Parkinson's and Alzheimers Drugs
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
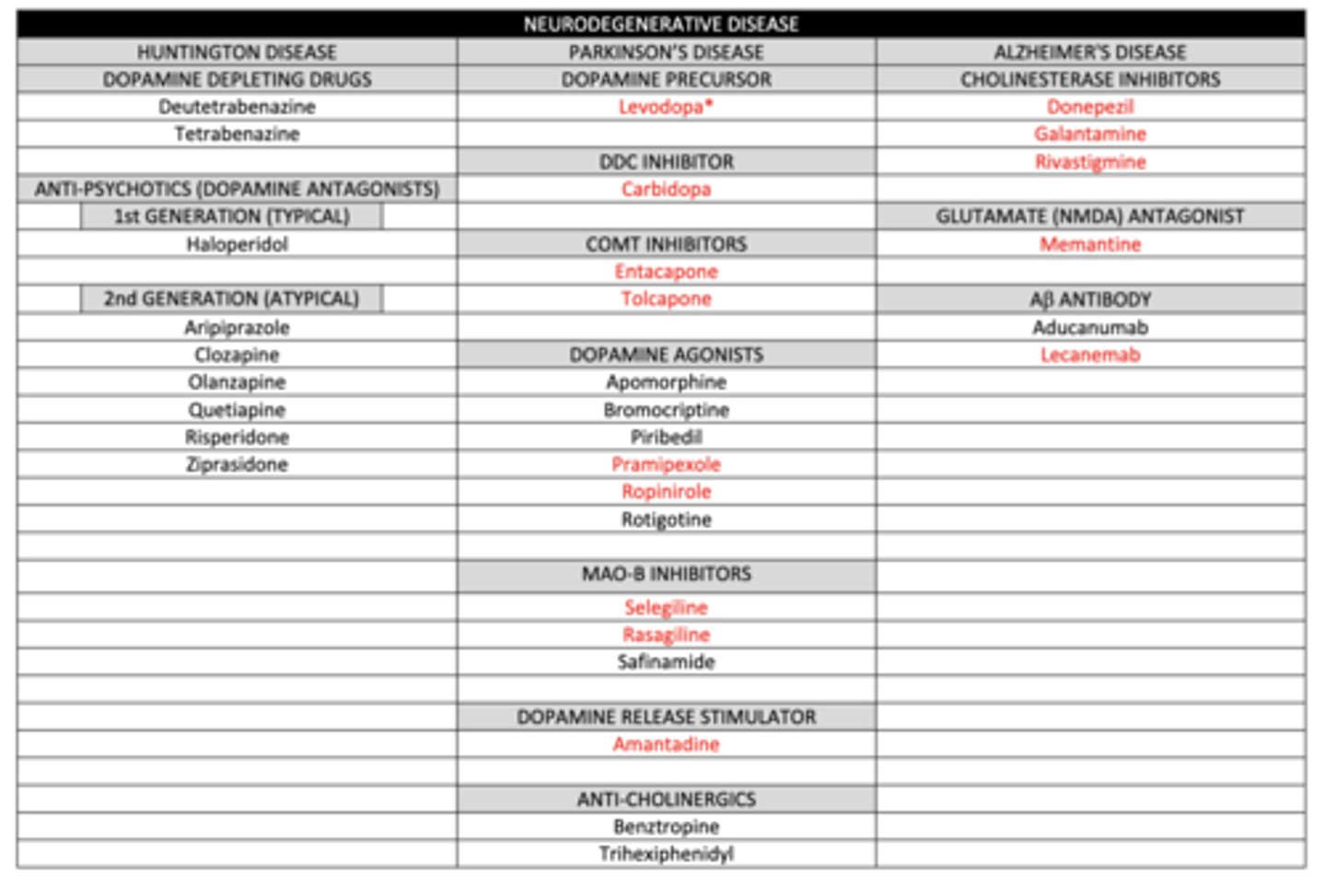
39 Terms
what dopamine receptor does the substantia nigra primarily project to to coordinate movement?
D2 receptor
T/F: we can treat the disease progression of parkinsons
false - drugs are used to treat symptoms, but there is nothing we can do to control the progression of the disease
what are the 2 goals of Parkinson's disease therapy?
1. increase supply of dopamine
2. suppress acetylcholine actions
list the steps in dopamine synthesis:
L-Tyrosine --> L-DOPA --> Dopamine
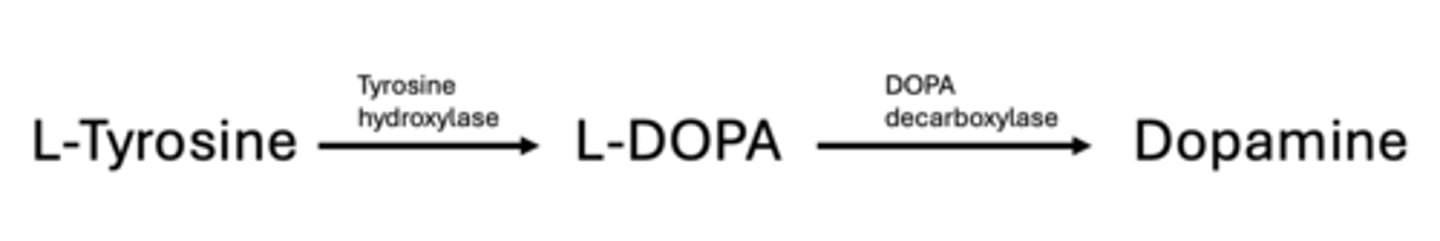
T/F: L-DOPA crosses the BBB
true
this is why we administer levodopa instead of dopamine in parkinson's treatment
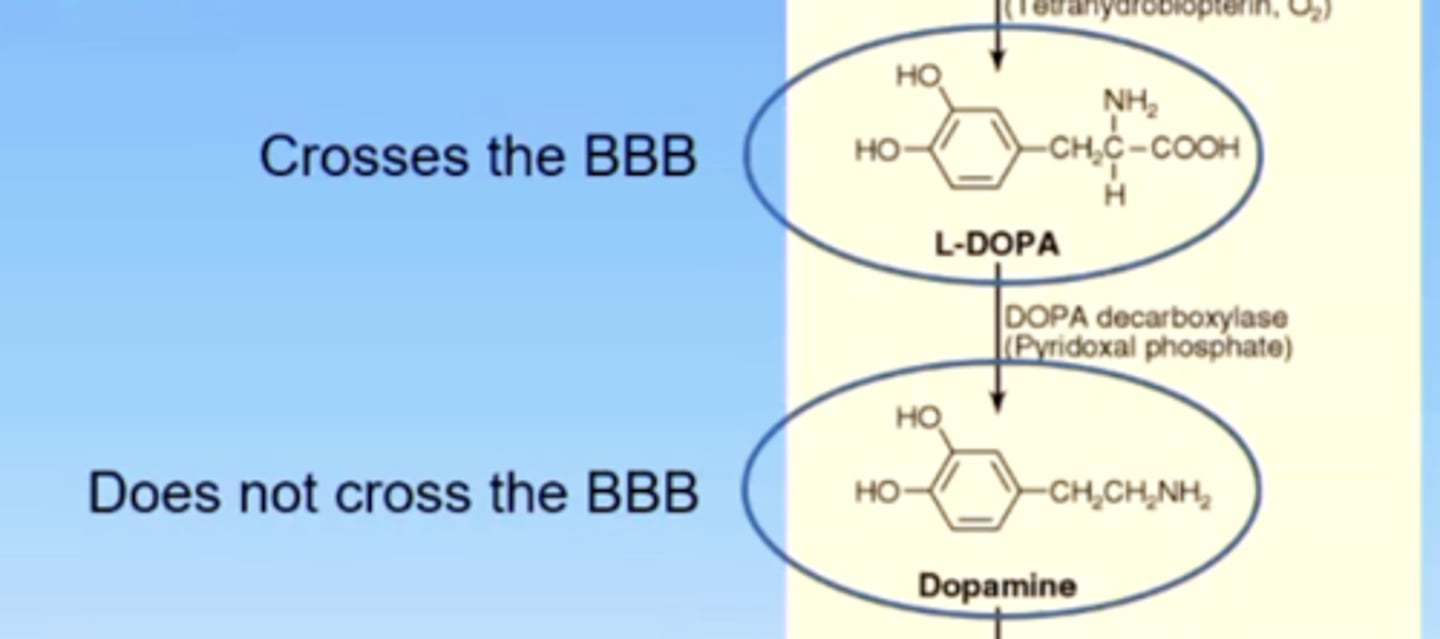
T/F: dopamine crosses the BBB
false
this is why we administer levodopa instead of dopamine in parkinson's treatment
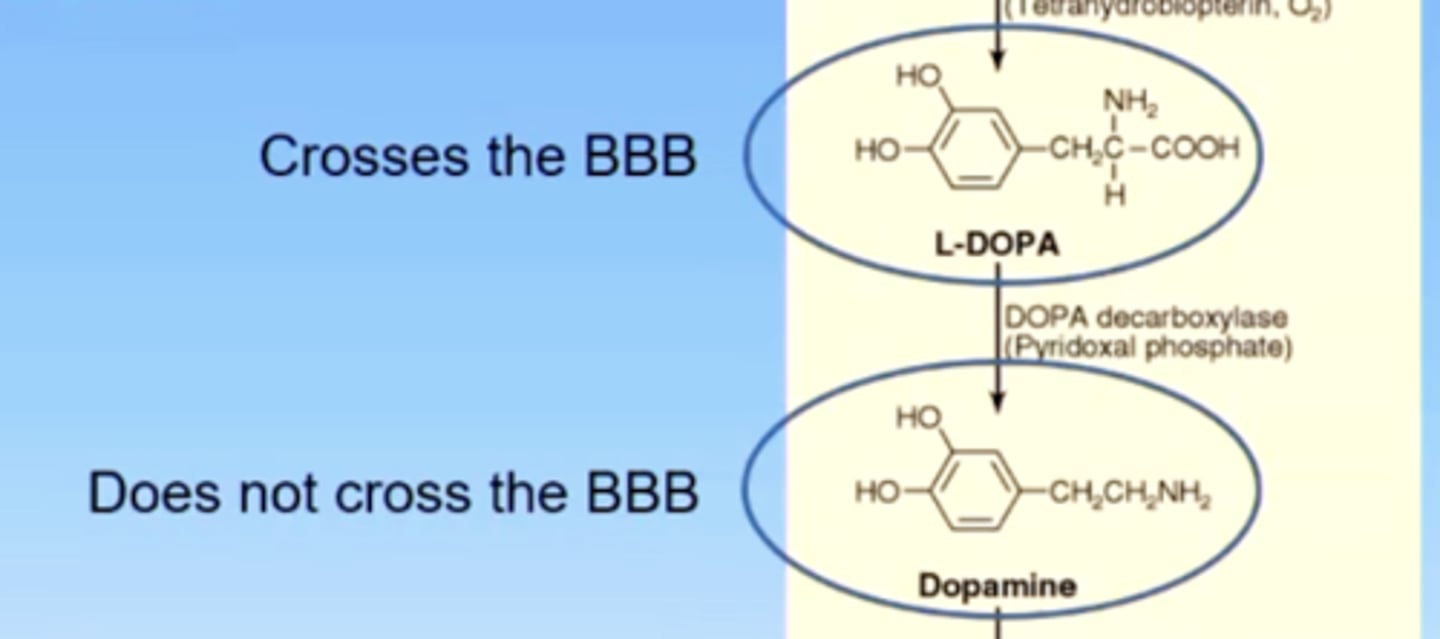
to treat parkinsons, you should combine levodopa with what other drug? why?
carbidopa
carbidopa inhibits DOPA decarboxylase, therefore deceasing levodopa metabolism in the periphery, allowing for more levodopa to get into the brain
what is the precursor to dopamine?
L-DOPA
what is the MOA of MAO-B inhibitors to treat parkinsons?
inhibits monoamine oxidase B, which inhibits the breakdown of dopamine
list the MAO-B inhibitors:
1. selegiline
2. rasagiline
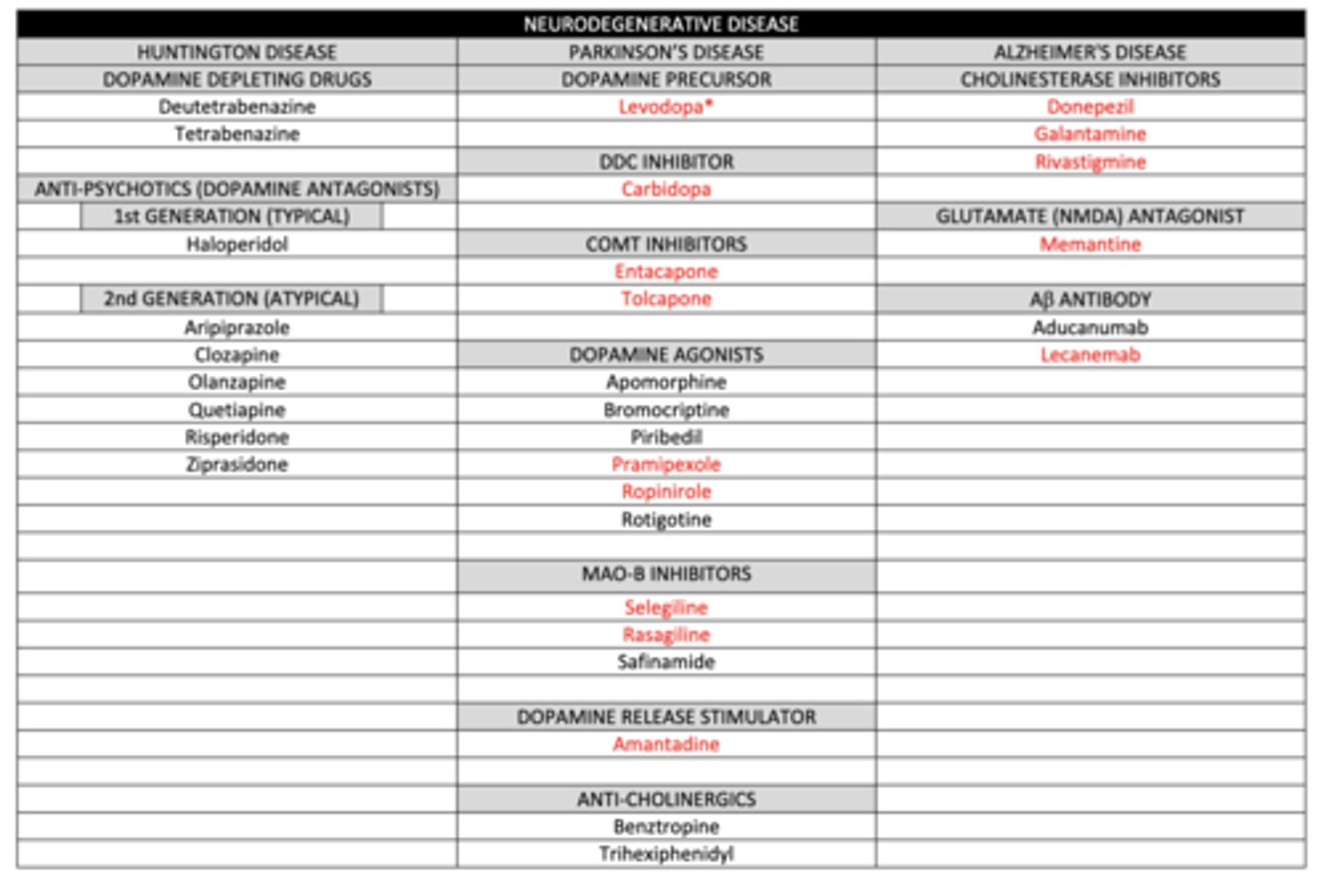
what is the MOA of COMT inhibitors to treat parkinsons?
inhibits catechol O-methyltransferase, which inhibits the breakdown of dopamine
list the COMT inhibitors:
1. entacapone
2. tolcapone
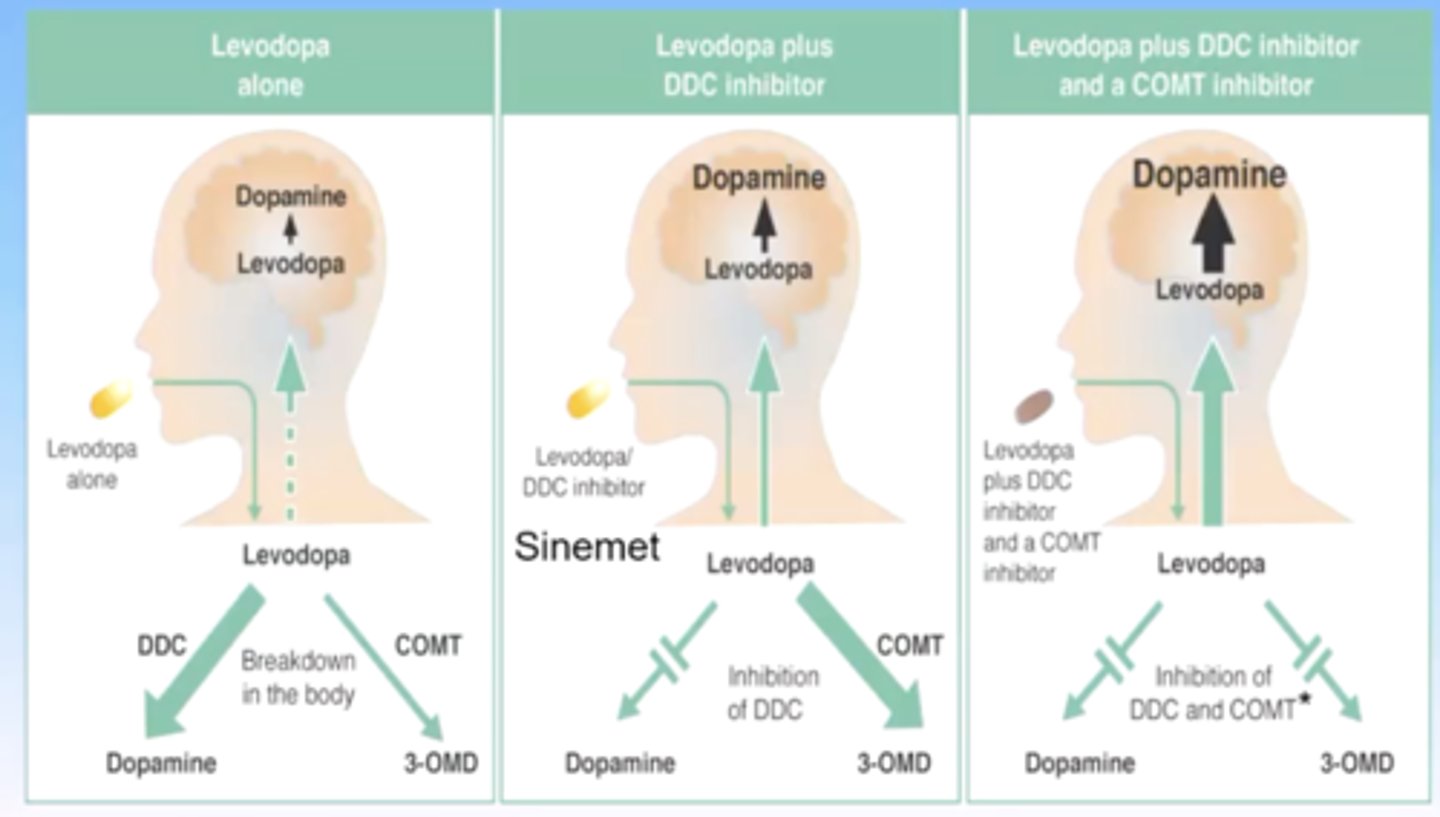
how can one optimize parkinsons disease therapy?
combing levadopa, DOPA decarboxylase (carbidopa), and a COMT inhibitor
this will maximize levadopa getting into the brain
what is levadopa-induced dyskinesia?
common and potentially disabling adverse effect of long-term levodopa therapy
it may involve multiple neurotransmitter dysfunction and the cortico-basal ganglia circuitry
what drug is used to treat levodopa-induced dyskinesia?
amantadine
amantadine is a NMDA receptor antagonist that increases dopamine production
which pain medications should be avoided in patients taking MAOIs? why?
medications that inhibit serotonin reuptake (meperidine, methadone, tramadol)
the combo of these drugs and MAOIs can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome
what is the most common form of dementia?
alzheimers
alzheimers is characterized by the loss of _______ neurons in the ________
loss of cholinergic neurons in the nucleus basalis of Meynert
what are some risk factors for sporadic alzheimers disease?
1. age
2. APO-E4 genotype
3. habits including type II diabetes, BMI, HTN, smoking, gut microbiome
4. periodontal disease
what type of stain is used to identify amyloid plaques in alzheimers?
modified Bielshowsky's silver stain
why is alzheimers disease hard to catch early?
the development of significant neuropathy precedes cognitive decline
aka plaques and tangles can build up for many years before any symptoms of cognitive decline appear
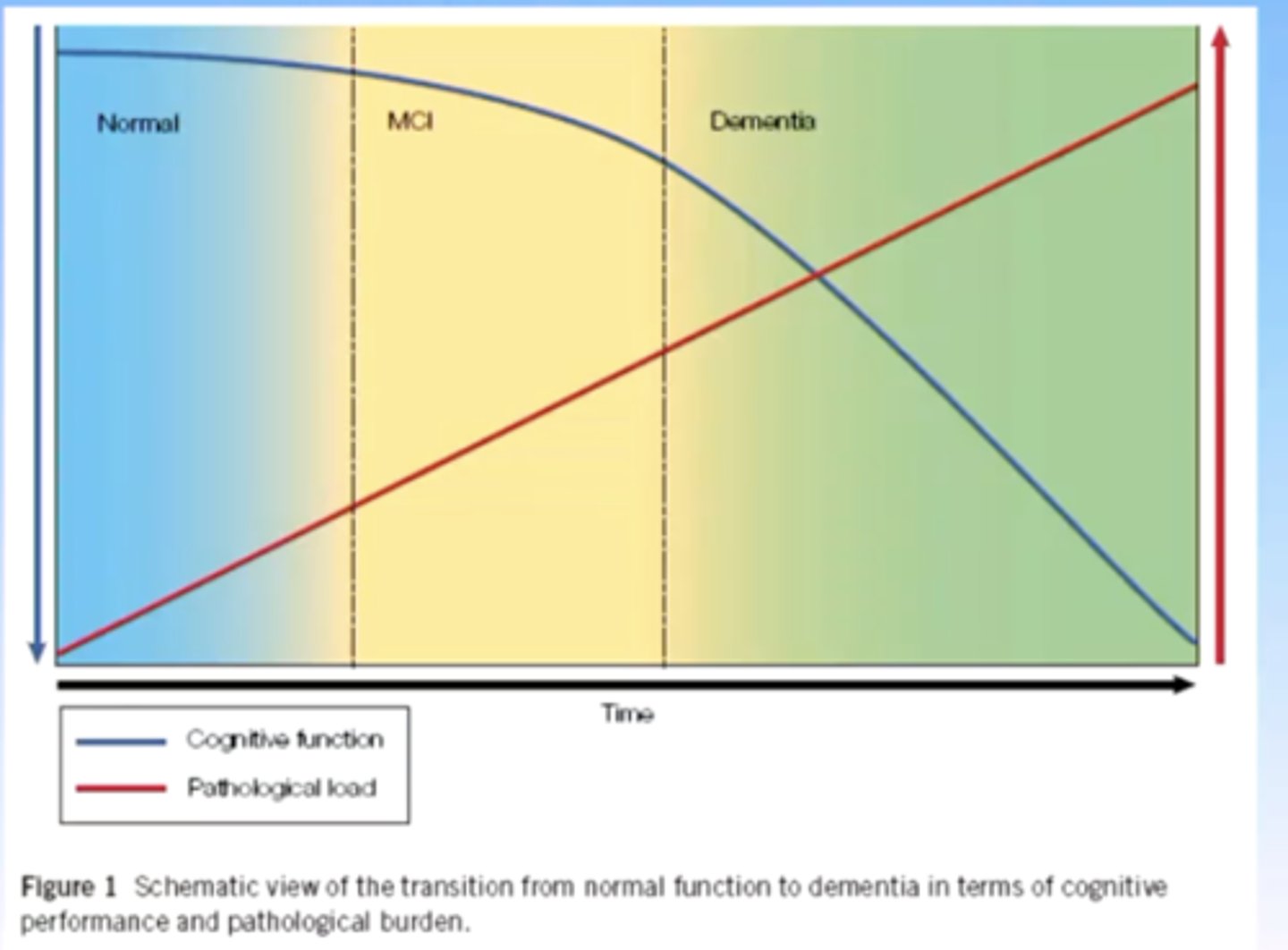
what is the foundational hypothesis for the pathogenesis of alzheimers?
amyloid beta deposition is an early and necessary event for pathogenesis of alzheimers
tau is still important, but amyloid beta is the bad guy in terms of alzheimers
besides alzheimers, amyloid deposits are associated with what other disease process in the brain?
inflammation in the brain
presence of microglia in the brain to try and clean up the plaques
according to research, why do patients with rheumatoid arthritis have a lower risk for alzheimers disease?
because these patients are taking anti-inflammatory medications
chronic use of NSAIDs can decrease risk for alzheimers (although you have other toxicities associated with chronic NSAID use)
the loss of what sense can be an early sign of alzheimers and can help predict the rate of progression?
olfaction
this is because cholinergic neurons project to the olfactory area, and when you lose cholinergic neurons in the brain, you can lose your sense of smell
what is the MOA of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in treating alzheimers?
they inhibit the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine (this helps preserve acetylcholine)
T/F: acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are reversible
why is this important?
true - if they were irreversible, it could be very dangerous and fatal
build up of too much acetylcholine in the brain can cause severe toxicities
list the acetylcholinesterase inhibitors:
1. donepezil
2. galantamine
3. rivastigmine
what are some toxicities associated with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors?
nausea, diarrhea, incontinence, arrhythmias
this is due to the overstimulation of parasympathetic responses caused by increased acetylcholine
what is the MOA of memantine?
glutamate (NMDA) antagonist
what drugs are used to treat mild to moderate alzheimers?
acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (donepezil, galantamine, rivastigmine)
what drugs are used to treat moderate to severe alzheimers?
memantine
what are the two main pharmacological strategies for reducing amyloid beta deposits?
1. inhibit the enzymes that metabolize the amyloid precursor protein (APP) into amyloid beta
2. enhance the clearance of brain amyloid beta deposits (by immunization)
the discovery of what antibodies have helped remove amyloid beta deposits in the brain?
1. lecanemab
2. adecanumab
lecanemab is used in passive immunization therapy to help clear amyloid deposits
what amyloid beta antibody is currently used in passive immunization to clear amyloid plaques in the brain?
lecanemab
what antibody is currently being tested/will be approved soon to be used as amyloid beta antibody treatment (alongside lecanemab)?
donanemab
showed same or better results after 6 months of therapy
why is periodontal disease a risk factor for alzheimers?
1. periodontal disease can result in systemic inflammation
2. P. gingivalis in periodontal disease can cause infections in the brain and promote the pathophysiology of alzheimers disease
what specific bacteria in periodontal disease can increase risk for alzheimers?
P. gingivalis
recent early phase clinical trials with what drug class are encouraging, in terms of alzheimers and periodontal disease?
gingipain inhibitors
gingipain is an proteolytic enzyme produced by P. gingivalis