microbiology lab exam 1
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
__________ is the single most important way to reduce the spread of microbes.
handwashing
Where is used media disposed?
biohazard
Where is a slide prepared by you disposed?
Wrapped in paper towel and then disposed in biohazard
Where are uncontaminated gloves disposed?
trash
Where is a broken stock slide disposed?
broken glass container
What are the last two things you should do before leaving lab?
wipe down bench wash hands
Why is incorrect to label a culture tube cap or the lid of a petri dish?
The tops can be separated, so if it is on the bottom you will know for certain that sample is what it is labeled. It cannot be separated from it.
You inoculated a broth with E. coli in lab and want to grow the culture for 48 hours and will check on the culture during the next lab period. What temp?
37 °C
You inoculated a broth with E. coli in lab but did so at the end of the week and won't be back in lab until after the weekend, so growth needs to be slowed down.
25°C (room temp)
You have observed your results but want to store them for future observation.
4°C (refrigeration)
media that contains agar
solid
media that does not contain agar
liquid
equipment used to sterilize the incoulating loops via incineration
incinerator
organism or material used for inoculation
inoculum
introduce cells or organisms into a culture medium
inoculate
equipment used to grow microorganisms in a controlled environment
incubator
bioremediation and the decay of dead organisms. Bioremediation is the use of living bacteria, fungi, and algae to detoxify polluted environments. We use microorganisms to remove pollutants and also to purify water. (recycling nutrients)
What two beneficial roles do microorganisms play in the environment?
It is important to appreciate the ubiquity of microorganisms and to maintain asceptic technique to ensure that there is no contamination of the pure culture. Although they are too. small to see, they can still contaminate your lab.
What four beneficial roles do microorganisms play as microbiota?
ocular lens x objective lens; 40x
Total magnification is calculated by multiplying _________. For example The total magnification for the scanning lens is ____.
increases; decreases
As magnification ____, field of view ___.
decreases: increases
As resolving power number ___, resolution ___
increases; decreases
As magnification of a lens ____; the resolving power number ____
refraction
Oil is necessary when using the 100x objective lens because it prevents the ___________ of light.
900 nm no
You are looking at algae under blue light (450 nm) with the low power lens. You know from previous experiments that they like to be 800 nm away from the nearest other algae cell. 1. What is the current resolving power?
2. Will you be able to see individual algal cells at this magnification?
Gram - Bacillus
After performing the Gram stain, you observe a smear of pink rod-shaped cells that are randomly dispersed across the smear. How would you describe the Gram stain and cell morphology of these cells using proper terminology?
corynebacterium
Which genus of bacteria is the only genus observed in this lab that produces palisades or snapping cell morphology?
longer wide
Coccobaccilli are different from cocci in that they are
_________ than they are __________
bacillus refers to any rod shaped bacterium, while Bacillus (italicized and capitalized) is a genus of bacteria
Explain the difference between bacillus and Bacillus
Anionic chromophores are also known as acidic dyes because they stain alkaline structures and work best in acidic environments. Cationic chromophores are called basic dyes because they combine with and stain acidic structures and work best in basic conditions. Cationic dyes are positively charged and anionic dyes are negatively charged. Basic dyes attach to the negatively charged molecules within cells, acidic dyes are repulsed by the negative charges on cells and do not stain them. This reveals the charge of the bacteria capsules
Why must both an anionic dye and a cationic dye be used for the capsule stain?
Green
What color are the endspores supposed to be in the endospore stain?
Spirilium Polar amphitrichous
When observing a flagellar stain, you clearly see corkscrew shaped bacterial cells with a single flagella projecting from each end of the cells. How would you describe the cell morphology and flagellar arrangement of these bacterial cells?
agar deep
Sterile agar poured into a culture tube and cooled upright; used to culture live bacteria.
complex media
Exact composition and quantity of nutrients is unknown; used to culture most microorganisms.
selective
Media that inhibits the growth of some microogranisms while allowing for the growth of others.
agar plate
A sterile agar poured into a petri dish and cooled; used to culture live bacteria.
agar slant
A sterile agar poured into a culture tube and cooled at an angle; used to culture live bacteria.
defined media
Exact composition and quantity of nutrients are known; used to culture fastidious organisms in research.
It is important to keep tubes as close to parallel as possible to the bench top while picking it up/transferring it to prevent any spills. However, once the cap is removed it is important to hold the tube at an angle to prevent any airborne contaminates from falling into the tube and contaminating the sample.
Explain why tubes should be kept as close to parallel as possible to the benchtop while performing any transfers or inoculations.
If one ignores the proper sterilization protocols regarding the inoculating loop or media tubes they could contaminate their sample which will effect their results, they could inoculate themselves, contaminate surfaces that others will touch, or burn themselves with the incinerator or the inoculating loop.
What can happen from a safety standpoint if one ignores the proper sterilzation protocols regarding the inoculating loop or media tubes?
Agar is useful in media preparations are providing a solid surface for bacterial growth because most microbes cannot digest agar. Another reason is because it solidifies at 40 degrees Celsius, so temperature-sensitive nutrients can be added without damage. Cooling liquid agar can be poured over most bacterial cells without harming them, so it is useful in pour-plate isolation. Another reason is that solid agar does not melt below 100 degrees Celsius so it can be used to culture some hyperthermophiles.
What are three reasons agar is so useful in media preparations if it not a source of nutrition for bactera?
The streak plate is the most common used isolation technique. The streak pattern gradually dilutes the sample to a point where CFU's are isolated from one another. After incubation, colonies develop from each isolate so the organisms present are distinguished from one another by differences in colonial characteristics. Samples from each variety can then be inoculated in new media to establish axenic cultures. The purpose is to obtain isolated, pure colonies from an inoculum by creating areas of increasing dilution.
Why do microbiologists use the streak plate method and what is its purpose?
To remove the microorganisms so that we are diluting when streaking.
Why do you have to flame the loop between each streak?
The less number of bacteria in quadrant III means they have more room to grow.
You streak a pure culture and find that the colonies in Quadrant III are larger in diameter that the colonies in Quadrant I. If both colonies are the same microorganism, what would account for this?
Yes, the components of the mixed culture need to be separated first. This is done by doing a streak plate or a spread-plate technique, then once you have individual colonies you can grow them as a pure culture. You distinguish between the pure cultures by looking for certain characteristics, then you can inoculate a certain colony of bacteria, which will isolate it from other colonies.
Can a pure culture containing a single type of microbe be prepared from a culture with a mixture of cells? Explain your reasoning.
All the colonies have the same characteristics.
How could you determine if a culture that you choose to isolate is a "pure culture"?
initials, date, name of medium, name of inoculum
how to label a culture
binary fission
colonies are billions of cells created by __________
neisseria gonorrhoeae
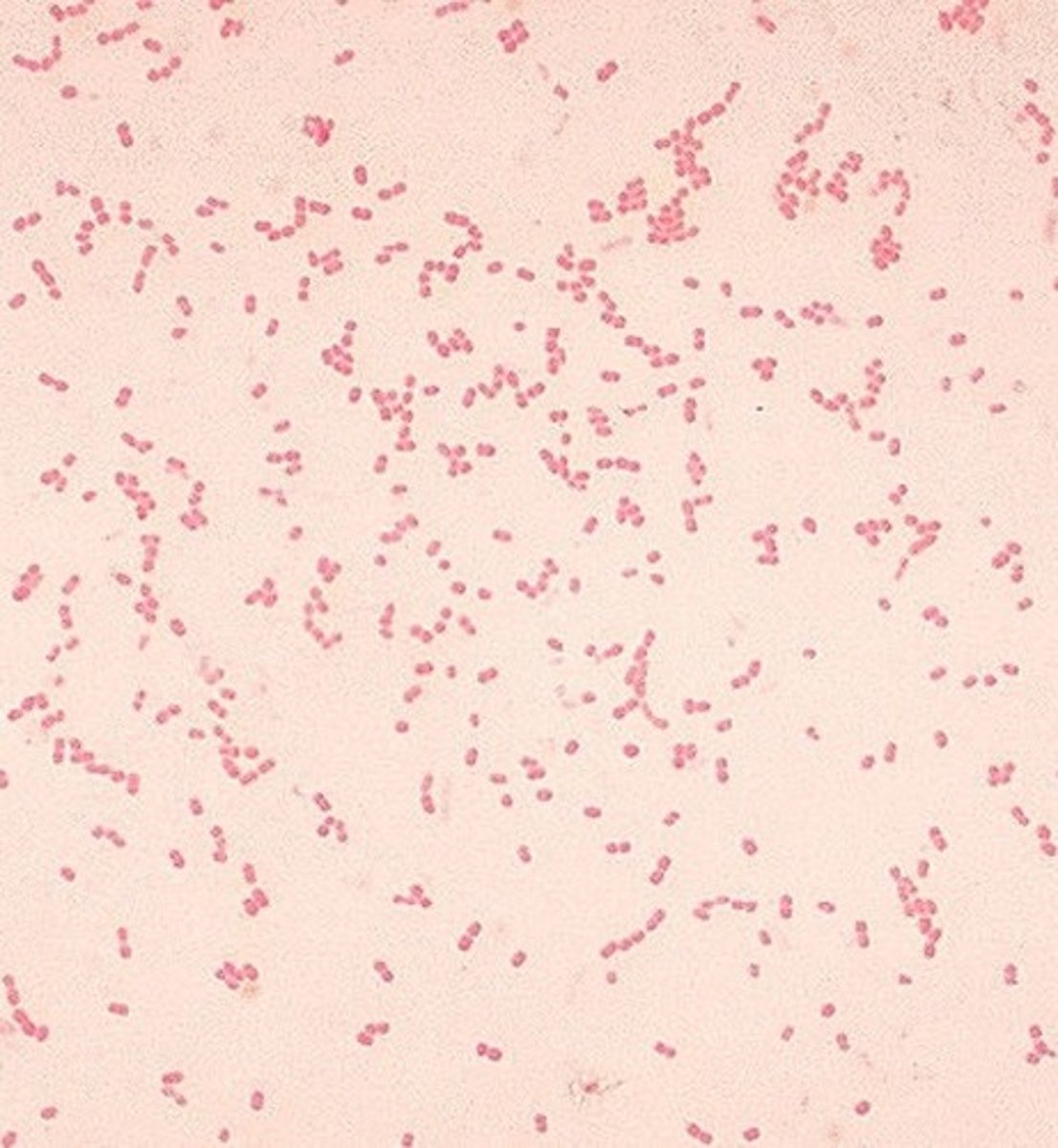
escherichia coli
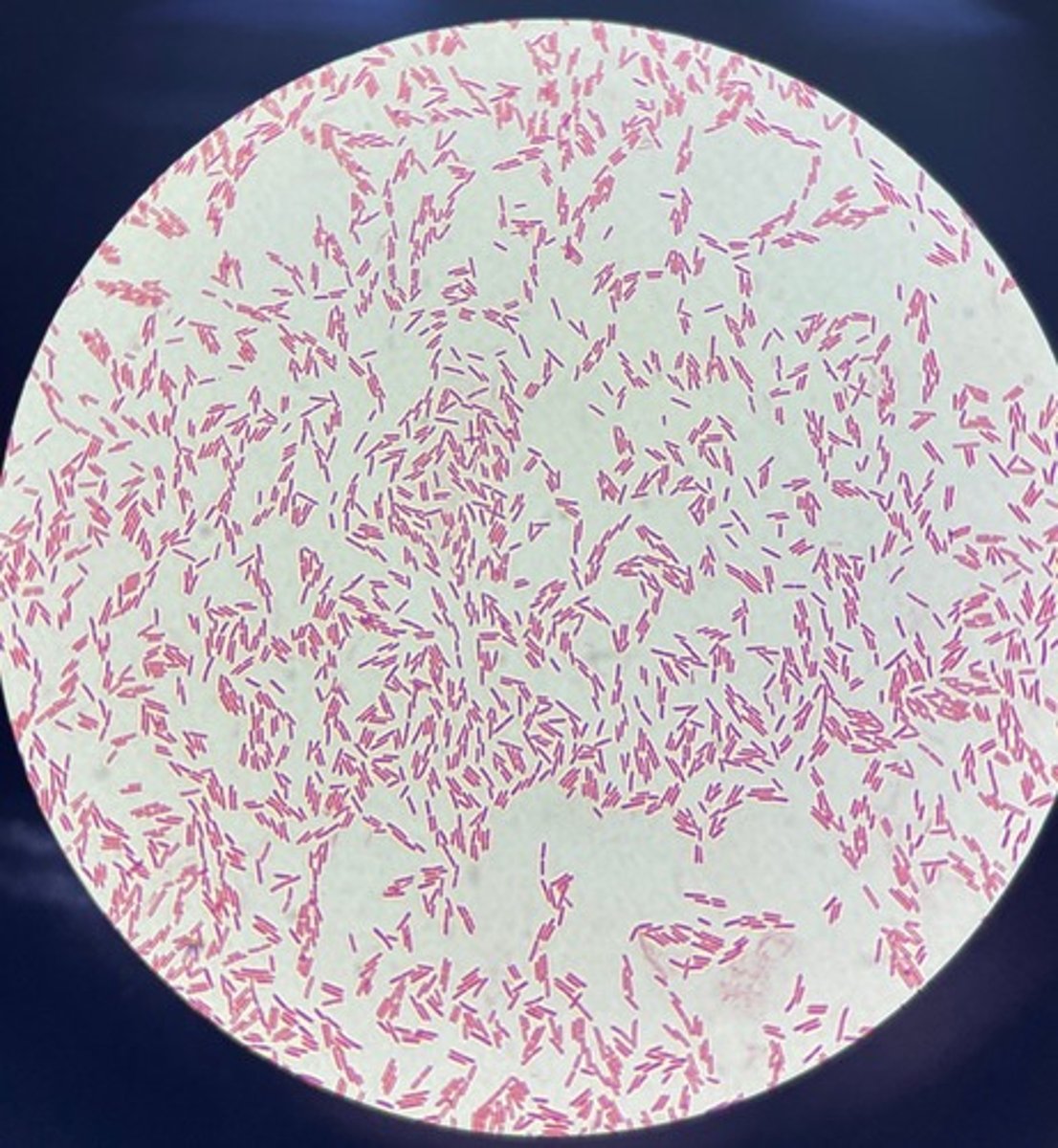
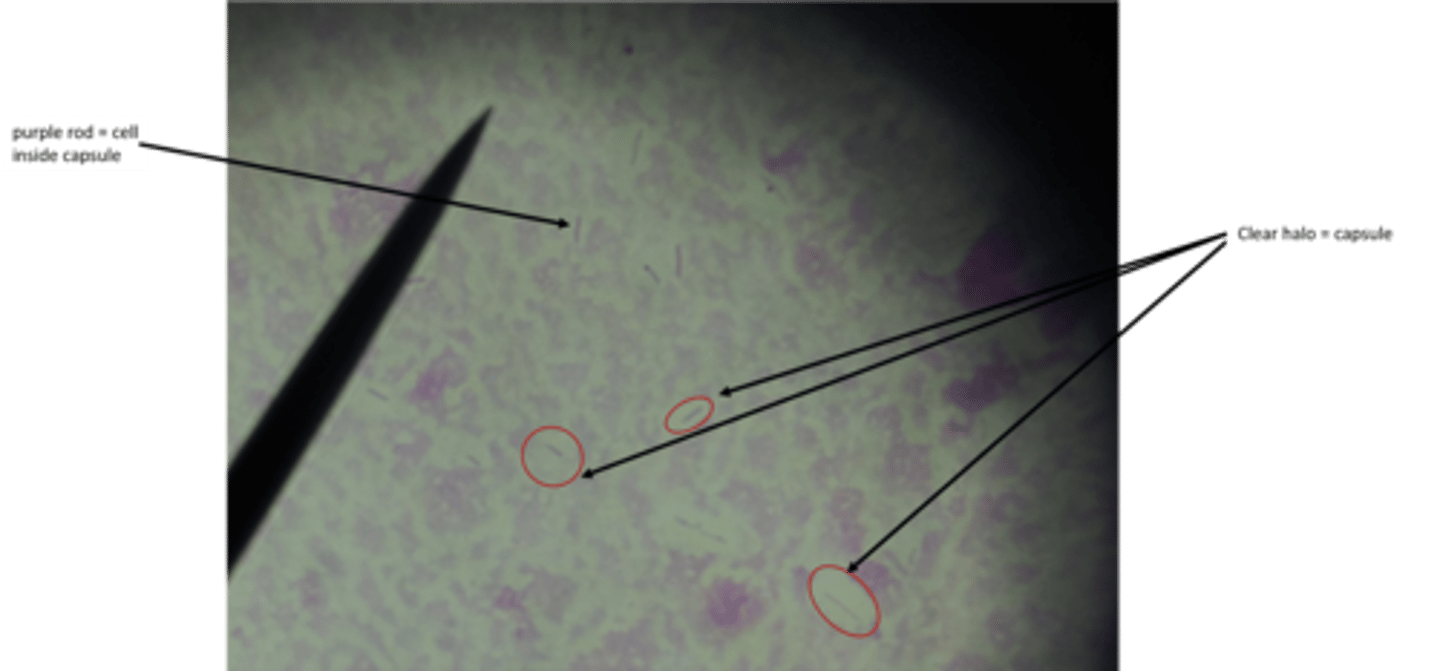
capsular
what type of stain is this?
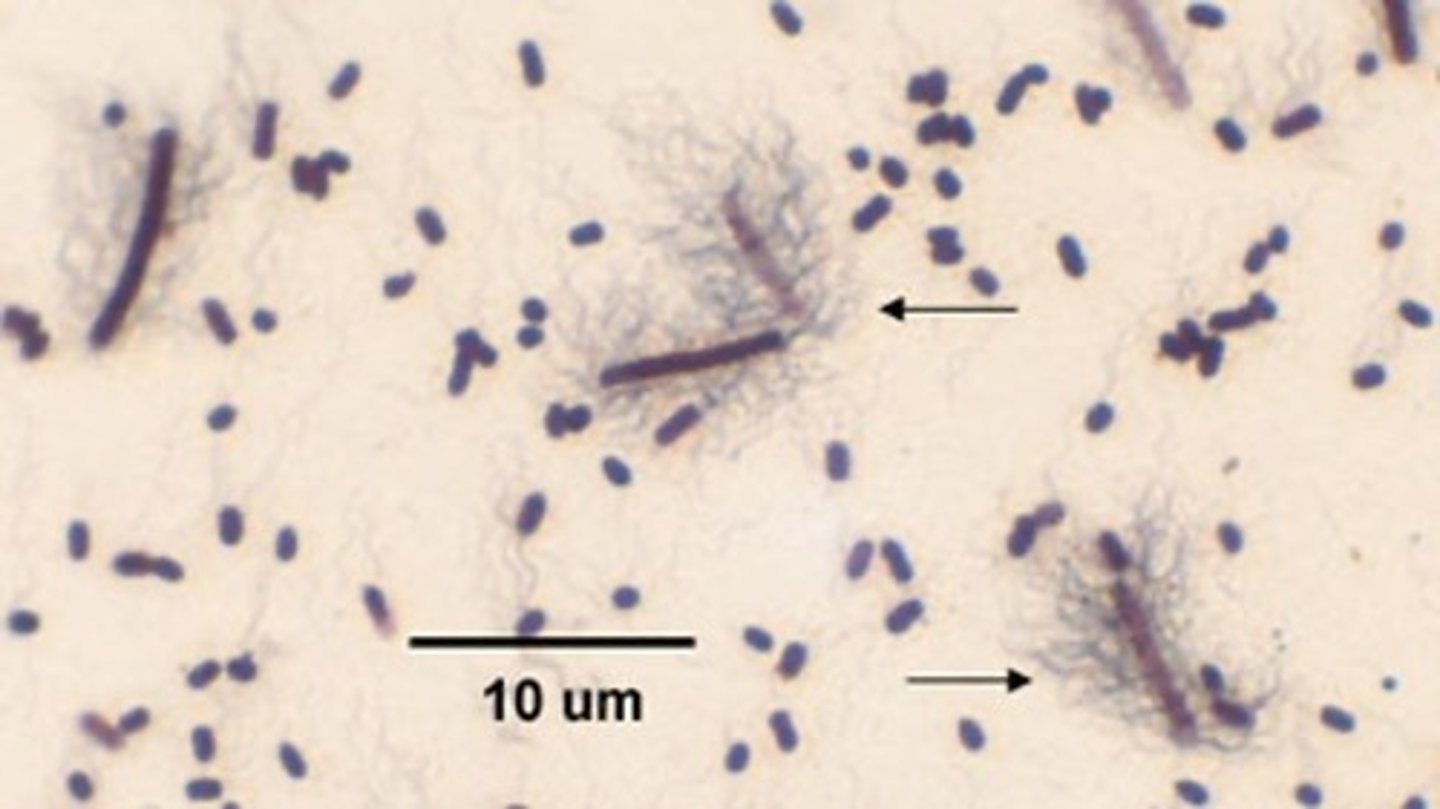
flagellar stain
what type of stain is this?
endospore stain
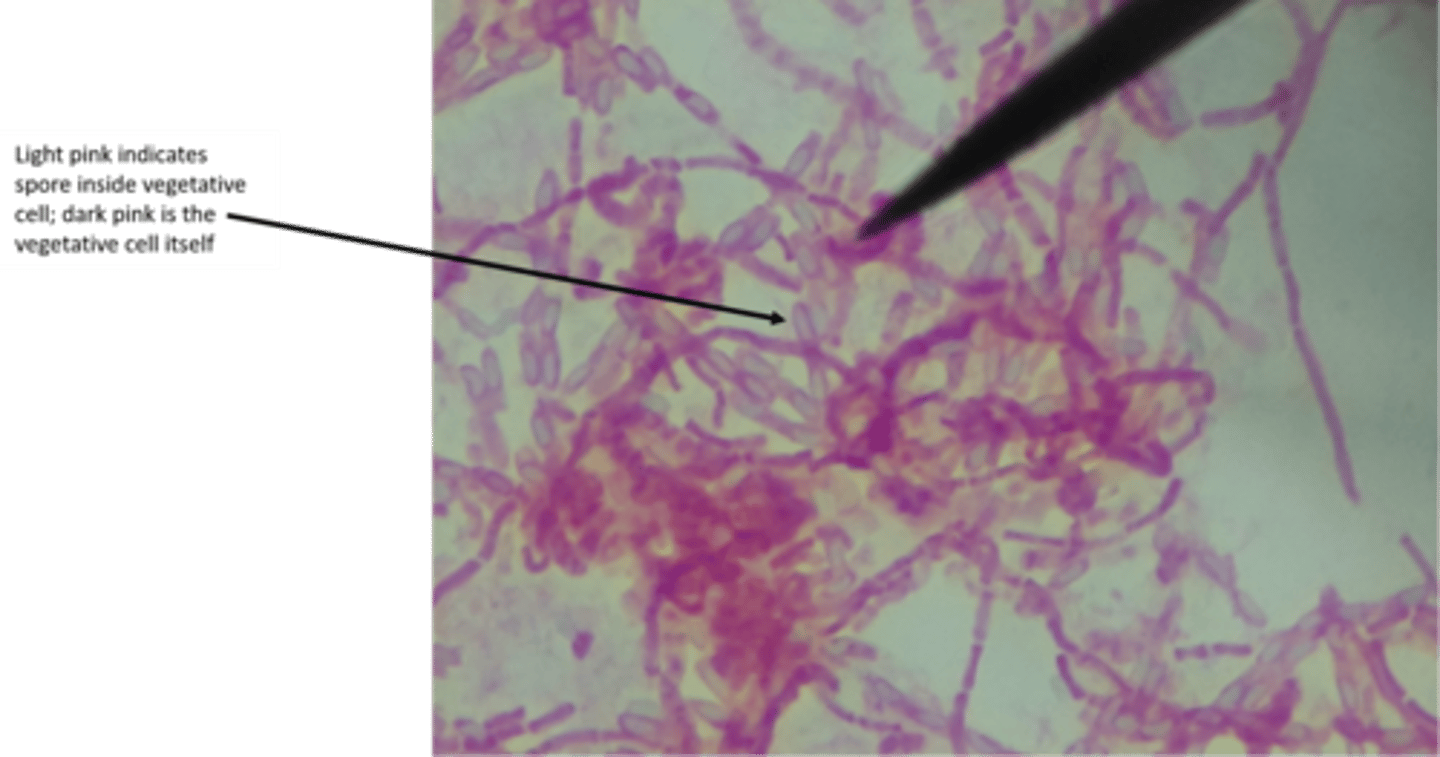
what type of stain is this?
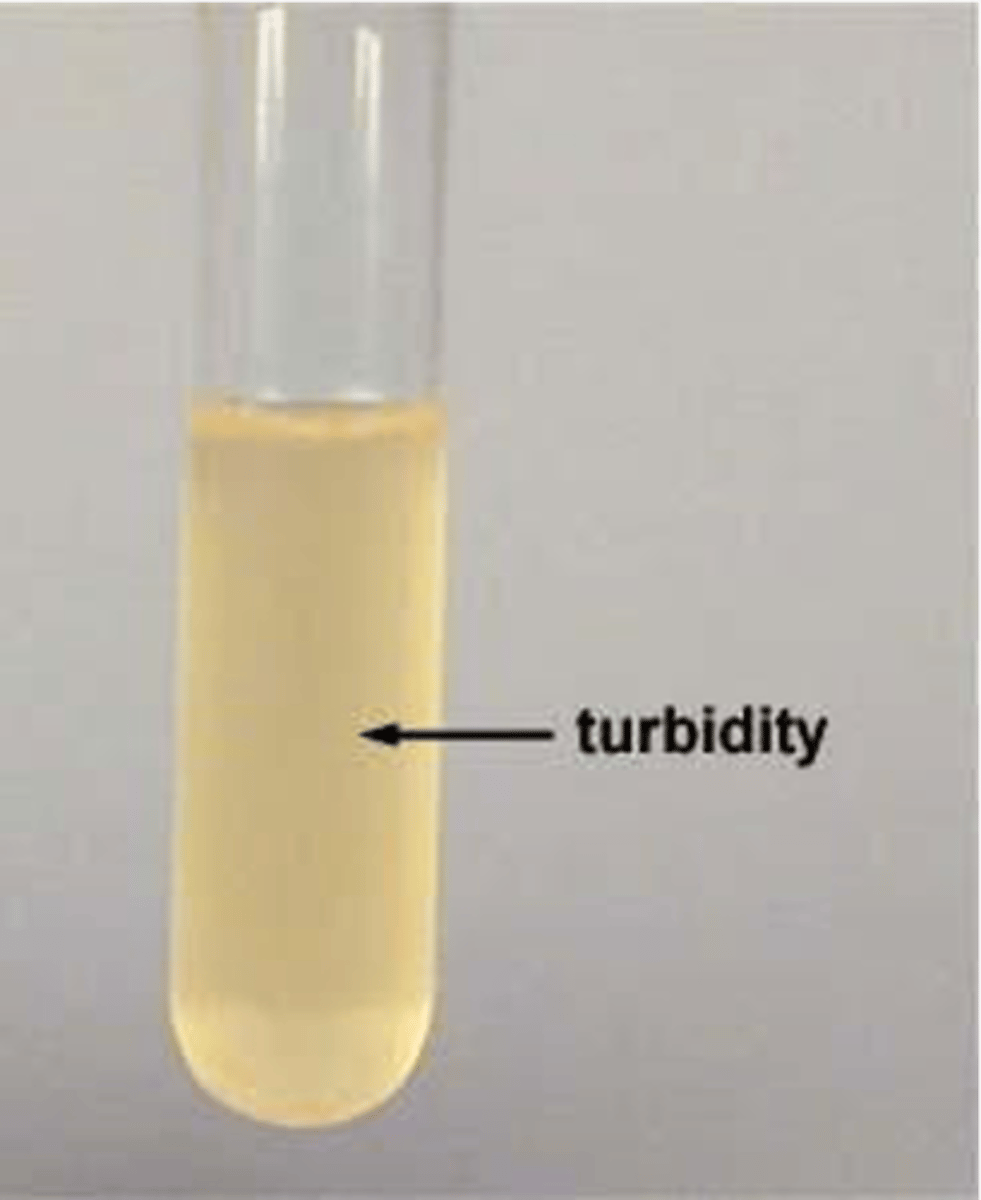
turbidity

sediment
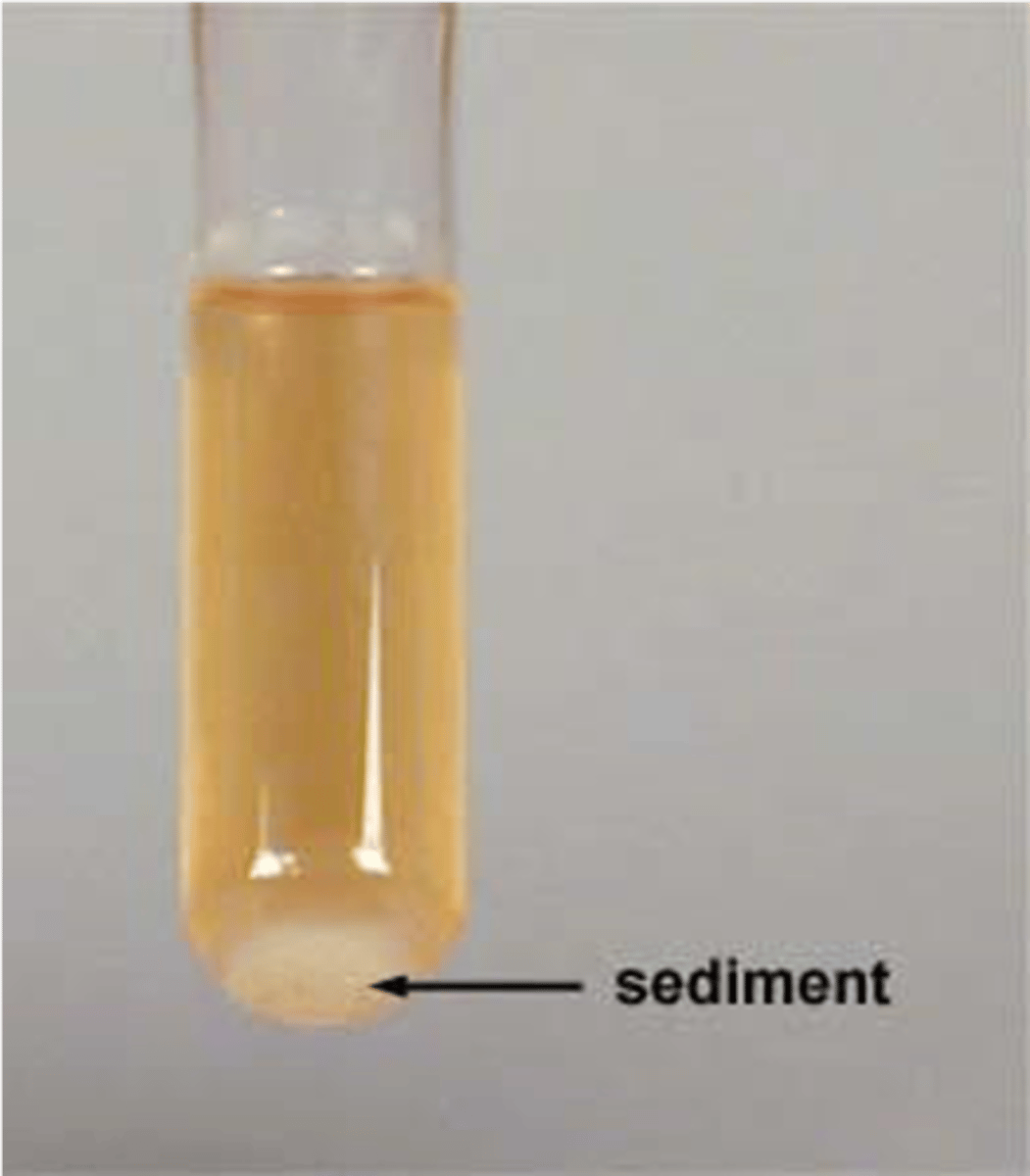
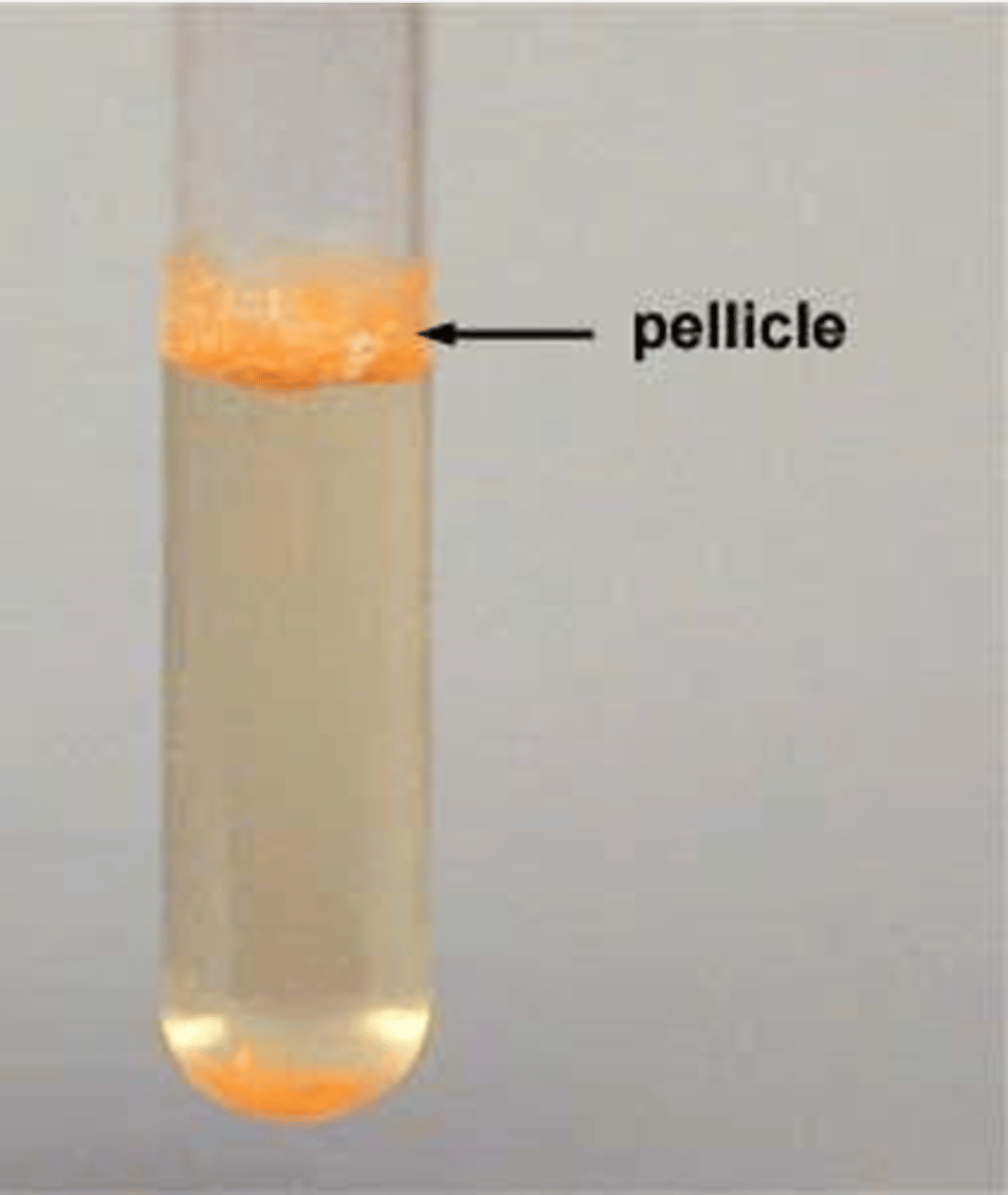
pellicle

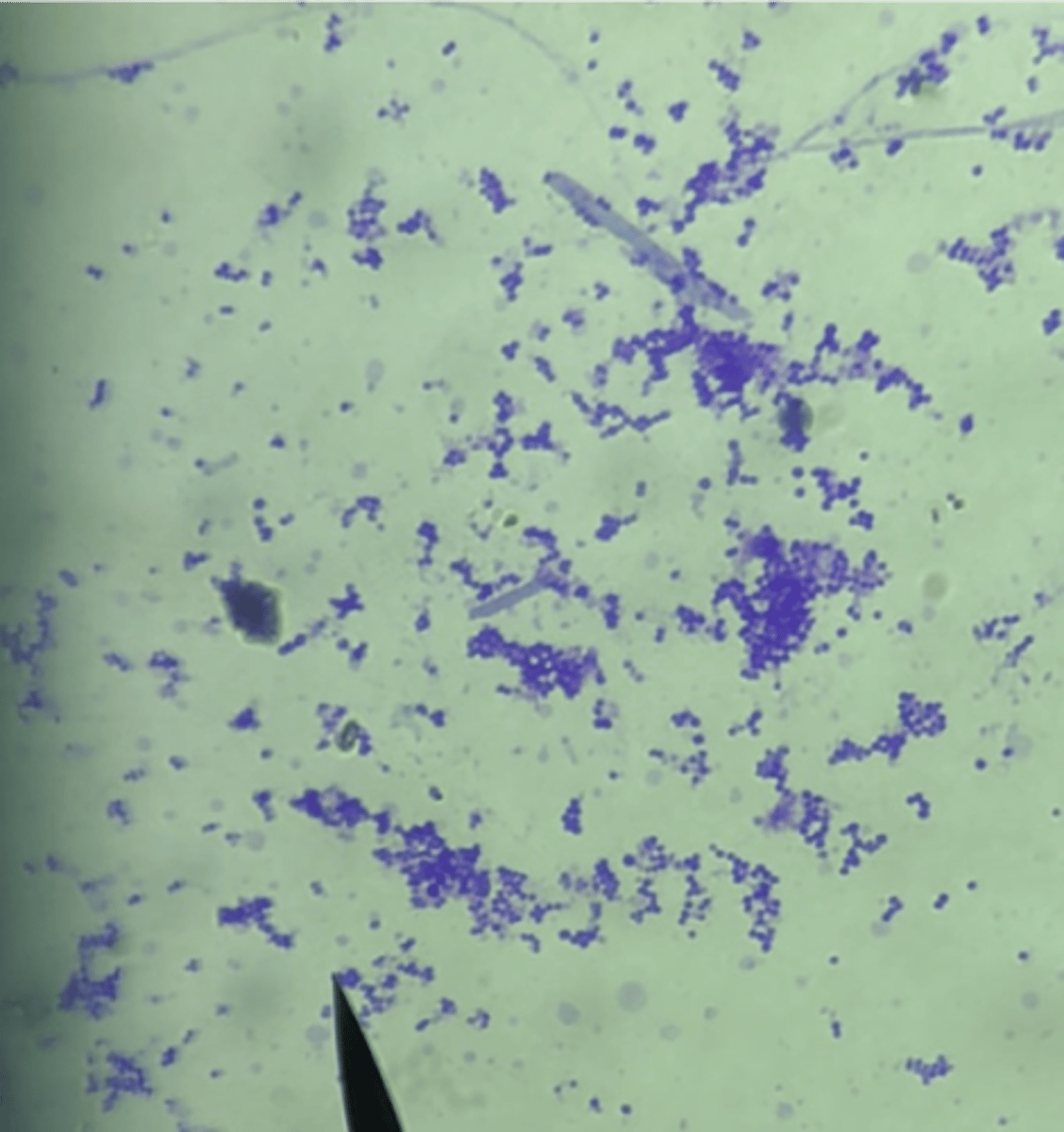
Staphylococcus aureus
What bacteria is this stained with methylene blue?
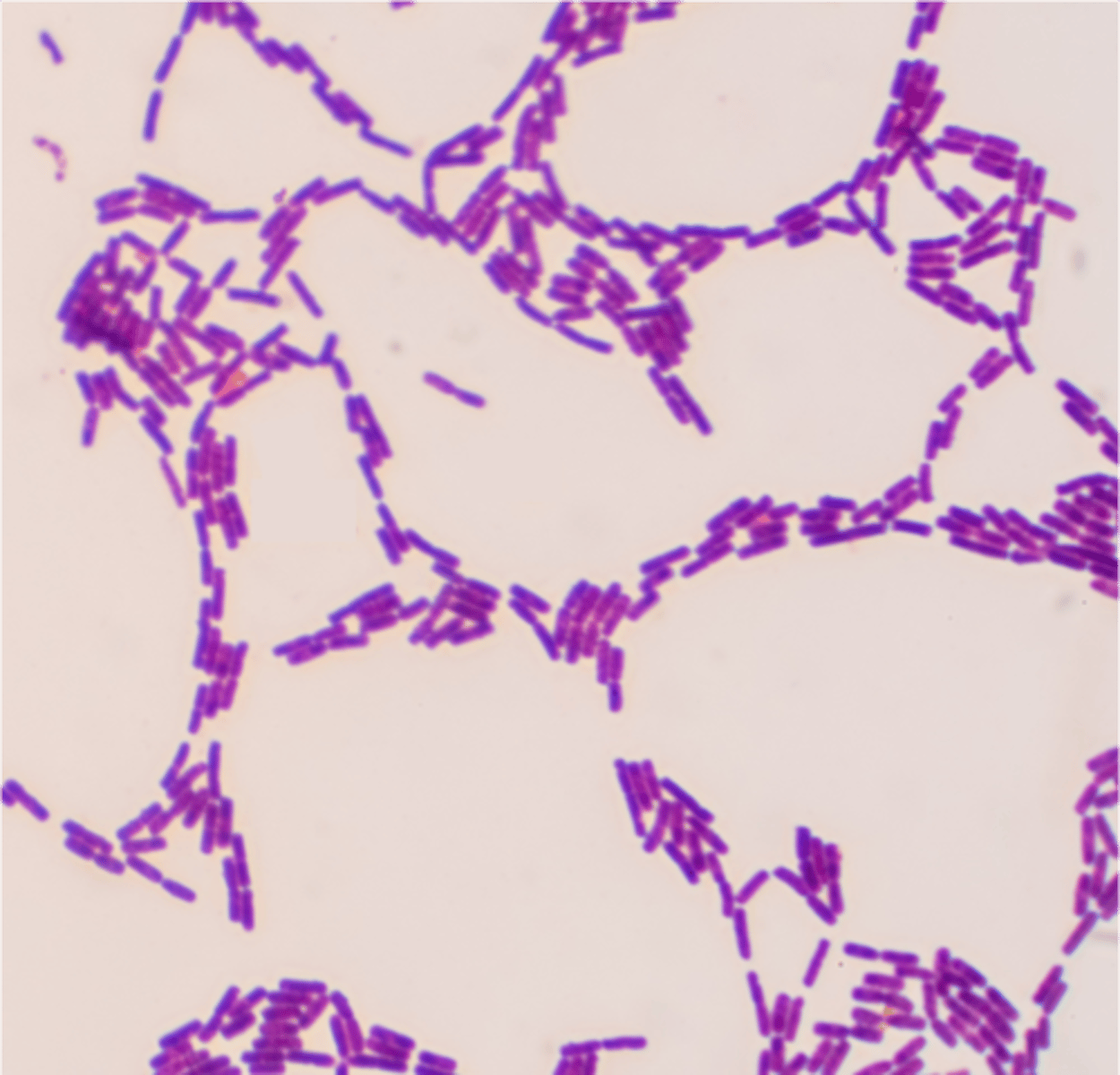
Escherichia coli
What bacteria is this stained with crystal violet?
We heat fix smears because it causes the proteins inside the cells to denature and coagulate, which adhere them to the slide. While it does kill the specimen, it allows the stain to enter the cell and bind to structures more easily.
Identify two reasons why smears are heat fixed.
Thick or dense smears are less likely to produce a good smear preparation because it will be hard to differentiate between individual cells and it can interfere with the staining process.
Why are thick or dense smears less likely to produce a good smear preparation for microscopic evaluation?
simple stain
single cationic stain used to gather information about cell shape and size
cationic chromogen
positively charged dye
anionic chromogen
negatively charged dye
chromogen
Another name for a dye
methylene bue
alkaline dye that is commonly used in simple stains.
gram stain
used to differentiate between bacterial cells based on cell wall composition
negative stain
employs a negatively charged stain to outline the shape of a cell
A differential stain uses two or more dyes to differentiate between cells or structures. It is used to divide bacteria into gram + and gram - bacteria. Gram + cells have a thick layer of peptidoglycan so they will hold the dye and turn purple even after decolorized is added. Gram - cells have a thin layer of peptidoglycan, so after the decolorized is added, they will lose all color. A counterstain can be added to turn gram - cells pink while gram + cells will remain purple.
what is a differential stain?
gram +
peptidoglycan collapses and traps the crystal violet/iodine inside the cell
gram + and -
has a cytoplasmic membrane
gram -
lipopolysaccaride
gram +
Gram stain purple
gram -
thin peptidoglycan layer
gram +
After adding the decolorizer the cell appears purple
gram -
outer membrane dissolves and allows escape of crystal violet/iodine complex
gram + and -
After adding the primary stain cell appears purple
gram -
Gram stain pink
gram +
Lipotechoic acid
gram +
thick peptidoglycan layer
gram -
Lipid A in cell wall
both types of cells will appear pink when viewed under the microscope
What would happen if the mordant wasn't added during the Gram stain?
t
Cell walls are needed to hold stains (T/F)
f
Safranin is the only possible counterstain that can be used. (T/F)
The negative cell wall repels the negative dye.
In terms of charges of the stains and the cell structures, when you perform a negative stain, why does the specimen appear light, while the background is stained dark?
repelled; attracted
India Ink is ____ by the negative cell wall, while Crystal violet is _____ by the negative cell wall.
The capsule will dissolve in water
Why do you want to avoid mixing the cells with water?
It will destroy the capsule
Why do you want to avoid heat fixing during the capsule stain?
Capsules are mostly composed of polysaccharides which aid in protecting against dehydration but also make a bacterium virulent by aiding in attaching to host tissues and escaping phagocytosis by white blood cells.
Why does the capsule make a bacterium virulent and more likely to cause a disease?
A capsule is a thick glycocalyx layer which is tightly bound to the cell which defines boundaries of the cell, while a slime layer is a thin glycocalyx layer that is loosely bound to the cell.
How do capsules and slime layers differ?
acid fast
what type of stain is this?
disinfectant
Chemical agent that reduces the number of microbes on inanimate objects.
sterilants
Chemical agent that destroys all microbes
microbiostatic
Chemical agent that inhibit microbial growth.
antiseptic
Chemical agent that reduces the number of microbes on living tissue
phenol
topical ointments, throat lozenges, and skin care creams
halogen
Betadine and Bleach
alcohol
Hand sanitizers and antiseptic wipes
Hibiclens
Chlorohexidine
quat
used along with alcohol in Lysol and Scope and Crest mouthwashes
aldehyde
Formalin and Cidex
hydrogen peroxide
surface and contact lens disinfectant