[PT13] Midterms Reviewer (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:10 AM on 4/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
Which triangle of the neck is a useful landmark for the ansa cervicales?
a. submental triangle
b. submandibular triangle
c. carotid triangle
d. muscular triangle
a. submental triangle
b. submandibular triangle
c. carotid triangle
d. muscular triangle
carotid triangle
2
New cards
Which muscles of the face are responsible for wrinkling the skin of the nose?
a. procerus
b. dilator naris
c. corrugator supercili
d. compressor nasi
a. procerus
b. dilator naris
c. corrugator supercili
d. compressor nasi
procerus
3
New cards
Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE regarding humeral shaft fracture?
a. The pectoralis major, teres major and latissimus dorsi muscles may adduct the proximal fragment if the fracture line is proximal to the deltoid insertion
b. The distal fragment can be pulled by the biceps and triceps proximally if the fracture line is distal to the insertion of the deltoid
c. The proximal fragment can be abducted by the deltoid if the fracture line is distal to its insertion
d. The distal fragment can be pulled proximally by the deltoid if the fracture line is distal to its insertion
a. The pectoralis major, teres major and latissimus dorsi muscles may adduct the proximal fragment if the fracture line is proximal to the deltoid insertion
b. The distal fragment can be pulled by the biceps and triceps proximally if the fracture line is distal to the insertion of the deltoid
c. The proximal fragment can be abducted by the deltoid if the fracture line is distal to its insertion
d. The distal fragment can be pulled proximally by the deltoid if the fracture line is distal to its insertion
‘The distal fragment can be pulled proximally by the deltoid if the fracture line is distal to its insertion’ is false. In this scenario, the deltoid does not pull the distal fragment proximally, it abducts it.
4
New cards
Which of the following triangles of the neck is bordered by the sternocleidomastoid, inferior omohyoid and trapezius?
a. carotid triangle
b. subclavian or supraclavicular triangle
c. occipital triangle
d. muscular triangle
a. carotid triangle
b. subclavian or supraclavicular triangle
c. occipital triangle
d. muscular triangle
occipital triangle
5
New cards
Which muscle of mastication opens the mouth?
a. external pterygoid
b. masseter
c. internal pterygoid
d. temporalis
a. external pterygoid
b. masseter
c. internal pterygoid
d. temporalis
external pterygoid
6
New cards
The following structures can be felt at the anatomical snuffbox, EXCEPT:
a. Trapezoid
b. Trapezium
c. Styloid process of of the radius
d. Scaphoid
a. Trapezoid
b. Trapezium
c. Styloid process of of the radius
d. Scaphoid
Trapezoid
\
Structures that can be palpated at the anatomical snuffbox: Styloid process of the radius, pulses of the radial artery, scaphoid and trapezium.
\
Structures that can be palpated at the anatomical snuffbox: Styloid process of the radius, pulses of the radial artery, scaphoid and trapezium.
7
New cards
The fibrocartilaginous rim that deepens the concavity of the glenoid and provides minimal stability to the joint is the:
a. Hyaline articular surface
b. Glenohumeral ligament
c. Glenoid capsule
d. Glenoid labrum
a. Hyaline articular surface
b. Glenohumeral ligament
c. Glenoid capsule
d. Glenoid labrum
Glenoid labrum
8
New cards
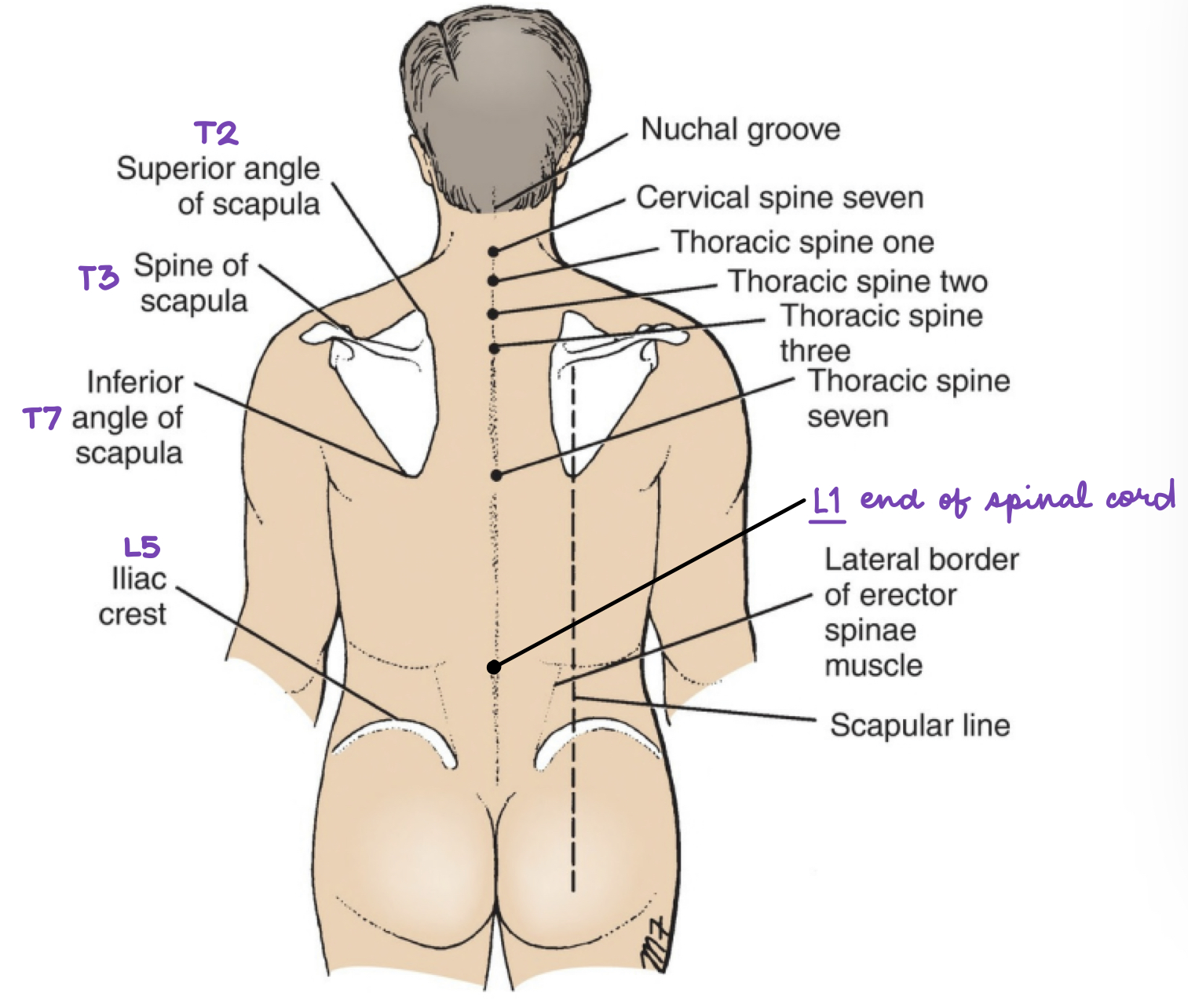
Which corresponding structure is the landmark of L5?
a. end of dural sac
b. tubercle of iliac crest
c. umbilicus
d. end of spinal cord
a. end of dural sac
b. tubercle of iliac crest
c. umbilicus
d. end of spinal cord
tubercle of iliac crest
9
New cards
Which of the following muscles of the posterior abdominal wall is the primary hip hiker?
a. iliacus
b. quadratus lumborum
c. respiratory diaphragm
d. psoas major
a. iliacus
b. quadratus lumborum
c. respiratory diaphragm
d. psoas major
quadratus lumborum
10
New cards
Which dermatome overlies the umbilicus?
a. T4
b. T7
c. T10
d. T12
a. T4
b. T7
c. T10
d. T12
T10
11
New cards
Which of the following muscles of the anterior thoracic wall is not innervated by a segmental intercostal nerve?
a. transversus thoracis
b. subcostal muscle
c. innermost intercostal muscle
d. levatores costarum
a. transversus thoracis
b. subcostal muscle
c. innermost intercostal muscle
d. levatores costarum
levatores costarum
12
New cards
The median and transumbilical planes divide the abdomen into four quadrants. Which quadrant is the spleen located?
a. Lower left quadrant
b. Upper left quadrant
c. Upper right quadrant
d. Lower right quadrant
a. Lower left quadrant
b. Upper left quadrant
c. Upper right quadrant
d. Lower right quadrant
Upper left quadrant
13
New cards
Which of the following superficial muscle of the anterior compartment of the forearm does the ulnar nerve innervate?
a.
Palmaris longus
b.
Flexor carpi ulnaris
c.
Pronator teres
d.
Flexor carpi radialis
a.
Palmaris longus
b.
Flexor carpi ulnaris
c.
Pronator teres
d.
Flexor carpi radialis
Flexor carpi ulnaris
14
New cards
The nipple denotes which dermatome?
a. T5
b. T12
c. C7
d. T4
a. T5
b. T12
c. C7
d. T4
T4
15
New cards
Abdominal flexion with rotation towards the left is accomplished by:
a. Right internal oblique and left external oblique abdominals
b. Left internal oblique and right external oblique abdominals
c. Right external and internal oblique abdominals
d. Left external and internal oblique abdominals
a. Right internal oblique and left external oblique abdominals
b. Left internal oblique and right external oblique abdominals
c. Right external and internal oblique abdominals
d. Left external and internal oblique abdominals
Left internal oblique and right external oblique abdominals
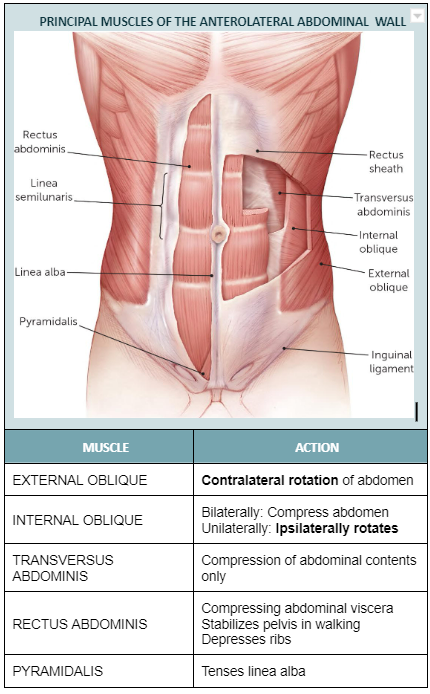
16
New cards
Which abdominal plane is drawn by touching the tips of the 10th ribs?
a. intertubercular
b. intercristal
c. transpyloric
d. subcostal
a. intertubercular
b. intercristal
c. transpyloric
d. subcostal
subcostal
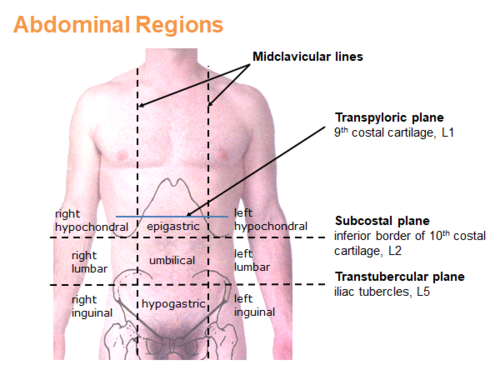
17
New cards
The ligament of the spine that limits hyperextension:
a. Supraspinous ligament
b. Anterior longitudinal ligament
c. Ligamentum flavum
d. Posterior longitudinal ligament
a. Supraspinous ligament
b. Anterior longitudinal ligament
c. Ligamentum flavum
d. Posterior longitudinal ligament
Anterior longitudinal ligament
18
New cards
Which nerve lesion will result to lateral winging and upward rotation of the scapula?
a. Dorsal scapular nerve injury
b. Long thoracic nerve injury
c. Spinal accessory nerve injury
d. Thoracodorsal nerve injury
a. Dorsal scapular nerve injury
b. Long thoracic nerve injury
c. Spinal accessory nerve injury
d. Thoracodorsal nerve injury
Dorsal scapular nerve injury.
Injury to the long thoracic nerve result to medial winging of the scapula.
Injury to the spinal accessory nerve result to lateral winging and downward rotation of the scapula.
Injury to the dorsal scapular nerve result to lateral winging and upward rotation of the scapula.
Injury to the long thoracic nerve result to medial winging of the scapula.
Injury to the spinal accessory nerve result to lateral winging and downward rotation of the scapula.
Injury to the dorsal scapular nerve result to lateral winging and upward rotation of the scapula.
19
New cards
Which of the following muscles of the shoulder girdle CANNOT anteriorly tilt the scapula forward?
a. Coracobrachialis
b. Subscapularis
c. Biceps short head
d. Pectoralis minor
a. Coracobrachialis
b. Subscapularis
c. Biceps short head
d. Pectoralis minor
Subscapularis.
Muscles attached to the coracoid process of the scapula functions to tilt the scapula anteriorly forward. These muscles are the short head of biceps brachii, coracobrachialis and pectoralis minor.
Muscles attached to the coracoid process of the scapula functions to tilt the scapula anteriorly forward. These muscles are the short head of biceps brachii, coracobrachialis and pectoralis minor.
20
New cards
What is the total range of flexion and extension of the atlanto-occipital joint?
a. 25 degrees
b. 35 degrees
c. 10 degrees
d. 15 degrees
a. 25 degrees
b. 35 degrees
c. 10 degrees
d. 15 degrees
35 degrees
21
New cards
A condition that causes pain on the attachment of the muscles of the anterior compartment of forearm:
a.
Golfer's elbow
b.
Popeye elbow
c.
Tennis elbow
d.
Student's elbow
a.
Golfer's elbow
b.
Popeye elbow
c.
Tennis elbow
d.
Student's elbow
Golfer's elbow
\
(Get Me LoTs of OPium)
Medial epicondylitis aka Golfer's elbow
Lateral Epicondylitis aka Tennis Elbow
Olecranon bursitis aka Student's elbow or Popeye Elbow
\
(Get Me LoTs of OPium)
Medial epicondylitis aka Golfer's elbow
Lateral Epicondylitis aka Tennis Elbow
Olecranon bursitis aka Student's elbow or Popeye Elbow
22
New cards
Which of the following muscles of the neck is a capital extensor and laterally rotates the head to the same side?
a. splenius cervicis
b. longus colli
c. splenius capitis
d. rectus capitis anterior
a. splenius cervicis
b. longus colli
c. splenius capitis
d. rectus capitis anterior
splenius capitis
23
New cards
Which of the following DOES NOT belong as a major muscle group of the transversospinalis?
a. Rotatores
b. Semispinalis
c. Multifidus
d. Spinalis
a. Rotatores
b. Semispinalis
c. Multifidus
d. Spinalis
Spinalis
24
New cards
Which of the following vertebra has a kidney-shaped body?
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
Lumbar
25
New cards
Which of the following statement is NOT TRUE regarding thumb opposition?
a. Movement of the thumb across the palm
b. Anterior surface of tip of thumb comes into contact with tip of any finger
c. Lateral rotation of first metacarpal bone occurs in the trapezium
d. Plane of thumbnail comes to lie parallel with the plane of the nail of opposed finger
a. Movement of the thumb across the palm
b. Anterior surface of tip of thumb comes into contact with tip of any finger
c. Lateral rotation of first metacarpal bone occurs in the trapezium
d. Plane of thumbnail comes to lie parallel with the plane of the nail of opposed finger
Lateral rotation of first metacarpal bone occurs in the trapezium
\
Explanation:
**Medial** rotation of the first metacarpal bone occurs in the trapezium so that the tip of the thumb comes into contact with the tip of any finger.
\
Explanation:
**Medial** rotation of the first metacarpal bone occurs in the trapezium so that the tip of the thumb comes into contact with the tip of any finger.
26
New cards
Which of the following DOES NOT abduct the thumb?
a. Abductor pollicis longus
b. Abductor pollicis brevis
c. Adductor pollicis
d. Opponens pollicis
a. Abductor pollicis longus
b. Abductor pollicis brevis
c. Adductor pollicis
d. Opponens pollicis
Adductor pollicis
27
New cards
Which nerve innervates the muscles of mastication?
a. facial
b. abducens
c. trochlear
d. trigeminal
a. facial
b. abducens
c. trochlear
d. trigeminal
trigeminal
28
New cards
Which of the following muscles of the forearm is not two-headed?
a. Flexor digitorum profundus
b. Flexor digitorum superficialis
c. Pronator teres
d. Flexor carpi ulnaris
a. Flexor digitorum profundus
b. Flexor digitorum superficialis
c. Pronator teres
d. Flexor carpi ulnaris
Flexor digitorum profundus
29
New cards
Which of the following vertebras has a bifid spine?
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
a. Cervical
b. Thoracic
c. Lumbar
d. Sacral
Cervical
30
New cards
The wrist extensors represent myotomal level:
a. C5
b. C6
c. C7
d. C8
a. C5
b. C6
c. C7
d. C8
C6
31
New cards
The following muscles has attachments on the vertebral spines, EXCEPT:
a. Latissimus dorsi
b. Levator scapulae
c. Rhomboid major
d. Trapezius
a. Latissimus dorsi
b. Levator scapulae
c. Rhomboid major
d. Trapezius
Levator scapulae
32
New cards
Which of the following ligaments limit elevation of the clavicle?
a. Costoclavicular ligament
b. Acromioclavicular ligament
c. Interclavicular ligament
d. Sternoclavicular ligament
a. Costoclavicular ligament
b. Acromioclavicular ligament
c. Interclavicular ligament
d. Sternoclavicular ligament
Costoclavicular ligament
\
Costoclavicular ligament limits elevation
Interclavicular ligament limits depression
Sternoclavicular ligaments limit retraction and protraction
\
Costoclavicular ligament limits elevation
Interclavicular ligament limits depression
Sternoclavicular ligaments limit retraction and protraction
33
New cards
Which of the following muscles distally attach to the lateral lip of the bicipital groove?
a. Teres major
b. Pectoralis minor
c. Teres minor
d. Pectoralis major
a. Teres major
b. Pectoralis minor
c. Teres minor
d. Pectoralis major
Pectoralis major
34
New cards
The following muscles of the anterior thoracic wall elevate the ribs, EXCEPT:
a. Transversus thoracis
b. External intercostal
c. Subcostal
d. Levatores costarum
a. Transversus thoracis
b. External intercostal
c. Subcostal
d. Levatores costarum
Transversus thoracis
35
New cards
The major factor controlling stability of the shoulder joint is:
a. Arrangement of the articular surfaces
b. Muscle tone of the short muscles around the shoulder joint
c. Ligamental support
d. Size and shape of the articular surfaces
a. Arrangement of the articular surfaces
b. Muscle tone of the short muscles around the shoulder joint
c. Ligamental support
d. Size and shape of the articular surfaces
Muscle tone of the short muscles around the shoulder joint.
\
Explanation:
There are 3 major factors for stability of joints. These are:
1. Congruency of the articular surface (size, shape, arrangement)
2. Ligamental support
3. Tone of muscles around the joint
The shoulder mainly relies on the tone of the rotator cuff muscles
\
Explanation:
There are 3 major factors for stability of joints. These are:
1. Congruency of the articular surface (size, shape, arrangement)
2. Ligamental support
3. Tone of muscles around the joint
The shoulder mainly relies on the tone of the rotator cuff muscles
36
New cards
Which is the anatomical landmark for the subcostal plane?
a. L5
b. S2
c. T10
d. L3
a. L5
b. S2
c. T10
d. L3
L3
37
New cards
The following are muscles acting on the fingers, EXCEPT:
a. Abductor digiti minimi
b. Extensor indicis propius
c. Flexor pollicis longus
d. Flexor digitorum superficialis
a. Abductor digiti minimi
b. Extensor indicis propius
c. Flexor pollicis longus
d. Flexor digitorum superficialis
Flexor pollicis longus
38
New cards
Which extraocular muscle of the eyes does the abducens innervate?
a. inferior oblique
b. lateral rectus
c. medial rectus
d. superior oblique
a. inferior oblique
b. lateral rectus
c. medial rectus
d. superior oblique
lateral rectus
39
New cards
Extrinsic muscles of the tongue are all innervated by the hypoglossal nerve, EXCEPT:
a. styloglossus
b. hyoglossus
c. palatoglossus
d. genioglossus
a. styloglossus
b. hyoglossus
c. palatoglossus
d. genioglossus
Palatoglossus. It is instead innervated by the Vagus nerve.
40
New cards
The following muscles are responsible for adduction of the shoulder joint, EXCEPT:
a. Pectoralis minor
b. Pectoralis major
c. Latissimus dorsi
d. Teres major
a. Pectoralis minor
b. Pectoralis major
c. Latissimus dorsi
d. Teres major
Pectoralis minor
\
Explanation:
Pectoralis major, teres major and latissimus dorsi are adductors and internal rotators of the GHJ
The pectoralis minor does not have any function in the GHJ
\
Explanation:
Pectoralis major, teres major and latissimus dorsi are adductors and internal rotators of the GHJ
The pectoralis minor does not have any function in the GHJ
41
New cards
The ligament that runs from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine is known as the:
a. round ligament
b. spermatic cord
c. linea alba
d. inguinal ligament
a. round ligament
b. spermatic cord
c. linea alba
d. inguinal ligament
inguinal ligament
42
New cards
The following muscles of the forearm acts as synergists for flexion of the elbow, EXCEPT:
a. Pronator teres
b. Supinator
c. Flexor carpi radialis
d. Extensor carpi radialis longus
a. Pronator teres
b. Supinator
c. Flexor carpi radialis
d. Extensor carpi radialis longus
Supinator
\
Explanation:
Pronator teres, ECRL and FCR all have attachment above the elbow and therefore crosses the joint anteriorly. It contracts synergistically during elbow flexion.
The supinator is a deep muscle of the posterior compartment of the forearm and mainly functions for supination of the forearm. By virtue of its attachment on the lateral epicondyle it might act as an elbow extensor when the elbow extends from the flexed position
\
Explanation:
Pronator teres, ECRL and FCR all have attachment above the elbow and therefore crosses the joint anteriorly. It contracts synergistically during elbow flexion.
The supinator is a deep muscle of the posterior compartment of the forearm and mainly functions for supination of the forearm. By virtue of its attachment on the lateral epicondyle it might act as an elbow extensor when the elbow extends from the flexed position
43
New cards
Which of the following muscles flexes the head and laterally rotate the head to the opposite side?
a. sternocleidomastoid
b. scalenes
c. splenius capitis
d. splenius cervicis
a. sternocleidomastoid
b. scalenes
c. splenius capitis
d. splenius cervicis
sternocleidomastoid
44
New cards
Which of the following is a primary curve of the spine?
a. Kyphosis
b. Scoliosis
c. Lordosis
d. Swayback
a. Kyphosis
b. Scoliosis
c. Lordosis
d. Swayback
Kyphosis
45
New cards
Which muscle of the neck is held to the clavicle and first rib by a fascial sling?
a. digastric
b. omohyoid
c. sternohyoid
d. sternocleidomastoid
a. digastric
b. omohyoid
c. sternohyoid
d. sternocleidomastoid
omohyoid
46
New cards
Which of the following muscles DOES NOT have attachments on the ribs?
a. Pectoralis minor
b. Serratus anterior
c. Trapezius
d. Latissimus dorsi
a. Pectoralis minor
b. Serratus anterior
c. Trapezius
d. Latissimus dorsi
Trapezius
47
New cards
The superior oblique muscle of the eye is innervated by:
a. occulomotor
b. optic
c. abducens
d. trochlear
a. occulomotor
b. optic
c. abducens
d. trochlear
trochlear
48
New cards
Which wall of the axilla is made up by the subscapularis, latissimus dorsi and teres major?
a. Anterior wall
b. Medial wall
c. Lateral wall
d. Posterior wall
a. Anterior wall
b. Medial wall
c. Lateral wall
d. Posterior wall
Posterior wall
\
Explanation:
Posterior wall is formed by the subscapularis, teres major and lats
Anterior wall contains the pectoralis major and the underlying pectoralis minor and subclavius muscle
Medial wall consists of the serratus anterior and thoracic wall (ribs and intercostal muscles
Lateral wall formed by the bicipital groove of the humerus
\
Explanation:
Posterior wall is formed by the subscapularis, teres major and lats
Anterior wall contains the pectoralis major and the underlying pectoralis minor and subclavius muscle
Medial wall consists of the serratus anterior and thoracic wall (ribs and intercostal muscles
Lateral wall formed by the bicipital groove of the humerus
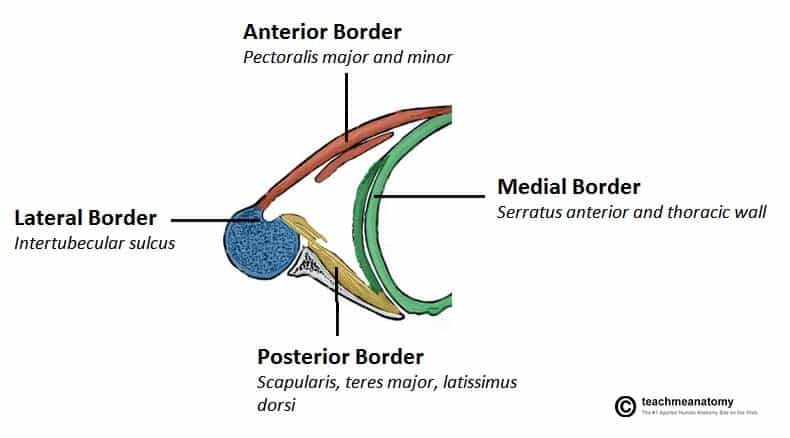
49
New cards
Which of the muscles distally insert on the floor of the intertubercular sulcus?
a. Teres major
b. Teres minor
c. Pectoralis major
d. Latissimus dorsi
a. Teres major
b. Teres minor
c. Pectoralis major
d. Latissimus dorsi
Latissimus dorsi
50
New cards
Which suboccipital muscle extends the head and rotates it to the same side?
a. Rectus capitis posterior minor
b. Obliquus capitis superior
c. Obliquus capitis inferior
d. Rectus capitis posterior major
a. Rectus capitis posterior minor
b. Obliquus capitis superior
c. Obliquus capitis inferior
d. Rectus capitis posterior major
Rectus capitis posterior major
51
New cards
Which of the following prevertebral muscles is a cervical flexor?
a. rectus capitis anterior
b. longus capitis
c. rectus capitis lateralis
d. longus colli
a. rectus capitis anterior
b. longus capitis
c. rectus capitis lateralis
d. longus colli
longus colli
52
New cards
The xiphisternal junction corresponds to the level of:
a. T10
b. T7
c. L1
d. L2
a. T10
b. T7
c. L1
d. L2
T10
53
New cards
The force couple for upward rotation of the scapula:
a. Trapezius an rhomboids
b. Levator scapulae and trapezius
c. Trapezius and serratus anterior
d. Rhomboids and levator scapulae
a. Trapezius an rhomboids
b. Levator scapulae and trapezius
c. Trapezius and serratus anterior
d. Rhomboids and levator scapulae
Trapezius and serratus anterior
\
Explanation:
The serratus anterior and trapezius works synergistically to upwardly rotate the scapula so that the glenoid fossa faces upward to act as a platform for the humerus to stand about during arm elevation
\
Explanation:
The serratus anterior and trapezius works synergistically to upwardly rotate the scapula so that the glenoid fossa faces upward to act as a platform for the humerus to stand about during arm elevation
54
New cards
Which of the following muscles of the forearm DOES NOT assist the biceps brachii during elbow flexion?
a. Flexor digitorum profundus
b. Brachioradialis
c. Flexor carpi radialis
d. Pronator teres
a. Flexor digitorum profundus
b. Brachioradialis
c. Flexor carpi radialis
d. Pronator teres
Flexor digitorum profundus. It does not cross the elbow joint and therefore does not have any action on the elbow
55
New cards
Which of the following abdominal muscles is incapable of flexing the thoracic spine?
a. External abdominal oblique
b. Transversus abdominis
c. Internal abdominal oblique
d. Rectus abdominis
a. External abdominal oblique
b. Transversus abdominis
c. Internal abdominal oblique
d. Rectus abdominis
Transversus abdominis
56
New cards
The ligament of the elbow that holds the radial head on the radial groove of the ulna:
a. Annular ligament
b. Annulos fibrosus
c. Lacertus fibrosus
d. Collateral ligament
a. Annular ligament
b. Annulos fibrosus
c. Lacertus fibrosus
d. Collateral ligament
Annular ligament
57
New cards
Which of the following muscles of the shoulder girdle is NOT supplied by a branch from the brachial plexus?
a. Latissimus dorsi
b. Levator scapulae
c. Teres minor
d. Trapezius
a. Latissimus dorsi
b. Levator scapulae
c. Teres minor
d. Trapezius
Trapezius. The trapezius is innervated by the spinal accessory nerve which is a cranial nerve emerging from the medulla oblongata of the brainstem.
58
New cards
The roof of the vertebral arch is formed by the:
a. Transverse processes
b. Lamina
c. Pedicle
d. Vertebral body
a. Transverse processes
b. Lamina
c. Pedicle
d. Vertebral body
Lamina
59
New cards
Which surface feature of the neck is the laryngeal prominence or "Adam's Apple"?
a. Thyroid cartilage
b. Hyoid
c. Cricoid cartilage
d. Philtrum
a. Thyroid cartilage
b. Hyoid
c. Cricoid cartilage
d. Philtrum
Thyroid cartilage
60
New cards
Which of the following statement is FALSE regarding brachial plexus?
a. The branches innervate the muscles, skin and joint of the shoulder girdle and upper limb
b. A network of spinal nerves from 5th cervical to 1st thoracic
c. Passes between the clavicle and 1st rib to the axilla
d. Comes from the anterior and posterior rami of the spinal nerve roots
a. The branches innervate the muscles, skin and joint of the shoulder girdle and upper limb
b. A network of spinal nerves from 5th cervical to 1st thoracic
c. Passes between the clavicle and 1st rib to the axilla
d. Comes from the anterior and posterior rami of the spinal nerve roots
Comes from the anterior and posterior rami of the spinal nerve roots
\
Explanation:
The brachial plexus comes only from the anterior primary rami of spinal roots C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1
The posterior rami of C5 - T1 innervates the muscle and skin of the back
\
Explanation:
The brachial plexus comes only from the anterior primary rami of spinal roots C5, C6, C7, C8 and T1
The posterior rami of C5 - T1 innervates the muscle and skin of the back
61
New cards
Which of the following muscles of the abdominal wall is NOT attached to the linea alba
a. rectus abdominis
b. transversus abdominis
c. external oblique abdominis
d. internal oblique abdominis
a. rectus abdominis
b. transversus abdominis
c. external oblique abdominis
d. internal oblique abdominis
rectus abdominis
62
New cards
The following muscles are proximally attached on the scapula, EXCEPT:
a. Rhomboid major
b. Subscapularis
c. Teres major
d. Infraspinatus
a. Rhomboid major
b. Subscapularis
c. Teres major
d. Infraspinatus
Rhomboid major.
Rhomboid major DISTALLY attach on the scapula
Teres major, infraspinatus, and subscapularis PROXIMALLY attach on the scapula
Rhomboid major DISTALLY attach on the scapula
Teres major, infraspinatus, and subscapularis PROXIMALLY attach on the scapula
63
New cards
Which intrinsic muscle of the hand does the Froment's sign test?
a. Opponens pollicis
b. Palmaris brevis
c. Flexor pollicis brevis
d. Adductor pollicis
a. Opponens pollicis
b. Palmaris brevis
c. Flexor pollicis brevis
d. Adductor pollicis
Adductor pollicis
\
Explanation:
Froment's is a test for ulnar neuropathy, specifically the action of the adductor pollicis
\
Explanation:
Froment's is a test for ulnar neuropathy, specifically the action of the adductor pollicis
64
New cards
Which of the following thenar muscle does the ulnar nerve innervate?
a. Adductor pollicis
b. Abductor pollicis brevis
c. Flexor pollicis brevis
d. Opponens pollicis
a. Adductor pollicis
b. Abductor pollicis brevis
c. Flexor pollicis brevis
d. Opponens pollicis
Adductor pollicis
\
Explanation:
Thenar muscles OAF are all innervated by the median nerve
Adductor pollicis is innervated by the ulnar
\
Explanation:
Thenar muscles OAF are all innervated by the median nerve
Adductor pollicis is innervated by the ulnar
65
New cards
Which ligament of the spine limits hyperflexion?
a. Posterior longitudinal ligament
b. Anterior longitudinal ligament
c. Ligamentum flavum
d. Supraspinous ligament
a. Posterior longitudinal ligament
b. Anterior longitudinal ligament
c. Ligamentum flavum
d. Supraspinous ligament
Posterior longitudinal ligament
66
New cards
Which ligament of the shoulder when ruptured or teared by severe trauma causes separation of the shoulder?
a. Costoclavicular ligament
b. Sternoclavicular ligament
c. Coracoclavicular ligament
d. Glenohumeral ligament
a. Costoclavicular ligament
b. Sternoclavicular ligament
c. Coracoclavicular ligament
d. Glenohumeral ligament
Coracoclavicular ligament
\
Explanation:
Mechanism of injury for shoulder separation is ruptured or teared coracoclavicular ligament due to trauma
\
Explanation:
Mechanism of injury for shoulder separation is ruptured or teared coracoclavicular ligament due to trauma
67
New cards
Cutaneous innervation of the hand is provided by the following, EXCEPT:
a. Musculocutaneous
b. Median
c. Ulnar
d. Radial
a. Musculocutaneous
b. Median
c. Ulnar
d. Radial
Musculocutaneous
68
New cards
Which of the following statements in NOT TRUE regarding the scapulohumeral rhythm?
a. The muscles responsible for the upward rotation of the scapula are your rhomboids and levator scapulae
b. For every 3 degrees of abduction of the arm, 2 degrees occurs in the shoulder joint and 1 degree occur by rotation of the the scapula
c. Further elevation of the arm above the head is accomplished by rotating the scapula
d. Abduction of the arm involves movement at the shoulder joint and rotation of the scapula
a. The muscles responsible for the upward rotation of the scapula are your rhomboids and levator scapulae
b. For every 3 degrees of abduction of the arm, 2 degrees occurs in the shoulder joint and 1 degree occur by rotation of the the scapula
c. Further elevation of the arm above the head is accomplished by rotating the scapula
d. Abduction of the arm involves movement at the shoulder joint and rotation of the scapula
The muscles responsible for the upward rotation of the scapula are your rhomboids and levator scapulae.
\
Explanation:
2:1 ratio occurs between GH and scapular rotation after 45-60 degrees of abduction. Total 180 degrees of abduction means 120 degrees occuring in GH and 60 degrees in scapula
The force couple for upward rotation of the scapula are your trapezius and serratus anterior
\
Explanation:
2:1 ratio occurs between GH and scapular rotation after 45-60 degrees of abduction. Total 180 degrees of abduction means 120 degrees occuring in GH and 60 degrees in scapula
The force couple for upward rotation of the scapula are your trapezius and serratus anterior
69
New cards
Which muscles of the neck is held to the hyoid bone by a fascial sling?
a. mylohyoid
b. digastric
c. geniohyoid
d. omohyoid
a. mylohyoid
b. digastric
c. geniohyoid
d. omohyoid
digastric
70
New cards
Inability to perform a thumbs up sign is pathognomonic for:
a. Ulnar neuropathy
b. Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome
c. Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome
d. Median neuropathy
a. Ulnar neuropathy
b. Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome
c. Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome
d. Median neuropathy
Posterior interosseous nerve syndrome. Thumbs up requires the function of the EPL which is innervated by the PIN
71
New cards
Which of the following nerves does the Phalen's test evaluate?
a. Ulnar Nerve
b. Radial nerve
c. Median Nerve
d. Posterior interosseus nerve
a. Ulnar Nerve
b. Radial nerve
c. Median Nerve
d. Posterior interosseus nerve
Median Nerve
\
Explanation:
Phalen's maneuver is a provocative maneuver used to test carpal tunnel syndrome. May provoke the ulnar nerve under the tunnel of Guyon.
\
Explanation:
Phalen's maneuver is a provocative maneuver used to test carpal tunnel syndrome. May provoke the ulnar nerve under the tunnel of Guyon.
72
New cards
The skin dimpling just above the intergluteal cleft is the surface landmark for:
a. L4
b. L5
c. S1
d. S2
a. L4
b. L5
c. S1
d. S2
S2
73
New cards
The following structures are proximal attachment of the rhomboid minor, EXCEPT:
a. 2nd thoracic spine
b. 7th cervical spine
c. 1st thoracic spine
d. Ligamentum nuchae
a. 2nd thoracic spine
b. 7th cervical spine
c. 1st thoracic spine
d. Ligamentum nuchae
2nd thoracic spine.
Rhomboid minor originates from nuchal ligaments and spinous processes of C7-T1. Spinous processes of T2-T5 however is the origin of the rhomboid major.
Rhomboid minor originates from nuchal ligaments and spinous processes of C7-T1. Spinous processes of T2-T5 however is the origin of the rhomboid major.
74
New cards
Which of the following is NOT considered an erector spinae?
a. Splenius cervicis
b. Longissimus
c. Iliocostalis
d. Spinalis
a. Splenius cervicis
b. Longissimus
c. Iliocostalis
d. Spinalis
Splenius cervicis
75
New cards
The end of spinal cord is at the level of:
a. level of S2
b. superior border of L1
c. superior border of L2
d. inferior border of L2
a. level of S2
b. superior border of L1
c. superior border of L2
d. inferior border of L2
superior border of L2
76
New cards
Which of the following compartment of the forearm does the extensor digiti minimi located?
a. Dorsal superficial
b. Dorsal deep
c. Volar deep
d. Volar superficial
a. Dorsal superficial
b. Dorsal deep
c. Volar deep
d. Volar superficial
Dorsal superficial
77
New cards
What important artery passes through the transverse foramina of C1-C6?
a. Vertebral artery
b. Jugular artery
c. Spinal artery
d. Subclavian artery
a. Vertebral artery
b. Jugular artery
c. Spinal artery
d. Subclavian artery
Vertebral artery
78
New cards
The cremasteric reflex test the integrity of which nerve?
a. iliohypogastric
b. subcostal
c. ilioinguinal
d. genitofemoral
a. iliohypogastric
b. subcostal
c. ilioinguinal
d. genitofemoral
genitofemoral
79
New cards
The inferior angle of scapula is a surface landmark for the spine of:
a. 3rd thoracic vertebra
b. 7th cervical vertebra
c. 2nd thoracic vertebra
d. 7th thoracic vertebra
a. 3rd thoracic vertebra
b. 7th cervical vertebra
c. 2nd thoracic vertebra
d. 7th thoracic vertebra
7th thoracic vertebra
80
New cards
Which roots of the spinal cord does the supply of the medial forearm sensation comes from?
a. C5-C6
b. C6-C7
c. C7-C8
d. C8-T1
a. C5-C6
b. C6-C7
c. C7-C8
d. C8-T1
C8-T1
81
New cards
The rib located lateral to the sternal angle of Louis:
a. 1st rib
b. 2nd rib
c. 3rd rib
d. 4th rib
a. 1st rib
b. 2nd rib
c. 3rd rib
d. 4th rib
2nd rib
82
New cards
Which type of joint is the sternoclavicular joint?
a. condylar joint
b. ball and socket joint
c. plane joint
d. saddle joint
a. condylar joint
b. ball and socket joint
c. plane joint
d. saddle joint
Saddle joint.
\
EXPLANATION:
The articular surface of the clavicle is slightly concave while that of the sternum is convex, thus forming a saddle joint.
\
EXPLANATION:
The articular surface of the clavicle is slightly concave while that of the sternum is convex, thus forming a saddle joint.
83
New cards
Which of the following tendons is located at the medial side of the dorsal tubercle of the wrist?
a. Extensor carpi radialis longus
b. Extensor pollicis longus
c.Extensor digitorum communis
d. Extensor indicis propius
a. Extensor carpi radialis longus
b. Extensor pollicis longus
c.Extensor digitorum communis
d. Extensor indicis propius
Extensor pollicis longus
Explanation:
The dorsal or Lister's tubercle act as a pulley by changing the mechanical direction of the EPL (45 degree angle turn) located at the medial side of it. The tubercle also separates the 2nd and 3rd extensor tunnels
Explanation:
The dorsal or Lister's tubercle act as a pulley by changing the mechanical direction of the EPL (45 degree angle turn) located at the medial side of it. The tubercle also separates the 2nd and 3rd extensor tunnels
84
New cards
The loss of the convex curve at the medial border of the hand is pathognomonic for:
a. Anterior interosseous neuropathy
b. Ulnar nerve palsy
c. Posterior interosseous neuropathy
d. Median nerve palsy
a. Anterior interosseous neuropathy
b. Ulnar nerve palsy
c. Posterior interosseous neuropathy
d. Median nerve palsy
Ulnar nerve palsy
\
Explanation:
The loss of convex curve of the medial border of the hand is secondary to the atrophy of the hypothenar muscles as a result of ulnar neuropathy
\
Explanation:
The loss of convex curve of the medial border of the hand is secondary to the atrophy of the hypothenar muscles as a result of ulnar neuropathy
85
New cards
Hyperextension of the wrist joint from a fall on outstretched hand (FOOSH) will often dislocate this carpal bone:
a. Scaphoid
b. Lunate
c. Capitate
d. Hamate
a. Scaphoid
b. Lunate
c. Capitate
d. Hamate
Lunate
86
New cards
The following areas are potential sites for entrapment of the ulnar nerve, EXCEPT:
a. Palmar carpal ligament
b. Cubital tunnel
c. Sublimis bridge
d. Struther's arcade
a. Palmar carpal ligament
b. Cubital tunnel
c. Sublimis bridge
d. Struther's arcade
Sublimis bridge
\
Explanation:
The sublimis bridge is an area between the 2 heads of the FDS where the median nerve can be entrapped.
Cubital tunnel, Arcade of Struther's and palmar carpal ligament are areas where the ulnar nerve can be entrapped.
\
Explanation:
The sublimis bridge is an area between the 2 heads of the FDS where the median nerve can be entrapped.
Cubital tunnel, Arcade of Struther's and palmar carpal ligament are areas where the ulnar nerve can be entrapped.
87
New cards
Which muscles of the tongue alters its shape?
a. intrinsics
b. styloglossus
c. genioglossus
d. hyoglossus
a. intrinsics
b. styloglossus
c. genioglossus
d. hyoglossus
intrinsics
88
New cards
The ligament of the spine that connects adjacent transverse processes is the:
a. Interspinous ligament
b. Intertransverse ligament
c. Supraspinous ligament
d. Ligamentum flavum
a. Interspinous ligament
b. Intertransverse ligament
c. Supraspinous ligament
d. Ligamentum flavum
Intertransverse ligament
89
New cards
Neuropathy of the hand caused by trauma or compression of the radial nerve:
a. Cheiralgia paresthetica
b. Struther's ligament syndrome
c. Klumpke palsy
d. Kiloh-Nevin syndrome
a. Cheiralgia paresthetica
b. Struther's ligament syndrome
c. Klumpke palsy
d. Kiloh-Nevin syndrome
Cheiralgia paresthetica
\
Explanation:
Clinical applications (neuropathy: sites and levels of entrapment)
Wartenberg (cheiralgia paresthetica): radial nerve at wrist
\
Explanation:
Clinical applications (neuropathy: sites and levels of entrapment)
Wartenberg (cheiralgia paresthetica): radial nerve at wrist
90
New cards
Which structure is an infolding of the external oblique abdomis that forms the base of the inguinal canal through which inguinal hernia may develop?
a. round ligament
b. superficial inguinal ring
c. deep inguinal ring
d. ligament of Poupart
a. round ligament
b. superficial inguinal ring
c. deep inguinal ring
d. ligament of Poupart
ligament of Poupart
91
New cards
Which of the following is NOT considered an intrinsic muscles of the back?
a. Longissimus
b. Rotatores
c. Longus colli
d. Splenius capitis
a. Longissimus
b. Rotatores
c. Longus colli
d. Splenius capitis
Longus colli
92
New cards
Violent contraction of the supraspinatus muscle could result to fracture of the:
a. Lesser tuberosity
b. Humeral head
c. Greater tuberosity
d. Surgical neck
a. Lesser tuberosity
b. Humeral head
c. Greater tuberosity
d. Surgical neck
Greater tuberosity
\
Explanation:
Mechanism of injury of avulsion fracture of the greater tuberosity where the supraspinatus distally attach
\
Explanation:
Mechanism of injury of avulsion fracture of the greater tuberosity where the supraspinatus distally attach
93
New cards
Unopposed pronation of the forearm in waiter's tip deformity is secondary to paralysis of:
a. Brachioradialis
b. Supinator
c. Pronator teres
d. Biceps brachii
a. Brachioradialis
b. Supinator
c. Pronator teres
d. Biceps brachii
Biceps brachii.
\
Explanation:
Waiter's tip deformity is secondary to an upper brachial plexopathy (C5-C6) which give rise to the lateral cord and its branches, namely: lateral pectoral nerve, musculocutaneous and lateral cord branch of the median. All the muscles therefore that this nerves supply may have weakness but the most characteristic is the waiter's tip deformity. Higher level involvement may be seen if you have weakness to the muscles supplied by the suprascapular or even the dorsal scapular and long thoracic nerves.
\
Explanation:
Waiter's tip deformity is secondary to an upper brachial plexopathy (C5-C6) which give rise to the lateral cord and its branches, namely: lateral pectoral nerve, musculocutaneous and lateral cord branch of the median. All the muscles therefore that this nerves supply may have weakness but the most characteristic is the waiter's tip deformity. Higher level involvement may be seen if you have weakness to the muscles supplied by the suprascapular or even the dorsal scapular and long thoracic nerves.
94
New cards
The following structures belong to the anterior pillar of the spine, EXCEPT:
a. Supraspinous ligament
b. Intervertebral disc
c. Vertebral body
d. Anterior longitudinal ligament
a. Supraspinous ligament
b. Intervertebral disc
c. Vertebral body
d. Anterior longitudinal ligament
Supraspinous ligament
95
New cards
The band or sheet of connective tissue that attaches, stabilizes, encloses or separates muscles and other internal organ is termed:
a. Fascia
b. Synovial sheath
c. Aponeurosis
d. Ligament
a. Fascia
b. Synovial sheath
c. Aponeurosis
d. Ligament
Fascia
96
New cards
An increased carrying angle of the elbow is a risk factor for neuropathy of:
a. Ulnar nerve
b. Radial nerve
c. Median nerve
d. Medial cutaneous nerve
a. Ulnar nerve
b. Radial nerve
c. Median nerve
d. Medial cutaneous nerve
Ulnar nerve
\
Explanation:
The ulnar nerve traversing the cubital tunnel is at risk when the elbow carrying angle increase as a result of elbow fractures as an example
\
Explanation:
The ulnar nerve traversing the cubital tunnel is at risk when the elbow carrying angle increase as a result of elbow fractures as an example
97
New cards
Which muscles of the inner ear are affected if you have facial nerve palsy?
a. mentalis
b. tensor tympani
c. auricularis
d. stapedius
a. mentalis
b. tensor tympani
c. auricularis
d. stapedius
stapedius
98
New cards
Which of the following structures does the subscapularis distally attach?
a. Lateral lip of the bicipital groove
b. Medial lip of the bicipital groove
c. Greater tubercle of the humerus
d. Lesser tubercle of the humerus
a. Lateral lip of the bicipital groove
b. Medial lip of the bicipital groove
c. Greater tubercle of the humerus
d. Lesser tubercle of the humerus
Lesser tubercle of the humerus
99
New cards
Which cranial nerve is responsible for opening the eyes?
a. optic nerve
b. oculomotor nerve
c. trochlear
d. abducens
a. optic nerve
b. oculomotor nerve
c. trochlear
d. abducens
oculomotor nerve
100
New cards
Which of the following muscles DOES NOT be attached to the axillary border of the scapula?
a. Teres major
b. Teres minor
c. Subscapularis
d. Triceps brachii
a. Teres major
b. Teres minor
c. Subscapularis
d. Triceps brachii
Subscapularis.
\
Explanation:
Muscles attaching at the lateral or axillary border of the scapula are triceps brachii on the infraglenoid tubercle, teres minor and major respectively below the inferior glenoid tubercle
Subscapularis originates from the anterior surface of the vertebral border of the scapula and subscapular fossa and insert on the lesser tuberosity of the humerus.
\
Explanation:
Muscles attaching at the lateral or axillary border of the scapula are triceps brachii on the infraglenoid tubercle, teres minor and major respectively below the inferior glenoid tubercle
Subscapularis originates from the anterior surface of the vertebral border of the scapula and subscapular fossa and insert on the lesser tuberosity of the humerus.