Unit 9: Discoveries About Galaxies and the Universe
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
What are the word origins for “nebula?”
cloud / mist
Latin
What are the name origins for the “Large / Small Magellanic Clouds?”
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese
reported nebulae when sailing around Earth
What did the telescope reveal about nebulae in the 1750s?
some are elliptical
What did Immanuel Kant propose about elliptical nebulae in the 17th century?
Island Universe theory
What is the Island Universe theory?
elliptical nebulae = billions of stars grouped in flattened circular system
→ if randomly oriented, random angles
What is a tilted disc’s appearance?
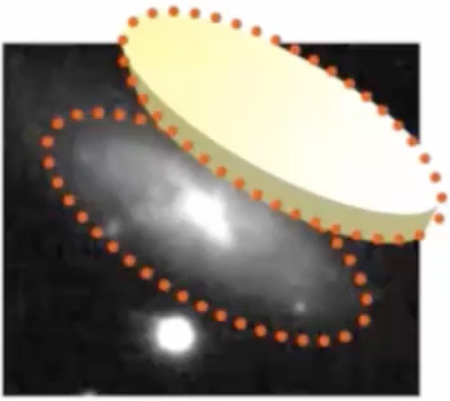
What is an edge-on disc’s appearance?
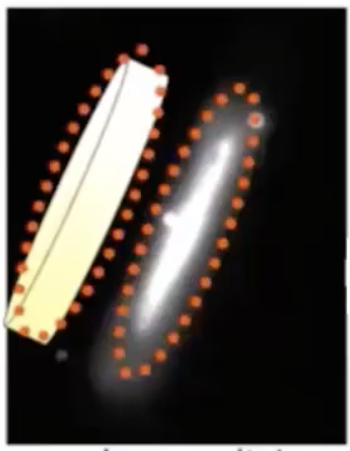
What is a face-on disc’s appearance?

What does Immanuel Kant explain about the star band?
if we live in elliptical star system,
Milky Way = view through length
What was the main theory before the Island Universe Theory?
our Galaxy is the only galaxy
What is the identity of William Herschel and Caroline Herschel’s son?
John Herschel
What was William Herschel, Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel’s biggest project?
sweep entire north sky & catalogue > 5000 nebulae for 20 years
What was William Herschel’s main study?
cosmology
What did William Herschel build in the 1780s?
20 foot telescope with 18 inch mirror
What was the identity of the largest nebulae catalogue author before the Herschel family?
Charles Messier
110 Messier objects (M1)
What was the reason for Charles Messier’s nebulae catalogue?
ensured he didn’t confuse with comet
What is the number of known nebulae before William Herschel’s health began to fail?
2500
What did William Herschel & John Herschel attempt to identify about nebulae?
distant star system
or
nearby glowing gas cloud
What did John Herschel do in response to William Herschel’s death?
moved 20 foot telescope & family to Cape of Good Hope
What did John Herschel publish in 1864?
General Catalogue of Nebulae & Clusters of Stars
1st all-sky nebulae catalogue
What nebulae catalogue do we use today?
New General Catalogue
expanded Herschels’ work
What is the largest & brightest nebula in the sky?
Orion Nebula
What was the reason that the Herschels could not come to a conclusion about nebulae composition?
gas nebula
parts look clumpier than others
furthest regions are distant to resolve into stars
What are some examples of nebulae that gave John Herschel a lot of trouble?
Lobster Nebula (M17)
Triangulum Galaxy (M33)
What map did William Herschel produce?
Solar System from outside
What did William Herschel incorrectly assume?
brightest stars = nearest
faintest stars = furthest
What did William Herschel correctly conclude about the Solar System?
Sun embedded in flat star disc
What was the identity of the Irish Earl that attempted to prove that all nebulae are star systems by resolving stars?
William Parsons / Lord Rosse
What did Lord Rosse build in 1845?
Leviathan of Parsons Town
What was the Leviathan of Parsons Town?
reflector with 6 foot diameter mirror
largest reflector in world for 70 years
What did Lord Rosse’s sketches reveal?
many elliptical nebulae = spiral nebulae
What did Lord Rosses’s sketches incorrectly assume?
bright dot = nebula star
foreground star
What did Lord Rosse conclude about nebulae?
all nebulae are star systems / gas clouds don’t exist
cloudy nebulae are so densely packed
What was also discovered in John Herschel’s & Lord Rosse’s Whirlpool Galaxy sketches?
NGC 5195
What is happening to NGC 5195?
galactic cannibalism
What is galactically cannibalizing NGC 5195?
Whirlpool Galaxy
What is galactically cannibalizing the Sagittarius Dwarf?
Milky Way
What are the 2 nearest galaxies?
Large & Small Magellanic Clouds
What did Henrietta Swan Leavitt discover?
thousands of variable stars
What is the definition of “variable star?”
star fluctuating in brightness at regular interval
What was one of Henrietta Swan Leavitt’s jobs aside from analyzing spectra?
measure apparent brightness & assign apparent magnitude
What are a Cepheid’s properties?
dramatically & rapidly pulsating brightness
over few nights, change 1/2 magnitudes
detectable by eye
high-mass
10-20x more massive than Sun
opaque surface
variable
What are the name origins of “Cepheid?”
1st variable star type found in 1780s
Delta Cephei
Cepheus constellation
What is the reason for a Cepheid’s opaque surface?
outward photons push surface out
→ expands star & reduces opacity
What was the date of the 1st variable star detection?
shortly after telescope invention
early 1600s
What do Cepheid spectra show?
unusual amount of helium ionized twice in atmosphere
electrons & nuclei float together
→ get closer together & denser
What struggle do stars undergo?
inward gravitational pull
outward radiation pressure
What is a Cepheid’s pulsation process?
photons get trapped by opaque atmosphere
outward radiation pressure builds up & breaks balance
star inflates
helium atoms spread out
light releases
outward radiation pressure returns to normal levels
inward gravitational pull returns to normal size
What is the definition of a “period” on a light curve?
time it takes to go through bright & dim cycle
What did Henrietta Swan Leavitt discover about Cepheids?
brighter = longer P
What method did Henrietta Swan Leavitt use to discover the Period-Luminosity relation for Cephoids?
graphed 25 Cephoid sample in Small Magellanic Cloud minimum & maximum brightness
roughly same distance from Earth
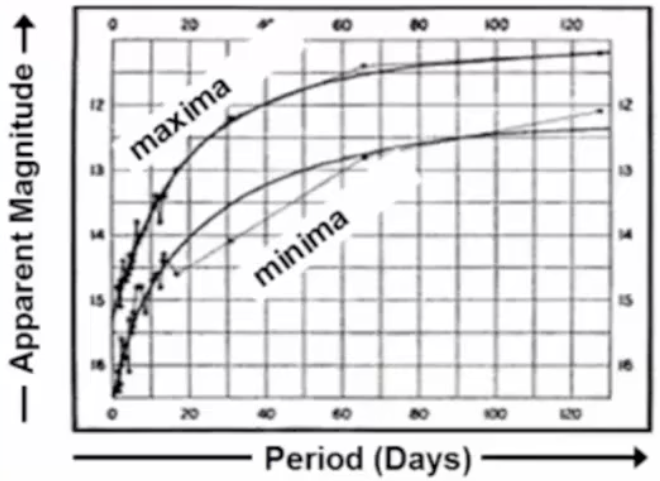
What is the P-L relation’s use?
calculate star distance
observe Cepheid until you know pulsation period
P-L relation → Cepheid luminosity
use apparent & absolute magnitude
What did Harlow Shapley do with the P-L relation?
used nearby Cepheid sample with known distances
found Cepheid stance in most distant star clusters
revealed our star system edges
What did Harlow Shapley incorrectly conclude about SMC?
in our Galaxy
What was the reason for Harlow Shapley’s incorrect conclusion about SMC?
measured 200 000 lightyear distance
What did Harlow Shapley incorrectly conclude about nebulae?
all are systems in our Galaxy
What was a globular cluster’s most important feature to Harlow Shapley?
some of most distant things in Galaxy
What did Harlow Shapley measurements reveal about the disc?
length
50 kiloparsecs + 30 kiloparsecs = 80 kilo parsecs / 265 000 → 300 000 light years
What was the reason for Harlow Shapley’s incorrect measurements?
didn’t know about dust between Milky Way & globular clusters
appear fainter = more distant
What did Harlow Shapley correctly conclude?
Galaxy’s not heliocentric
Galaxy’s surrounded by sphere halo containing star clusters
Milky Way centre → Sagittarius direction
What did spiral nebulae maps reveal in the 1860s?
spirals aren’t seen near Milky Way disc
What was Harlow Shapley’s response to spiral nebulae maps’ revelations in the 1860s?
spirals are pushed from disc by radiation pressure from high star density
→ Zone of Avoidance
What did Heber Curtis do with spiral nebulae?
completed high-res survey & revealed observing matter (dust)
What did Heber Curtis correctly conclude about spiral nebulae?
believed Island Universe theory
our Galaxy = spiral galaxy
spirals are not seen in Zone of Avoidance because they are obscured by dust band
if spirals move faster than our Galaxy’s star, outside our Galaxy
What was Heber Curtis’ reason for concluding each spiral nebula is its own spiral galaxy?
observing matter resembled Milky Way dark patchiness across sky
What makes up our Galaxy’s disc?
microscopic metallic grains from dying stars
→ absorbing starlight
carbon & silicon & iron
micron in size
What is proof that our disc is filled with dust?
when heated, glow red in infrared light
What did Vesto Slipher’s 1st spiral nebula spectrum measure in 1913?
large redshift in calcium absorption line
→ spiral nebulae were made of stars
absorption line is produced by star
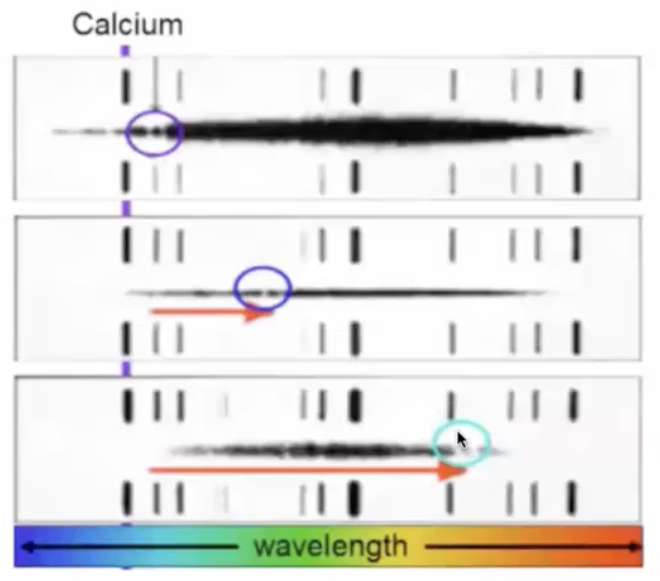
What was Vesto Slipher’s method of measuring radial velocity?
plug wavelength shift distance in Doppler equation
What did Vesto Slipher produce in 1913?
1st spiral nebula spectrum
What is the average spiral velocity relative to stellar velocity?
25:1
What debate was held in 1920?
Shapley-Curtis debate / Great Debate of 1920
What was the Shapley-Curtis debate outcome?
neither was conclusive
What was Heber Curtis’ debate document?
The Spiral Nebulae as Island Universes
What were Heber Curtis’ arguments in The Spiral Nebulae as Island Universes?
spiral radial velocity > star velocity
spiral spectra = solar systems
absorption lines
spiral novae appear fainter
dust explains Zone of Avoidance
What was proven by Edwin Hubble 3 years after the Shapley-Curtis debate?
Island Universe theory
What did Edwin Hubble find in 1923?
Cepheid novae in Andromeda Nebula (M31)
What are the name origins of the Andromeda Nebula?
located in Andromeda constellation
What are the word origins of “Andromeda?”
Greek princess
What did Edwin Hubble find of the Andromeda Nebula with the PL relation?
distance of 1 000 000 lightyears
What was Edwin Hubble’s observation process of the Andromeda Nebula?
got light curve
measured pulsation P
31 days
got distance
What was Edwin Hubble’s response to his results in February 1924?
wrote Harlow Shapley a letter
What was launched in honour of Edwin Hubble’s discovery in 1990?
Hubble Space Telescope
What does the James Webb Space Telescope improve from the Hubble Space Telescope?
bigger primary mirror
6x larger
spectroscope
probe galaxy chemical composition
What is the definition of “S galaxy?”
spiral
flat disc containing spiral arms & possibly central bulge
What is the definition of “SB galaxy?”
barred spiral
spiral with central bar
What is the S & SB galaxy subclassification?
arm tightness & bulge brightness
What is the definition of “Hubble Sequence” or “Hubble tuning fork?”
galaxy classification system by appearance
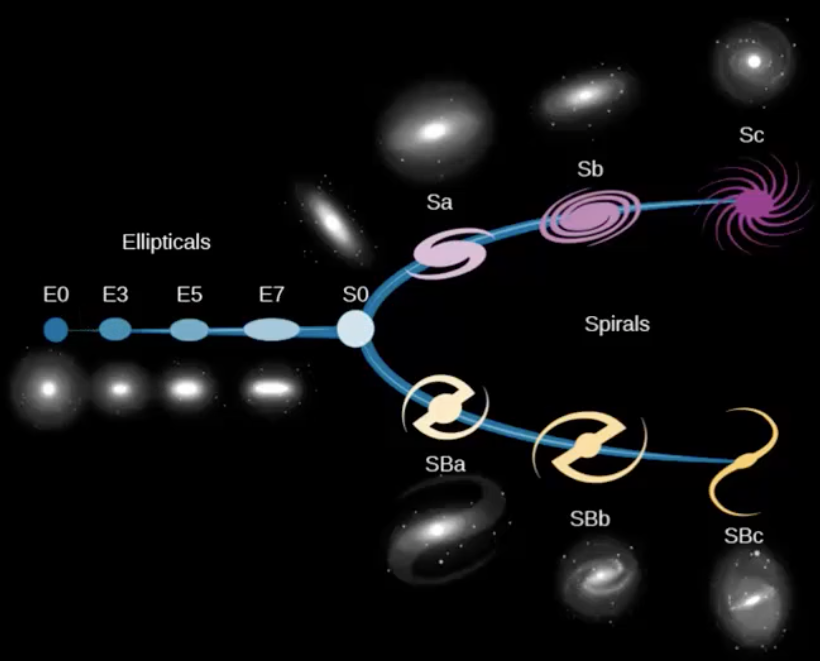
What is the percentage of S galaxies relative to known galaxies?
30%
What is the percentage of SB galaxies relative to S galaxies?
60%
What is the reason that the Milky Way is a SB galaxy?
further away from bulge = less stars
infrared
What are some possible reasons for SB galaxies?
temporary & recurring phenomenon
collision
What is the current reason for S galaxies?
2 non-S galaxies merge
What is the definition of “S//B0 galaxy?”
lenticular
flat disc & possible central bulge
no spiral
What is the percentage of S0 galaxies relative to known galaxies?
15%
What are some possible reasons for S//B0 galaxies?
old spiral whose arms faded away
new spiral that didn’t develop arms yet
What is the definition of “E galaxy?”
elliptical
elongated spheroid
What is the percentage of E galaxies relative to known galaxies?
5%
What do E galaxy numbers assign?
higher number = more elongated
What is a possible reason for E galaxies?
2 approximately equal mass galaxies merge