Nephro- A&P
1/30
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the functional unit of the kidney?
Nephron
What does the nephron consist of?
Renal corpuscle (glomerulus & bowman’s capsule) & a renal tubule
What does a renal tubule consist of?
Proximal convoluted tubule, loop of henle (ascending limb & descending limb), distal convoluted tubule (drains into collecting duct)
How do the kidneys help regulate blood pH?
Excrete H+ into urine & conserve HCO3
How do the kidneys regulate blood volume?
Conserving or eliminating water in the urine
How does an increase in blood volume affect blood pressure?
Increase
How does a decrease in blood volume affect blood pressure?
Decrease
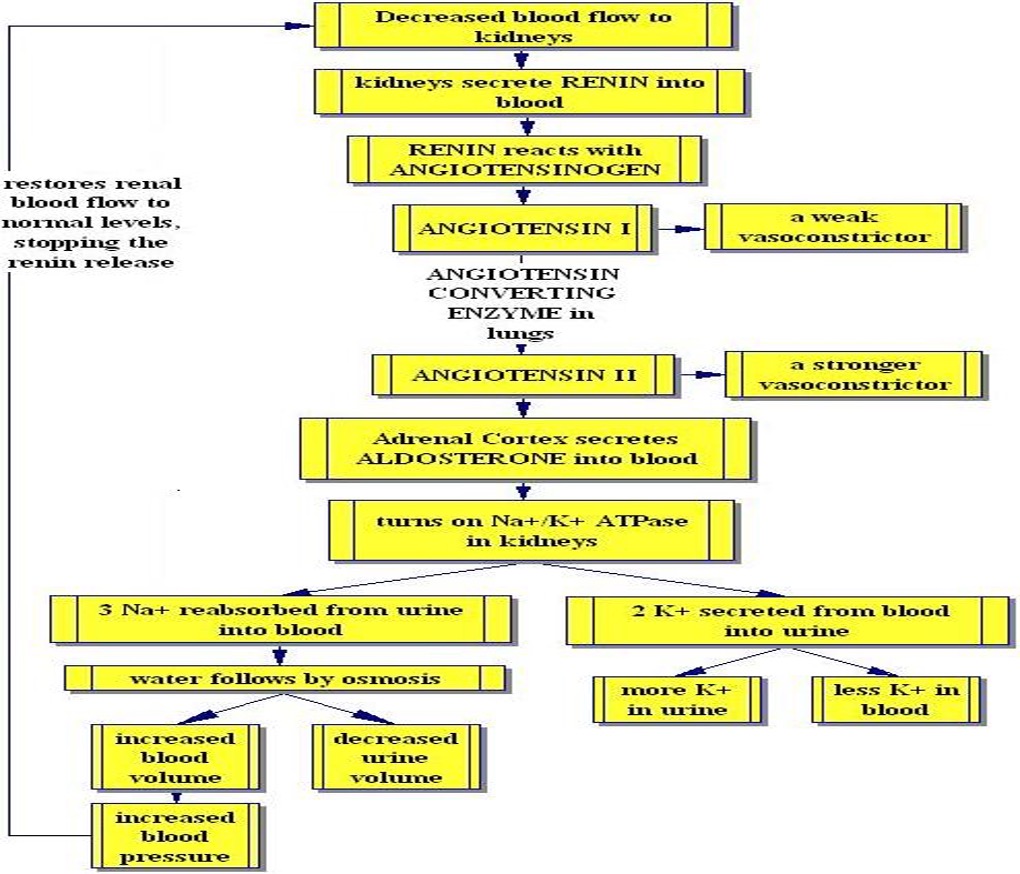
How do kidneys help regulate BP?
Secreting renin which activates renin-angiotensin-aldosterone pathway
How does an increase in renin affect BP?
Increase
How do the kidneys maintain blood osmolarity?
Separately regulating loss of water & loss of solutes in urine; maintain relatively constant blood osmolarity ~ 300 milliosmoles/L
What 2 hormones do the kidneys produce?
Calcitriol (active form of vit D) to regulate Ca homeostasis
Erythropoietin which stimulates production of RBCs
How do the kidneys help regulate blood glucose?
Use glutamine in gluconeogenesis & release glucose into blood
What wastes do the kidneys secrete?
Ammonia, urea, bilirubin, creatinine, uric acid
What are the 3 basic processes the nephrons & collecting ducts perform to produce urine?
Glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion
What is the first step of urine production?
Glomerular filtration: Water & most solutes in blood plasma move across walls of glom capillaries → glomerular capsule → renal tubule
What process?
2nd step of urine production
Filtered fluid flows along renal tubule & through collecting duct & tubule cells reabsorb 90% of filtered water & solutes
water & solutes return to blood & flow through peritubular capillaries & vasa recta
Tubular reabsorption
What process?
3rd step of urine production
As fluid flows along renal tubule & collecting duct, tubule & duct secrete other materials such as wastes, drugs, excess ions into fluid
Tubular secretion
What is urine mainly made of?
Water
What is a normal adult urine volume?
1-2 L in 24 hr period
What are the 3 components of the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)?
Juxtaglomerulus cells: afferent arteriole, baroreceptors
Macula densa; DCT, chemoreceptors sensing solute load
Lacis cells: vasoconstriction/dilation w/in mesangium
What is fluid that enters the capsular space?
Glomerular filtrate
Over 99% of glom filtrate is reabsorbed into blood stream, how much is excreted as urine?
1-2 L
What are the 3 phases that glomerular filtration depends on?
GBHP: 55mmHg, promotes filtration of water/solutes
CHP: 15mmHg, opposes filtration
BCOP: 30mmHg, opposes filtration
*net filtration pressure 10mmHg
What is a normal GFR?
100-120 ml/min
What are the 2 main GFR regulation mechanisms?
Control of BF by changing diameter of afferent/efferent arterioles
Control of glom SA via contraction/relaxation of mesangial cells
What is the best overall index of kidney function?
GFR
What hormone is released by the posterior pituitary in response to increased plasma oncotic pressure, LA distention, exercise, & emotional states?
ADH (vasopressin)
Where does ADH act?
Collecting tubules to promote resorption of free water
What deficiency results in the kidneys not being able to concentrate fine, leading to symptoms of polyuria & polydipsia?
ADH insufficiency / DI
What condition is an excess of ADH that results in excessive resorption of free water, hyponatremia, cerebral edema, and neurological dysfunction?
SIADH
RAAS BP control
woohoo