IMED1001 - Homeostasis (Week 10)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Multicellular Organism
- specialisation means that each cell cannot 'know' everything
- interactions aming cells results in homeostasis
- maintenance of static or constant conditions in the internal environment
- communication is critical
- coordinated body activity requires integration of many systems
- transmission of information between cells
Homeostatic Control Systems
- Cardiovascular
- Circulatory
- Respiratory
- Gastrointestinal
- Renal, Urinary
IMPORTANT
- Endocrine
- Neurophysiological (Nervous)
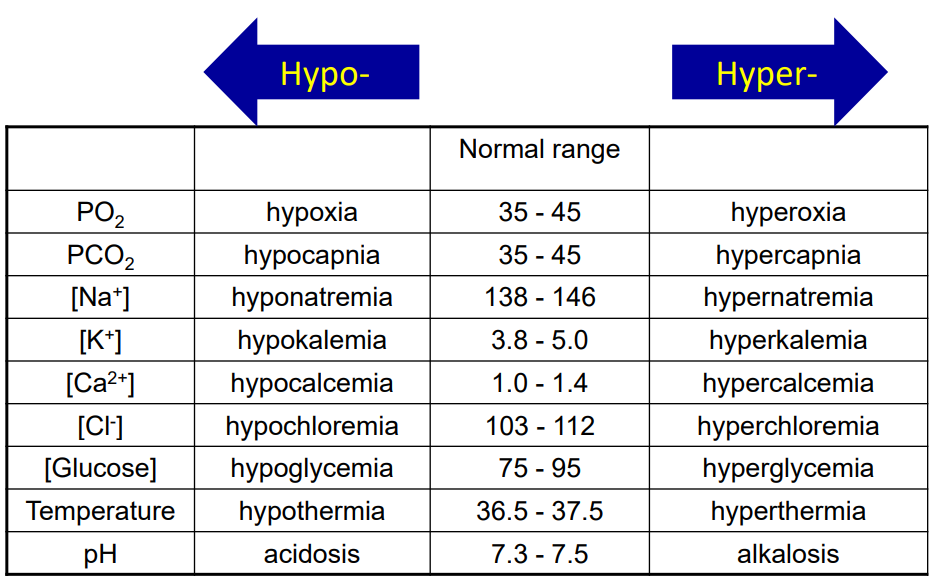
Bathing medium of cells is
extracellular fluid
- very stable (can define physiolgy as maintenance of ECF)
(stable talks about how homeostasis occurs)
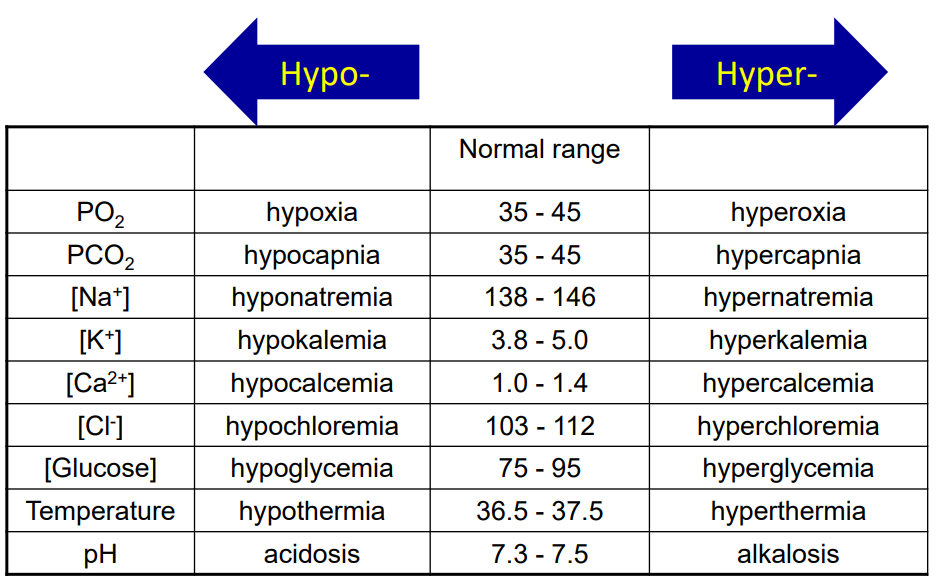
ECF Values
- need to know all the names
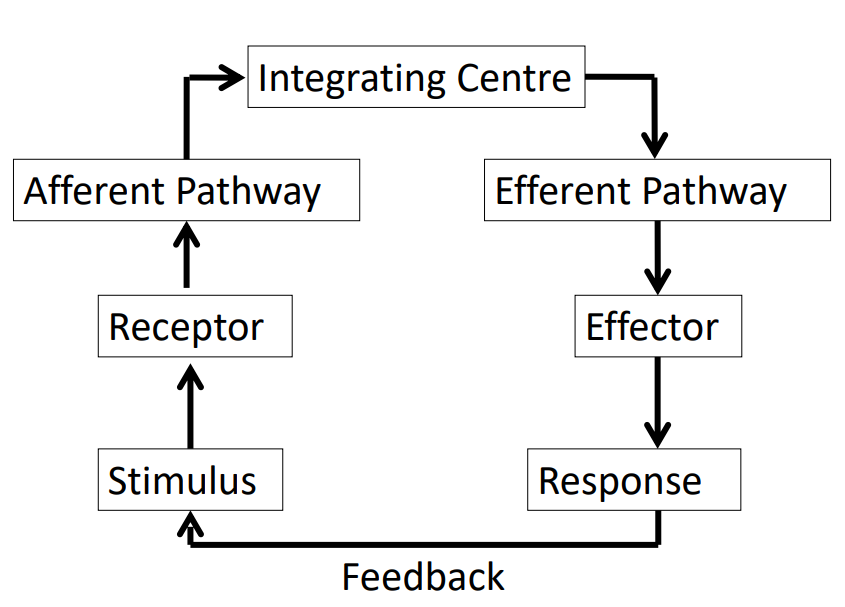
Control System
1. Some way to measure regulated variable
2. Some way to alter (effect) the regulated variable
3. Something is linking the two
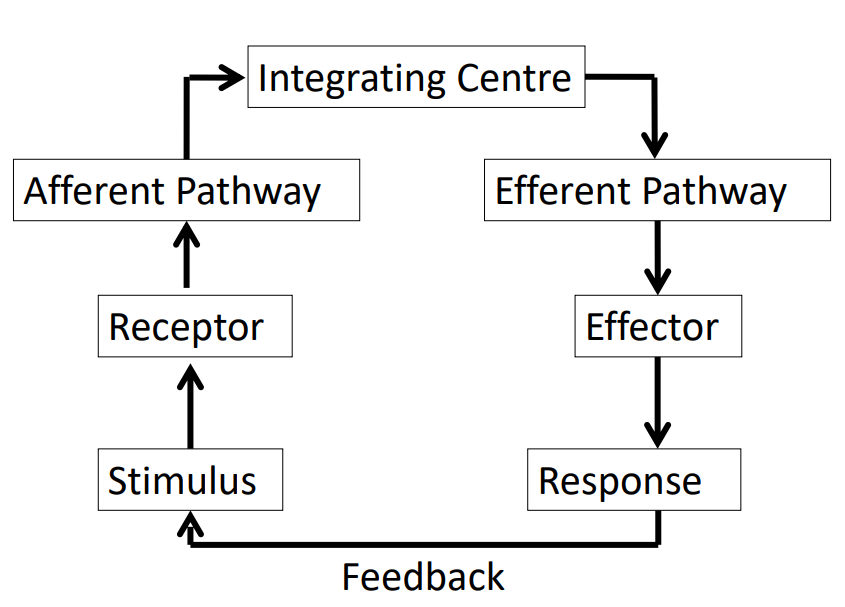
Stimulus Response DIAGRAM
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 14
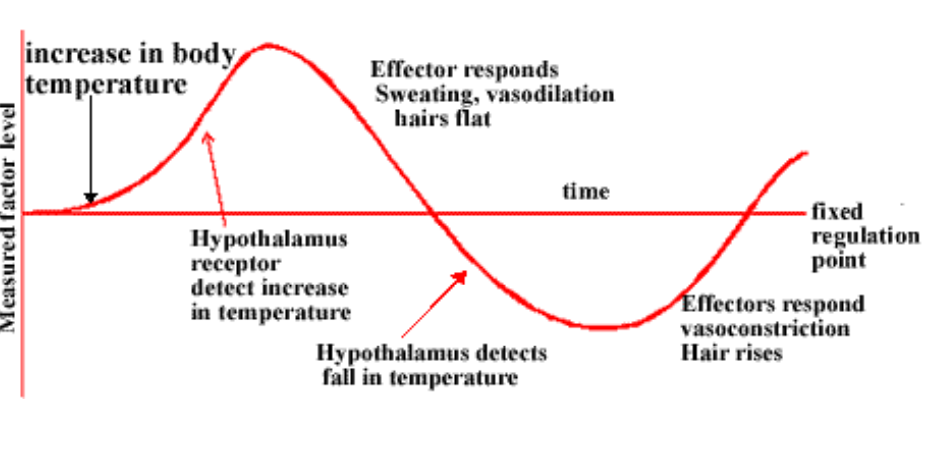
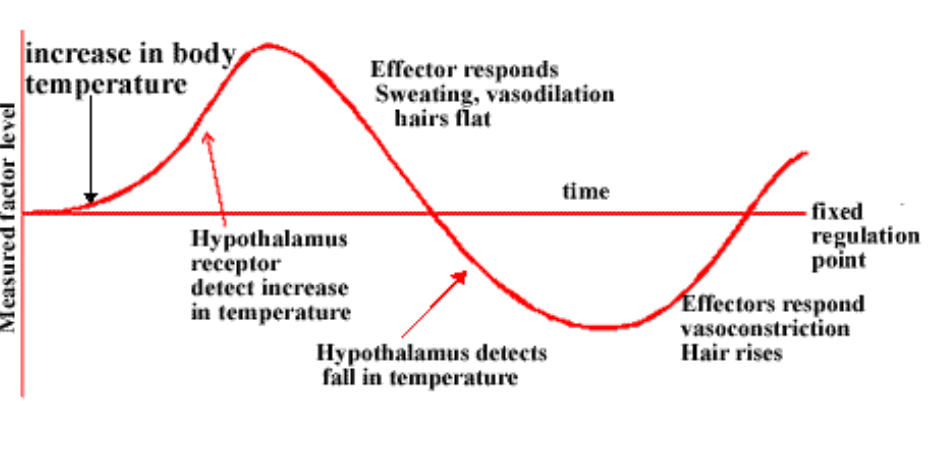
Body Temperature Feedback DIAGRAM
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 15
Control Concepts
- Negative Feedback: most common
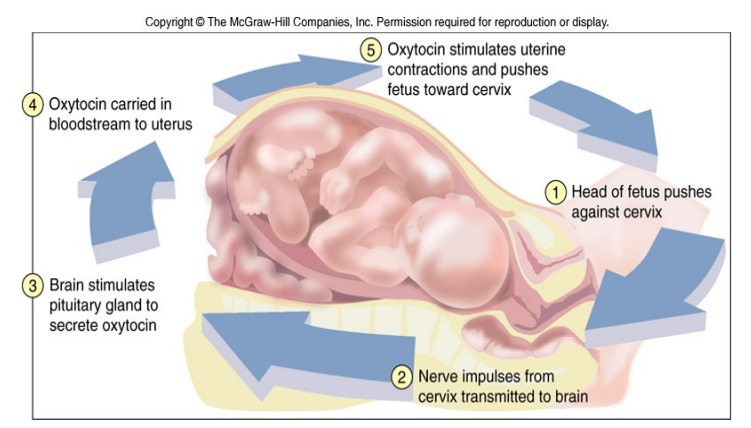
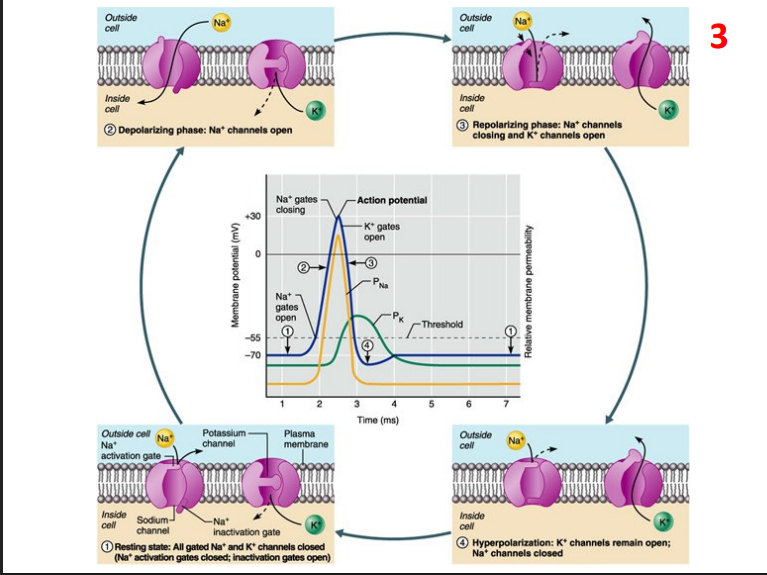
- Positive Feedback: rare - non-homeostatic (increases the instability). Blood clotting, action potentials (both part of -ve feedback systems), childbirth
- require an "error signal"
- System always playing "catch-up"
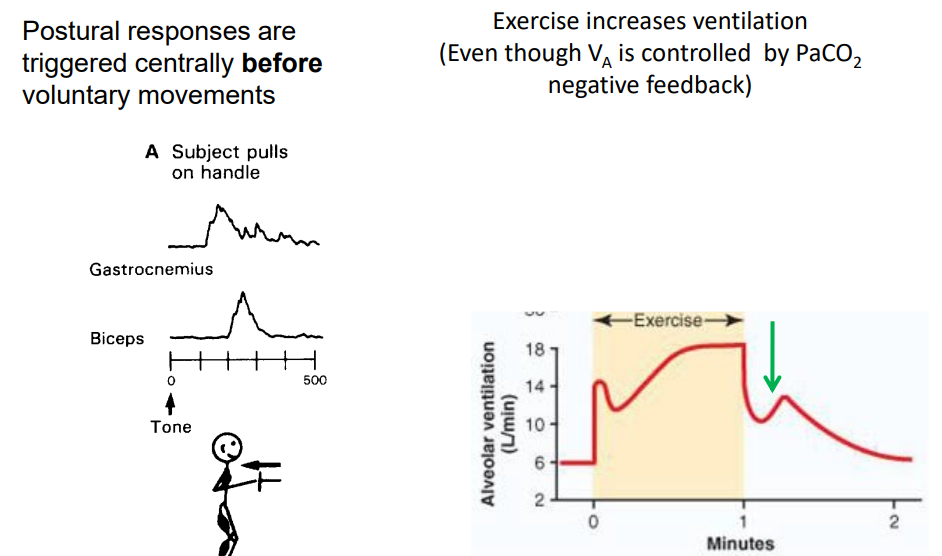
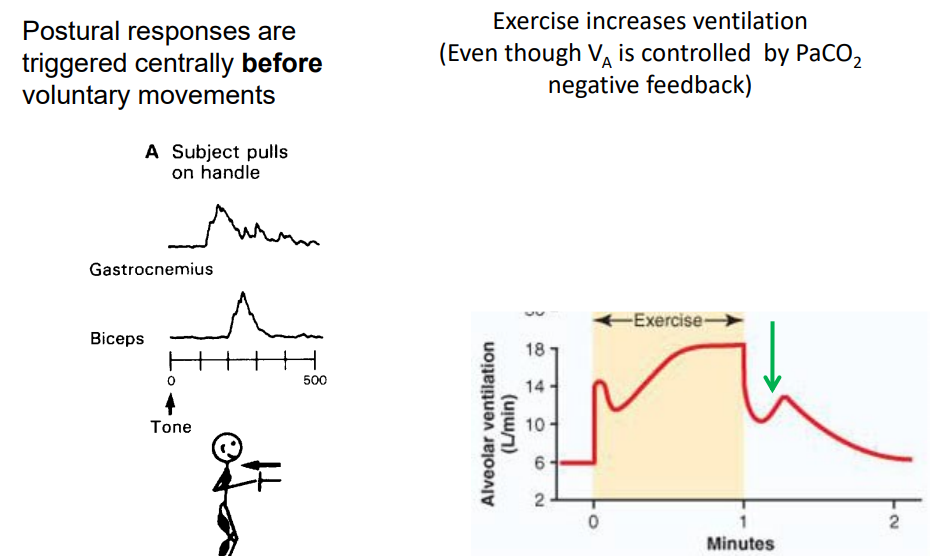
Feed-forward Control
- negative feedback normally is really slow, need a stimulus etc. it would be useful if we had a system that could just activate straight away. Thats what Feed-forward control is
- an "anticipatory" alteration of effectors - independent of feedback
- Parametric feed-forward (adaptive control): system 'learns' (adapts from previous failures). eg - ballistic control, ball throwing.
- Predictive homeostasis (anticipatory control): e.g increasing cardiorespiratory function in anticipation of exertion
- best example is if a lion suddenly is in front of you. You're body prepares to use muscles (its not -ve feedback, its a sort of pre-sponse not response)
Things you need to look at when looking at homeostatic control
1. What is the variable that is maintained relatively constant (the regulated variable, e.g plasma [K+], temperature, blood pressure. etc.
2. Where are the receptors that measure, and so detect changes in that variable
3. Where is the afferent information integrated, and efferent information generated, and what is the nature of that information?
4. What are the effectors, and how do they operate so as to maintain the regulated variable?
- for the rest of the slides, we will be looking at "the nature of the information"
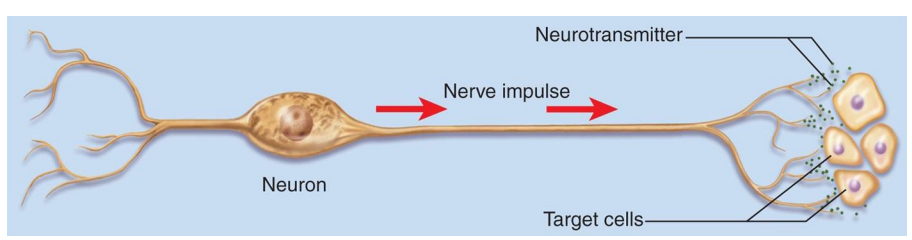
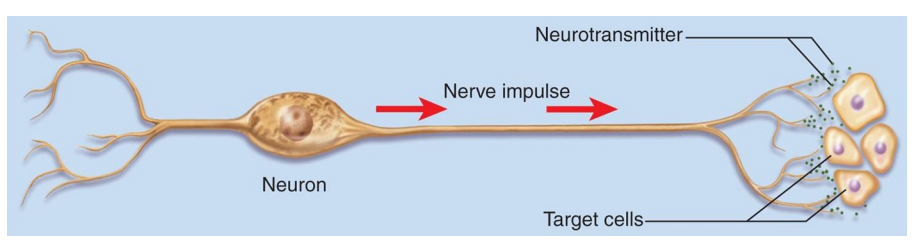
Neural Communication
- long distance
- really, really fast
- target cells = very specific (synapse), nerve, muscle and gland
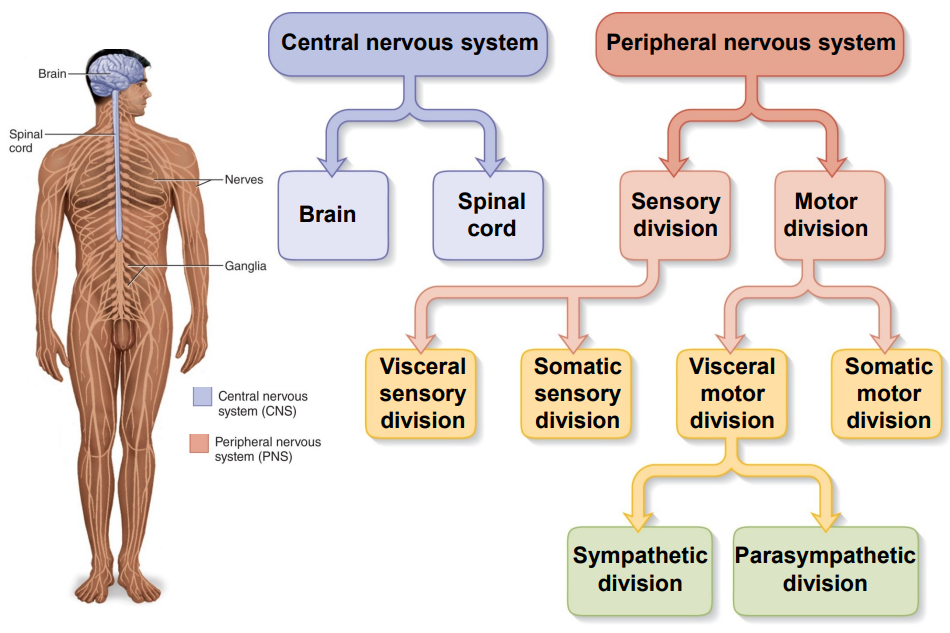
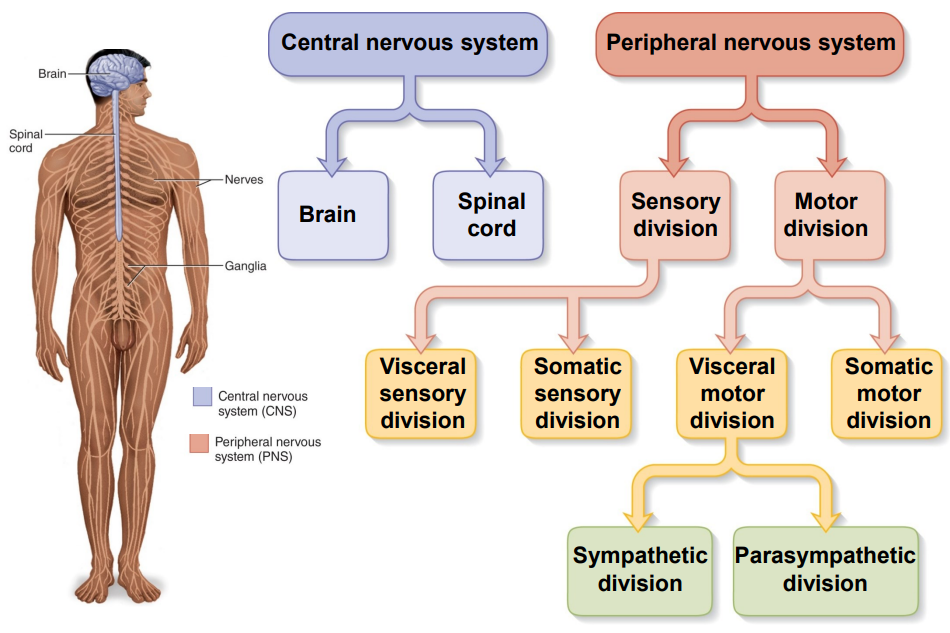
Subdivisions of the Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
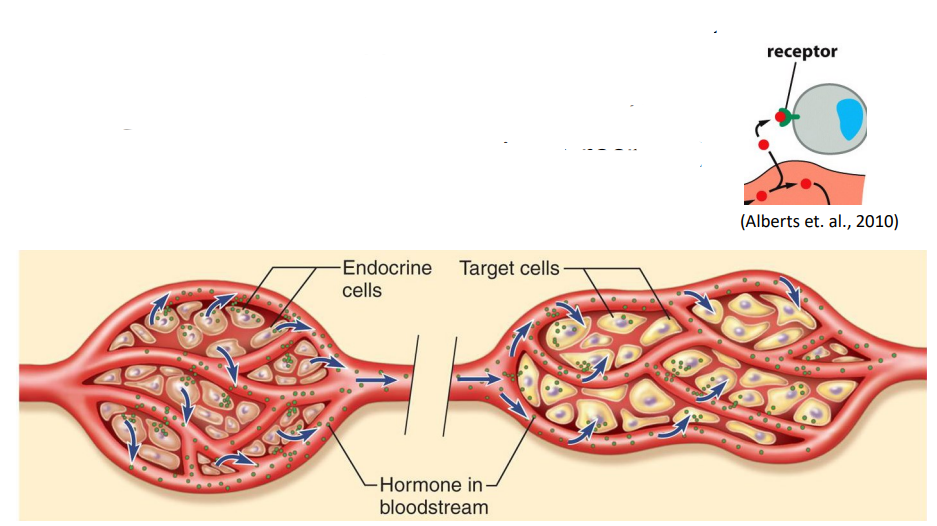
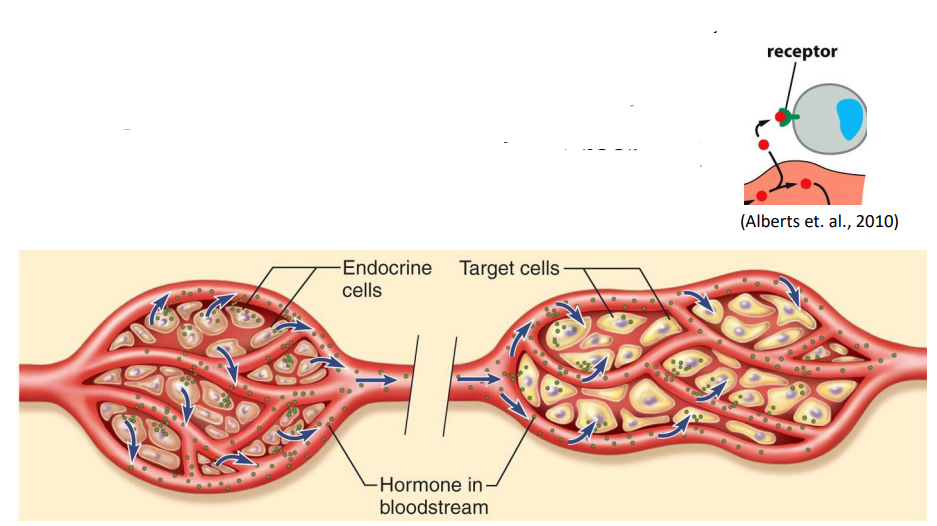
Endocrine Communication
- long distances - transport via bloodstream
- hormones secreted by glands
- target organs or cells - cells that have receptors for a hormone and can respond to it
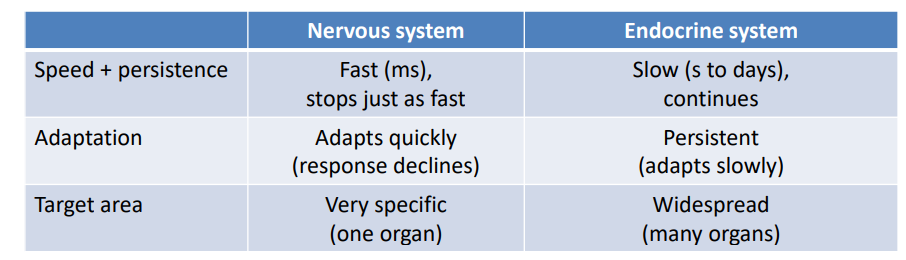
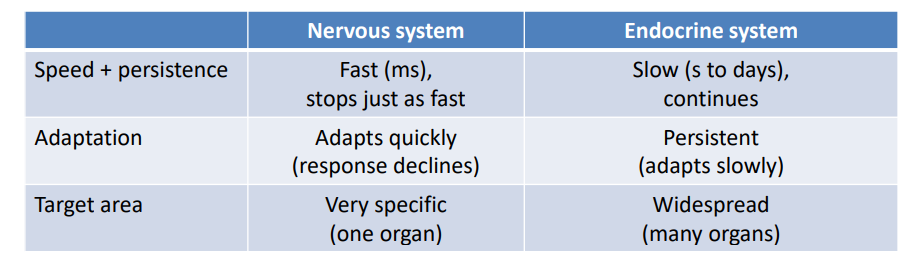
Nervous Vs Endocrine Systems
- several chemicals function as hormones and neurotransmitters (noradrenaline, dopamine, and ADH)
- Both systems can have similar effects on target cells (noradrenalin and glucagon both cause glycogen hydrolysis in liver)
- The two systems can regulate each other (neurotransmitters can affect glands, amd hormones can affect neurons)
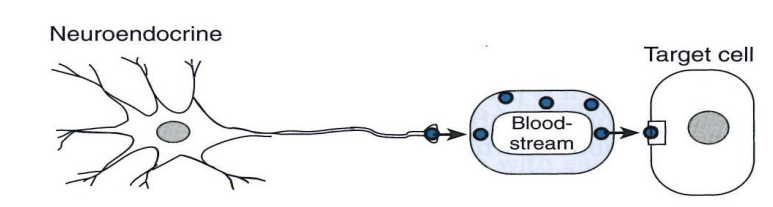
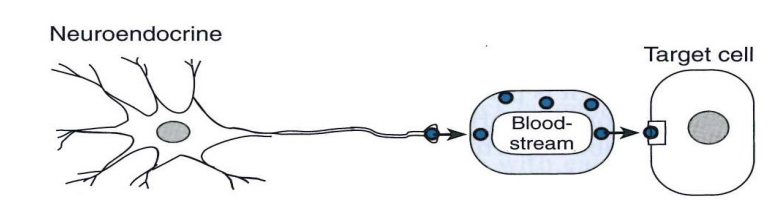
Neuroendocrine Communication
- combined neural and endocrine signalling
- Neuron secretes hormones into blood
- Adrenal medulla (adrenaline) and posterior pituitary (ADH, oxytocin)
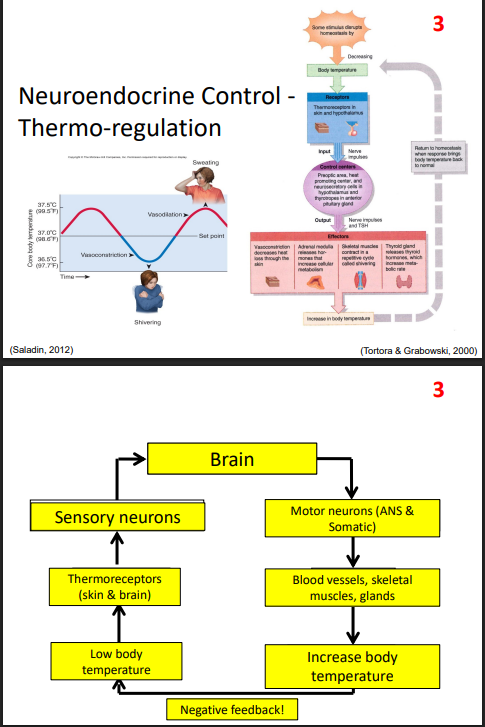
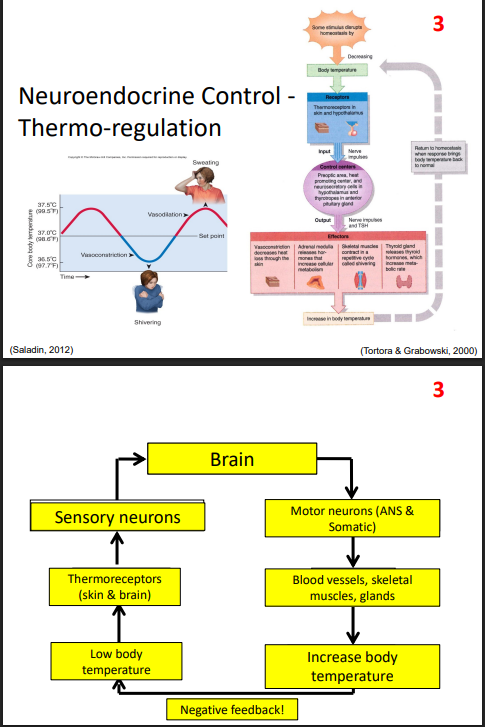
Neuroendocrine Control - Thermoregulation
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 28 and 29
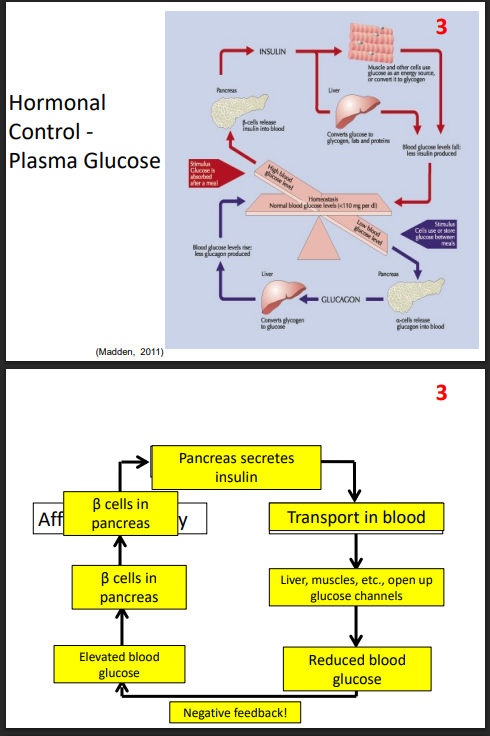
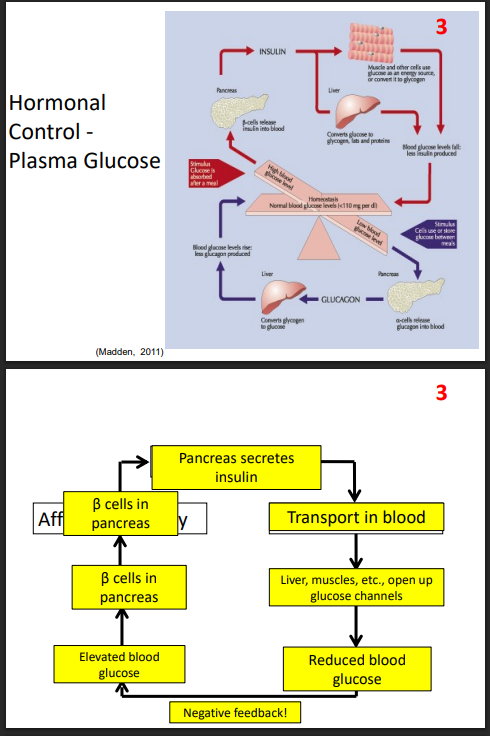
Hormonal Control - Plasma Glucose
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 30 and 31
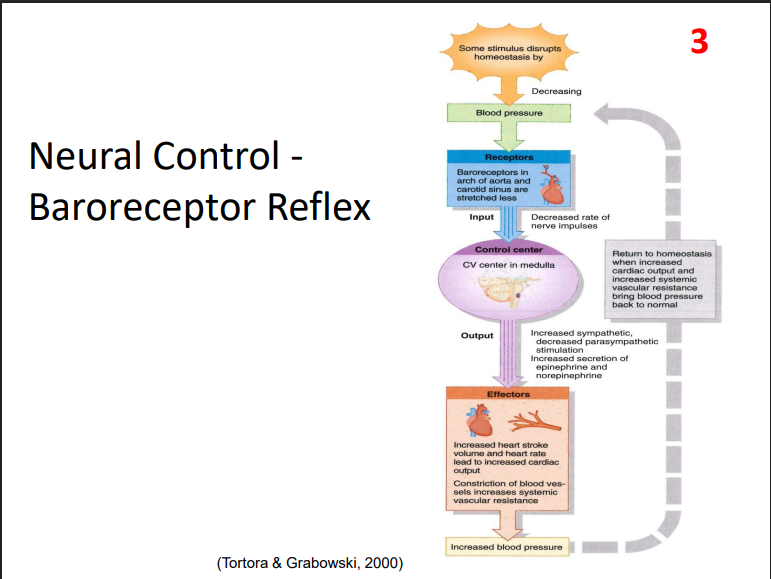
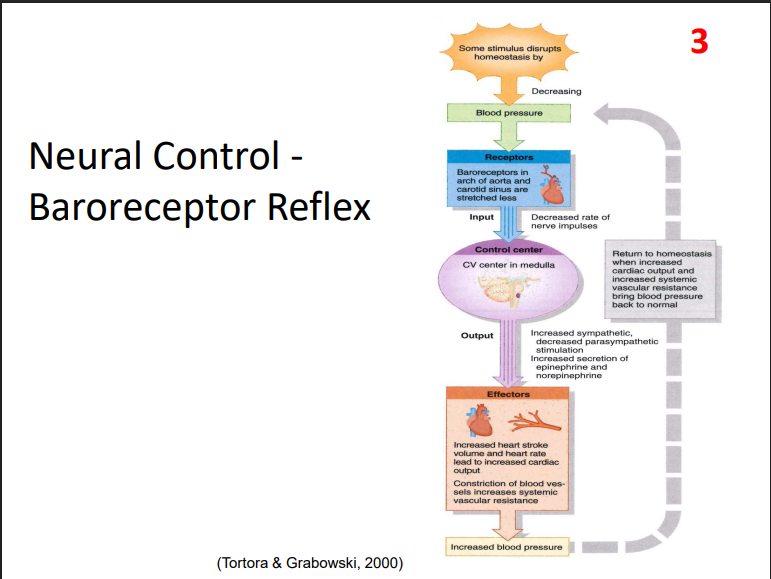
Neural Control - Baroreceptor Reflex
- decrease in blood pressure stimulates these
- receptor: baroreceptor in arch of aorta and carotid sinus are stretched less
- Control centre: cardiovascular centre in medulla oblongata
- Effectors: increased heart stroke volume and heart rate lead to increased cardiac output. constriction of blood vessels increase systemic vascular resistance.
- leads to an increase in blood pressure
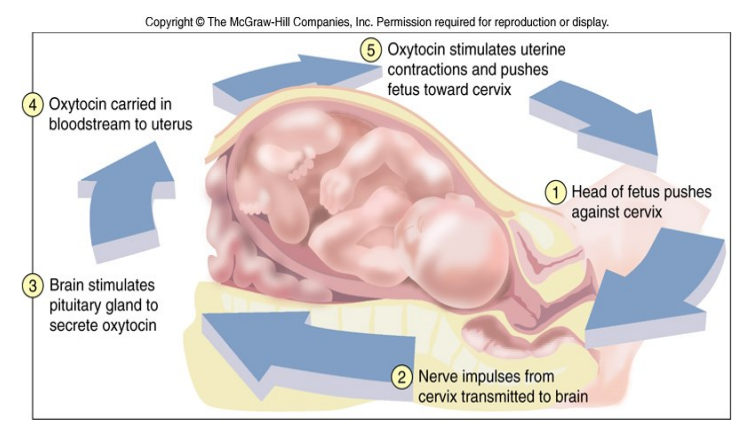
Positive Feedback - Childbirth
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 33
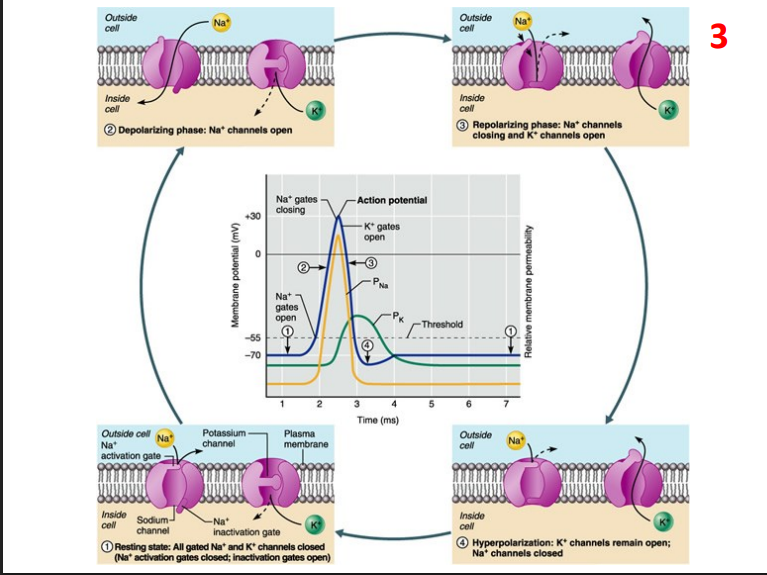
Positive Feedback - Action Potentials
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 34

SUMMARY
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 35
