KIN 120 Midterm (UBC 2021)
1/338
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
339 Terms
hormone
a chemical messenger produced in the body and transported in the bloodstream to targeted cells or organs for specific regulation of their activities
Homeostasis
a state of stability and consistency in a person's physiological functioning
Stessor
A physical or psychological event or condition that produces physical and emotional reactions
stress response
the physiological changes associated with stress (acute or chronic)
Stress
the collective physiological and emotional responses to any stimulus that disturbs an individual's homeostasis
autonomic nervous system
the branch of the peripheral nervous system that controls basic body processes; consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
Parasympathetic
moderates the excitatory effect of the sympathetic division (bodily functions)
sympathetic
reacts to danger or other challenges by accelerating body processes (fight or flight)
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter released by the sympathetic nervous system onto specific tissues to increase their function; involved in arousal, as well as in learning and mood regulation. Also a hormone, released by adrenal gland
endorcrine system
the system of glands, tissues and cells that secrete hormones into the bloodstream to influence metabolism and other body processes
Cortisol
a steroid hormone secreted by the cortex (outer layer) of the adrenal gland; also called hydrocortisone; depletes dopamine, which decreases activity in the pleasure pathways of the brain; reduced norepinephrine, leading to a lack of motivation and alertness; and lower serotonin, reducing feelings of happiness and well-being. Also exacerbates anxiety
Epinephrine
a hormone secreted by the medulla (inner core) of the adrenal gland and also neurotransmitter in medulla oblongata, that affects the functioning of organs involved in responding to a stressor; also called adrenaline
Dopamine
happy hormone
Serotonin
mood, sleep, digestion
Endorphins
have pain-inhibiting effects; produced by the pituitary gland (hormone) and hypothalamus (neurotransmitter, dopamine)
somatic nervous system
branch of the peripheral nervous system that governs motor functions and sensory information, largely under conscious control
Personality
the sum of behavioural, cognitive and emotional tendencies
General Adaptation Syndrome
a pattern of stress responses consisting of three stages: alarm, resistance, and exhaustion
Eustress
stress resulting from a pleasant stressor
distress
stress resulting from an unpleasant stressor
allostatic load
the long-term negative impact of the stress response on the body
Gluconeogenesis
sugar production
Glucagon
hormone that raises blood glucose level/concentration
Insulin
A protein hormone secreted by the pancreas that is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates and the regulation of glucose levels in the blood
Renin
hormone secreted by the kidney that raises blood pressure and impacts water retention
Vasopressin
nonapeptide synthesized in the hypothalamus; controls the body's somatic balance
Oxytocin
chemical messenger in the brain
Aldosterone
balances sodium and potassium in your blood
Antidiruretic hormone
helps to control blood pressure by acting on the kidneys and the blood vessels
Ghrelin
gurgling feeling in the stomach when hungry
Leptin
Full feeling
Glucose
sugar levels
Atherosclerosis
a form of CVD in which the inner layers of artery walls are made thick and irregular by plaque deposit; arteries become narrowed, and blood supply is reduced
plaque
A deposit of fatty material on the inner lining of an arterial wall
heart attack
The damage or death of cardiac muscle tissue resulting from prolonged blockage of one or more coronary arteries (myocardial infarction)
angina pectoris
heart muscle does not receive enough blood, causing severe pain in the chest, arm and/or shoulder
sudden cardiac death
a nontraumatic, unexpected death from sudden cardiac arrest, most often due to arrhythmia; in most instances, victims have underlying heart disease
congestive heart failure
A condition resulting from the heart's inability to pump out all the blood that returns to it; blood backs up in the veins leading to the heart, causing an accumulation of fluid in various parts of the body
Hypertension
sustained abnormally high blood pressure
LDL stands for
low-density lipoprotein
low-density lipoprotein
a lipoprotein containing a moderate amount of protein and a large amount of cholesterol; "bad" cholesterol
HDL stands for
high-density lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein
a lipoprotein containing relatively little cholesterol that helps transport cholesterol out of the arteries; "good" cholesterol
Trigylcerides
a type of lipid found in fat cells that stores excess energy for long-term use
RCT
converts bad LDL good HDL
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
decreased removal of LDL; bad cholesterol
visceral fat
the fat that surrounds your organs
Ischemia
blood vessels aren't able to provide enough oxygen to the tissues
FITT
frequency, intensity, time/duration, and type of activity
lymphatic system
a system of vessels that return proteins, lipids, and other substances from fluid in the tissues to the circulatory system
malignant tumor
a tumor that is cancerous and capable of spreading
benign tumor
a tumour that is not cancerous
Carcinogen
any substance that causes cancer
Oncogenes
a gene involved in the transformation of a normal cell in cancer cell
Pap test
a scraping of cells from the cervix for examination under a microscope to detect cancer
UV
light rays of specific wavelength, emitted by the sun mist UV rays are blocked by the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere
Essential fat
fat incorporated in various tissues of the body that is critical for normal body functioning
Adipose tissue
connective tissue in which the fat is stored
Sodium Intake
recommended- 2300mg/day
population at risk (hypertension, middle aged/older adults, some ethnic groups)- 1500mg/day
Subcutaneous fat
fat located under the skin
visceral fat
fat located around major organs
BMI/Body Comp ranges
normal- 18.5-24.9
underweight-
intra-abdominal fat
fat located around the major organs, also called visceral fat
HDL ranges
normal- >60mg/dL
women middle- 40-59mg/dL
men middle- 50-59mg/dL
danger women-
BP ranges
normal: less than 120/80
pre HTN: 120-139/80-89
stage 1 HTN: 140-159/ 90-99
stage 2 HTN: greater than 160/ greater than 100
WHR ranges
ideal women-
RHR ranges
idk look it up too much lol
Glucose/Blood Sugar levels
fasting:
normal person without diabetes- 3.9-5.5mmol/L
with diabetes- 4.4-7.2mmol/L
1-2 hours after eating:
normal without diabetes- 7.8mmol/L
normal with diabetes- 10.0mmol/L
Drinks per day recommendation
2 drinks/day
exercise per week recommendation
150mins/week overall
- 30 mind of moderate-intensity physical activity 5 days/wk or 20 min of vigorous activity 3 days/wk, if not every day
- 8-10 muscular strengthening exercises (8-12 reps, 2-3 sets) at least 2 days per week
percentage body fat
the percentage of total body weight that is composed of fat
overweight
body weight above the recommended range for good health (BMI 25.0-29.9)
obesity
severely overweight, characterized by an excessive accumulation of body fat; may also be defined in terms of some measure of total body weight or a body mass index of 30 or more
chronic inflammation
a response of blood vessels to harmful substances, such as germs, damaged cells, or irritants; can lead to heart disease, cancer, allergies, and muscle degeneration
fatty liver
increased fat storage in the liver that can lead to liver inflammation and failure
Amenorrhea
absent or infrequent menstruation, sometimes related to low levels of body fat and excessive quantity or intensity of exercise
Body Mass Index (BMI)
a measure of relative body weight correlating highly with more direct measures of body fat, calculated by dividing total body weight (in kilograms) by the square of body height (in meters)
calliper
a pressure-sensitive measuring instrument with two jaws that can be adjusted to determine thickness
eating disorders
a serious disturbance in eating patterns or eating-related behavior, characterized by a negative body image and concerns about body weight or body fat
anorexia nervosa
an eating disorder characterized by a refusal to maintain body weight at a minimally healthy level and an intense fear of gaining weight or becoming fat; self-starvation
bulimia nervosa
an eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of binge eating and then purging to prevent weight gain
body image
the mental representation a person holds about her or his body at any given moment in time, consisting of perceptions, images, thoughts, attitudes, and emotions about the body
resting metabloic rate (RMR)
the energy equired (in calories) to maintain vital body function, including respiration, heart rate, body temperature and blood presssure while the body is at rest
metabolic syndrome
A cluster of symptoms present in many overweight and obese people greatly increases their risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic illnesses; symptoms include insulin resistance, abnormal blood fats, abdominal fat deposition (especially around waist), type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and chronic inflammation. (must have at least 3)
LDL ranges
optimal-
Purging
The use of vomiting, laxatives, excessive exercise, restrictive dieting, enemas, diuretics, or diet pills to compensate for food that has been eaten and that the person fears will produce weight gain
binge eating disorder
an eating disorder characterized by binge eating and a lack of control over eating behaviour in general
Health
the overall condition of body or mind and the presence or absence of illness or injury; can be determined or influenced by factors beyond your control (genes, age, and family history)
Wellness
ability to achieve optimal health and vitality; influenced by one's decisions of how you live
Determinants of health
the range of personal, social, economic, and environmental factors that influence health status
Dimensions of Wellness (9)
physical, emotional, intellectual, interpersonal, cultural, spiritual, environmental, financial, occupational
Wellness Continuum
composed of interrelated dimensions, all of which must be developed in order to achieve overall wellness
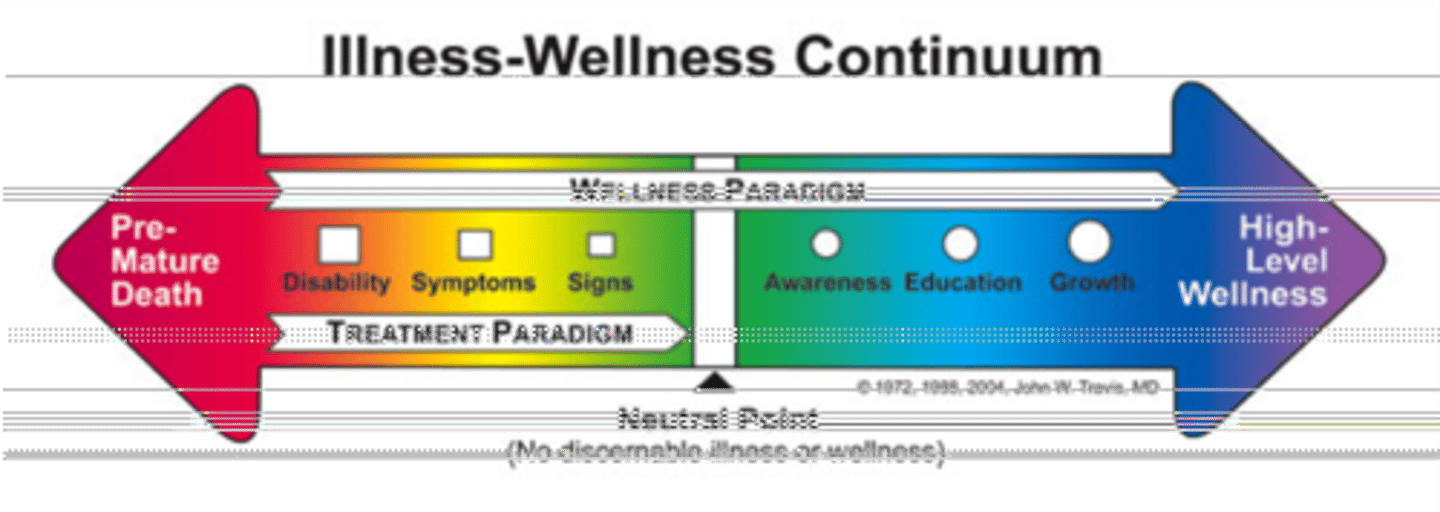
The absence of mental illness is not the same thing as...
the presence of mental wellness
Physical Wellness
Includes fitness level and ability to care for one's self
Emotional Wellness
the ability to understand your own feelings, accept your limitations, and achieve emotional stability
Intellectual Wellness
The ability to have an open mind, and the desire to learn and improve
Interpersonal Wellness
Communication skills, capacity for intimacy, ability to establish and maintain satisfying relationships. ability to cultivate support system of friends and family.
Cultural Wellness
Creating relationships with those who are different from you, Maintaining and valuing your own cultural identity, Avoiding stereotyping based on ethnicity, gender, religion, or sexual orientation
Spiritual Wellness
Capacity for love, compassion, forgiveness, altruism, joy, fulfillment, caring for others, sense of meaning and purpose, sense of belonging to something greater than oneself.
Environmental Wellness
Having abundant, clean natural resources, maintaining sustainable development, recycling whenever possible, reducing pollution and waste.