Key Concepts in Microbiology and Infectious Diseases
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms

Describe the lifecycle of Plasmodium
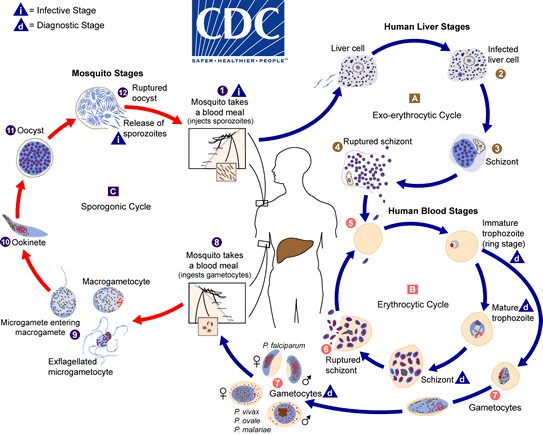
Sporozoite → hepatic schizont → merozoite → erythrocytic trophozoite → schizont → gametocyte
Describe the mechanism of action of Artemisinin and what disease it treats
Artemisinin is an antimalarial drug
Direct molecular damage:
acts by generating reactive oxygen species in the food vacuole of the malaria parasite, leading to damage of essential biomolecules (e.g. proteins, lipids, membranes) and ultimately resulting in the rapid death of the blood-stage parasites.
Interference with haeme clearance:
Artemisinin radicals form covalent adducts with haeme, blocking the parasite’s haeme detoxification pathway and amplifying oxidative stress
PfEMP1
Mediates cytoadherence of infected RBCs to endothelium, avoiding splenic clearance and causing microvascular occlusion
P. vivax relapse
P. vivax forms dormant hypnozoites in hepatocytes, causing relapses months later
HRP2-based lateral-flow assay
Detecting P. falciparum antigen in blood
EHEC toxin
Shiga-like toxin inhibits 60S ribosome → HUS
ETEC toxin
Heat-labile/stable toxins ↑ cAMP/cGMP → secretory diarrhea
Type 1 and P fimbriae
Mediate adhesion to uroepithelial cells
K1 capsule
Inhibits complement deposition and MAC formation on bacterial surface
O157:H7 virulence locus
Pathogenicity island carrying Shiga-like toxin genes and T3SS components
TLR4
On innate immune cells binds LPS → NF-κB activation
Pneumolysin
Lyses host cells, activates complement, and induces inflammation
Asplenic patients
They lack splenic macrophages and marginal-zone B cells needed to clear encapsulated bacteria
Pneumococcal capsule
Inhibits opsonin binding and prevents complement C3b deposition
Autolysin (LytA)
Cleaves cell wall, releasing inflammatory components
IgA1 protease
Cleaves IgA hinge region, allowing mucosal attachment
Tuberculous granuloma
Caseating necrotic core surrounded by epithelioid macrophages, Langhans giant cells, lymphocytes, and fibroblasts
ESX-1 secretion system
Secretes ESAT-6 and CFP-10, which disrupt phagosomal membrane and aid cytosolic escape
Cord factor
Induces TNF-α, causes granuloma necrosis, and inhibits neutrophil migration
IGRA test
Detects IFN-γ release by T cells in response to ESAT-6/CFP-10 peptides
M. tuberculosis acid-fast
Mycolic acids in the cell wall retain carbol fuchsin dye during acid-alcohol wash
Lytic cycle
Phage replicates, lyses host
Lysogenic cycle
Phage DNA integrates as prophage, replicates with host
Generalized transduction
Random bacterial DNA packaged into phage capsid and transferred to new host
Phage therapy
Targets antibiotic-resistant bacteria and can disrupt biofilms
Prophage induction
DNA damage (e.g. UV) activates SOS response, cleaves phage repressor, triggering lytic cycle
CRISPR defense
Integrate phage DNA snippets into CRISPR array → guide RNAs direct Cas nucleases to destroy matching phage DNA
viral quasispecies
A cloud of genetically diverse but related genomes generated by high-error RdRp, enabling rapid adaptation
antigenic drift
Point mutations accumulate slowly
antigenic shift
Reassortment of segments between strains → novel HA/NA combos
drivers of viral emergence
Zoonotic spillover, global travel, ecological disruption (deforestation, climate change)
R₀
Basic reproduction number; R₀ > 1 → epidemic potential; R₀ < 1 → outbreak dies out
reassortment
Swap entire genome segments
recombination
Exchange of nucleotide sequences within a genome
Trypanosoma brucei antigenic variation
Periodic switching of Variant Surface Glycoprotein (VSG) genes to evade antibody response
T. brucei transmission
Tsetse fly → African sleeping sickness
T. cruzi transmission
Reduviid bug → Chagas disease (cardiomyopathy)
kinetoplast DNA
Network of interlocked minicircles & maxicircles in trypanosome mitochondrion essential for gene expression
diagnosis of African trypanosomiasis
Detection of trypomastigotes in blood smear or CSF by microscopy
glycosomes
Peroxisome-like organelles compartmentalizing glycolytic enzymes for rapid ATP production
common HAI pathogens
MRSA (mecA β-lactam resistance), VRE (vanA D-Ala-D-Lac target), P. aeruginosa (efflux pumps)
C. difficile persistence
Spores resist disinfectants and germinate when microbiota are disrupted
catheter-associated biofilm formation
Pili & exopolysaccharide matrix protect bacteria from antibiotics and immunity
van gene for vancomycin resistance
vanA operon encodes ligase that synthesizes D-Ala-D-Lac termini
prevent MRSA spread
Contact precautions, hand hygiene, decolonization, environmental cleaning
toxoplasmosis lifecycle in humans
Ingest oocysts or tissue cysts → tachyzoites disseminate → bradyzoite cysts in brain/muscle
congenital defects from fetal infection
Hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications, chorioretinitis
T. gondii host immunity manipulation
Inhibits apoptosis & modulates cytokine responses to establish chronic infection
diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis
Serology: detection of IgM and rising IgG titers
HIV patients risk for toxoplasmic encephalitis
CD4+ T cell loss allows reactivation of bradyzoite cysts in CNS
incidence vs prevalence
Incidence: new cases/time; Prevalence: total cases at a point in time
herd immunity threshold
Proportion immune needed to prevent sustained transmission = 1 - 1/R₀
attack rate calculation
(New cases during outbreak / Population at risk) × 100%
case-fatality rate
(Deaths from disease / Confirmed cases) × 100%
R₀ > 1 significance
Each case infects >1 person → potential epidemic spread
horizontal gene transfer
Accelerates bacterial adaptation.
Acquisition of novel genes
Acquisition of novel genes (via conjugation, transformation, transduction) bypasses slow point mutations, enabling instant new traits.
Muller's ratchet
Irreversible accumulation of deleterious mutations in asexual lineages reduces fitness over time without recombination.
Clonal interference
Competition among different beneficial mutations in separate clones slows overall adaptation in large asexual populations.
Genome reduction in endosymbionts
Loss of genes dispensable inside host cells streamlines the genome for a host-dependent lifestyle.
Lenski's Long-Term Evolution Experiment
E. coli populations evolved increased fitness, novel traits (like citrate utilization), and parallel mutations over tens of thousands of generations.
Sigma-factor specificity
Sigma factors redirect RNAP to stress-response promoters.
Two-component systems
Two-component systems sense extracellular cues via sensor kinase and response regulator.
Riboswitch
Ligand binding alters mRNA secondary structure to form a terminator or sequester the ribosome binding site, toggling transcription/translation.
Catabolite repression of the lac operon
High glucose → low cAMP → CRP-cAMP dissociates from lac promoter → lac operon transcription blocked until glucose is gone.
Small RNAs (sRNAs)
Base-pair with target mRNAs to block ribosome binding or recruit RNases, fine-tuning stress and virulence gene expression.
Regulon
Regulon: operons controlled by one TF.
Stimulon
Stimulon: all regulons responding to a specific stimulus (e.g. heat shock).
DnaA's role
DnaA-ATP binds oriC to unwind DNA and recruit replisome.
RIDA and datA sites
RIDA and datA sites hydrolyze DnaA-ATP to prevent early re-initiation.
Theta replication
Theta: bidirectional forks on circular chromosome.
Rolling-circle replication
Rolling-circle: unidirectional nick generates concatemeric DNA in some plasmids/phages.
Tus-Ter complex
Tus bound to Ter sites stalls replication forks in one direction, ensuring forks meet in the termination zone.
SeqA
Binds hemimethylated oriC after replication, blocking DnaA access until Dam methylase restores full methylation.
Cytokinetic Z-ring
FtsZ polymerizes into a midcell ring, recruiting division machinery for septum synthesis and cell scission.
Replication strategies of (+)ssRNA, (-)ssRNA, and dsDNA viruses
(+)ssRNA: genome = mRNA. (-)ssRNA: carry RdRp to make mRNA. dsDNA: use host RNAP in nucleus; some bring own enzymes.
Enveloped viruses budding
Viral matrix proteins and glycoproteins cluster at membrane, induce curvature, and scission releases virion with host-derived envelope.
Viroporin
Virus-encoded ion channel in host membranes that alters permeability to aid assembly or release of progeny virions.
Poxviruses replication
Carry their own polymerases, capping and polyadenylation enzymes in the virion, bypassing the need for nuclear machinery.
DNA viruses assembly in the nucleus
They depend on host DNA polymerases and splicing factors, which are only available in the nucleus.
Dynamic population of closely related genomes
Generated by high-error RdRp, enabling rapid adaptation to host or drug pressures.
Major drivers of viral emergence
Zoonotic spillover, global travel/trade, ecological change (e.g. deforestation, climate warming).
Gram-positive envelopes
Thick peptidoglycan, teichoic acids.
Gram-negative envelopes
Thin peptidoglycan, outer membrane with LPS, periplasmic space.
Fungal chitin
Provides tensile strength.
β-glucans
Form crosslinked matrix for rigidity and porosity.
LPS and septic shock
Lipid A engages TLR4 on macrophages → massive TNFα/IL-1 release → systemic vasodilation and organ failure.
Echinocandins
Inhibit fungal β-1,3-glucan synthase, weakening the cell wall; high specificity with low human toxicity.
Bacterial S-layer function
Crystalline protein layer on some bacteria for protection against environmental stress and host immunity.
Polyprotein strategy in (+)ssRNA viruses
Single ORF yields large polyprotein, then viral proteases cleave it into multiple functional proteins.
Cap-snatching
Endonuclease cleaves 5′ caps from host mRNAs to prime viral mRNA synthesis (e.g. influenza).
IRES-mediated translation
Internal ribosome entry sites bypass cap recognition, recruiting ribosomes directly for cap-independent initiation.
Leaky scanning
Ribosomes bypass weak Kozak-context AUGs to initiate at downstream start sites, producing protein isoforms.
−1 ribosomal frameshifting in retroviruses
Slippery sequence + downstream pseudoknot cause ribosome to shift −1, generating Gag-Pol fusion necessary for replication.
+ssRNA viruses and membrane-associated replication complexes
Concentrates polymerases, hides dsRNA from host sensors, and provides lipid environment optimal for replication.
Rough ER functions
Ribosome-bound: secreted/membrane protein synthesis.
Smooth ER functions
Lipid synthesis, detoxification, Ca²⁺ storage.
Peroxisomes and innate immunity
Generate reactive oxygen species to degrade invading microbial components.
Endosomal acidification in viral entry
Low pH triggers conformational changes in viral fusion proteins (e.g. influenza HA) to penetrate host membranes.
Golgi's role in viral glycoprotein maturation
Processes and glycosylates viral envelope proteins before trafficking to budding sites.