parenteral solid dosage forms
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
topical, transdermal, and mucosal
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
stratum corneum characteristics (outermost layer)
barrier (dead cells) to permeation (lipid barrier)
permeation b/t dead cells through lipid
hydration state relative to ease of permeation
living epidermis (viable epidermis)
skin color, living cells w/o capillaries (nutrition source via diffusion)
dermis
pain/thermal, capillaries (drugs here acheive systemic action)
skin function
protective barrier
topical drug delivery
local barrier effects, glands, deep tissues
transdermal drug delivery
systemic effects, helps with short systemic half-life drugs
topical drug delivery local barrier effects example(s)
surface effects (deordorant, lip balm)
stratum corneum effects (emolliency, keratolysis/horny tiss removal)
topical drug delivery skin’s glands effects example
acne, antiperspirants
topical drug delivery deep tiss effects example
skin cancer, NSAIDs, local anesthetics
ointment types
hydrocarbon bases, silicone bases, absorption bases, water soluble bases
hydrocarbon base example (ointment)
petrolatum, polyethylene in mineral water (hydrophobic)
silicone base example (ointment)
polydimethylsiloxane oil
absorption base example (ointment)
contain W/O emulsifiers
water soluble base example (ointment)
polyethylene glycol (hydrophilic)
types of skin formulations
pastes, creams, gel, rigid foams
transdermal drug delivery diagram
…
transdermal drug delivery characteristics
impenetrable, permeation correlates w drug MW/Kow, useful for low dose drugs and high skin permeability
scopolamine and nitroglycerin transdermal patches
membrane-modulated
short half-life
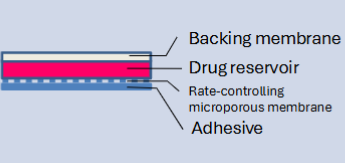
nitroglycerin (deponit) transdermal patches
adhesive dispersion (ex: rivastigmine)
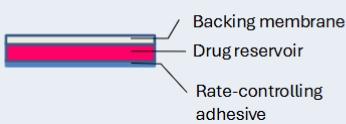
nitroglycerin (nitrodur) transdermal patches
matrix dispersion
list of transdermal patch active ingredients
clonidine, .. oestradial ,N, fentanyl, lidocaine, epi, nicotine, nitroglycerin, norenthindrone, oxy, scopolamine, testosterone
transdermal contraceptive
combination, matrix-type transdermal system
factors affecting skin permeability
hydration, stratum corneum drug solubility, excipients, pH
penetration enhancements
iontophoresis, electroporation, ultrasound, prodrugs, chemicals
enhancers examples
ionic surfactants, ascorbate/dithiothreitol, azone, DMSO
azone enhancer
nonpolar liquid, fluidize intracell stratum corneum lipid
DMSO enhancer
dipolar solvent, interact w lipid polar heads in aq region of stratum corneum
microneedle types
dissolving, separable, hydrogel, hollow
patches
applied in areas without body hair, frequency largely depends
transdermal patch errors
preparation, removal, application, monitoring, storage/disposal
mucoadhesion purpose
prolong mucosal residence time, enable controlled release systems, enhance absorption, immobilize dosage form at site of action
mucoadhesion mechanisms
electrostatic (cationic polymer and anionic sialic acid), hydrogen bonding, covalent (disulfide between mucin and polymer)
mucus characteristics relevant to mucoadhesion
goblet cell secretion, diffusion barrier and lubricant, variable thickness, mucin negatively charged (sialic acid), cystein-rich domains (disulfide), high water content (glycoproteins)
desirable drug properties for mucosal delivery
lipophilic, small MW (enhancers for larger/hydrophilic molecules), stability against enzymes
sublingual vs buccal
more permeable, rapid onset, short-term emergencies, affected by saliva
less permable, slow onset, less influenced by saliva, sustained delivery
proper way of applying buccal drug
place flat side of tablet on fingertip
apply round side to upper gum
hold placement for 30s
let dissolve
alternate application sides each dose