Lab 06 & 07 - Part I: Connective Tissue & Musculoskeletal System
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Connective Tissue
made up of loose and densely packed elastic fibers, fibroblasts, and collagen fibers
Loose Connective Tissue
Holds organs and other tissues in place by providing a flexible network of fibers embedded in a gel-like ground substance.
Areolar Tissue
contains loosely arranged collagen and elastic fibers with scattered fibroblasts.
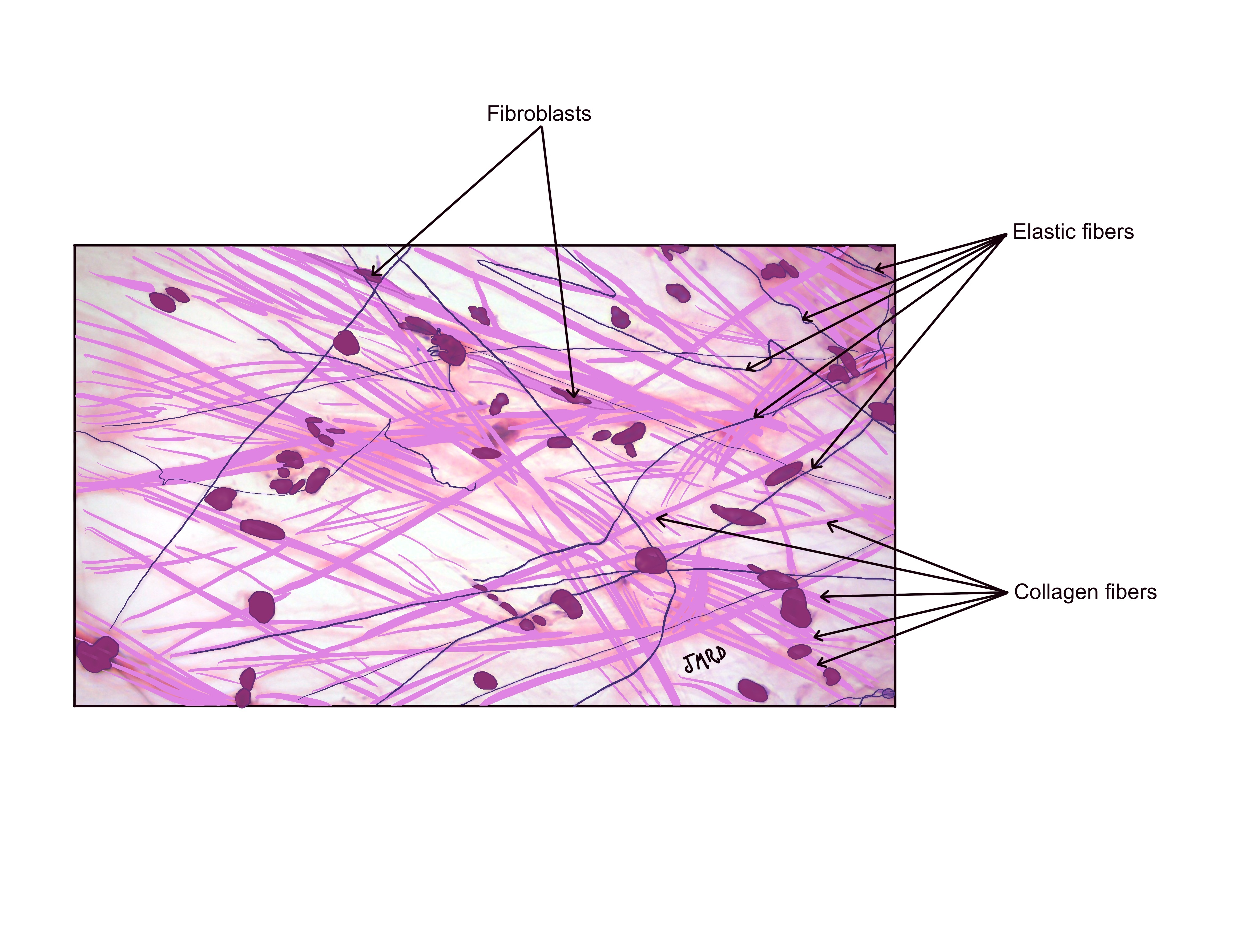
areolar tissue location
papillary layer of the dermis
Reticular Tissue
composed of loosely arranged collagen fiber called reticular fibers
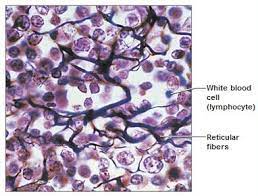
reticular tissue location
liver, spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes
3, Adipose Tissue
stores excess calories as fats, contains adipocytes
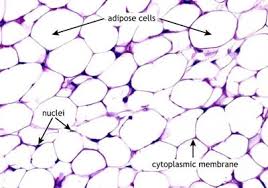
adipose tissue location
under the skin, around organs, and in bone marrow
Dense Connective Tissue
Primarily composed of tightly packed collagen fibers and fibroblasts, making it flexible and resistant to tension.
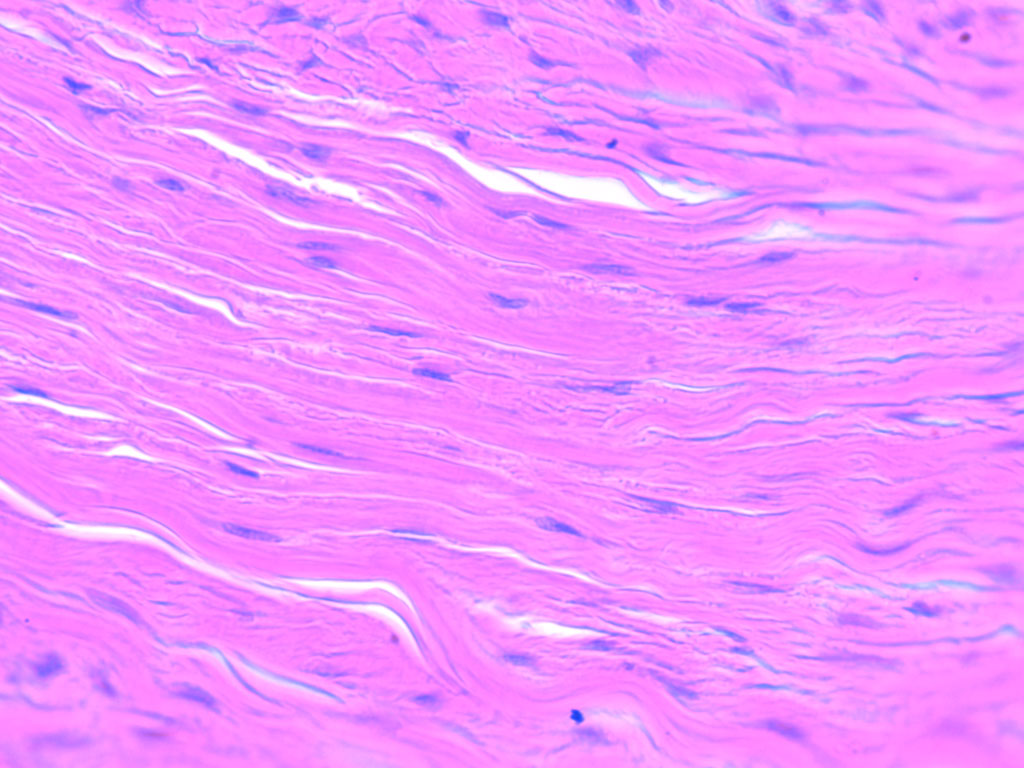
Dense Regular Tissue
densely arranged collagen fiber matrix, elastic fibers, and a few fibroblasts, fibers are parallelly arranged
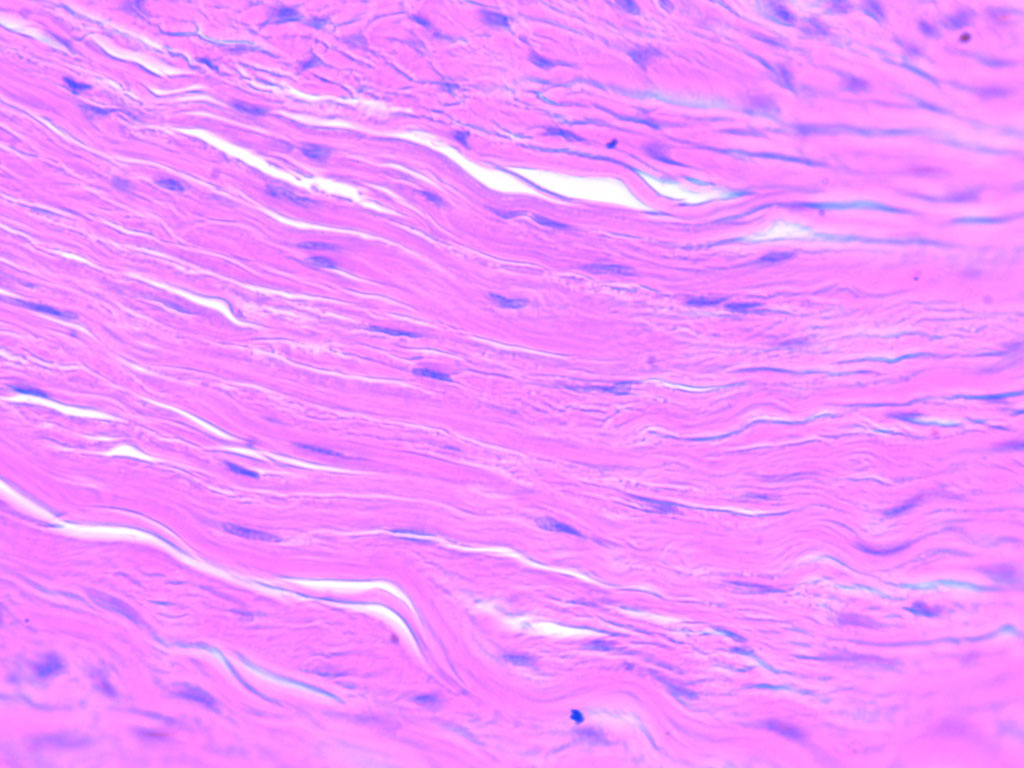
dense regular tissue location
tendons and ligaments
Dense Irregular Tissue
composed of a dense matrix of collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and few fibroblasts, randomly oriented
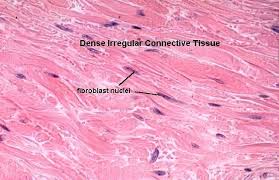
dense irregular tissue location
deep dermis
Cartilage
Composed of a rigid matrix formed by chondroblasts, chondrocytes, collagen fibers, and elastic fibers.
chondrocytes
mature cartilage cells
cartilage function
withstand tension, flexibility, and strength
3 types of cartilage
hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage
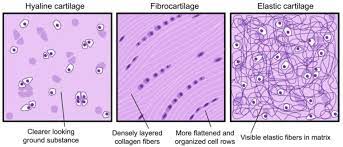
Hyaline Cartilage
has an Amorphous (no define shape) and rigid matrix
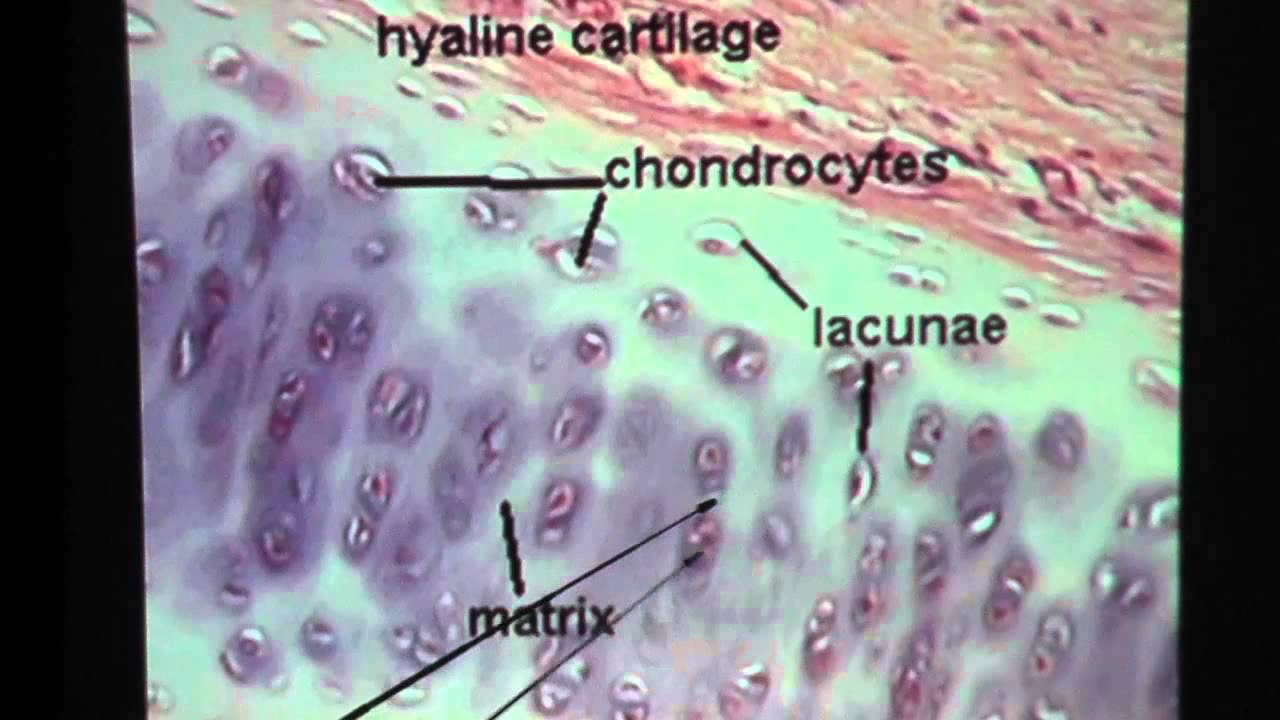
hyaline location
articular cartilage in long bones, costal cartilage connecting ribs to sternum, embryonic skeleton
Elastic Cartilage
Similar to hyaline, but with more elastic fibers
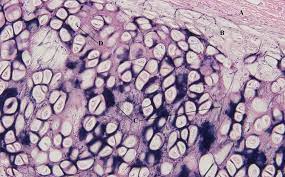
elastic location
ear, epiglottis
Fibrocartilage
Contains thick collagen in the matrix, less firm that hyaline, absorbing shock
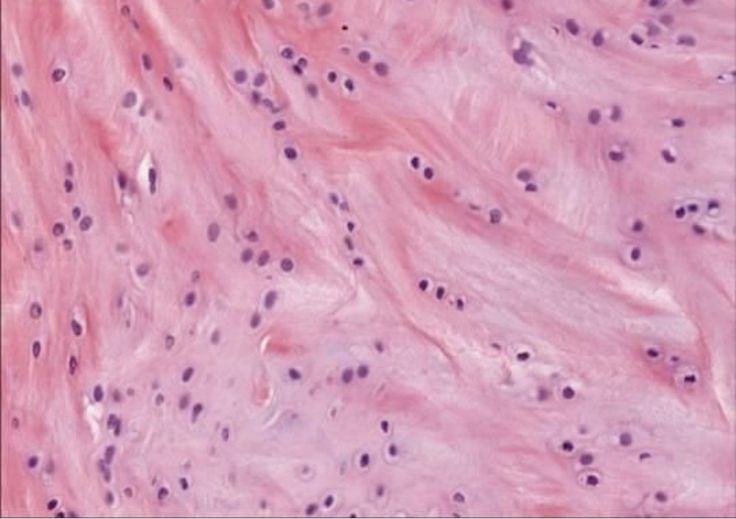
fibrocartilage location
intervertebral discs, knee joints
Bone
Has a rigid matrix formed of collagen fibers, osteoblasts, and calcium salts
osteocytes
mature bone cells
Musculoskeletal System
system of bones, muscles, joints, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and connective tissue.
musculoskeletal functions
protection
support
movement
mineral storage
Upper Body Anatomy
Includes skull bones and vertebral column, as well as muscles of the thoracic and abdominal regions.
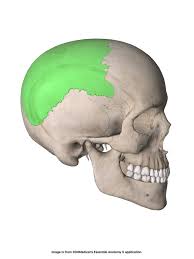
parietal
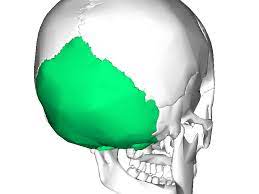
occipital
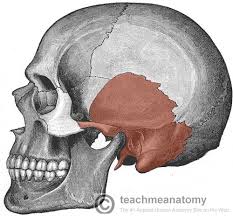
temporal
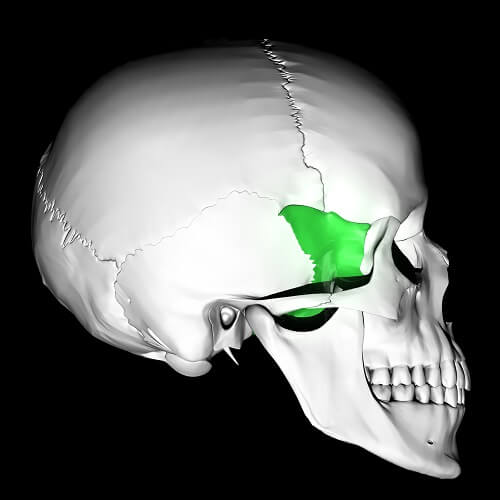
sphenoid
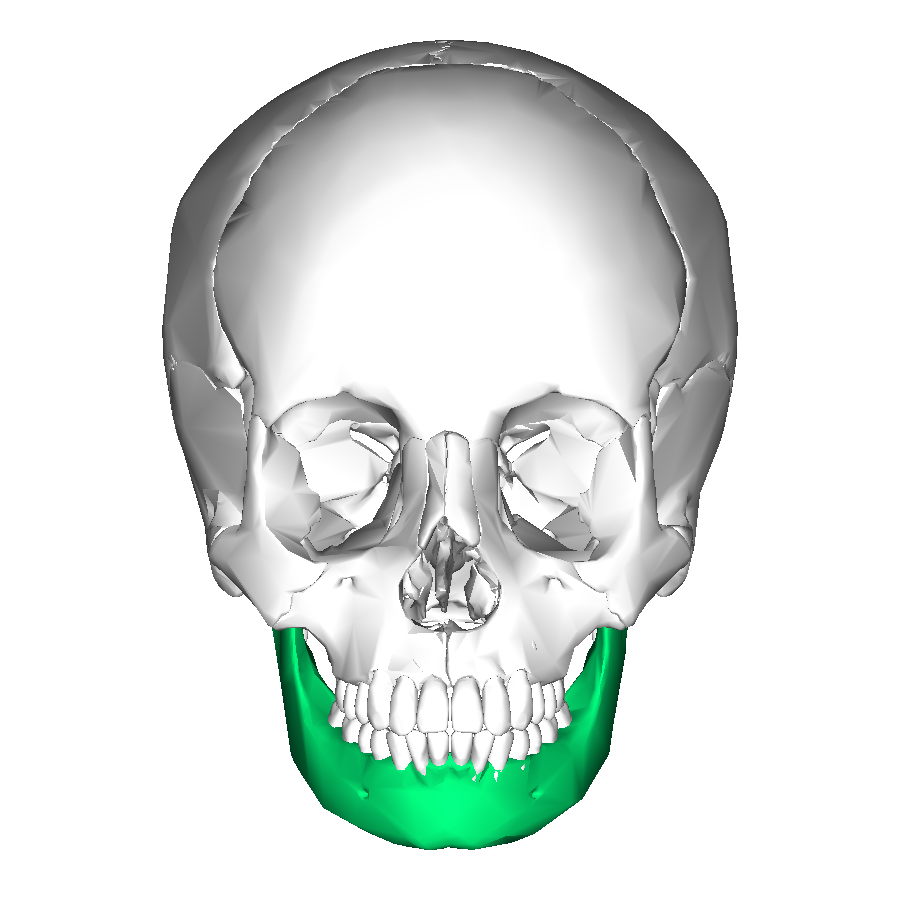
mandible
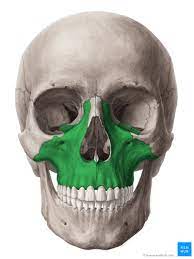
maxilla
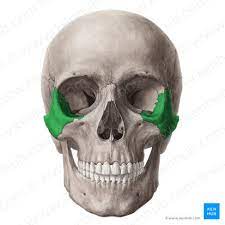
zygomatic
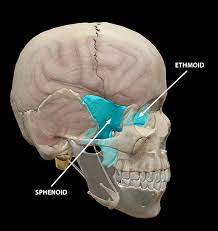
ethmoid
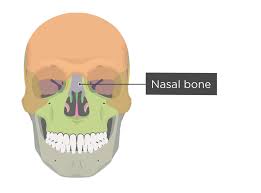
nasal
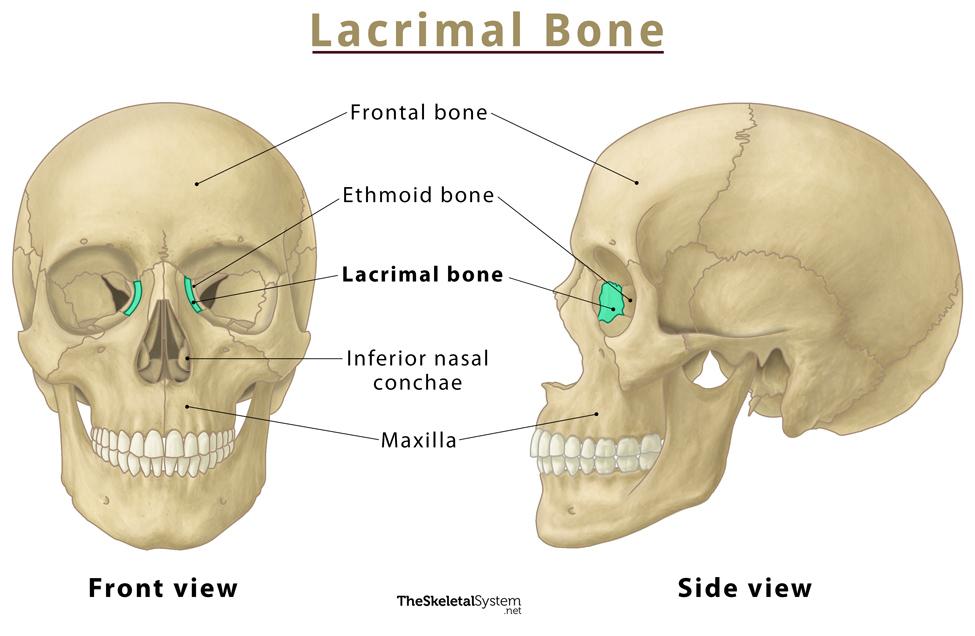
lacrimal
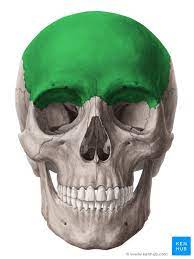
frontal
temporal region
external auditory meatus
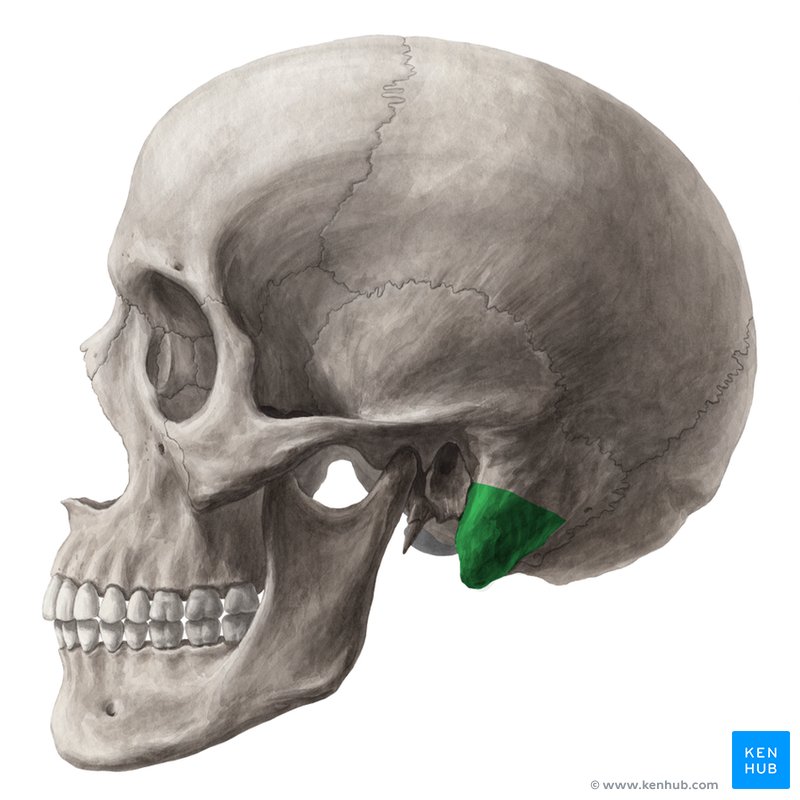
temporal region
mastoid process
temporal region
zygomatic process
occipital region
foramen magnum
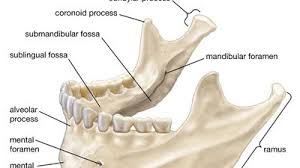
mandible
condylar process
mandible
coronoid process
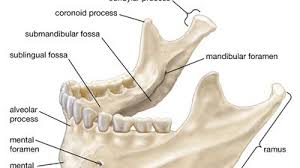
mandible
ramus
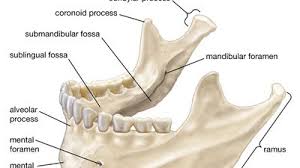
maxilla
palatine process
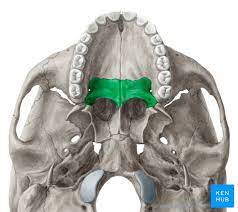
sutures of the skull
are fibrous joints that connect the bones of the cranium

sagittal suture
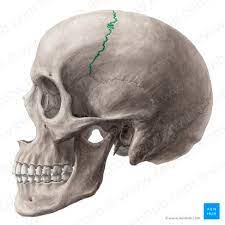
coronal suture
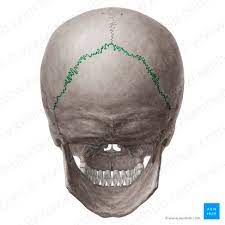
lambdoid suture
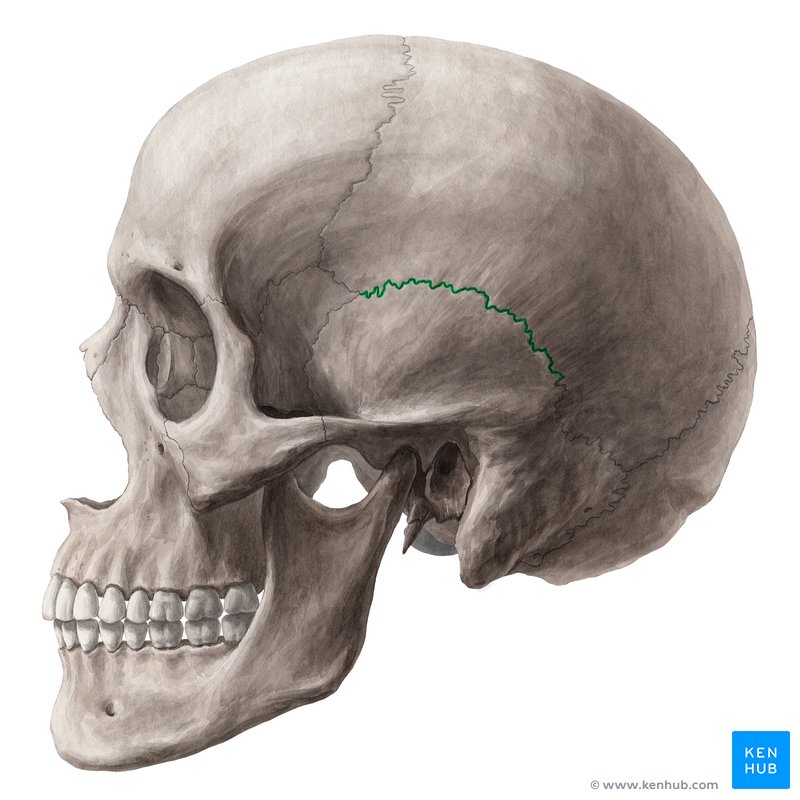
squamous suture
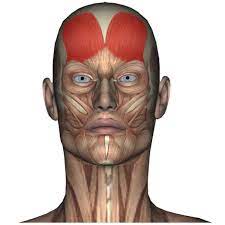
raises eyebrows
frontalis

open\closes eyelids
orbicularis oculi
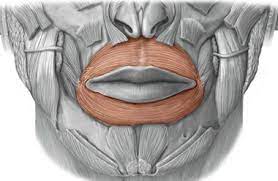
open/close mouth
orbicularis oris
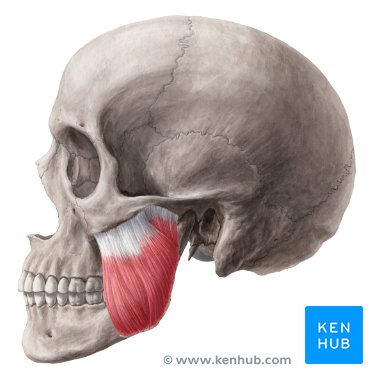
moves mandible
masseter
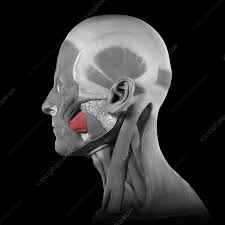
compresses cheeks against teeth
buccinator
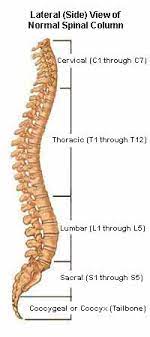
cervical
7
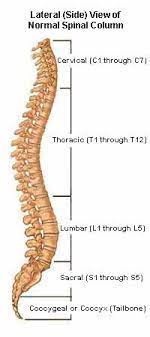
thoracic
12
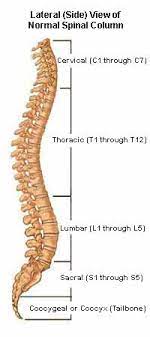
lumbar
5
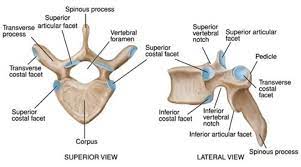
anatomy of a vertebra
Birds Eye view
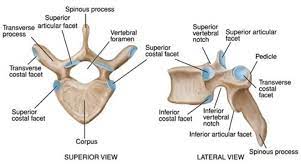
anatomy of a vertebra
side view
3 sternum process
manubrium
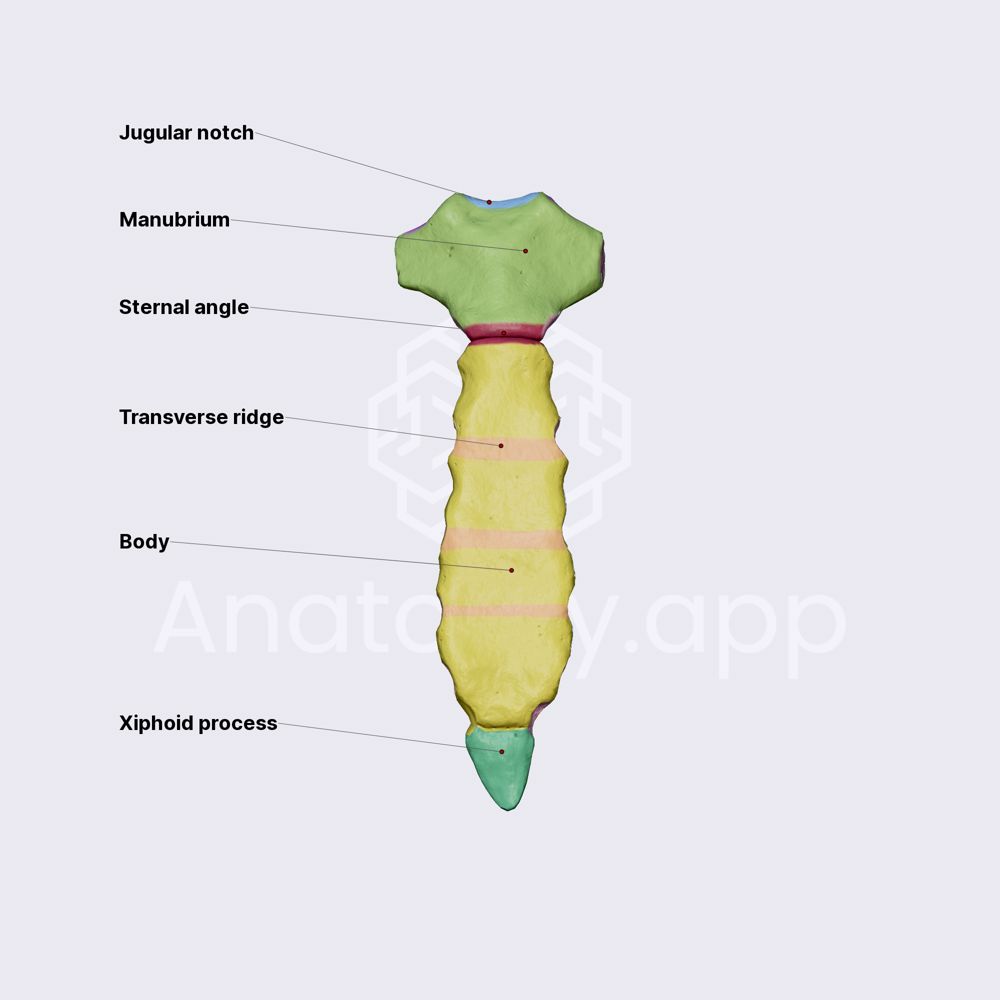
3 sternum process
body
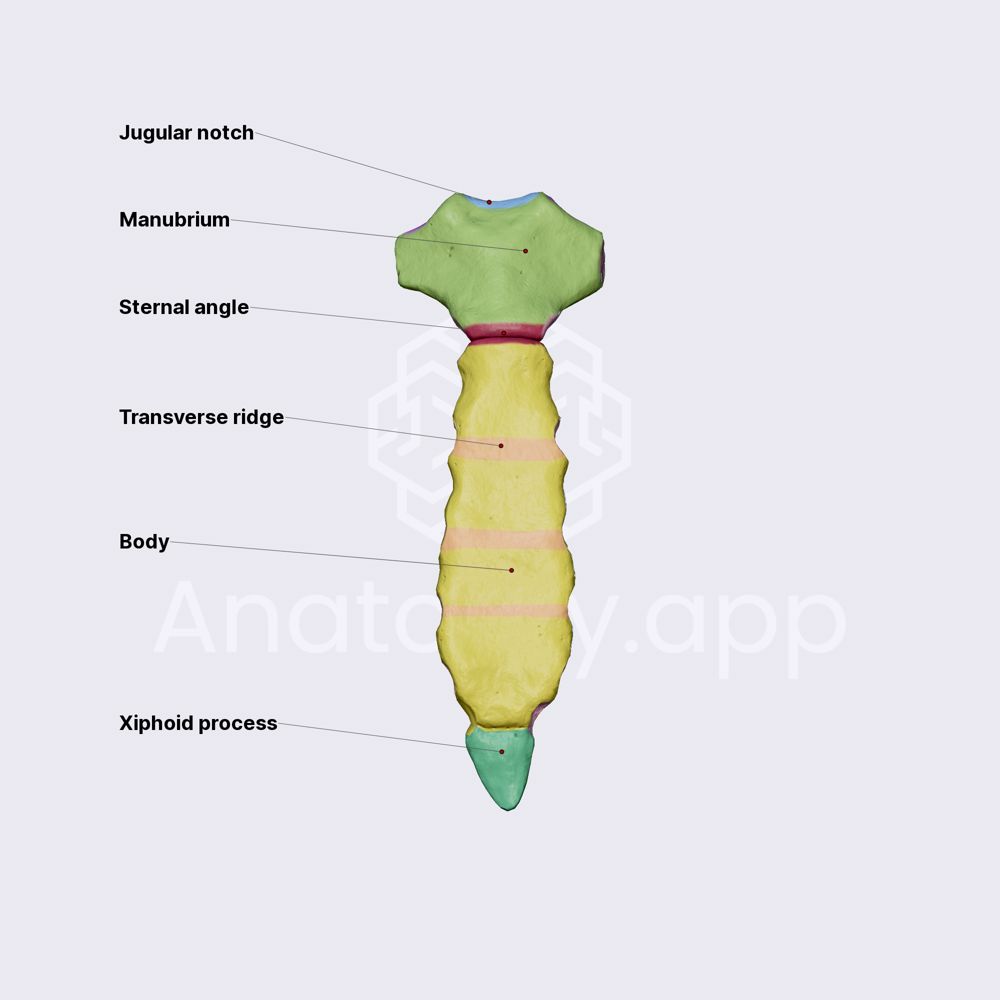
3 sternum process
xiphoid process
muscles of inspiration
external intercostals, contracts to elevate ribs and expand the thoracic cavity.
muscles of expiration
internal intercostals, contacts to pull ribs down and reduces thoracic cavity
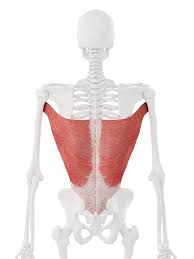
medial rotation, adduction, and extension of humerus, respiration
Latissimus Dorsi
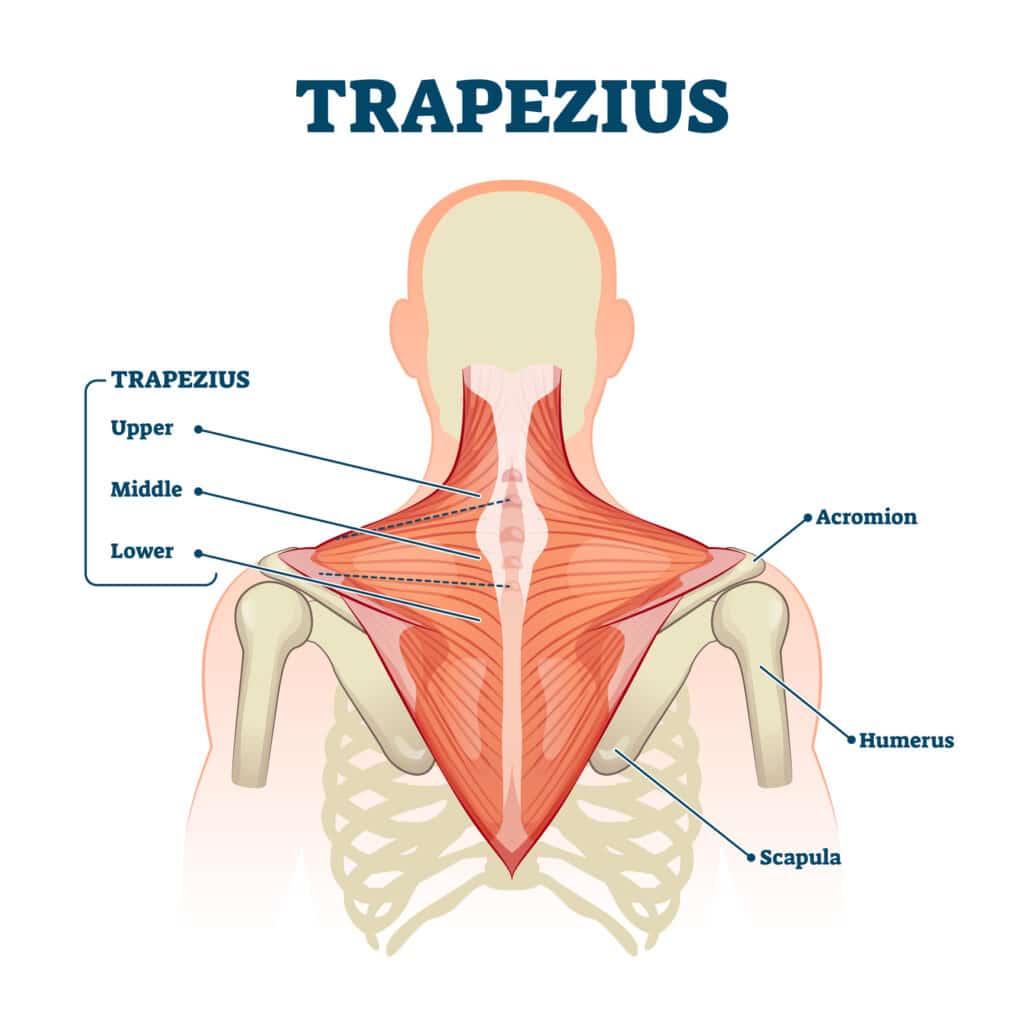
side bending, rotation of head, elevating and depressing the shoulders, and internally rotating the arm
Trapezius
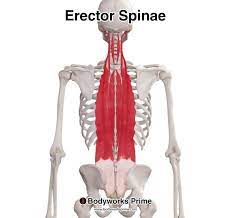
bilateral contaction of these muscles extends the sine, while unilateral contraction causes lateral flexion
erector spinae group
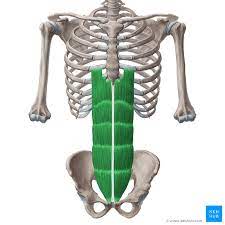
flexes the vertebral column and tenses abdominal wall.
Rectus Abdominis
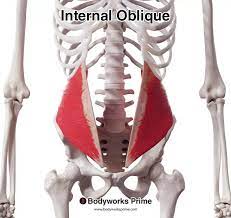
bilateral: Compresses abdominal viscera, flexes spine, unilateral: laterally flexes and rotates trunk on same side
Internal Oblique
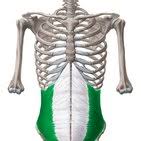
bilateral: Compresses the abdomen, flexes spine, unilateral: laterally flexes trunk on same side, rotates trunk to the opposite side.
External Oblique