ATI TEAS Immune System
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
immune system
-protects our bodies from foreign pathogens, or infectious agents
-comprised of the lymph nodes, thymus, bone marrow, and spleen
-all immune cells are born in the bone marrow but can mature in different locations across the body
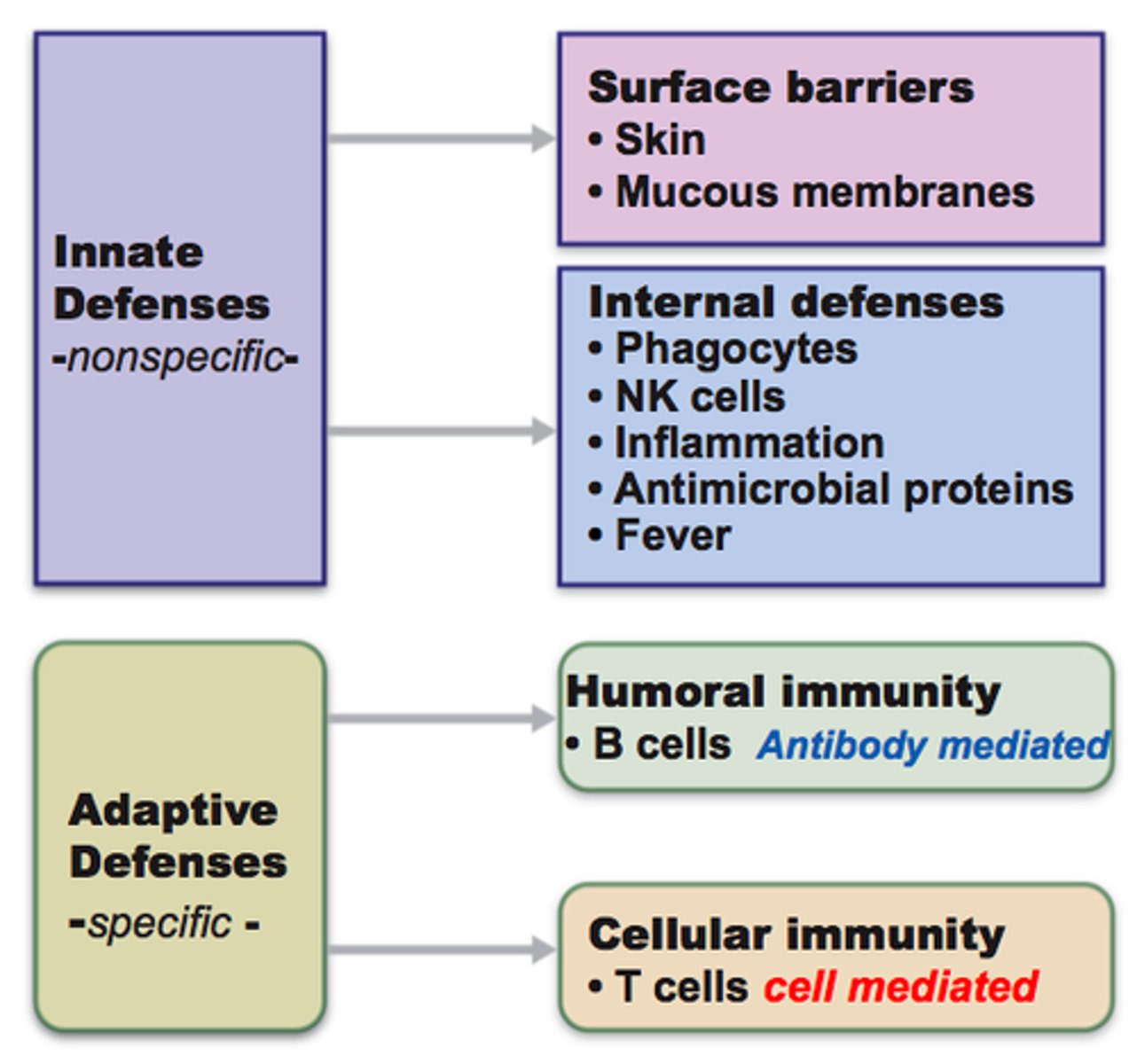
first line of defense
-physical barriers, such as the skin, which prevent most pathogens from accessing our bodies
-when these barriers are breached, immune cells from the innate and adaptive arms target pathogens for destruction
-skin has a acidic pH b/t 3 and 5, which discourages replication of most pathogens
-skin is inhabited by flora
pathogens
foreign infectious agent
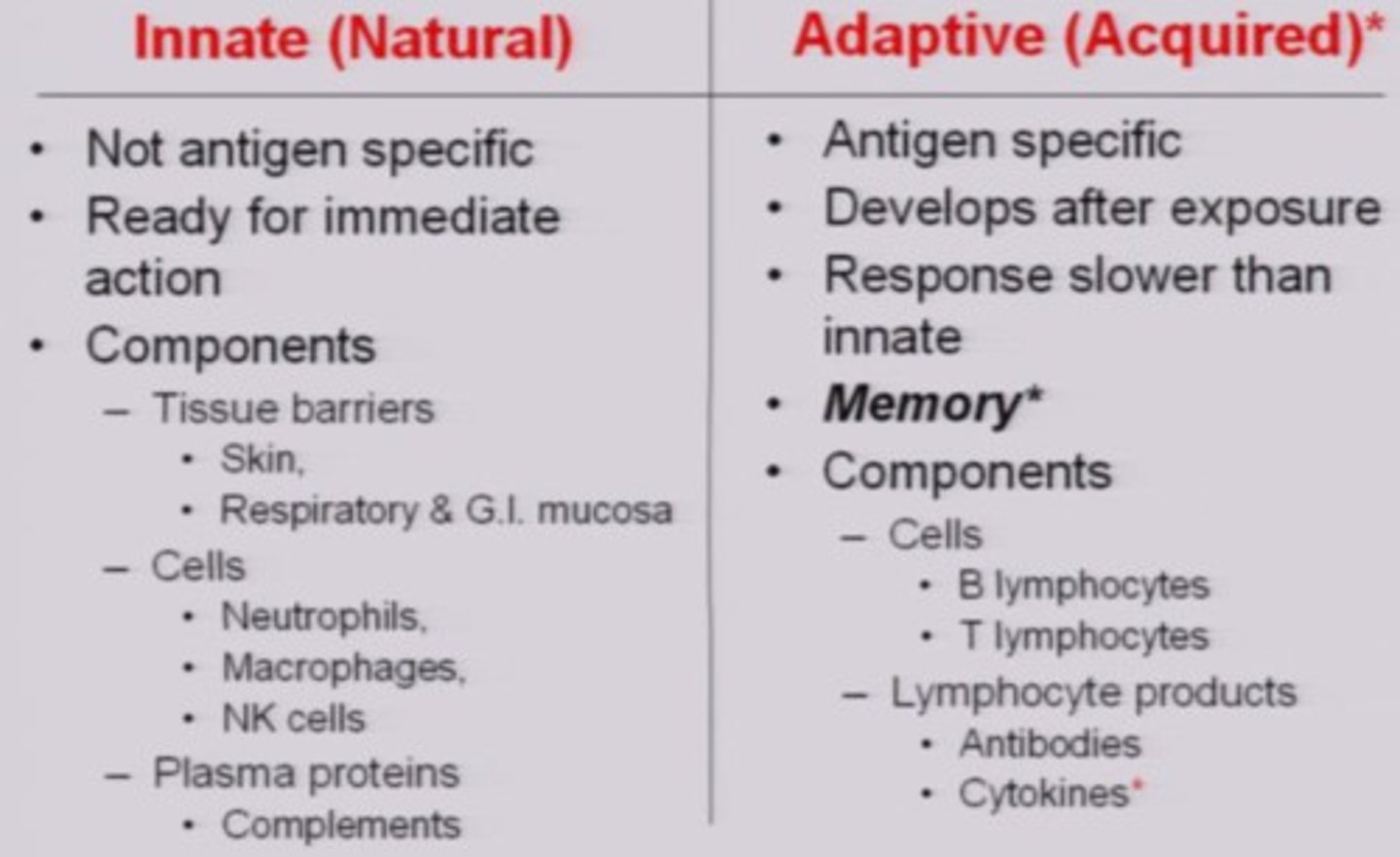
innate arm
-quick to respond, but not specific to individual pathogens nor does it form memory cells
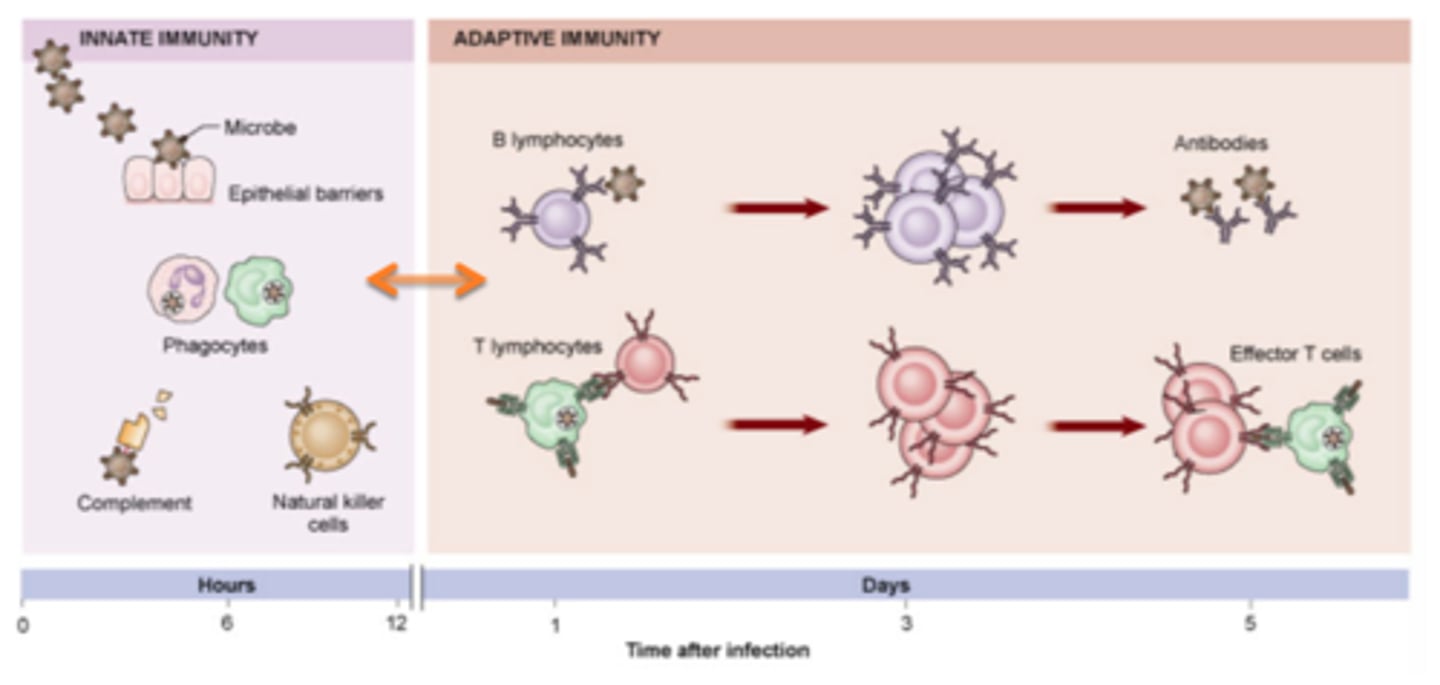
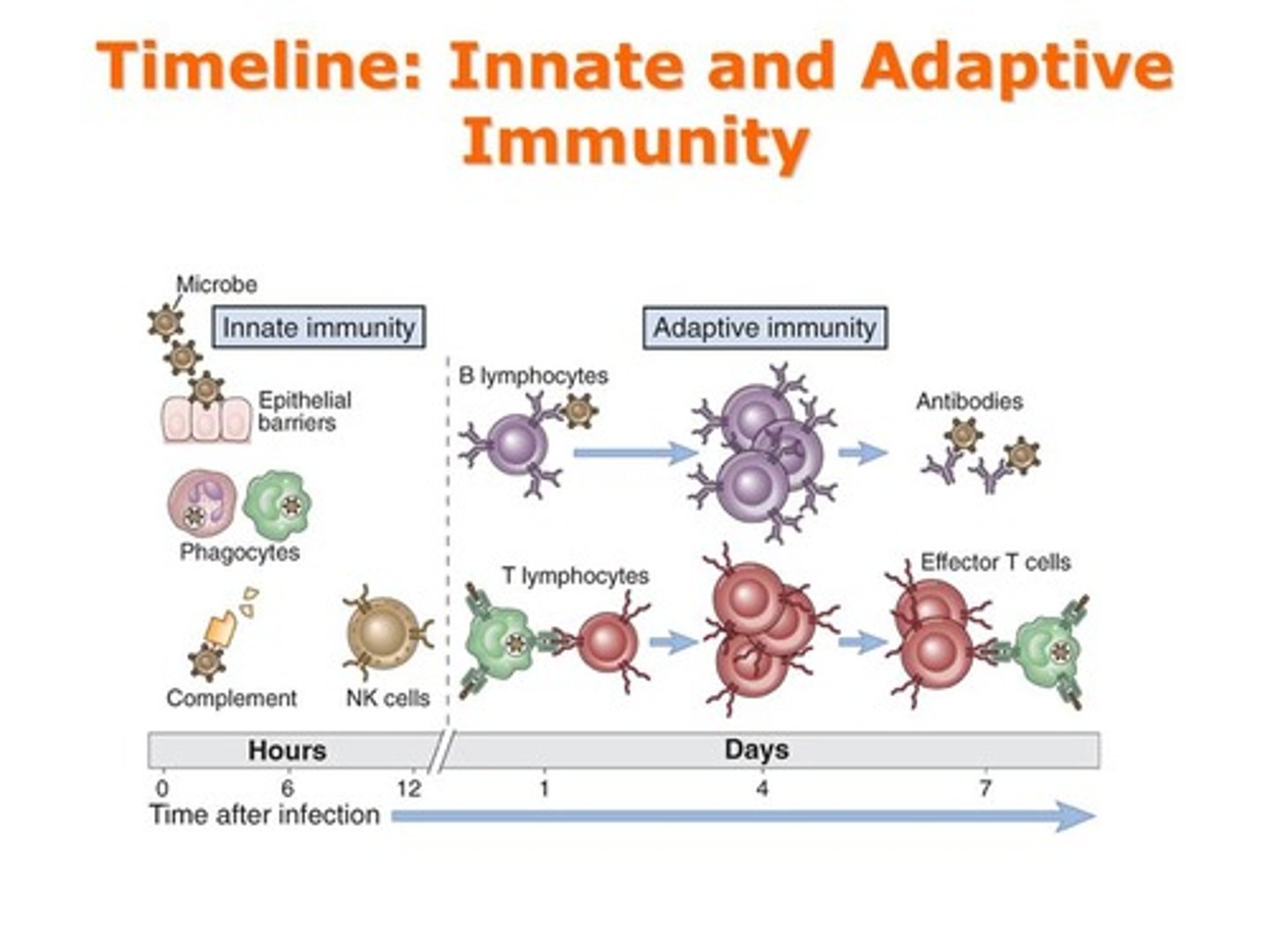
adaptive arm
-slower to activate, but it specifically targets a pathogen and forms memory cells
adaptive immunity (slow response)
-B cell releases antibodies
-T cell forms a CD4+ T cell and a CD8+ T cell
-quick to respond but unable to form memory
-this system consists of granulocytes, monocytes, and natural killer cells
-slower to respond b/c it must first be activated by antigen presentation by cells of the innate immunity system
-once activated, it will specifically target pathogens and host cells displaying the presented antigen
-includes both T and B cells
-normally self tolerant
innate immunity (fast response)
-involves macrophages and natural killer cell, lysozyme, interferons, and antimicrobial peptides
-basophil --> eosinophil --> neutrophil
-quick to respond but unable to form memory
-this system consists of granulocytes, monocytes, and natural killer cells
-DOES NOT include antibodies!
barriers to infection
-include both physical barriers that block entry of pathogens and proteins that impede pathogen replication
-largest physical barrier is the skin
-skin has a acidic pH b/t 3 and 5, which discourages replication of most pathogens and is inhabited by flora
flora
nonpathogenic microbes that compete for resources and thus prevent pathogen occupancy
respiratory tract
-lined w/ mucus to trap incoming pathogens
-mucus can either be expelled through coughing, eliminating harmful microbes from the body, or swallowed
-swallowed microbes will enter the stomach, where most are killed by the low pH of 2, and survivors must compete for resources w/ gut flora in the intestines
chemical barriers to infection
-saliva, tears, and mucus which all contain the enzyme lysozyme, which degrades bacterial cell walls and causes them to lyse, or burst
-cells continuously secrete antimicrobial peptides into the bloodstream
lysozyme
-degrades bacterial cell walls and causes them to lyse, or burst
-found in saliva, tears, and mucus
antimicrobial peptides
-these small molecules are broad-spectrum antimicrobials that target and kill many bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens to prevent infection
interferon
-if cells become infected, they secrete interferons
-a small chemical messenger, to signal nearby cells the presence of a foreign pathogen ad activate innate defenses in those cells
memory
the ability to remember a pathogen that has been previously encountered
granulocytes
-cells of the innate immune system named for the dense granules, containing reactive oxygen compounds and cytokines in their cytoplasm
-include basophils, eosinophils, and neutrophils
basophils
granulocytes responsible for releasing histamine and mediating allergic reactions
eosinophils
granulocytes responsible for killing parasites
neutrophils
most common of the granulocytes and are responsible for phagocytosing, or eating, bacteria and medicating inflammatory responses
phagocytosing
eating bacteria
inflammation
leads to swelling of the tissue and fever, as well as recruitment of immune cells
monocytes
include macrophages and dendritic cells
dendritic cells
-phagocytic cells that kill extracellular pathogens
-they recognize pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
-following phagocytosis, present microbial antigens to cells of the adaptive immune system leading to their activation
pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
common proteins and carbohydrates found on the surface that are not specific to one antigen
antigen
the term for a microbial protein
macrophages
-digest dying cells, especially in the spleen where red blood cells die
-can also present antigens, but not as effectively as dendritic cells
natural killer cells
-attack and kill cells that contain intracellular pathogens or display abnormal surface antigens
-ex: tumor cells
vaccination
-the quick activation of memory cells underlies the usefulness of vaccination
-during vaccination, the immune system is challenged by a weakened pathogen and forms memory cells
-these cells will quickly activate and kill the pathogen when exposed a second time, preventing or minimizing infection and the development of symptoms
T cells
-born in the bone marrow
-released into the bloodstream as immune cells then travel to the thymus for maturation
-while in the thymus, T cells can mature into either helper T cells or cytotoxic T cells and then released to circulate in the blood and lymph systems
helper T cells
-following activation by antigen-presenting cells, help to activate other adaptive immune cells such as cytotoxic T and B cells
-are targeted and killed by HIV
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
-the virus responsible for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), leading to a loss of immune function
-when the cause of death is written as complications related to AIDS, this indicates that the individual succumbed to infections caused by pathogens that are typically harmless to healthy individuals
cytotoxic T cells
-when activated, will kill a host cell that expresses a foreign antigen
-cytotoxic T cells are antigen specific, meaning that they will only kill a cell that displays the single antigen they were primed to recognize
B cell
-born and mature in the bone marrow
-following activation, they develop into plasma cells and secrete antibodies
-will only produce one type of antibody
antibodies
-proteins that specifically bind to viral antigens
-will either target pathogens for phagocytosis, coating them to render them noninfectious or target them for complement-mediated lysis
-antibodies can be acquired either by active immunity or passive immunity
complement system
-composed of multiple proteins that are free floating in the blood
-when coating a pathogen, antibodies recruit these proteins, leading to the formation of a pore in the membrane of the pathogen and causing cell lysis
active immunity
-antibodies can be acquired by active immunity through production of plasma cells
-production of antibodies by plasma cells
passive immunity
-antibodies can be acquired through passive immunity through the introduction antibodies from an external source
-introduction of antibodies from an external source (breastfeeding)
self-tolerant
-it does not respond to normal cellular antigens
-a description of the fact that a healthy adaptive immune system does not respond to normal cellular antigens
autoimmune disease
a disease in which the adaptive immune system targets healthy body cells
An individual receives an influenza vaccine and mounts a very strong immune response, evidenced by a high titer of circulating antibodies. Six weeks after the vaccination, memory B and T cells can be found in circulation. However, six months later, the individual is exposed to influenza and becomes ill. Which of the following best explains why the vaccination appears to have failed?
The individual was infected with an influenza strain that expressed a different surface antigen.
T cells are born in the bone marrow and released into the bloodstream as immature lymphocytes. Where in the body do they finish maturation?
Thymus.
A client is diagnosed with infection by Naegleria fowleri, a parasitic pathogen that infects the brain. An elevation of which of the following immune cells would support the physician's diagnosis?
Eosinophils, due to them targeting parasites.
Which of the following immune system components is NOT part of the innate immune system?
-Antibodies
-Interferons
-Antimicrobial peptides
-Lysozyme
Antibodies.
Which of the following helps to prevent bacteria from entering the bloodstream?
-Capillaries
-Pancreas
-Lymph nodes
-Bone marrow
Lymph nodes.
Which of the following best describes what occurs when an individual is infected with a viral pathogen two years after receiving a vaccination against that pathogen?
Memory T cells are quickly activated to kill cells displaying the viral antigen.
What is the function of lysozyme in the immune system?
Breaking down the cell walls of bacteria.
Bare lymphocyte syndrome accounts for approximately 5 percent of immunodeficiencies. It is caused by a defect in the MHC protein expressed by macrophages and dendritic cells, resulting in a failure to present antigen. Individuals with this disease cannot effectively fight infection despite normal B and T cell counts. Currently, the only treatment is a bone marrow transplant. Which of the following best expresses the reason why individuals with this disease are immunocompromised?
Although B and T cells are present, antigen-presenting cells fail to activate them.
Hashimoto's disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States. This autoimmune condition is caused when the immune system attacks and slowly destroys the thyroid gland. Which of the following statements best describes how this condition develops?
B cells produce antibodies that target thyroid cells, and cytotoxic T cells actively kill thyroid cells.