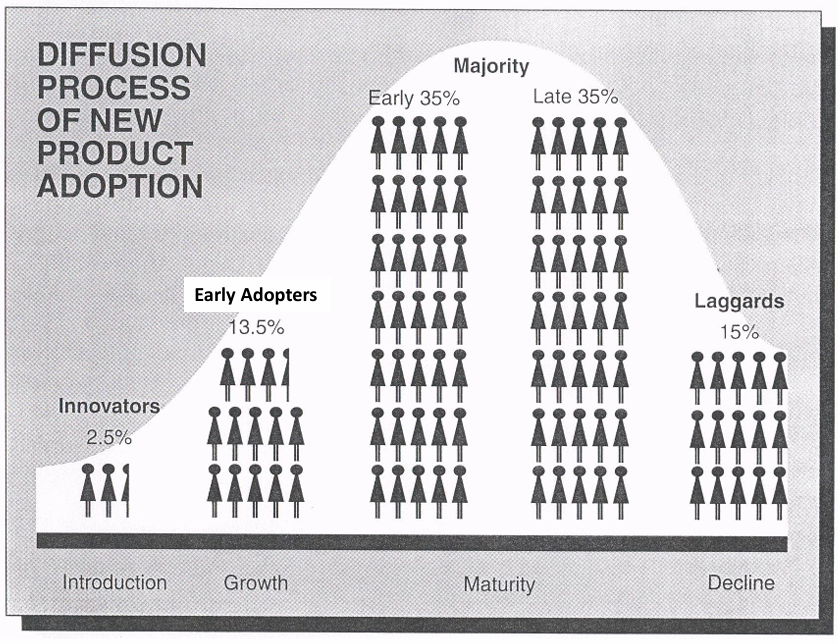
1) Introduction
sales are low
Losses → high R&D and promotional costs
Monitor product adoption process or “diffusion process of new product adoption”
Key role of innovators, trendsetters
2) Growth
Sales growth
Increasing acceptance
More and more trials plus first repeat purchases
High profit potential → profit margins peak
New rivals are attracted because of success
3) Maturity (eg. coca cola stretched maturity range by changing small things over time)
Sales peak and flatten: saturation is reached
Mainly repeat purchases, while innovators have already switched to something new
Profit margins under pressure
Survivors battle for market share
Brand leaders are the strongest and survive
Long life cycle = extended maturity stage
4) Decline
Sales and profits fall → profit turns into loss
Changing consumer taste and preference
New technologies take over
Seek to maintain profit margin
Cease / Stop production
Message
“Try to maintain possible profits as long as possible, but stop before it is too late”
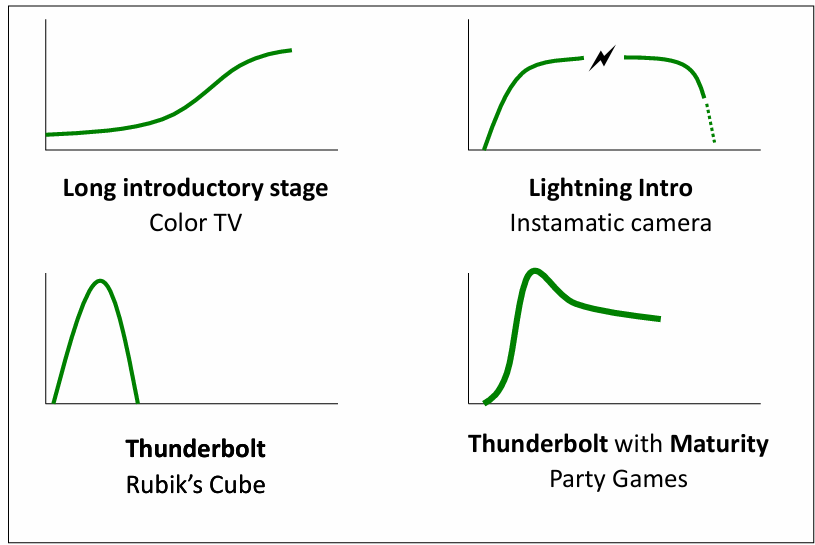
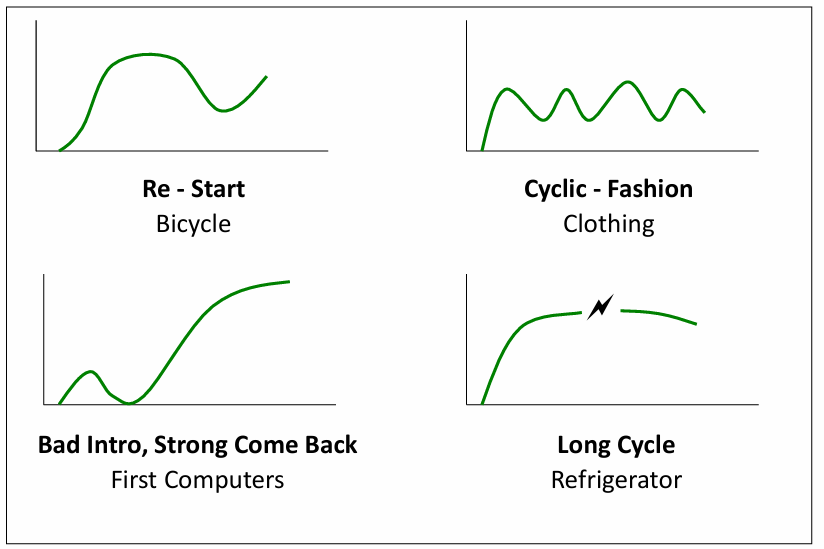
Product strategy: Product Life Cycle (3) - Types
Product strategy: Product innovations (4)
Repositioning products
Extending the maturity stage
Real vs. psychological repositioning
Product strategy: Product innovations (4) - New product categories
Me-tooproducts = copies of existing products
Line extensions = new variants or flavours in existing product line
New forms of existing products (e.g., powders)
Reformulations: new formula, e.g., sugar-free version
New packaging, e.g., modified atmosphere packaging
Innovative products: ready-to-cook, convenience added
Creative products: real new products, real (radical) innovations
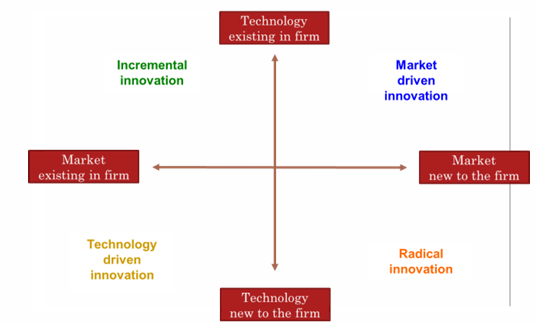
Product strategy: Product innovations (4) - Reasons for new product failure
Product lacks meaningful uniqueness
Poor planning during introduction
Badly timed introduction
Market is not ready for the product
Too enthusiastic take off
Inconsistencies in marketing mix
= Poor marketing
Product strategy: Product innovations (4) - Launch Pricing Strategies (during introduction)
Skimming strategy (intro with high price)
High product value
Ability to pay
Consumer differs from bill payer
Lack of competition
Pressure to buy
Price penetration strategy (intro with low price)
If this is the only feasible alternative
To quickly gain market presence
To realise experience curve effect
Make money later
Product strategy: The broader P of product (5)
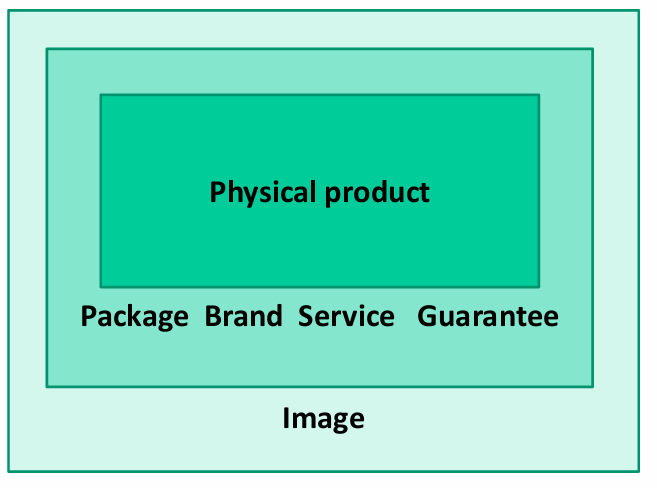
1) Packaging
2) Branding
3) Guarantee
4) Service
5) Image
Product strategy: The broader P of product (5): Packaging
Definition
activities related to
box
wrapper
container
Significance of packaging
packaging is costly
Many products are packed several times
Importance of packaging in terms of cost / benefit
provides benefits | raises costs |
|
|
Product strategy: The broader P of product (5): Packaging - Components / Functions of packaging
1) Protection
Against physical damage
Longer shelf life
Refrigeration, moisture, light
Let in
Keep out
2) Cost efficiency
Packaging materials
Fabrication, manufacturing of packaging
Labour involved in packaging
3) Recognition
Colour, Shape, Size, Font type
4) Handling
Transport
Display
Handle, Store, Open, Close
Disposal of used packaging (recycling, reuse)
5) Vehicle for information
Price, quantity
List of ingredients
Nutritional information
Dates: production, packaging, expiry
Nutritional and environmental performance (EcoScore, NutriScore)
Guarantee, label
Use: storage, preparation, recipes
Product strategy: The broader P of product (5): Branding
Definition
Any Name, Term, Sign, Symbol, Design
Name = by which the product can be called
Mark = by which it can be visually recognised
Importance
Source of consumers’ trust
Key to advertising
Key to brand loyalty, repeat sales
Umbrella or platform for intro of new products
Indication of a specific quality level
Reducing uncertainty for buyers / consumers
Problems with building brands
Time-consuming and expensive
Heavy competition from other brands including private brands (private labels)
Generic or non-branded products
Product strategy: The broader P of product (5): Guarantee
Sales promotion element (= additional value)
Protection of and added value to consumer
Protection of producer
Product strategy: The broader P of product (5): Service
Content?
What is included in the service?
How far does the service reach?
Make or buy?
Do it ourself?
Have somebody doing it for us?
Price?
Included in the product’s base price
Sold as an extra to consumers
Product strategy: The broader P of product (5): Image
Overall picture
How people think and feel about the product / brand / company
All P’s together