Anatomy II - PreMT
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
angio-
vessel (a)
Bar/o-
pressure, weight
brady-
slow
cardi/o-
heart
coagul/o-
clotting, to clot ( c)
Coron/o-
heart (corono)
-emia
blood (-e)
hem/o-
blood (he)
-megaly
enlargement
mi/o-
smaller, less
Palpit/o-
to throb, flutter
-plasty
surgical correction, repair
scler/o-
hard
-stenosis
narrowed, constricted
tachy-
fast
Thromb/o
clot, thrombus
vas/o-
vessel, vas deferens
Ven/o-
vein
What are the three main components of the cardiovascular system?
Blood, the heart, and blood vessels
What is the cardiovascular system responsible for?
Transportation, regulation, and protection
What is transported by the blood?
Oxygen and CO2, nutrients, cellular waste, and hormones
What does the cardiovascular system regulate?
temperature and blood pressure in tissues
What is vasoconstriction?
Narrowing of the blood vessels, caused by contraction of muscles in their walls
What is vasodilation?
Widening of blood vessels, caused by wall muscles relaxing
How does the cardiovascular system protect the body?
Blood clotting and immune cells
What is an artery?
Thick, strong vessels that carry blood away from the heart
What is an arteriole?
Small branches of arteries that control blood flow into capillaries
What is a capillary?
Tiny, think-walled vessels where oxygen and nutrient exchange happens with tissues
What are venules?
Small vessels that collect blood from capillaries and begin carrying it back toward the heart
What are veins?
Vessels that carry blood toward the heart, thinner than arteries and often have valves
What are the two main parts of the thoracic cavity?
Pleural cavities and mediastinum
What is found in the pleural cavities?
Lungs and pleura
How many pleural cavities are there?
two, one per lung
What is in the mediastinum?
The organs that lie in the centre of the chest between the lungs
What organs can be found in the mediastinum?
Heart and pericardium, thymus, esophagus, trachea
What cavity can be found within the mediastinum?
The pericardial cavity
What is the average size of the human heart?
About the size of a closed fist, about 1 lb.
What is the apex of the heart?
The bottom pointed end
What is the pericardium?
A double-walled sac that surrounds and protects the heart and the roots of the great vessels
What are the two main parts of the pericardium?
Fibrous pericardium (superficial), and serous pericardium (deep)
What are the two layers of the serous pericardium?
Parietal pericardium and visceral pericardium
What is another name for the visceral pericardium?
the epicardium
Where does the parietal pericardium attach?
It attaches to fibrous pericardium
Where does the visceral pericardium attach?
It attaches to the heart
What is found in between the parietal and visceral pericardium?
The pericardial cvity
What is found in the pericardial cavity?
Pericardial fluid, or serous fluid
What is the heart enclosed by?
The pericardium (NOT IN the pericardium)
Which layer of the pericardium is not involved in the pericardial cavity?
The fibrous pericardium
What is the normal volume of serous fluid in the pericardial cavity?
15-50 mL of fluid
What does pericardial fluid do?
Reduces friction as heart beats, helps layers glide easily over each other, cushions the heart and helps maintain surface tension
What is the heart in?
In the pericardial sac (NOT pericardial cavity)
What are the three layers of the heart wall?
Epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium
What is the epicardium?
Most superficial layer of the heart wall, also the visceral layer of the serous membrane
What is significant about the myocardium?
It is the cardiac muscle
What are the purposes of each of the heart wall layers?
The epicardium protects and makes beating smoother, myocardium contracts the heart and pumps blood, and the endocardium forms a smooth surface for blood flow
What can be found at the base of the heart?
Great arteries and veins enter the heart
What are the chambers of the heart?
Right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
What separate the chambers of the heart?
The sulci
What does the right atrium receive?
O2 poor blood from the body
What does the left atrium receive?
O2 rich blood from lungs
What are auricles?
Small pouch on the surface of each atrium of the heart, slightly increases capacity of each atrium
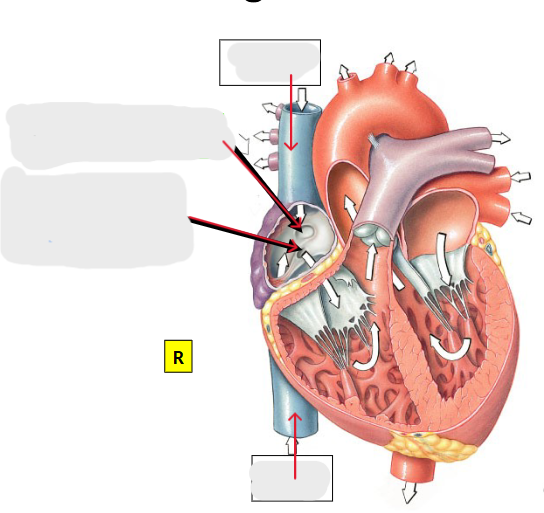
What significant structures are found on the right atrium?
Fossa ovalis, coronary sinus, superior vena cava, and inferior vena cava
What significant structures are found on the left atrium?
The pulmonary veins (ss)
What does the right ventricle pump, where and how?
Pumps O2 poor blood to lungs with low pressure
What does the left ventricle pump, where and how?
Pumps O2 rich blood to the rest of the body with higher pressure
How does the myocardium compare between the left and right ventricles?
Myocardial muscle of left ventricle is 2 to 4 times larger than right ventricle (bc left works harder)
What do the atrioventricular valves do?
prevent back flow into the atrium
What is the right atrioventricular valve called?
The tricuspid valve
What is the left atrioventricular valve called?
The mitral or bicuspid valve
When do the atrioventricular valves open?
When atrial pressure is higher than ventricular pressure
When do the atrioventricular valves close?
When ventricular pressure rises during contraction
What is the scientific name for the heartstrings?
Chordae tendineae
What is the function of the chordae tendineae?
During contraction, blood pressure rises and pushes AV valves closed; CT tense and anchor the valve to prevent prolapse and backflow
What are the two semilunar valves?
The aortic valve and pulmonary valve
Where is the aortic valve found?
Between the left ventricle and the aorta
Where is the pulmonary valve found?
Between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
What is the purpose of semilunar valves?
Preventing backflow into the ventricles
Describe deoxygenated blood flow through the heart
IVC/SVC → Right atrium → Tricuspid → Right ventricle → pulmonic valve → pulmonary artery → lungs
Describe oxygenated blood flow through the heart
Lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium → mitral valve (bicuspid) → left ventricle → aortic valve → aorta → body
What do the cardiac muscles do?
Make the heart contract
What are the nodal cells and their function?
Pacemaker cells in the heart (two groups), set the pace of heartbeat
What are conducting cells?
Cells that work with nodal cells to get signal to cardiac muscle cells
What does automaticity mean in terms of the heart?
Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own in the absence of neural or hormonal stimulation
What is significant about the function of the conducting system?
It can work without the brain
What is the sinoatrial node and it’s function?
The primary pacemaker, initiates action-potential ~100 times faster than any other region in conducting system
What influences the sinoatrial node?
neurotransmitters and hormones
What can the autonomic nervous system affect about the heart?
Can modify heart rate but does not determine rhythm
Where is the sinoatrial node located?
In the right atria wall, inferior to SVC opening
What does the sinoatrial node do in conduction?
Creates the action-potential, and conducts to both atria so they finish contracting at the same time
How does the action potential from the sinoatrial node reach the left atrium?
via Bachmann’s bundle
Where is the atrioventricular node located?
In the interatrial septum, inferior to coronary sinus
What does the atrioventricular node do?
Slows down the action potential to allow the atria to finish emptying before contracting ventricles
What is another name for the bundle of His?
The atrioventricular bundle
Where is the bundle of His located?
The interventricular septum
What is significant about the interventricular septum?
Holds bundle of His, only site where action-potential can conduct from atria to ventricles
Where do the right and left bundles branches extend to?
Through interventricular septum towards apex
What is the bundle of His?
Specialized muscle fiber bundle that carries electrical signals from AV node to ventricles
What are Purkinje fibers?
Specialized cardiac muscle cells that conduct electrical impulses rapidly from apex to remainder of ventricular myocardium
Where are the Purkinje fibers located?
They originate near apex and extend upwards
What does an electrocardiogram do?
Records the electrical changes that accompant a heartbeat