Unit 3 Cellular Energetics AP BIO
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Reactions
Transfer of energy
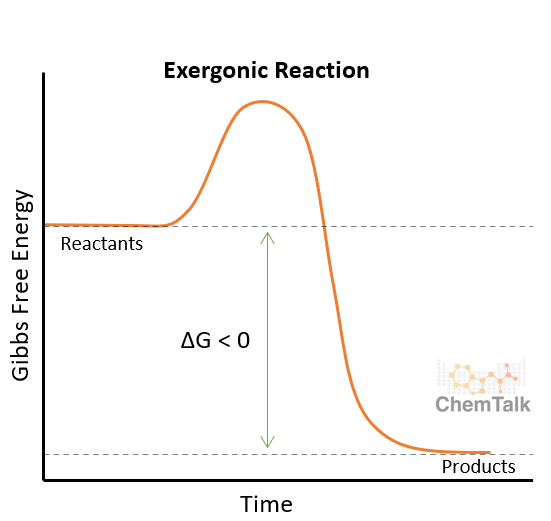
Exergonic
Releases energy (transfers energy out)
ΔG < 0
When energy is released it is typically heat
-ΔH < 0
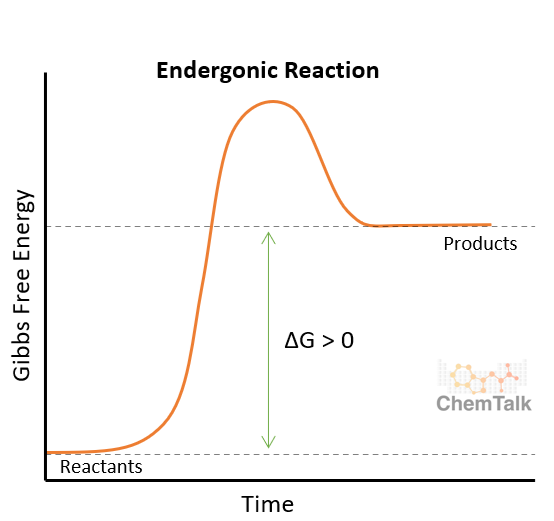
Endergonic
Takes in energy (transfers energy in)
-ΔG > 0
-ΔH > 0
Gibbs Free Energy
Energy available to do work
Work - amount of force within a distance
Entropy
Measure of disorder within the universe
Enthalpy
Total amount of energy within the system
Activation Energy
Amount of energy needed to begin a Rxn
Enyzmes
Lowers the activation energy of a reaction without putting anything into them
They are specific PROTEINS!!
Modifies the transition state to make is easier to complete the reaction
Provides an alternative pathways for reaction to occur
Protein Structure (Review)
Primary - Chain of amino acids
Secondary - Beta pleated sheets & Alpha helix
Tertiary - Folding by additional bonds (disulfide, hydrogen bonding, etc.)
Quartenary - Multiple polypetides
Enzyme Substrates
A “lock & key mechanism”
Very specific to their enzyme
e.g. catalyse ONLY bonds to hydrogen peroxide
Undergoes confirmational change
Inactive - Same folding
Active - Folding changes
Allosteric Bonding Site
Controls the activity of an enzyme
Can inhibit activity OR
Promote activity
Allosteric/Non-Competitive Inhibitor
Binds to the allosteric bonding site
Changes the proteins shape so it CANNOT bind to the substrate (rids of activity)
Cofactors/Inorganic Partners
Can promote reactivity through the allosteric bonding site
Activates an enzyme and helps them to function as a catalyst
Enzyme Endings
Oftentimes Substrate + Ase
Positive Control
A similar product known to work is used to compare results
Negative Control
A product known to have no effect is used to decipher a cause
Anabolic Pathway
Builds molecules/synthesizes them
Requires more energy than it produces
Does NOT happen spontaneously
Catabolic Pathway
Breaks down molecules/decomposes them
Requires little energy to proceed and uses less than it produces
Does NOT happen spontaneously
Catalyst
Something that speeds up the rate of reactions
Best example —> Enzymes
Active Sites
Pockets on enzymes used to attach to certain molecules
Substrate
The molecule an enzyme binds to
Synonym for reactants in a biochemical reaction
Coenyzmes/Organic Partners
Small molecules that can separate from the protein component of the enzyme and participate directly in the reaction.
They can transfer electrons, atoms, or molecules from one enzyme to another.
Feedback Inhibition
Occurs when product concentration becomes too high
Product binds to the initial enzyme, stopping the entire pathway, effectively stopping production
This is reversible as the bonding is NOT permanent
Environmental Conditions That Affect Enzyme Function
Substrate Concentration
Enzyme Concentration
Temperature
pH
Inhibitors
Allosteric
Competitive
Cofactors & Coenzymes
Organic & Inorganic
Competitive Inhibitors
Binds to the ACTIVE site
Competes with the substrate
1st Law of Thermodynamics
In an isolated system, the amount of energy stays constant but can change forms, meaning energy cannot be created or destroyed
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Energy transfers are inherently inefficient because the entropy of a closed system ALWAYS increases
As energy transfers occur, not all energy is converted to usable energy, some is lost as heat
Oxidizing Agent
A compound that oxidizes another
Oxidized Compounds
They have been REMOVED an electron
Results in a decrease in potential energy
Reducing Agent
A compound that reduces another
Reduced Compounds
They have been GIVEN an electron
Results in an increase in potential energy
Electron Shuttles
These compounds bind and carry high-energy electrons between compounds through biochemical pathways
Oxidized Form of Compounds
Compound (+)
Reduced Form of Compounds
Compound (H)
Electron Carriers
NAD+ → NADH
FAD → FADH
Glycolysis
4 ATP - 2 ATP = 2 ATP
Produces 2 NADH Electron Carriers
Breaks down into 2 Pyruvate
Contains Energy Investment Phase & Energy Payoff Phase
EIP - 2 ATP → 2ADP + Pi
EPP - 4ADP + Pi → 4ATP AND 2NAD+ + 4e- + 4H+ → 2NADH + 2H+
In every cell (points to common ancestry)
Occurs in cytosol
ATP → ADP
Generates 1 ATP
Adenosine TRIphosphate → Adenosine DIphosphate
ADP → ATP
Uses 1 ATP
Adenosine DIphosphate → Adenosine TRIphosphate
NAD+ → NADH
Reduction Rxn
Electron Carrier
Created through glycolysis
FADH→ FAD
Oxidation Rxn
Electron Carrier
Used in photosynthesis
Hydrolysis of ATP
Creates ADP, inorganic Phosphate ion (Pi), & free energy
Water is broken down into Hydrogen and Hydroxide ions & is regenerated when ADP is reformed into ATP
Intermediate Complex
The enzyme binds to several substrates that react with each other
This allows substrates like ATP to break off a phosphate ion and transfer it to ADP (Substrate-level Phosphorylation)
Dephosphorylation
The release of 1 or 2 phosphate groups from ATP, forming ADP and RELEASING energy
Phosphorylation
The addition of phosphate groups, REQUIRING energy
Typically for storage of energy
Substrate-level Phosphorylation
A covalently bonded phosphate group is removed from an intermediate reactant and transfers onto an available ADP compound, producing ATP
Uses free energy
Chemiosmosis
Takes place in the mitochondria
Produces ATP in cellular metabolism, generating 90% of the ATP created during glucose catabolism and is used in photosynthesis
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The production of ATP using the process of chemiosmosis
Contains the involvement of oxygen within the process
Uses electron transport chain with electron carriers NADH & FADH2
Levels concentration gradient of H+ ions to synthesize ATP by using necessity to transfer to lower concentration gradient to synthesize ADP & Pi (With the presence of oxygen)
Cell Domains (Intro to Cells Review)
Prokaryote
Bacteria
Archaea
Eukaryote
Eukarya
Anoxygenic Photosynthesis
Photographs that use compounds other than water as electron donors
Does NOT release oxygen as a byproduct
Oxygenic Photosynthesis
Phototrophs that use water as electron donors
Creates oxygen as a byproduct
Bacteriochloropylls
Used by anoxygenic organisms
Absorbs light at longer wavelengths than chlorophyll
Used in areas where light is scarce
Great Oxidation Event
A period when free oxygen accumulated in the atmosphere
Resulted in the extinction of many anaerobic lifeforms (oxygen was toxic)
Jumpstarted the evolution of aerobic respiration
Endosymbiosis
The process of a cell engulfing another cell, resulting in the engulfed cell becoming an organelle
Resulted in the creation of Chloroplasts as the engulfed cyanobacterium transferred its genes to the host cell’s nucleus, integrating its functions into the new cellular structure.
Explains the appearance of photosynthesis within several distinct lineages
Secondary Endosymbiosis
A eukaryotic cells engulfs another eukaryotic cell that was already photosynthetic
Some eukaryotic groups acquired chloroplasts through engulfing red or green algal in this process
These are characterized by having more than two membranes
Tertiary Endosymbiosis
The engulfment of a secondary endosymbiotic organism
Further distributed photosynthetic capabilities
Stroma
Where the Calvin Cycle takes place and contains enzymes for glucose production
CO2 → C6H12O6
Within chloroplasts
Calvin Cycle
Cyclic electron flow
Utilizes ATP & NADPH to reduce CO2 to sugar (G3P)
Goes through 3 phases
Carbon Fixation
Reduction
Regeneration of RuBP
Occurs in the Stroma
Carbon Fixation (Phase 1)
CO2 is incorporated into the Calvin Cycle one at a time (3 times total to produce 1 net G3P)
Each CO2 attaches to a molecule of RuBP, being catalyzed by the Rubisco enzyme to form 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA)
Reduction (Phase 2)
Each molecule of 3-phosphoglycerate is phosphorylated by ATP (uses 6 total)
6 NADPH molecules donate electron to 1, 3-biphosphoglycerate
Reduces to G3P
6 molecules of G3P are formed but only ONE is counted as a net gain
The other 5 G3P molecules are used to regenerated RuBP
Regeneration of RuBP (Phase 3)
5 G3P molecules are used to regenerate 3 molecules of RuBP
3 ATP used for regeneration
Cycle becomes ready to take in CO2 again
Calvin Cycle (Inputs/Outputs)
Inputs
3 CO2 → From environment
9 ATP → From light reactions
6 NADPH → From light reactions
Outputs
1 G3P → Sugar for mitochondria
9 ADP → To light reactions
6 NADPH+→ To light reactions
Light Reactions
Occurs in the Thylakoid & Thylakoid Membrane
Convert light energy into chemical energy through the production of ATP and NADPH.
Water is split, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
G3P
Three carbon sugar produced by Calvin Cycle
2 are used to synthesize 1 glucose
C3 Plants → Basic
3 Carbon (G3P)
On hot days, they close their stomata to stop water less
Results in less CO2 & more O2 present
Rubisco binds to O2 & uses ATP
Produces O2 & uses ATP
NO sugar produced
Bad for the plant
C4 Plants → Change location
4 Carbon molecule
Spatial separation of steps
Stomata PARTIALLY closes to conserve water
Mesophyll cells fix CO2 into 4-C molecule
CAM Plants → Changes time of day
Carbon AM
Light dependent reactions occur during the day
Carbon fixation occurs at night (sugar)
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
The breakdown of sugars to get ATP (energy!)
C6H12O6 + O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ ATP)
Produces 30-32 ATP per glucose molecule
Evolutionary Conserved!
Prokaryotes do NOT partake b/c they have no mitochondria! 😙
Stage 1 Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
Yields 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH, & 2 ATP per glucose molecule
Outside of Mitochondria (cytosol)
Anaerobic respiration
Stage 2 Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Pyruvate Oxidation + Citric Acid Cycle (If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondria!)
Pyruvate Oxidation
Pyruvate → Acetyl CoA (1st Molecule in Citric Acid Cycle)
Produces NADH + CO2
Stage 3 Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Electron Transport Chain & then Oxidative Phosphorylation
Electron Transport Chain
ATP Synthase synthesizes ADP & Pi into ATP
Energy from H+ ion transferred to synthesize ADP & Pi
Chemiosmosis
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Occurs in the inner folds of mitochondria (Cristae)
Final stage of aerobic respiration that generates the majority of ATP
Uses electrons from NADH and FADH2 to create a proton gradient (H+) for ATP production
Red Blood Cells
DON’T have mitochondria
Relies on glycolysis to produce ATP
Lifespan of ~120 days
Citric Acid Cycle/Krebs Cycle
Uses 2 Acetyl CoA
Produces 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 & 4 CO2
Occurs in the Mitochondrial Matrix
H+ produced is also used in Oxidative Phosphorylation
Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
Pyruvate from Glycolysis is turned into 2 lactic acid
Does not go through Pyruvate Oxidation or the Citric Acid Cycle. It produces a net gain of 2 ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation.
Less efficient compared to other forms as it produces very little ATP
Fermentation
Pathway of anaerobic respiration!
Pyruvate from Glycolysis is turned into 2 Acetyl Aldehyde
Acetyl Aldehyde is turned into 2 Ethanol (Alcahawlll 😛)
Is turned into lactic acid within the muscle cells of most animals
Produces 2 ATP
Photorespiration
Occurs in Calvin Cycle step 1
RuBP is oxygenated instead of carboxylated
Bad for plants since carbon is used to create sugar!
Earth’s Early Formation
Chemosynthetic bacteria evolved first because earth’s early atmosphere had no oxygen! (Mainly hydrogen and helium)
The atmosphere couldn’t protect bacteria from outside radiation
Photosynthetic bacteria evolved next as there was still not free oxygen
Heterotrophs & cellular respiration evolved after photosynthetic bacteria dude to the presence of oxygen
Chemosynthetic Bacteria
Microorganisms that obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic molecules, typically in an environment devoid of sunlight.
They play a crucial role in early Earth conditions by sustaining life through chemical reactions.
Photosynthetic Bacteria
Utilized carbon from ash in the air to produce energy through photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy and releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
They played a significant role in altering Earth's atmosphere and enabling aerobic life.
Heterotrophs
Utilized aerobic cellular respiration once oxygen was produce by photosynthetic respiration