Unit 13 - Lesson 4: Heat of Fusion and Vaporization
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Heat of Fusion:
the quantity of energy needed to melt or freeze a substance under a constant pressure.
For example, water possesses a Heat of Fusion (Lf) of 334J/g. It will require 334J of absorbed energy to melt 1g of ice and 334J of released energy to freeze 1g of water.
Heat of Vaporization:
the quantity of energy needed to evaporate or condense a substance under a constant pressure.
For example, water possesses a Heat of Vaporization (Lv) of 2257J/g. It will require 2257J of absorbed energy to boil 1g of liquid water and 2257J of released energy to condense 1g of water vapor.
Time-Temperature Graph
Latent Heat
On the previous graph, you may have noticed that the temperature does not change when a solid transitions to a liquid. Likewise, the temperature does not change when a liquid transitions to a gas.
This energy is used to loosen the bonds between separate molecules and overcome the intermolecular forces.
This energy is known as Latent Heat.
Molar Heat of Fusion
the amount of heat absorbed by one mole of a substance as it transitions from a solid to liquid (or amount released to transition from liquid to solid).
For example, water has a Molar Heat of Fusion of 6.02kJ/mol
Molar Heat of Vaporization
the amount of heat absorbed by one mole of a substance as it transitions from a liquid to gas (or amount released to transition from gas to liquid).
For example, water has a Molar Heat of Vaporization of 40.67kJ/mol
How determine Heat of Fusion and Heat of Vaporization
The formula for Specific Heat Capacity Q = mCpΔT can be adapted to help determine ΔHfus and ΔHvap:
Heat of Fusion: Lf = ΔHfus / Molar Mass
Heat of Vaporization: Lv = ΔHvap / Molar Mass
From there, we can use the concept of Molar Mass to help determine the Molar Heat of Fusion and Molar Heat of Vaporization:
Molar Heat of Fusion: ΔHfus = Molar Mass x Lf
Molar Heat of Vaporization: ΔHvap = Molar Mass x Lv
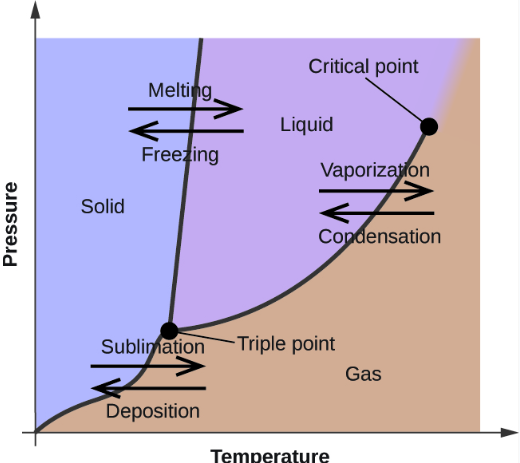
Critical Point:
The specific temperature and pressure of a substance in which the distinction between a liquid and a gas can’t be made, and overall have equal densities.
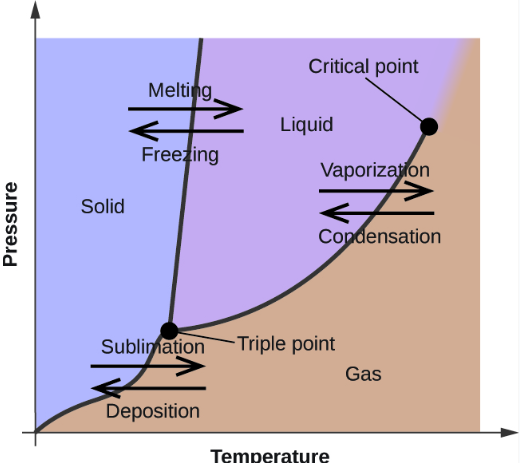
Triple Point
The specific temperature and pressure of a substance that is needed in order to have all states of matter (i.e. solid, liquid, and gas) coexist in equilibrium)