Blood Brain Barrier
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what dye was used to reveal the idea of the blood brain barrier?
trypan blue
What does the blood brain barrier consist of?
a wall of brain capillaries
how many arteries supply the brain with oxygen?
4
name the two types of arteries that supply the brain with oxygen
x2 carotid artery
x2 vertebral artery
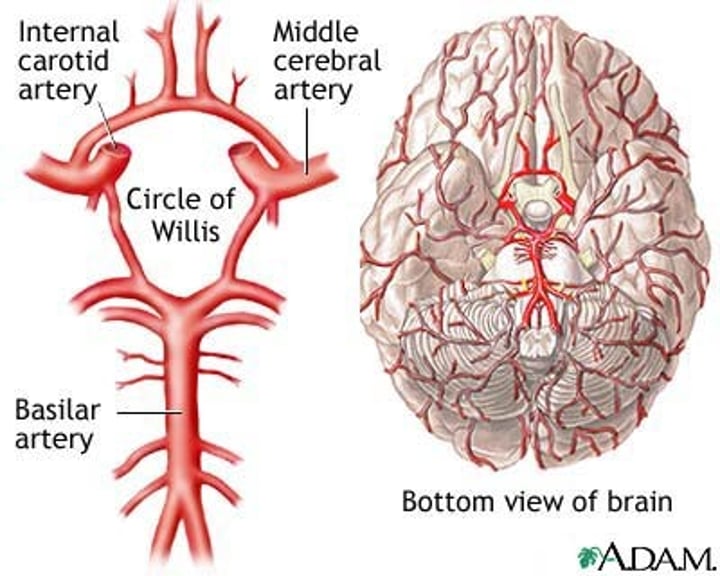
What is the Circle of Willis?
A circle of the 4 arteries that supply blood to the brain
what does India ink stain?
vascular system
what is the capillary density of the human brain?
2500-3000/mm3
walls of blood vessels are composed of ...?
endothelial cells (monolayer/single cell)
what can be used to identify astrocytes?
GFAP- glial fibrillary acidic protein staining
where are glial limitans located
surface of the brain
can astrocytes form more than one endfoot?
ys
what component of astrocytes contains water channels?
aquaporin
what is the process which materials move through the endothelial membrane?
passive diffusion
name 5 permeation mechansims
1) simple diffusion
2) passive diff
3) transporter influx
4) transporter efflux
5) endocytosis
Where are adherens junctions found?
between capillaries
what structure between cells restrict movement of molecules?
tight junctions
what are the 2 transmembrane proteins that make up adheren junction?
PECAM and VE
transmembrane proteins of the tight and adheren juctions are separated, true or false?
false- they are interlinked
what are the transmembrane proteins of tight junctions?
ZO, JAM, ESAM
where is electrical resistance higher, in the brain or peripheral capillaries?
much higher in the brain
why is it difficult for morphine to cross the BBB
low lipophilicity due to presence of -OH groups
Why is heroin more potent than morphine?
It is acetylated, can cross BBB easier
what are the 2 types of transport proteins
SLC and ABC (ATP binding cassette)
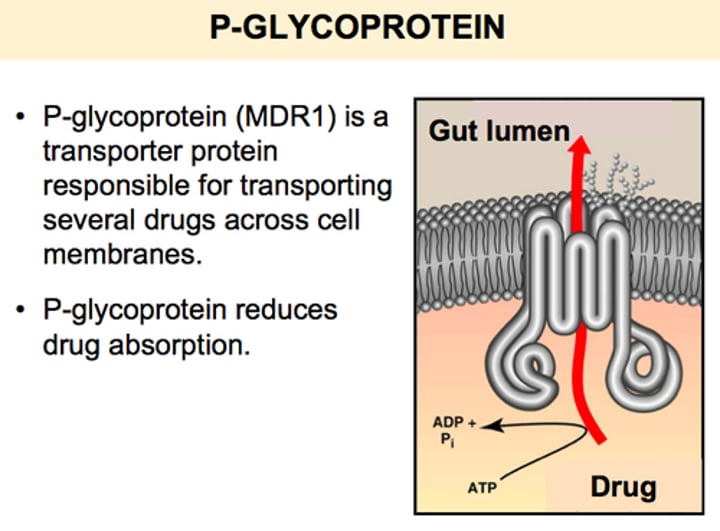
Why does cyclosporin have a low bioavailability?
presence of ABC transporters
describe the structure of PGPs ( P-glycoproteins)
2 repeating units, 2 drug binding sites
accumaltion of amyloid B in the brain can cause what?
Alzheimer's
What does LRP-1 do?
removes toxins (e.g. amyloid b) from brain
what forms the Blood-CFS Barrier?
choroid plexus and arachnoid membrane
What is ISF & where is it found?
interstitial fluid surrounding the brain