OMIS 2010 - Week 4 : Sourcing & Procurement
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What are the supply chain manufacturer internal functions?
process
purchase
plan / control
quality
ship
What is the purchasing department role?
select & monitor & develop & maintain supplier
negotiate / administer long-term contract
place order
What is procurement?
plan purchase
negotiate price
handle storage
What is sourcing?
stage before purchase
vet / select / manage supplier
create / execute strategy
define quality / quantity metric
What do companies purchase?
OEM
MRO
corporate service
What is OEM?
|:| original equipment manufacturer
direct production product
What are some OEM examples?
part
fabrication
component
What is MRO?
|:| maintenance, repair, operation
indirect production product
What are some MRO examples?
supply
furniture
ticket
janitor
What is a corporate service?
supply chain service
What are some corporate service examples?
distribution
warehouse
info system
What are some sourcing service options?
repair firm
retirement provider
employment agency
info system provider
3rd party logistic firm
engineer & health service
What does global sourcing seek to do?
balance economic factor & delivery performance / quantity requirement
What are the procurement concepts?
on-demand delivery
continuous replenishment
What is on-demand delivery?
// direct-response delivery
supplier delivers when customer demands
What is continuous replenishment?
supply to sched in short time
What explains why purchasing’s role has increased importance?
material costs = 50% - 60% COGS
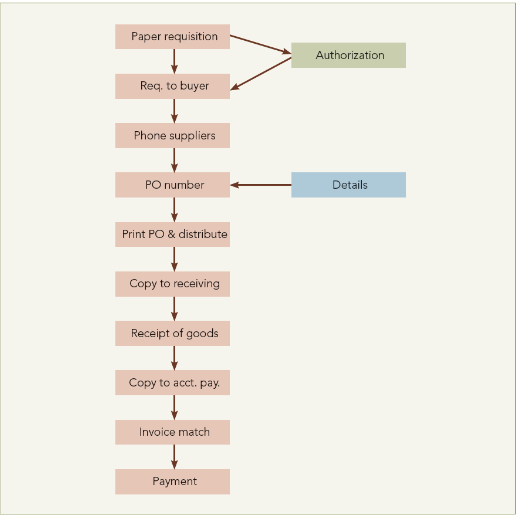
What characterizes traditional purchase?
order
price / availability
requisition request
incoming inspection
paper requisition →
authorize → request buyer
phone supplier
detail → PO number
print / distribute PO number
copy to receive
product receipt
copy to A/P
match invoice
pay
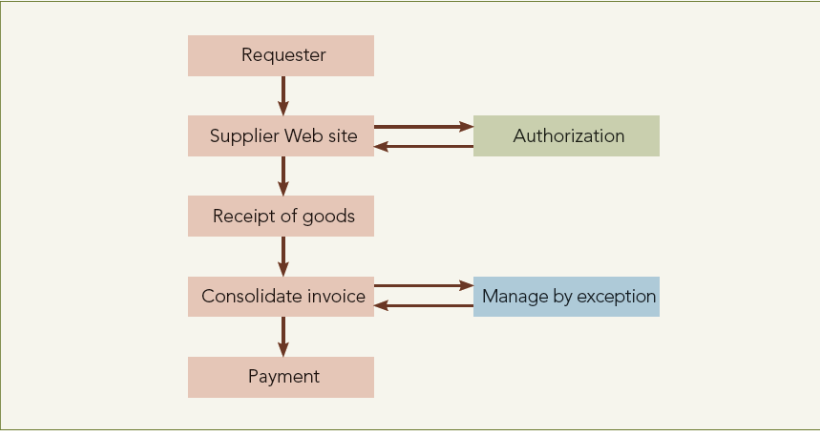
What characterizes e-purchase?
electronic info / comms use → enhance purchase
source strategy
request
authorize ↔ supplier site
product receipt
manage by exception ↔ consolidate invoice
pay
What are the e-purchase key features?
e-mail using e-signature
web-based order approval
recipient receipt notification
auto order requiring recipient authorization
e-archive facilitating supplier evaluation & trend analysis
What are the e-purchase advantages?
decreased order process cost / cycle time
decreased order process error & time
decreased & consolidated data entry → purchase / supplier analysis
decreased buyer research time
catalog / marketplace
increased info distribution
shared performance data → increased supplier performance → decreased inventory
What is e-procurement?
direct supplier purchase by software package / e-hub / trading exchange
What is an e-hub?
// e-marketplace
firm & supplier B2B site
What is a reverse auction?
firm e-hub order for supplier to bid on
What is an e-distributor?
independent marketplace representing thousands of suppliers for spot purchase
What is an e-purchase firm?
MRO supplier & firm connector paying to join market for long-term contract purchase
What is an exchange marketplace?
large firm’s spot requirement
What is an industry consortium?
industry-owned market for buyer to directly purchase from limited suppliers
What are some government e-commerce value chain examples?
credit card
food stamp
tax file / direct deposit
studen loan application
What are the B2B e-commerce advantages?
decreased procurement admin & global supplier cost
decreased inventory cost
price transparency
decreased reply time
increased quality
buyer / seller design / development cooperation
What are the B2C e-commerce models?
transaction fee model
sales revenue model
affiliate revenue model
advertising revenue model
subscription revenue model
What is the transaction fee model?
firm receives fee for executing transaction
What is the sales revenue model?
firm directly sells product / info
What is the affiliate revenue model?
firm receives referral fee for directing business to affiliate
What is the advertising revenue model?
firm provides product info for supplier to advertise
What is the subscription fee model?
firm charges fee for site access
What is blockchain?
data network making event tamper-resistant
record every transaction
distribute over multiple computers
What is a blockchain advantage?
no 1 firm has total control
What are blockchain goals?
intelligent
collaborative
transparent
secure
& max customer service at min cost
What is the sourcing decision?
product to produce in-house / provide by other
What is vertical integration?
measure of how much supply chain’s owned / operated by manufacturer
What are the vertical integration types?
backward integration
forward integration
What is backward integration?
own / operate raw material / component inventory
What is forward integration?
own / operate distribution channel
What are the contract manufacturing advantages?
advanced manufacture tech
regional market customization
decreased product time-to-market & cost
economies of scale
What is offshoring?
build / acquire / move operation to foreign location maintaining ownership / control
What is reshoring?
build / acquire / move operation back to domestic location
What is the outsourcing cost formula?
TC_{B}=FC_{B}+\left(V_{B}\cdot Q\right)
What is the insourcing cost formula?
TC_{M}=FC_{M}+\left(V_{M}\cdot Q\right)
What is the make-or-buy analysis indifference point formula?
TC_{B}=TC_{M}
What are the top supplier criteria?
price
quality
delivery
What are one supplier reasons?
prerequisite
small order
increased reply & relation
quantity discount
outstanding supplier
easily scheduled delivery
EDI / JIT support
exclusive essential patent / process owner
order split & duplicate prohibition
What are multiple supplier reasons?
regulation
risk spread
supplier dependence elimination
competition → service / price
increased volume flexibility & capability
new supplier test without jeopardizing material flow
What is a certified supplier?
high-quality supply → unnecessary routine test
continuously improve
attract business
What characterizes partnerships?
strategic
long-term
end customer expectation
share info & vision & risk / opportunity
What are partnership advantages?
design process ESI
decreased time-to-market
What is ESI?
|:| early supplier involvement
use supplier expertise to develop / share cost improvement