Human Physiology Chapter 5: Chemical Messengers
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Intercellular Communication
communication between cells nearby or at a distance
direct
indirect
Intercellular Communication Process
2 or more cells sharing/communication of info and response to the communicated info
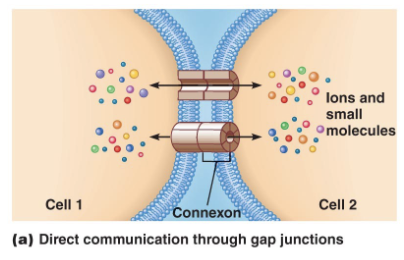
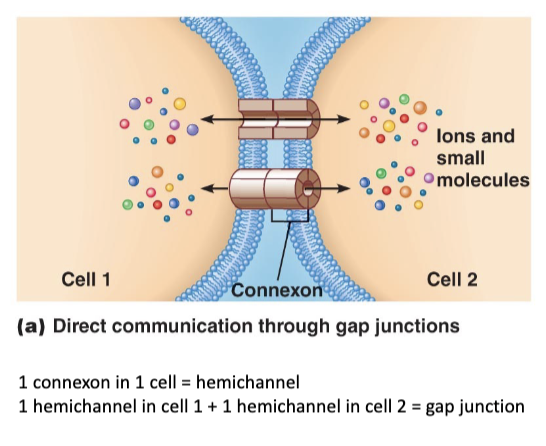
Direct Intercellular Communication
direct communication: gap junctions
involves: connexins and connexons
communicated info: ions and small molecules
ex: heart muscle, smooth muscle that controls intestines and blood vessels, between glands, neurons and retina
response: functions to synchronize cells, electrically coupling cells
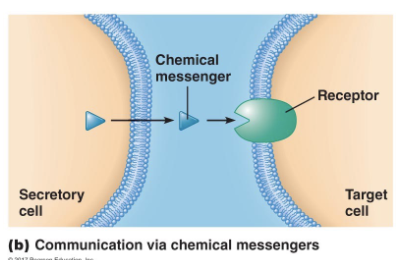
Indirect Intercellular Communication
transport of chemical messenger through the interstitial fluid
strength of target cell response depends on
concentration of the messenger near the target cell
number of receptors available to bind the messenger
sensitivity of the receptors for the messenger
identity of the responding receptor
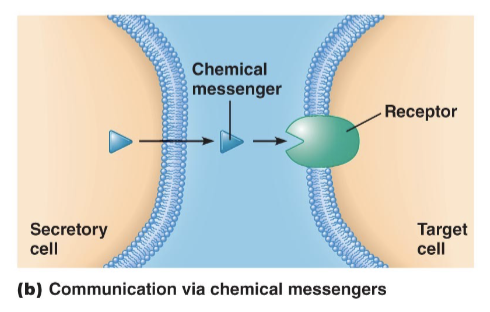
Functional Classes of Chemical Messengers
paracrine
autocrine
neurotransmitters
hormones
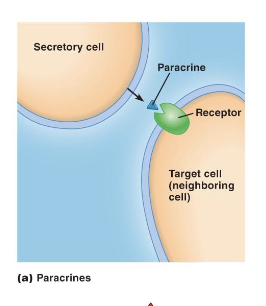
Paracrine Based Chemical Messenger
molecules diffuse through extracellular fluid to reach target molecule
target cell is nearby the secreting cell
autocrine molecules are secreted by and act on the same cell
Example of Paracrine Messenger
growth factors that control cell growth and differentiation
clotting factors
cytokines with a role in immune defense
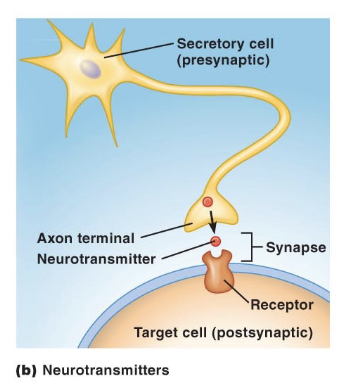
Neurotransmitters
released by neurons (presynaptic cell) at the axon terminal
diffusion across the synapse
received by a neuron, gland cell, or muscle (postsynaptic cells), cells associated with the axon terminal
synaptic signaling
Example of Neurotransmitters
acetylcholine, impacts skeletal muscles
Hormones
synthesized and released by endocrine cells into interstitial fluid and move rom here into the blood
transported through the blood stream to target cells
only cells with a receptor for the hormone can respond
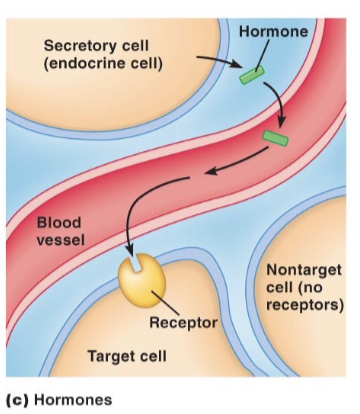
Example of Hormones
insulin produced by B-cells in the pancreas
it impacts insulin receptor containing cells
Neurohormones
secreted by specialized hormones
vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) secreted by neurosecretory cells in the posterior pituitary, travels in blood to the kidney
Functional Classification of Chemical Messengers
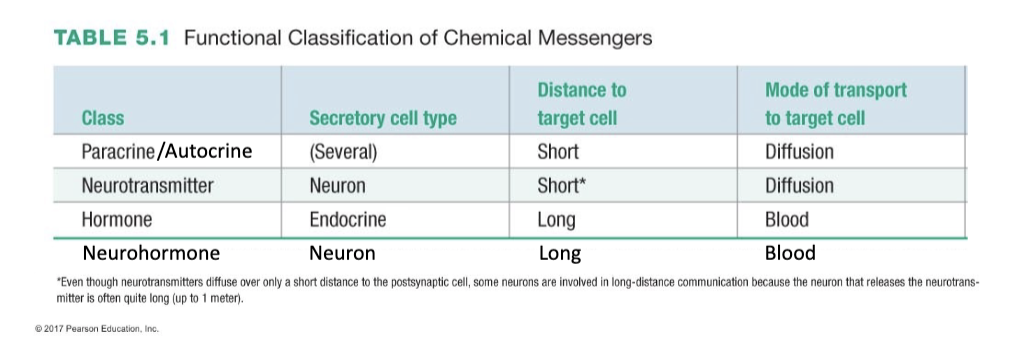
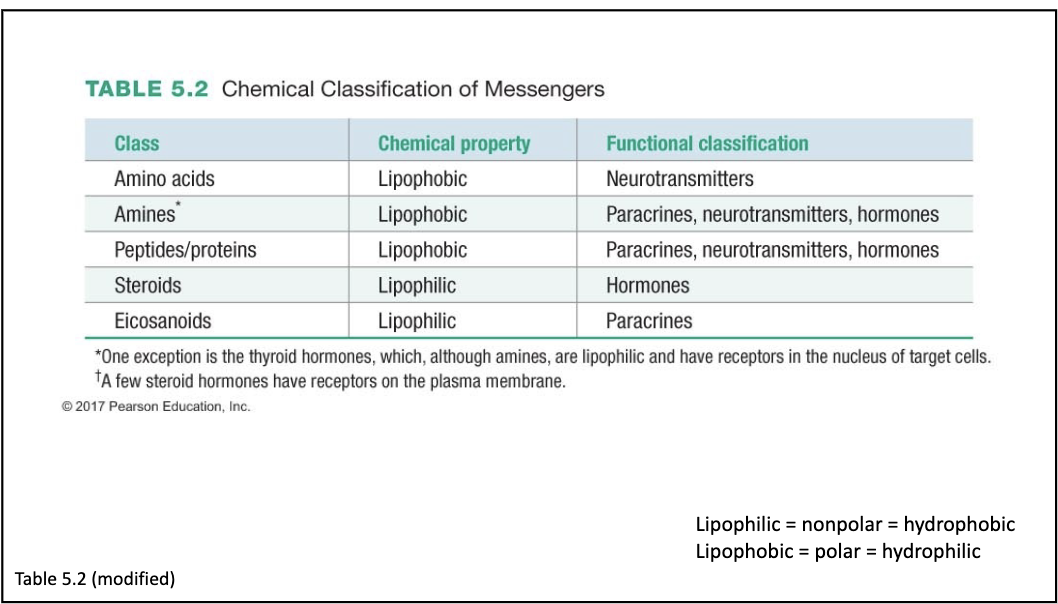
Chemical Classification of Messengers
major characteristic off chemical messengers
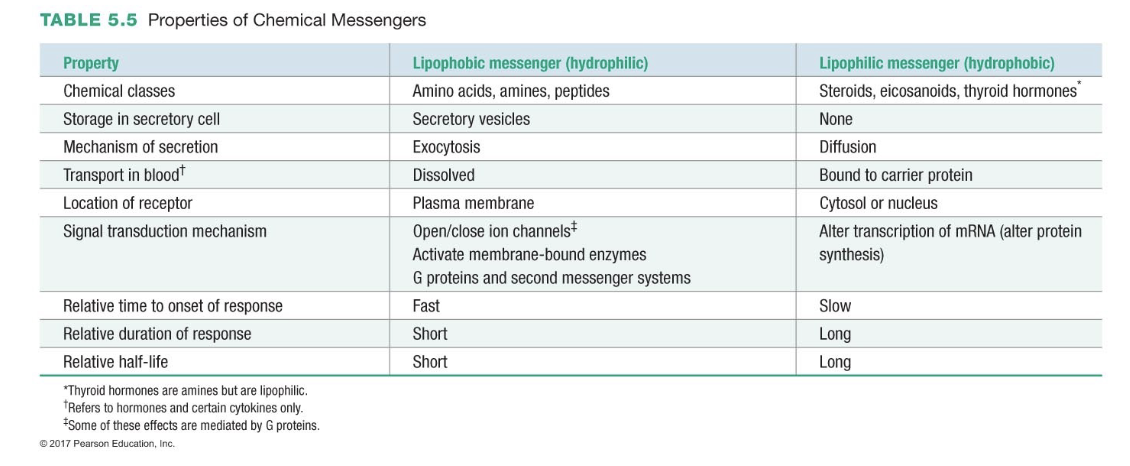
lipophilic
lipophobic
amino acid messengers
Lipophilic
lipid soluble; hydrophobic
cross a membrane environment, not freely transported in the plasma
Lipophobic
water soluble; hydrophilic
must be transported across a membrane environment, transported in plasma
Amino Acid Messengers
lipophobic/hydrophilic
neurotransmitters
glutamate, aspartate, glycine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
synthesized in the cytosol of neurons using intermediates from the oxidation o glucose
stored in membrane bound vesicles until exocytosis
Amine Messengers
primarily lipophobic/hydrophilic
derived from amino acids
neurotransmitters
dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and histamine
hormone
epinephrine, thyroid hormone
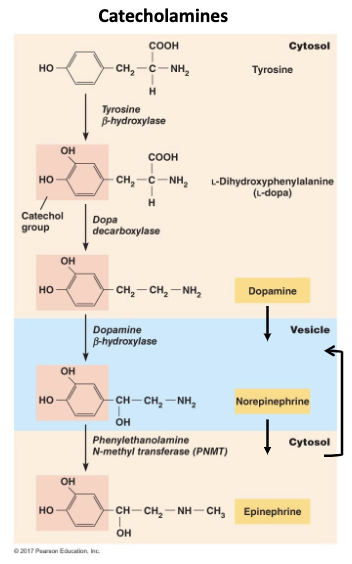
Catecholamines
synthesized in secretory cells from tyrosine
Serotonin
synthesized from tryptophan in the cytosol
Histamine
synthesized from histidine in the cytosol
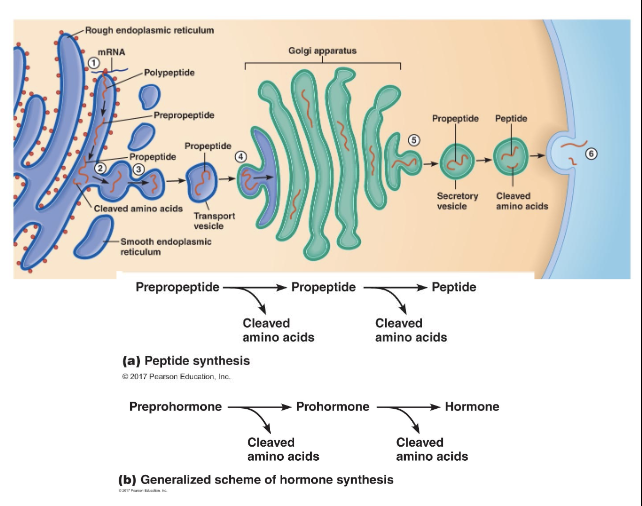
Peptide/Protein Messengers
2-100 amino acids
lipophobic/hydrophilic
synthesized on the RER
cleavage and transport to Golgi
packaged into secretory vesicle
final cleavage can occur in the golgi or secretory vesicle
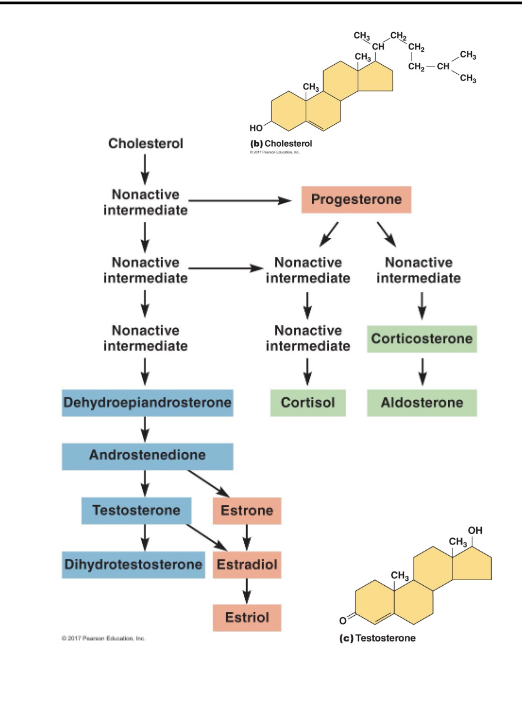
Steroid Messengers
lipophilic/hydrophobic
derived from cholesterol
hormones: estradiol
synthesized by enzymes located in the SER and mitochondria
can not be store, synthesized on demand
difffuses into intersitial fluid
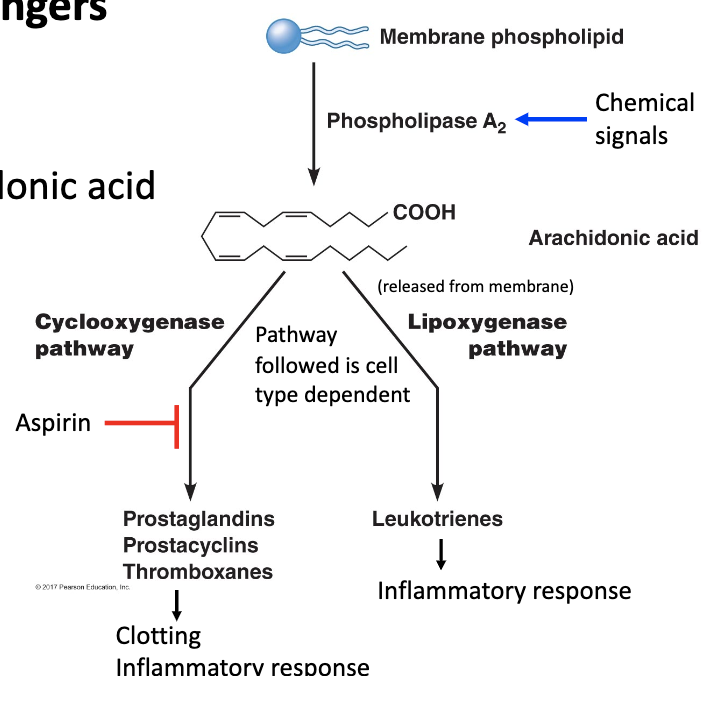
Eicosanoid Messengers
lipophilic/hydrophobic
derived from phospholipid/arachinidonic acid
paracrine
utilizes enzymes found in the ER and mitochondria
can not be stored, synthesized on demand
diffuses into interstitial fluid
Chemical Classification off Messengers
Hydrophilic Messengers Transport
freely soluble in the interstitial fluid/blood
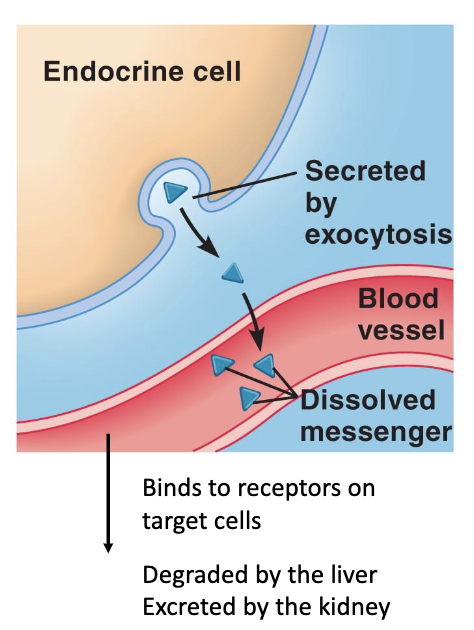
Paracrine and Neurotransmitters Messengers Transport
hydrophilic messenger
release near the target cell; diffuses to target
degradation in the interstitial fluid reduces activity to a local
Hormones, Peptides, and Amines Messengers Transport
hydrophilic messenger
dispersal through blood stream
some amines (catecholamines) are bound to carrier proteins
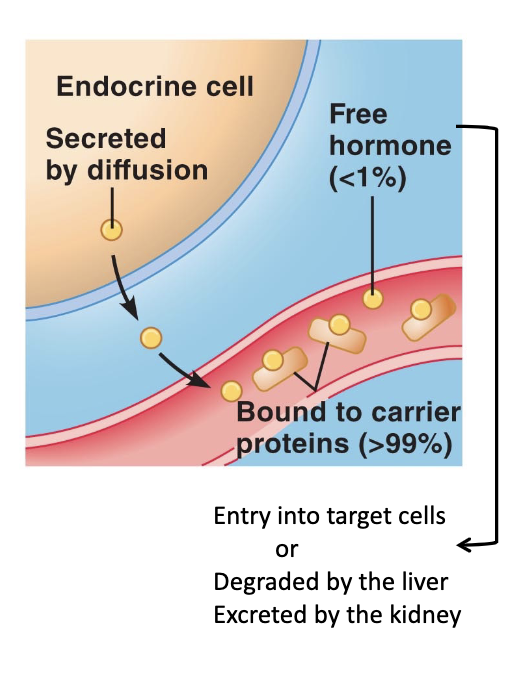
Hydrophobic Messenger Transport
not very soluble in the interstitial fluid/blood
bound to carrier proteins
carrier proteins may be specific to the messenger or general (albumin)
steroids, thyroid hormones
99 percent of hydrophobic messengers are bound to a carrier proteins for transport
free hormone can leave plasma and bind to receptors on target cells
Receptors
located in plasma membrane, cytosol, or nucleus of the target cell
a single chemical messenger can bind to multiple different receptors
a single cell has multiple receptors and can respond to multiple different chemical messengers
skeletal muslce have receptors for acetylcholine and insulin
Chemical Messenger
receptor interactions are either
specific
transient
reversible
Factors That Influence Target Cell Response
concentration of the messenger
number of receptors
affinity of the receptor for the chemical messenger

Receptor Agonists
ligands that bind to receptors and induces a response
Receptor Antagonists
ligands that bind to receptors and block a response, competes with agonists
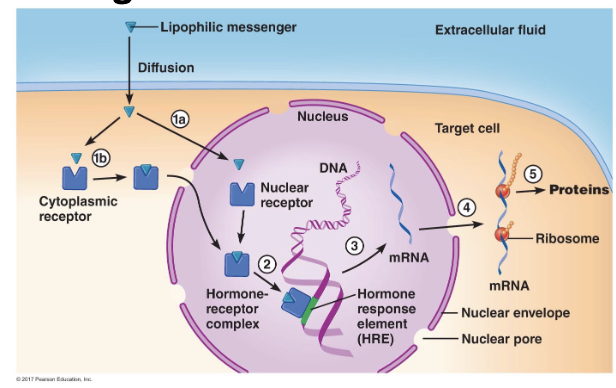
Target Cell Response: Lipophilic Messengers
freely enters the cytosol
binds to cytoplasmic/nuclear receptors and the receptor binds to DNA and activates transcription
mRNA translated into protein
long activation process
persist past the presence of the messenger
steroid receptors found in the cytoplams and nucleus
thyroid hormone receptors found in nucleus
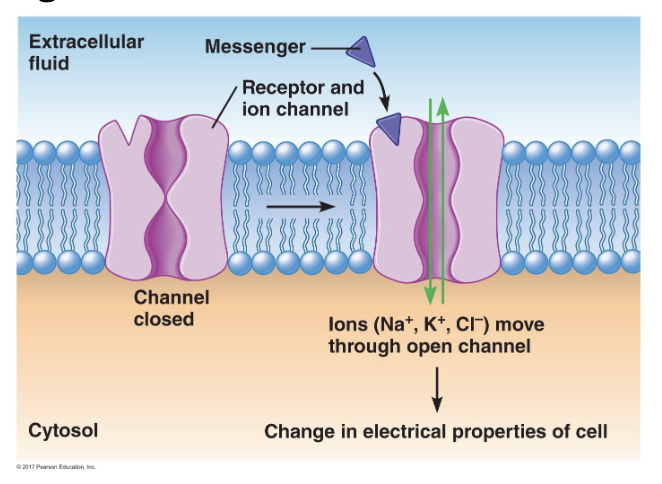
Receptor For Lipophobic Messengers (Channel Linked)
chemical messenger binding promotes opening of an ion channel
the influx of ions alters the membrane potential of target cell and ions can associate with intracellular proteins and alter their activity
target cell response is fast and continues as long as the chemical messenger is bound to its receptor
ex; acetylcholine binding to nicotinic cholinergic receptor on skeletal muscle leads to influx of sodium ions
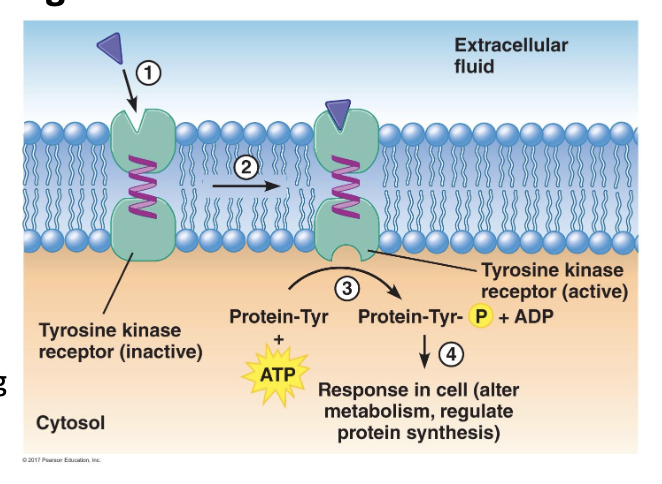
Receptor For Lipophobic Messengers (Enzyme-Linked Receptor)
messenger binding to an enzyme-linked receptor induces a change in conformation
autophosphorylation of the cytosolic domain of the receptor activates its kinase activity
activated receptor targets intracellular proteins for phosphorylation, triggering an intracellular response
Receptor For Lipophobic Messengers (G-Protein Linked)
chemical messenger binding activates an associated heterotrimeric G-protein
the alpha-subunit, with GTP bound, activates an effector molecule (channel or enzyme)
GTP hydrolysis by the alpha-subunit reverts it back into its inactivate state
Comparison of Liphophobic and Lipophilic Messenger