Understanding Neoplasia and Cancer Development
1/337
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
338 Terms
Cancer
Leading cause of death in adults globally.
Neoplasia
Abnormal tissue growth exceeding normal tissue.
Tumor
Swelling caused by various conditions.
Benign Neoplasm
Well-differentiated cells, localized growth.
Malignant Neoplasm
Poorly differentiated, invades and metastasizes.
Cell Differentiation
Process by which cells become specialized.
Hypertrophy
Increase in cell size, not number.
Hyperplasia
Increase in cell number, not size.
Fibrous Capsule
Connective tissue surrounding benign tumors.
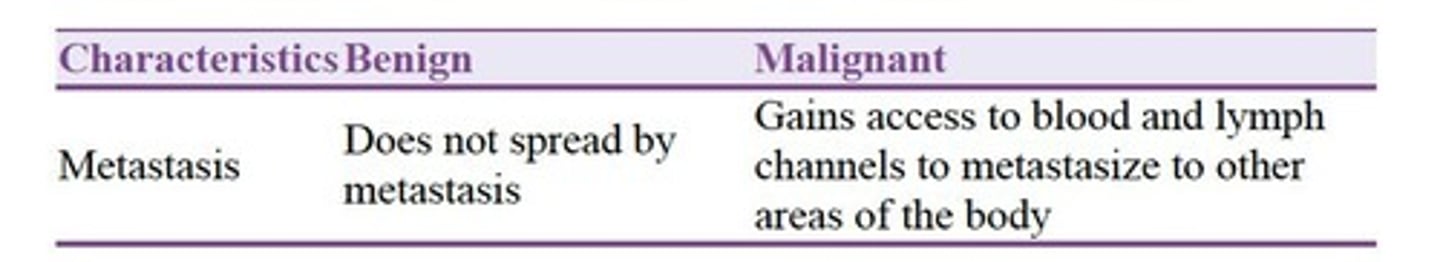
Metastasis
Spread of cancer to distant sites.
Ischemia
Insufficient blood supply to tissues.
Survival Rates
Affected by cancer type and treatment availability.
External Factors
Environmental influences like tobacco and radiation.
Internal Factors
Genetic and biological influences on cancer risk.
Secondary Tumors
New tumors formed from metastasis.
Rate of Growth
Speed at which a tumor increases in size.
Capacity to Invade
Ability of tumor to infiltrate surrounding tissues.
Potential for Death
Risk associated with tumor type and behavior.
Hormone Production
Some benign tumors produce hormones abnormally.
Cytokines
Proteins that mediate immune responses.
Solid Tumors
Confined to specific tissues or organs.
Hematologic Cancers
Cancers affecting blood and bone marrow.
Inflammatory Response
Body's reaction that can damage normal tissue.
Well-Differentiated Cells
Cells that closely resemble normal tissue.
Progressive Growth
Continuous increase in tumor size.
Pressure Effects
Disturbances caused by tumors on adjacent structures.
Cancer Treatment
Methods to manage or eliminate cancer.
Metastasis
Spread of tumor cells to distant sites.
Hematologic cancers
Cancers involving blood and lymph cells.
Carcinoma in situ
Localized preinvasive lesion, often removable.
Abnormal proliferation
Rapid and uncontrolled cell growth.
Loss of differentiation
Cells lack normal features of differentiated cells.
Anaplasia
Loss of cell differentiation in cancerous tissue.
Undifferentiated tumors
Tumors with cells resembling embryonic cells.
Genetic instability
Hallmark of cancer involving chromosomal abnormalities.
Aneuploidy
Loss or gain of chromosomes in cells.
Intrachromosomal instability
Insertions, deletions, and amplifications in DNA.
Microsatellite instability
Changes in short repetitive DNA sequences.
Point mutations
Alterations in a single nucleotide of DNA.
Growth factor independence
Cancer cells proliferate without external growth factors.
Contact inhibition
Growth cessation upon cell density reaching a limit.
Anchorage independence
Cancer cells grow without attachment to other cells.
Faulty cell communication
Impaired signaling between cancer cells.
Unlimited lifespan
Cancer cells divide indefinitely in culture.
Telomeres
Chromosome ends that shorten with each division.
Telomerase
Enzyme that maintains telomere length in cancer cells.
Tumor antigens
Surface molecules identified as foreign by the immune system.
Fetal antigens
Antigens not produced by adult cells, found in some cancers.
Intercellular connections
Connections between cells that may be impaired in cancer.
Bizarre mitotic figures
Atypical cell division patterns in undifferentiated tumors.
High mitosis rate
Increased cell division in undifferentiated tumors.
Morphologic changes
Structural alterations in undifferentiated cancer cells.
Recurrence chances
Likelihood of cancer returning after treatment.
Surgical removal
Procedure to excise localized tumors.
Progressive growth
Continuous increase in tumor size or spread.
Cancer cells
Cells that proliferate uncontrollably, invading tissues.
Degradative enzymes
Enzymes that break down tissues, aiding invasion.
Hormone synthesis
Production of hormones by cancer cells.
Procoagulant substances
Substances affecting blood clotting mechanisms.
Cytoskeletal changes
Alterations in cell structure affecting movement.
Intermediate filaments
Cytoskeletal components involved in cell integrity.
Actin filaments
Protein filaments facilitating cell movement and shape.
Microtubules
Cylindrical structures aiding in cell division.
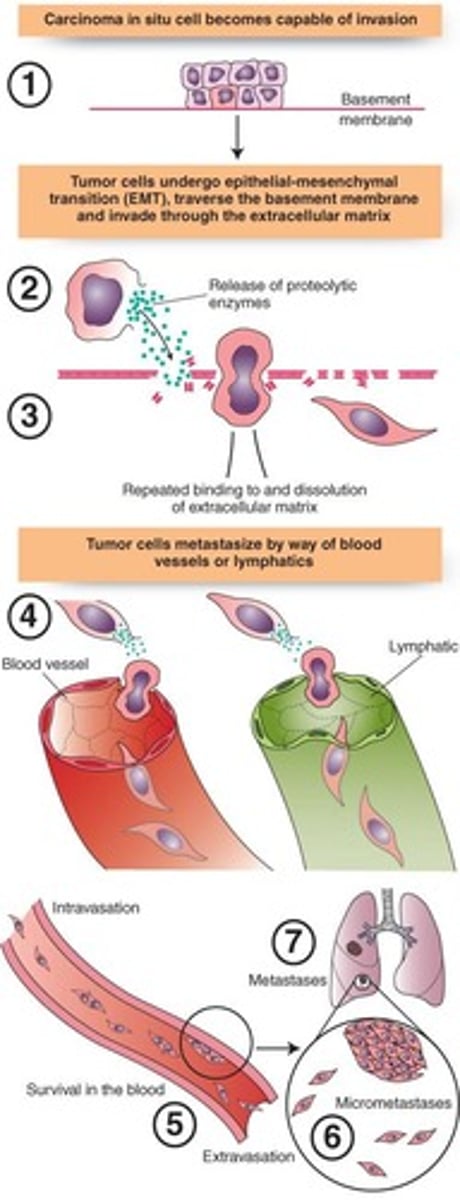
Invasion
Direct penetration of cancer cells into tissues.
Metastatic spread
Dissemination of cancer cells to distant sites.
Seeding
Release of cancer cells into body cavities.
Peritoneal cavity
Abdominal cavity often involved in cancer seeding.
Pleural cavity
Space surrounding the lungs, can harbor cancer cells.
Metastasis
Formation of secondary tumors away from primary site.
Sentinel node
First lymph node draining the primary tumor.
Hematologic spread
Cancer spread through the bloodstream.
Extracellular matrix
Network providing structural support to tissues.
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)
Process allowing epithelial cells to become migratory.
Proteolytic enzymes
Enzymes that degrade proteins in the extracellular matrix.
Micro metastases
Small clusters of cancer cells in new locations.
Blood supply establishment
Formation of blood vessels to support tumor growth.
Cell cycle
Series of phases for cell division and replication.
Lymphatic system
Network transporting lymph, involved in cancer spread.
Tumor characteristics
Unique features aiding identification of tumor origin.
Adhesion molecules
Proteins facilitating cell attachment to extracellular matrix.
Tumor invasion mechanisms
Steps by which tumors penetrate surrounding tissues.
Cancer cell ecosystem
Microenvironment supporting cancer cell survival and spread.
Metastatic tumor growth
Expansion of cancer cells at distant sites.
Cell Cycle
Sequence of phases for cell division.
Dividing Cells
Cells actively undergoing the cell cycle.
Growth Fraction
Ratio of dividing to resting cells.
Doubling Time
Time for cell mass to double.
Cancer Cell Cycle
Cancer cells cycle at similar rates to normal cells.
Cell Pool
Active cells engaged in the cell cycle.
Cell Loss
Rate of cells lost versus produced.
Tumor Growth Rate
Rapid growth due to cell cycle dynamics.
Genetic Damage
Mutations leading to cancer transformation.
Epigenetic Factors
Gene silencing affecting cancer development.
Microenvironment
Surrounding cells and factors influencing cancer.
Proto-Oncogenes
Normal genes that can become oncogenes.
Oncogenes
Mutated genes promoting uncontrolled cell division.
Tumor Suppressor Genes
Genes inhibiting cell proliferation.
Retinoblastoma Gene
Prevents cell division under normal conditions.
TP53 Gene
Activates apoptosis in DNA-damaged cells.
Chromosomal Translocations
Genetic alterations linked to specific cancers.