Labor and Delivery Archer
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What slows down contractions?
tocolytics
tocolytics examples
terbutaline
and
magnesium sulfate
oxytotics does what
stimulate contractions
oxytocin is what?
oxytotics
terbutaline indications
preterm labor
is also used as a resuce medication for astham
terbutaline: monitor
HR of mom and baby when used in labor
monitor fetal heart monitor strips closely
blood glucose
and EKG
terbutaline can cause
Hypokalemia,
HTN,
hyperglycemia
CNS overstimulation (vs will go uo so do frequent VS)
magnesium sulfate indidcations
Hypomagnesemia
torsade de point
pre-eclampsia
preterm labor
seizures
asthma exacerbation
magnesium sulfate considerations
Give IV Slowly (can cause over sedation)
monitor for hypermagnesemia
monitor for hypermagnesemia
confusion
dizziness
weakness
decreased reflexes -> turn down of off
Oxytocin indications
induction of labor
and
post post part hemorage
oxytocin considerations
monitor contractions
monitor fetus reponse
warn mother contractions will be more painful
oxytocin monitor
BP
HR
glucose
K
mentus
chin first in birth cancal
sacral
butt bound in birth cancal
occiput
back part of the skull(we want this)
determinign the position of the baby
right or left
what is presenting
how they are lying
what is the best position for birthing
ROA or LOA
at isichial spine
0 station
negative - further up in beith cancal
positive station - mom is ready to start pushing
variability
fluctuation in the fetal heart rate
Acceleration
a speeding up of the fetal heart rate
deceleration
a slowing down of the fetal heart rate
reassuring
the baby looks healthy
HR for fetus
110-160
Absent variability
bad
Doesn't go up or down
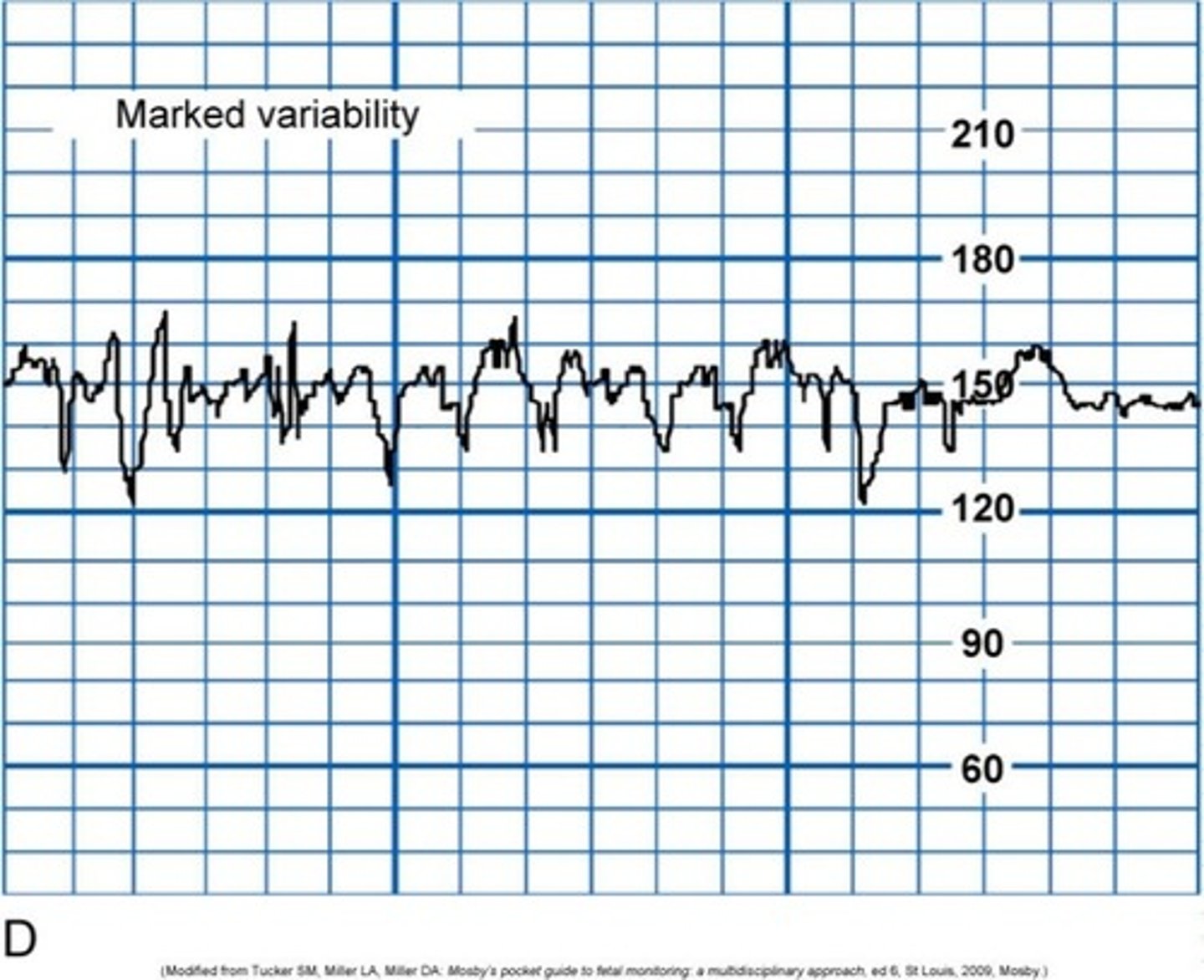
Marked variability
can be either bad or good
moderate variability
A reassuring sign
decelerations
early
variable
late
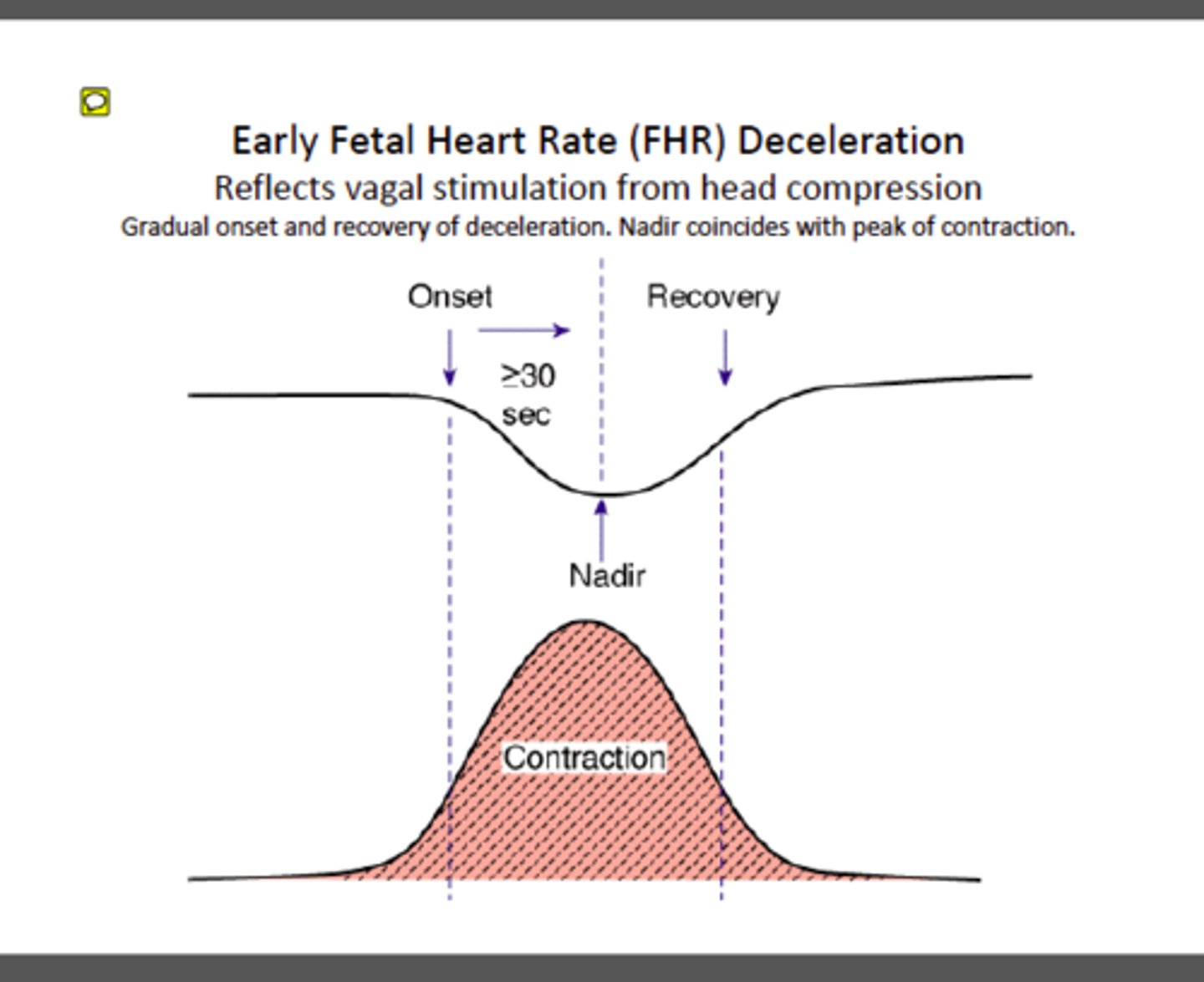
early decelerations
Head pressed on. This is ok.
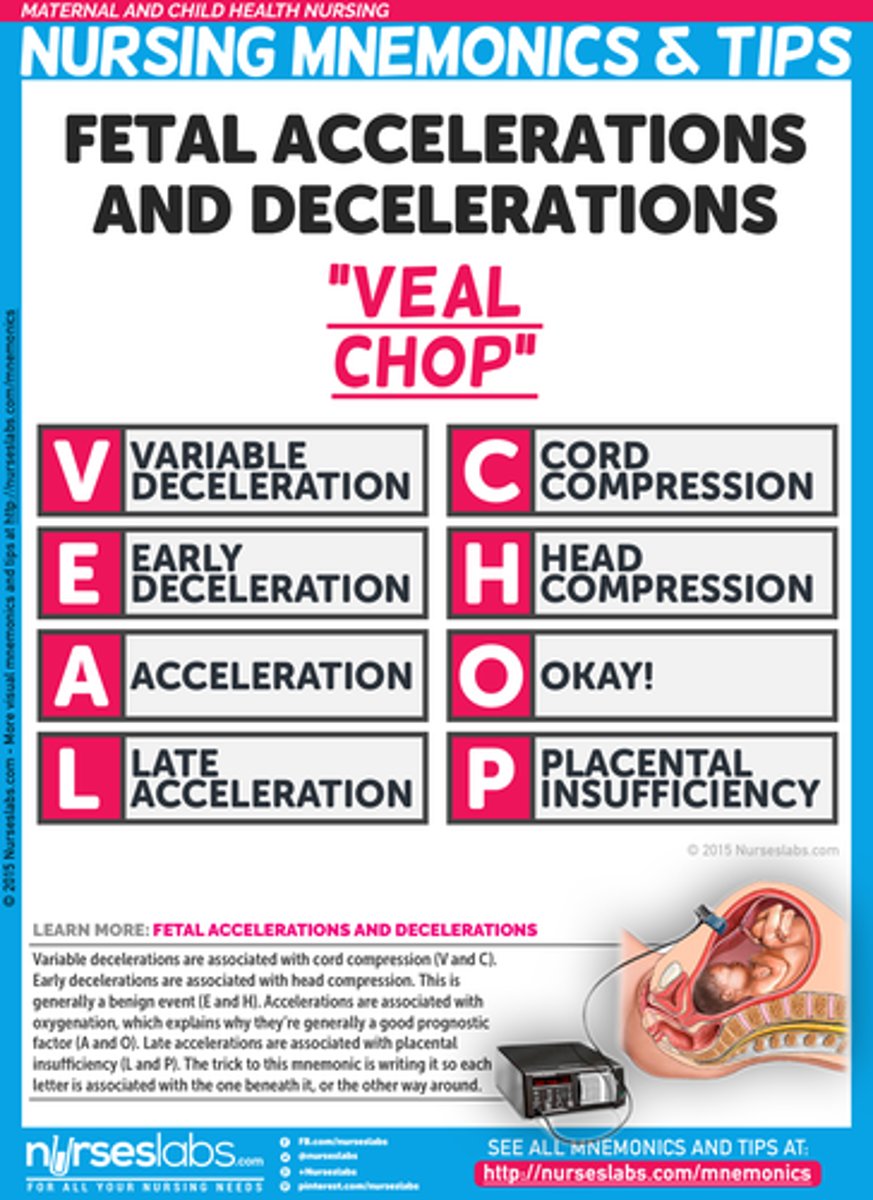
VEAL CHOP
V- Variable C- Cord Comphression
E- Early Decels H- Head Compression
A- Accelerations O - OK
L-Late Decels P - Placenta
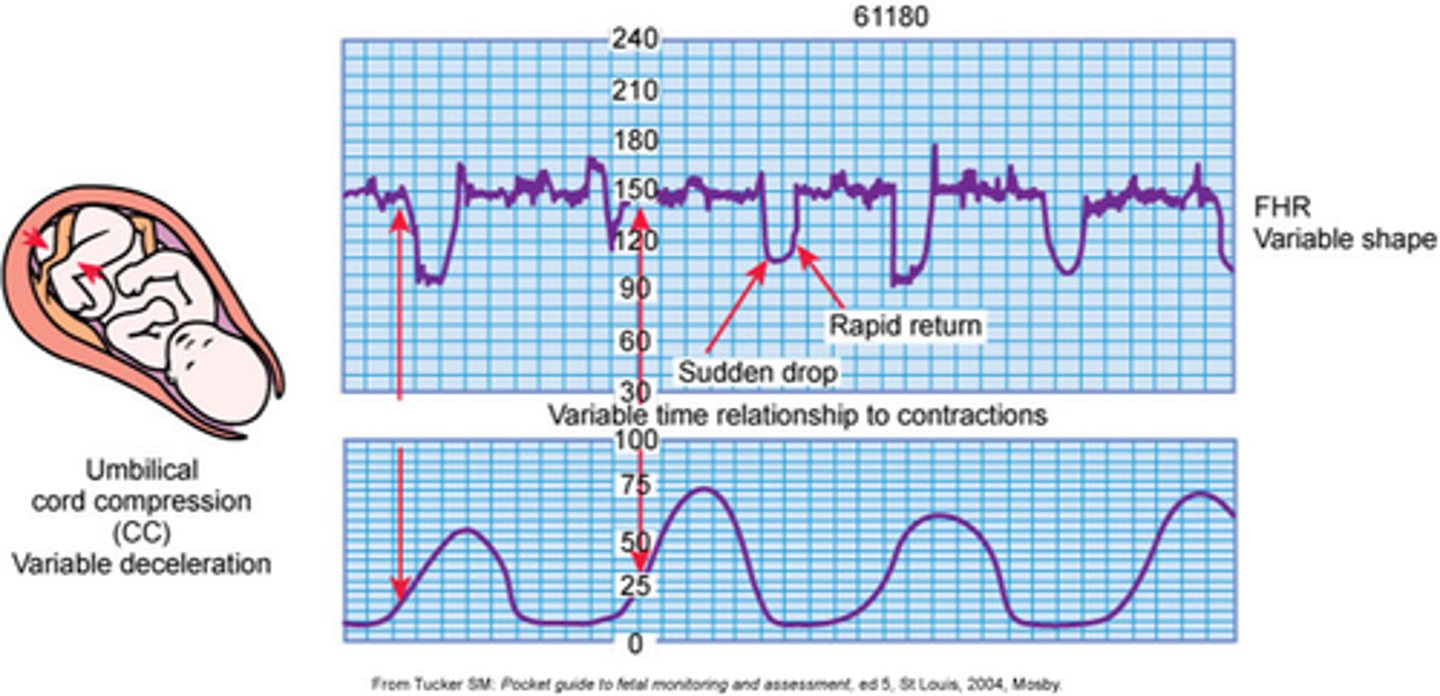
variable deceleration
cord compression
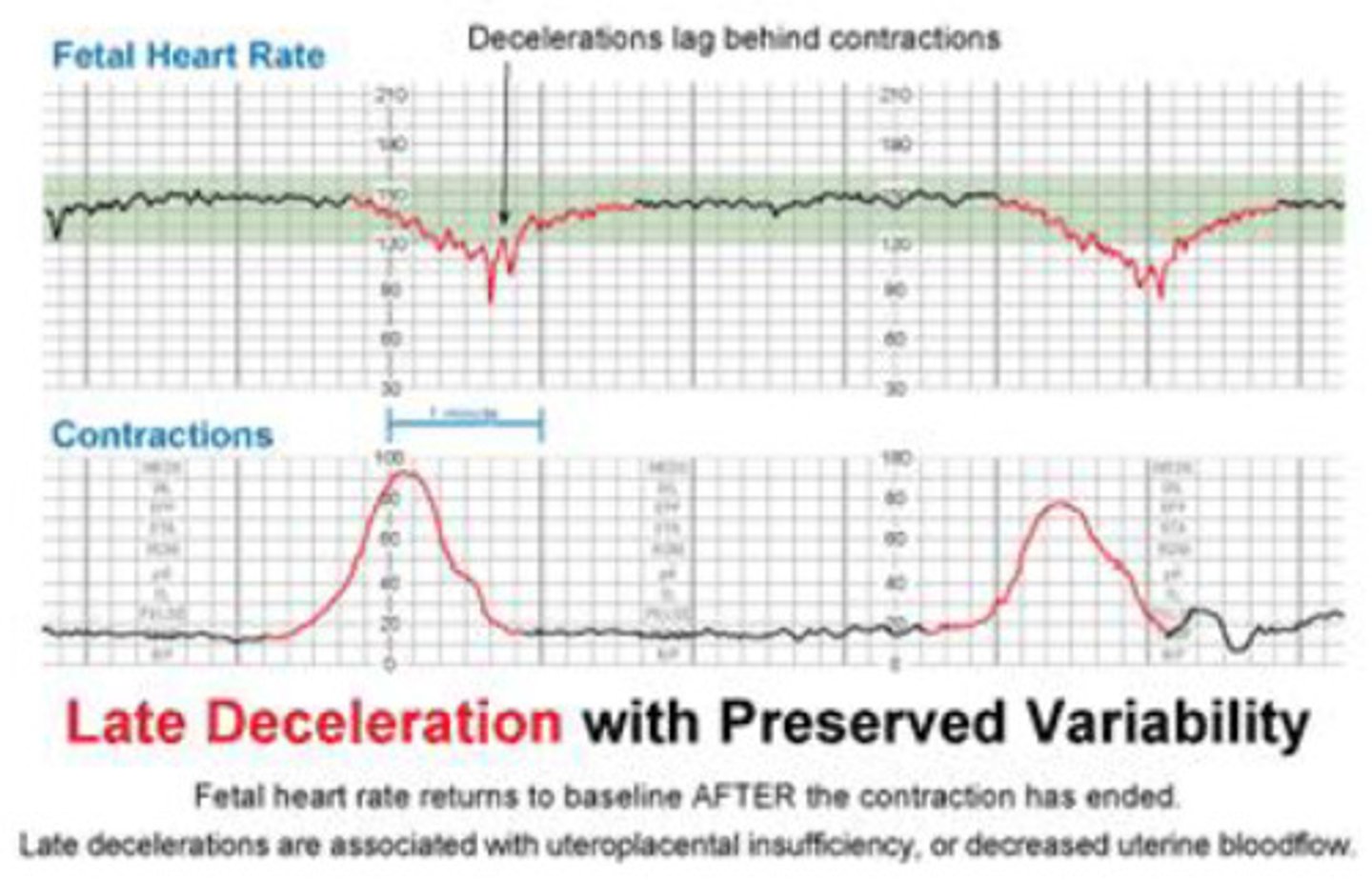
late decelerations
Bad (placental insufficiency)
LION
Non reassuring fetal heart rate
LION PIT
Lay the mother on her LEFT side
Increase IV fluids
Oxygen
Notify the healthcare provider
PIT: discontinue pitocin
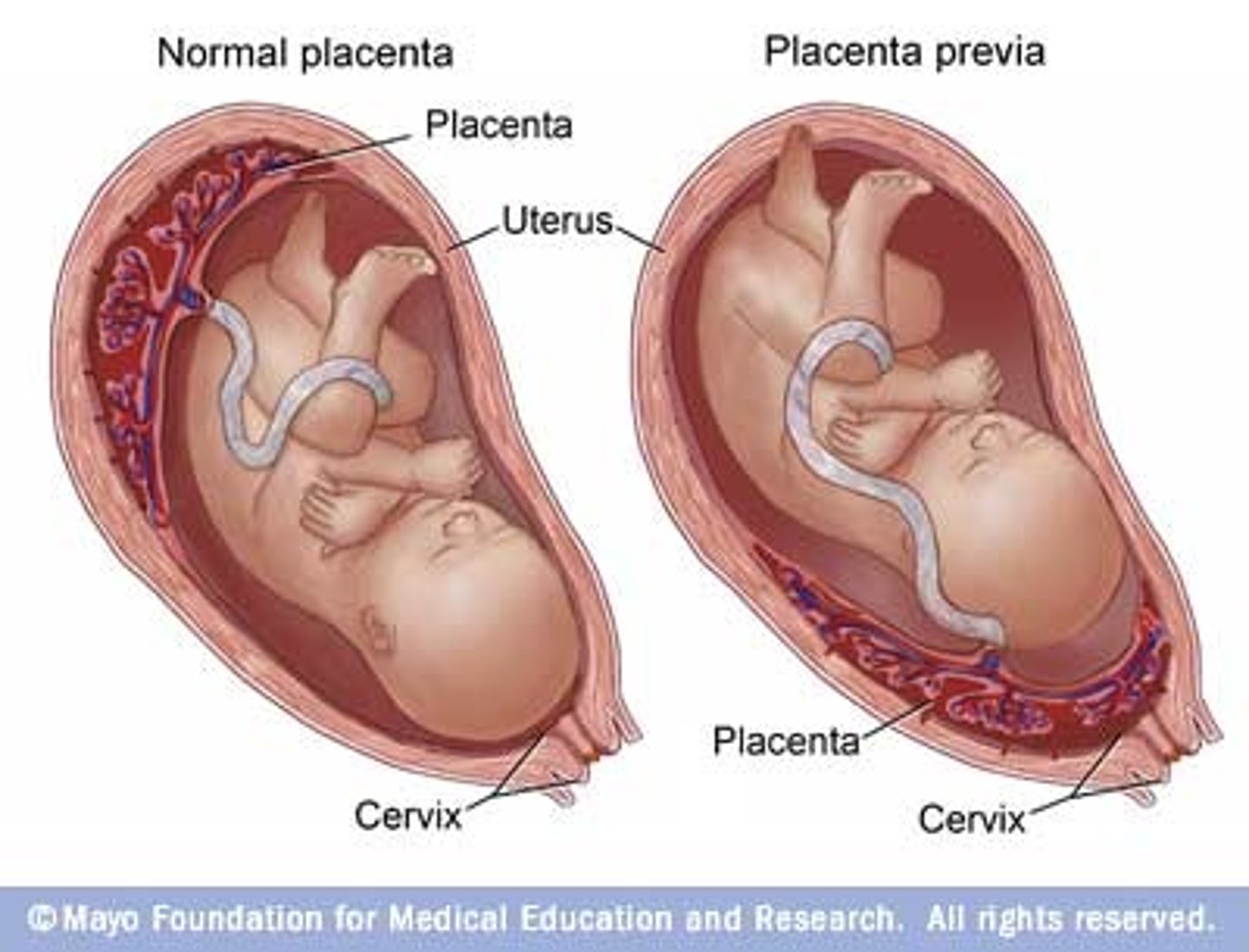
Placenta previa
Major symptom is PAINLESS bright red bleeding
placenta is covering the cervix
placenta previa assess
bleeding:
pad count to determine the amount
clot
color
placenta previa what is used to confirm diagnosis
ultra sound
This will determine the type of previa
Transvaginal ultrasound is
safe in placenta previa
Nursing interventions for placenta previa
never ever perform a vaginal exam if you suspect this_> can break placenta and cause more hemmoraage
would never want to irritate the placenta
monitor fetus
bed rest: minimize blood loss
c-section indicated in most cases
1 gram
1 mL of blood loss
Abruptio placentae
premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall (placenta is in the right place)
abruptio placenta s/s
causes massive amount of painful bleeding (dark red )
incomplete abruptio placenta
causes internal bleeding
blood backs up behind the placenta
complete abruptio placenta
causes massive external bleeding
very painful
abruptio placenta assessment
Board like abdomen ( due to internal bleeding)
rigid uterus
hypotension
maternal tachycardia
fetal brady cardia
abruptio placentae intervention
-Monitor for fetal distress
-Monitor maternal bleeding
-monitor fundal height
-keep the BP up with IVF and or blood product
-prepare for delivery- most likely C-section
prolapsed cord
umblical cord slips out
during delivery the prolapsed cord can become compressed by the presenting part of the fetus which cuts off oxygen to the fetus
do cervical exam or visual
pulsing tissue
prolapsed cord interventions
elevate the presenting part of the fetus off of the prolapse cord
keep your hand on the baby's head lifting it up and call for help
administer oxygen
wrap cord in sterile moist towel
prolapsed cord position
knees to chest position- open the pelvis
trandelenburg- let gravity shift the baby off the cord
what not to do with patient who has a prolapsed cord
never attempt to push the cord back in
postpartum hemorrhage risk factor
-twins or triplets
-macrosomia fetus
-preeclampsia
-prolonged labor
-precipitous labor
-use of forceps or vacuum during delivery
-placenta previa
-abruptio placenta
Boggy uterus
This is a uterus that is not contracting to clamp down on the blood vessels
INDICATES BLEED
The fundus will feel soft instead of hard as it should
hemorrhage blood loss
-PPH client are saturating pad every 15 minutes
-puddle of blood in the bed
-if they try to stand up for the first time there could be a huge gush of blood
hemorrhage interventions
fundal massage- every 15 minutes at a minimum
meds:
oxytocin
methylergonovine
blood product
Methylergonovine (Methergine)
Acts directly on the uterine muscle to stimulate forceful contractions. Used for postpartum hemorrhage.