Earth and Space Science Midterm '26
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
What is a galaxy?
A collection of billions of stars, held together by gravity.
Definition of Solar System
A star and the system of celestial objects that go around it.
What is the theory of how the Universe began
Big Bang Theory
When did the Big Bang occur?
13.8 billion years ago
Proof of the Big Bang?
Red shift in most galaxies, background radiation, similar spectral lines in all stars, composition of matter in the Universe. (further explanation coming)
What instrument is used to see spectral lines?
Spectroscope
What are spectral lines?
A pattern of lines that are given off by certain elements. Each element gives off a different pattern.
Star composition supports the Big Bang Theory because they are all made of
Hydrogen (so they were created from the same event).
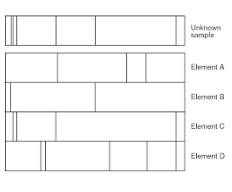
Which elements are in the sample?
B and C
What is the Doppler effect?
sound or light waves get smaller as they come toward you and bigger as they move away from you.
Red shift is when something (like a star or galaxy) is moving ___ and wavelengths are ___
moving away from us (Earth), wavelengths are longer
Blue shift is when something (like a star or galaxy) is moving ___ and wavelengths appear ___
moving toward Earth, and wavelengths appear shorter.
Most stars we view are ___ shifted
RED, which shows that the universe is expanding because most stars and galaxies are moving away.
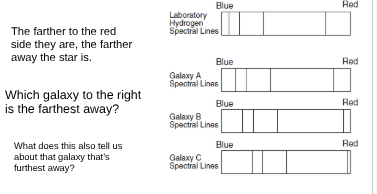
In spectral lines, the farther to the red side the lines are, the farther the star is. (This is not a question)
What is cosmic expansion?
Galaxies are moving away from each other as space time expands.
Hubble Constant
Galaxies are moving away from each other and the farthest ones appear to be moving the fastest.
Dark Energy
The mysterious force pulling the universe apart.
Dark Matter
The unseen matter around galaxies that gives them their shapes.
Is there more of Dark energy or dark matter in the universe?
Dark ENERGY
What percent of the Universe is visible?
5%
What percent of the universe is dark matter?
27%
What percent of the universe is dark energy?
68%
Which elements were made during Big Bang Nucleosynthesis?
Hydrogen, Helium, Deuterium
What is Nucleosynthesis?
the formation of atomic nuclei; how elements are made
Nucleosynthesis occurs (mainly) when
lighter elements combine (fusion) or heavier elements break apart (fission and radioactive decay)
**We haven’t discussed this so don’t worry about it too much, I included it just because it is in the notes.
What percent of all of the elements in the universe does helium make up?
25%
The amount of helium proves Big Bang theory how?
Though helium is made in stars during nuclear fusion, it makes up too much of the universe for it to only be from stars. This means that the rest of the helium was created during the Big Bang.
Epoch of Recombination
Period of time where elements formed during cooler temperatures - elements had to wait for the universe to cool from the Big Bang in order to form.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
Leftover radiation from the Big Bang
What is it called when stars make elements?
Stellarnucleosynthesis
Theory of Special Relativity (by Einstein)
E=mc² [ Energy = mass x speed of light (constant)² ] - (basically) states that energy can become matter (such as during the Big Bang) and matter can become energy (such as during nuclear fusion).
Nuclear fusion
The process that makes energy in stars - 2 lighter elements FUSE to form a larger, heavier element. ex: 2 hydrogens fuse to make 1 helium in a proton-proton chain reaction.
Where does nuclear fusion occur and under what conditions?
Core of a star, high temperature and high pressure
Larger stars can fuse
heavier elements (than smaller stars)
Elements heavier than Iron are formed through
Supernovas (explosion of supergiant star)
Hottest stars are what color?
Blue
Coolest stars are what color?
Red
All stars begin as a
Nebula (cloud of gas and dust)
Protostars become stars when they
get hot enough and begin nuclear fusion.
90% of stars are what type?
Main sequence (sun-like)
Stars stay in the main sequence for?
10 billion years
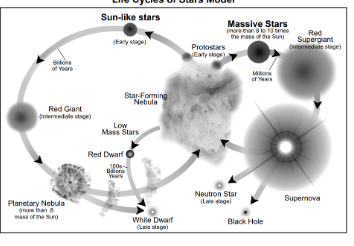
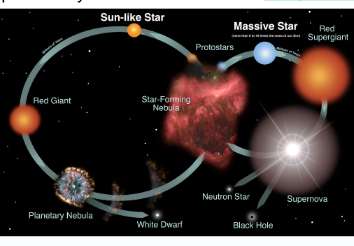
Life cycle of small - medium sized stars
Nebula
Protostar
Main Sequence
Red Giant
Planetary Nebula
White Dwarf
The sun is not liquid, solid, or gas; it is
plasma
Energy is carried to the sun’s surface through
convection currents
The sun rotates faster at its
equator
Supergiant stars die in a
Supernova explosion, and leave behind a neutron star (8-40 solar masses) or a black hole (+40 solar masses)
Sunspots
cooler magnetic storms - birthplace of solar flares and cme’s
Coronal Mass Ejections
eruptions of plasma sent into space off of the sun - *cause space weather, which disrupts satellite function and creates auroras.
Solar maximum
times of increased sunspot activity
Insolation =
sunlight
What types of surfaces absorb heat
dark and rough
What types of surfaces reflect heat
white and smooth
Steps in the formation of the solar system
Molecular cloud
Solar nebula
Nuclear fusion
Accretion
Molecular cloud
shockwaves from a supernova hit the cloud of dust and elements and collapses due to gravity. Once it flattens and spins it becomes a Solar Nebula.
Solar nebula
spinning disk of gas (hydrogen and helium) that becomes a star once it begins fusion (next step)
Accretion
when cooler, outer areas of rock fuse together to form planets
When did the solar system form
4.6 billion years ago
How did the moon form?
A collision with a Mars-sized object
When did the moon form
during Late Heavy Bombardment (4 billion years ago)
What dwarf planet is the largest
Eris
Formula for eccentricity
distance between foci divided by length of major axis = a # between 0-1**
What rate do things move across the sky?
15 degrees / hour
Why do things “move” across the sky (Apparent motion)?
Earth’s rotation from West to East
Anything that orbits something else in Space is considered a
Satellite
An object being orbited (like the sun) is called the
Primary/Central body
Which forces keep an object in motion?
Gravity and inertia
Kepler’s 1st law
Law of Orbits - States that planets orbit the sun on elliptical paths with the sun on one or focus points.
Kepler’s 2nd Law
Law of areas - States that the planet will cover the same area in space in the same time frame as other areas in its orbit.
Basically, area when faster and closer to the sun = area when slower and farther from the sun, during the same amount of time
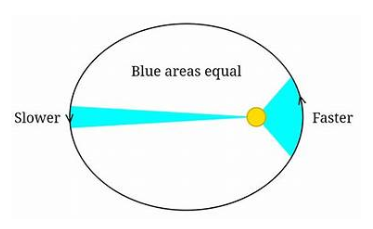
Kepler’s 3rd Law
Law of Periods - states that the farther a planet is from the sun, the longer its period of Revolution
Law of Universal Gravitation
Anything with mass attracts anything else with mass - Isaac Newton
What 2 factors affect gravity
mass and distance
Earth’s tilt
23 ½ degrees
Parallelism of Earth’s axis
Earth stays tilted the same way throughout its whole revolution.
Rocky Terrestrial Planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars.
Gas Giants
Jupiter, Saturn
Ice Giants,
Uranus, Neptune
Which planet is the least dense?
Saturn
Convection currents occur in the
Asthenosphere
Which layer of the Earth is fully liquid
Outer core
The core of the Earth is made of
iron and nickel
Everything in our sky (apparently) moves
East → West
The Sun is directly over the equator on the
Equinoxes (3/21, 6/21)
The sun is directly over 23 ½ degrees North on
6/21 (summer solstice)
The sun is directly over 23 ½ degrees South on
12/21 (winter solstice)
How many days does it take for the moon to go around the Earth
27.3
How many days does it take for the moon to go from new moon to new moon
29.5 - because the Earth is also moving around the sun so the moon has to travel just slightly farther to get back between the sun and earth.
Annular solar eclipse
the moon is farther from the sun and does not cover all of it - leaves a ring of light around it
Umbra
inner, darkest part of a shadow
Penumbra
an outer, lighter, partial shadow
Why don’t we always have lunar/solar eclipses when the moon gets to the full/new moon phases?
The moon’s orbit is inclined, so it doesn’t always line up that way.
How much is the moon’s orbit inclined
5 degrees
Spring tides
highest high tides and lowest low tides, happen when sun, moon, and earth line up (syzygy)
High tides occur where?
On the side of Earth that the moon is on and the opposite side.
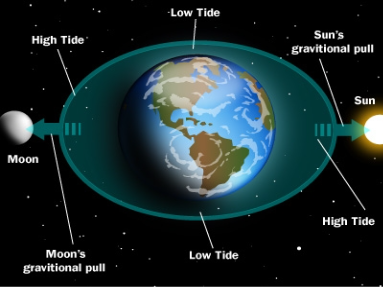
Neap tides
regular high tides that happen when the sun, moon, and earth form a 90 degree angle (moon at its quarter phases)
ceres and Pallas are located
in the asteroid belt
dwarf planets in our solar system
ceres, Pluto, and eris
differentiation
when the earth’s layers were separated - dense materials sank (iron and nickel)
Earth was dated to be 4.6 billion years old by
Radioactive dating of rocks
What changes an isotope’s rate of decay
nothing