Probability Models
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Bernoulli Trial Requirements
There are only 2 possible outcomes (categorized as a success or failure) for each trial
The probability of success, denoted as p, is the same for each trial
The trials are independent
10% Condition
Overrides the violation of independence assumption by sampling without replacement as long as not more than 10% of the population is not sampled (probabilities would not change too much)
Geometric Model
Probability Model used to see how long it will take to achieve the first success in a series of Bernoulli Trials; denoted Geom(p)
Geometric Model Formula
P(X=x) =q^x-1 *p
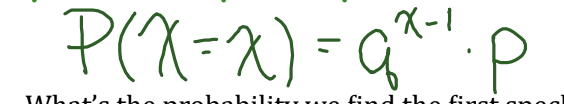
Expected value Formula (Geometric)
E(x)= μ: =1/p
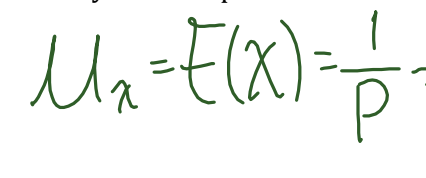
Standard Deviation Formula (Geometric)
σ=sqr(q/p²)
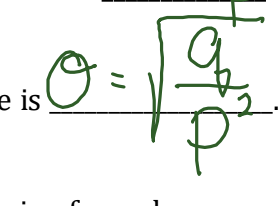
Binomial Model
The probability model used when trying to find the # of successes in a specified # of trials (want to find P(X=#); denoted as Binom (n,p)
Difference b/w Geometric and Binomial
In a Geometric model, a sample size isnt given, while a Binomial model does
There are many different __ to get a specific # of successes in a specific # of trials
COMBINATONS
Combination
Each different order we have k successes in n trials
Combination formula
(n k) = n!/k!(n-k)!
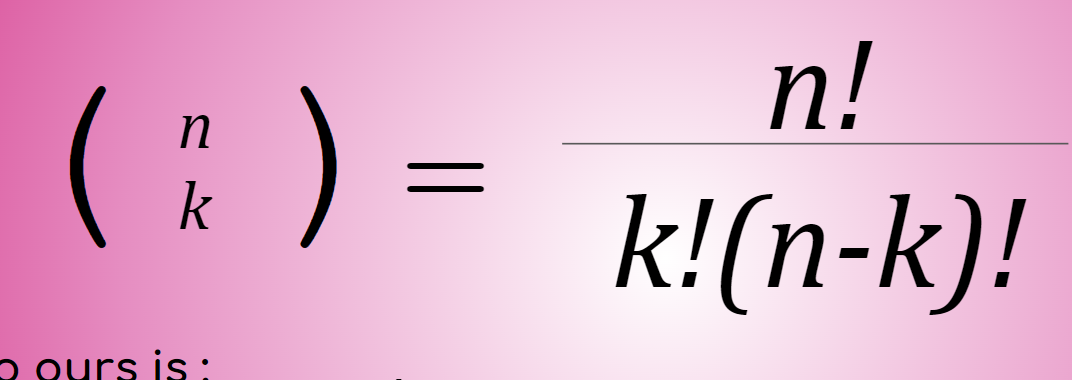
Mean Formula (Binomial)
μ= np
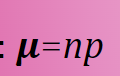
Standard Deviation Formula (Binomial)
σ= sqr(npq)
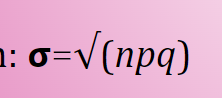
Probability Formula (Binomial)
P(X=x)= (n x) p^x q^n-x
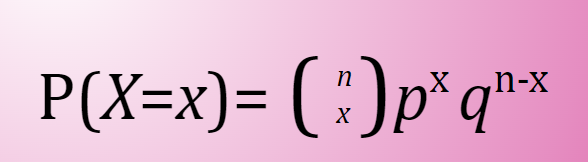
A sample size being LARGE ENOUGH depends on..
the probability of success (the smaller the probability of success (or larger/small q), the larger sample size needed
Success/Failure Condition
States that a Binomial model is approx. Normal if we expect at least 10 successes and 10 failures (np > or = 10 and nq > or =10)
Statistically Significant
When the results of an experiment or a sample are not reasonable to believe they occurred just by chance (Use Binomial/ Normal Model if Bernoulli Trials and Success/Failure Conditions are met)
What Can go Wrong?
Before using any probability model, make sure that you have Bernoulli Trials
Don’t confuse Geometric and Binomial Models
Don’t use Normal Model approx. with a small end
Parameters of Probability Models
p= Probability of success
q (aka 1-p) = Probability of failure
x= number of success in n trials (binomial) or number of trials until first success (geometric)
n= number of trials (binomial)