ACS Gen Chem 2 Final Exam Study Guide
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
C
Where is the hydrophilic (attracted to water) region of the molecule?
(A) Region 1
(B) Region 2
(C) Region 3
(D) The three regions are equally hydrophilic
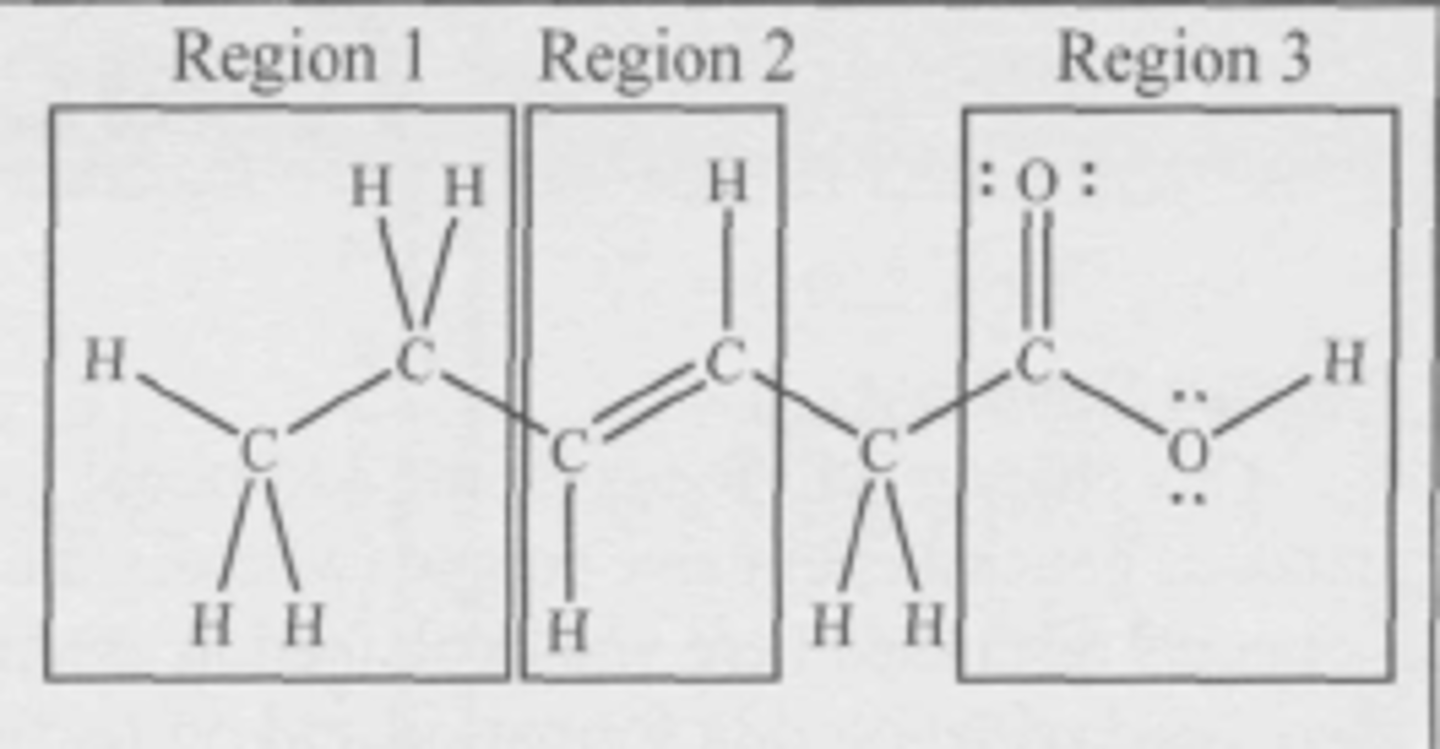
C
Which molecule is most soluble in water?

D
A solution of NaCl in water has a concentration of 20.5% by mass. What is the molal concentration of the solution?
Molar Mass NaCl = 58.44 g/mol
(A) 0.205 m
(B) 0.258 m
(C) 3.51 m
(D) 4.41 m
B
What is the mole fraction of water in 200 g of 89% (by mass) ethanol, C2H5OH?
Molar Mass C2H3OH = 46 g/mol
(A) 0.11
(B) 0.24
(C) 0.32
(D) 0.76
D
A mixture of 100 g of K2Cr2O7 and 200 g of water is stirred at 60 degrees C until no more of the salt dissolves. The resulting solution is poured off into a separate beaker, leaving the undissolved solid behind. The solution is now colled to 20 degrees C. What mass of K2Cr2O7 crystallizes from the solution during the cooling?
(A) 9 g
(B) 18 g
(C) 31 g
(D) 62 g
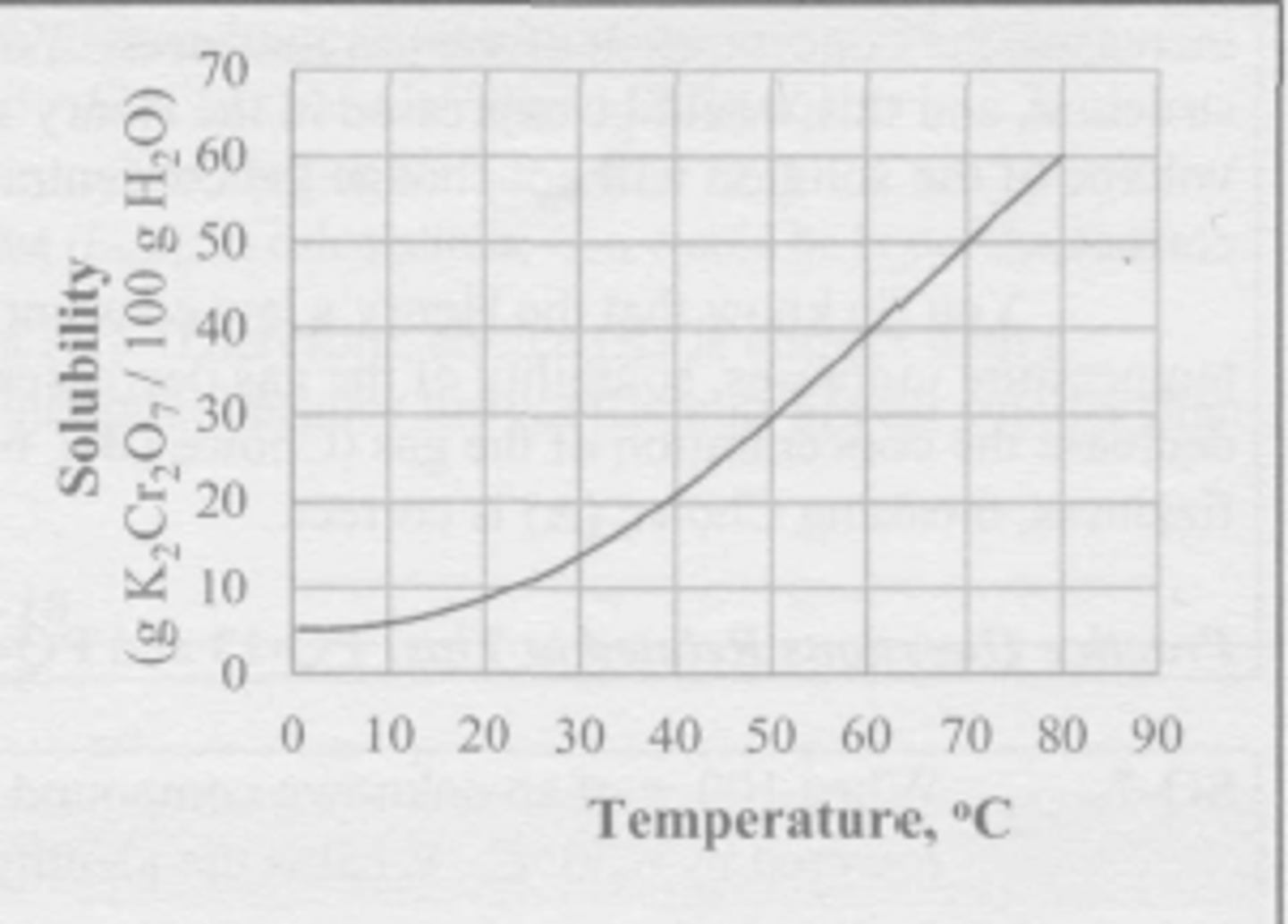
A
Carbonated beverages have a fizz because of gas dissolved in the solution. What increases the concentration of gas in a solution?
(A) cooling the solution
(B) heating the solution
(C) increasing the volume of solution
(D) decreasing the volume of solution
D
When 100 g of an unknown compound was dissolved in 1.00 kg of water, the freezing point was lowered by 6.36 degrees C. What is the identity of this unknown compound?
Kf for water = 1.86 degrees C/m
(A) CsCl
(B) KCl
(C) LiF
(D) NaCl
A
Which 0.1 molal aqueous solution will have the lowest freezing point?
(A) Al(NO3)3
(B) CaCl2
(C) C2H5OH
(D) NaCl
B
What is the rate law of this reaction?
2H2 (g) + 2NO (g) --> N2 (g) + 2H2O (g)
(A) rate = k[H2]^2 [NO]
(B) rate = k[H2] [NO]^2
(C) rate = k[H2]^2 [NO]^2
(D) rate = k[N2] [H2O]^2 / [H2]^2 [NO]^2
![<p>What is the rate law of this reaction?</p><p>2H2 (g) + 2NO (g) --> N2 (g) + 2H2O (g)</p><p>(A) rate = k[H2]^2 [NO]</p><p>(B) rate = k[H2] [NO]^2</p><p>(C) rate = k[H2]^2 [NO]^2</p><p>(D) rate = k[N2] [H2O]^2 / [H2]^2 [NO]^2</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/88e53ab2-bb7c-46ae-9da7-402019af0a5d.png)
B
The rate law for the reaction
A + B --> C + D
is first order in [A] and second order in [B]. If [A] is halved and [B] is doubled, the rate of the reaction will
(A) remain the same
(B) be increased by a factor of 2
(C) be increased by a factor of 4
(D) be increased by a factor of 8
C
The half-life for the first order conversion of cyclobutene to ethylene,
C4H8 (g) --> 2C2H4 (g)
is 22.7 s at a particular temperature. How many seconds are needed for the partial pressure of cyclobutane to decrease from 100 mmHg to 10 mmHg?
(A) 0.101 s
(B) 52.0 s
(C) 75.5 s
(D) 5233 s
A
The half-life for the first-order radioactive decay of 32P is 14.3 days. How many days would be required for a sample of a radio pharmaceutical containing 32P to decrease to 20.0% of its initial activity?
(A) 33.0 d
(B) 49.2 d
(C) 71.0 d
(D) 286 d
D
Plots are shown for the reaction N02 (g) --> NO (g) + 1/2 O2 (g)
What is the rate law for the reaction?
(A) rate = k
(B) rate = k x 1/[NO2]
(C) rate = k[NO2]
(D) rate = k[NO2]^2
![<p>Plots are shown for the reaction N02 (g) --> NO (g) + 1/2 O2 (g)</p><p>What is the rate law for the reaction?</p><p>(A) rate = k</p><p>(B) rate = k x 1/[NO2]</p><p>(C) rate = k[NO2]</p><p>(D) rate = k[NO2]^2</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ca3003cb-c80a-410f-a126-26b4e33e613e.png)
A
What changes when a catalyst is added to the reaction described by this energy diagram?
(A) I and II
(B) I and III
(C) I only
(D) III only
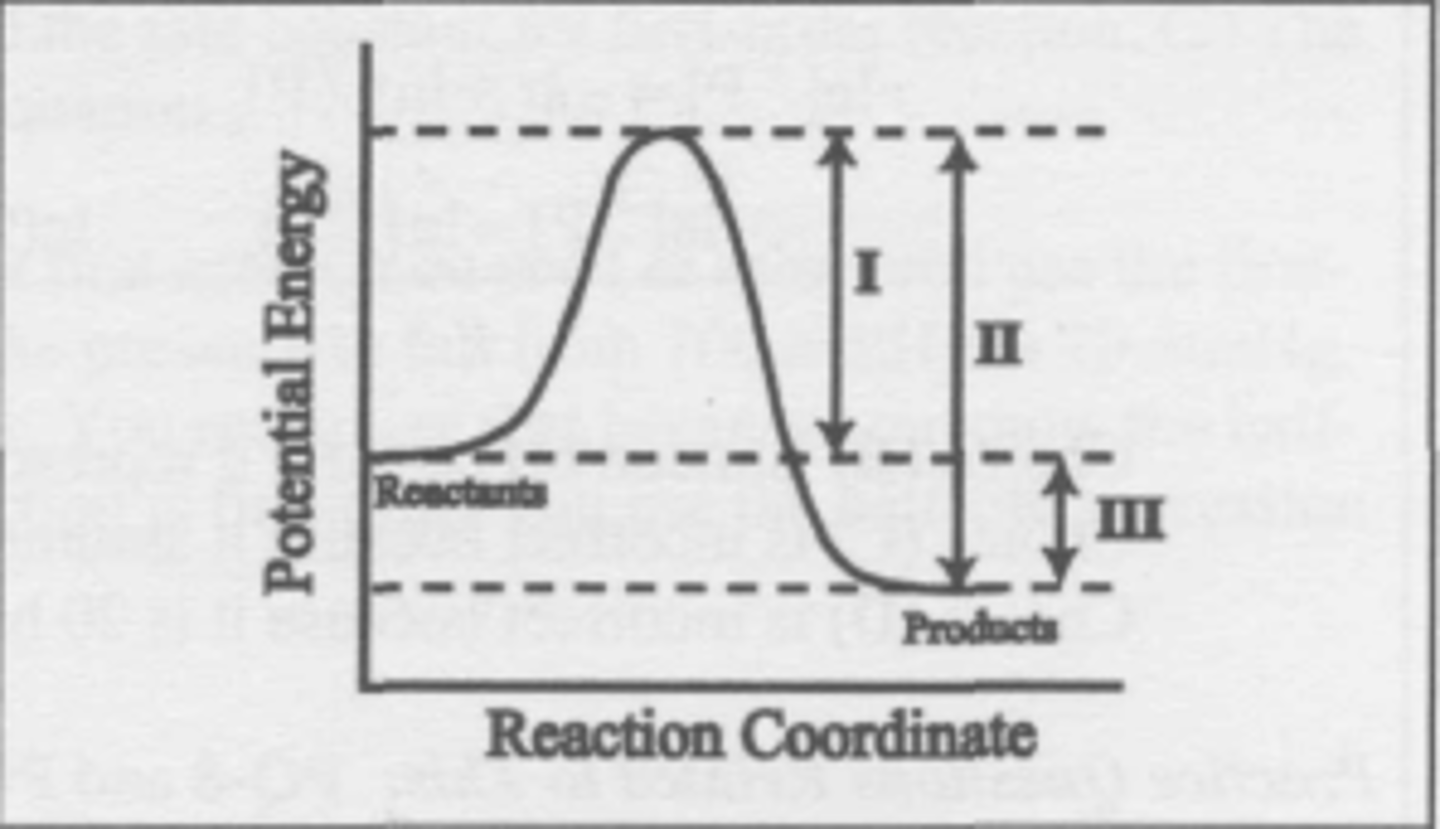
C
Which statement regarding chemical reactions is true according to collision theory?
(A) All molecular collisions result in chemical equations.
(B) Catalysts make individual collisions more effective, increasing reaction rates.
(C) Proper orientation of molecules is required for collision to result in chemical reactions.
(D) Increasing the temperature of a reaction decreases the kinetic energy of molecules, making collisions more effective.
B
The activation energy for a particular reaction is 83.1 kJ/mol. By what factor will the rate constant increase when the temperature is increased from 550.0 degrees C to 60.0 degrees C?
(A) 2.53
(B) 1.00
(C) 0.927
(D) 0.395
C
Consider the reaction.
2NO2 (g) + F2 (g) <--> 2 NO2F (g)
A proposed mechanism for the reaction is
NO2 + F2 <--> NO2F + F (slow)
NO2 + F <--> NO2F (fast)
What is the rate law for this mechanism?

A
Consider this equilibrium:
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) <--> 2SO3 (g)
The forward reaction is proceeding at a certain rate at some temperature and pressure. When the pressure is increased, what might we expect for the forward reaction?
(A) a greater rate of reaction and a greater yield of SO3 at equilibrium
(B) a greater rate of reaction and a same yield of SO3 at equilibrium
(C) a lesser rate of reaction and a smaller yield of SO3 at equilibrium
(D) a lesser rate of reaction and a greater yield of SO3 at equilibrium
A
What is the equilibrium expression for this reaction?
Ni(CO)4 (g) <--> Ni (s) + 4CO (g)
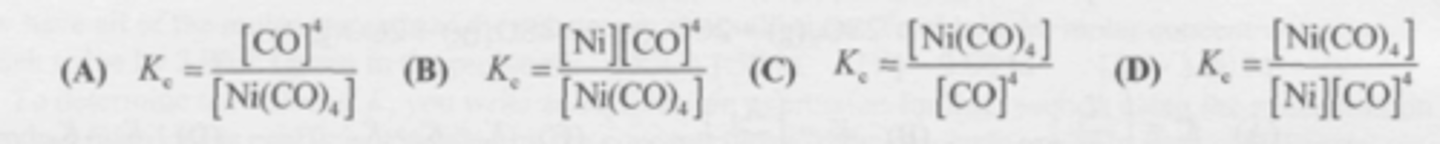
C
Given the reaction and equilibrium constant:
2SO3 (g) <--> 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Ke = 2.3 x 10^-7
What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction at the same temperature?
SO3 (g) <--> SO2 (g) + 1/2 O2 (g)
Ke = ?
(A) 1.2 x 10^-7
(B) 4.6 x 10^-7
(C) 4.8 x 10^-4
(D) 4.3 x 10^6
A
Consider the equilibrium reactions:
K1
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) <--> 2SO3 (g)
K2
2CO (g) + O2 (g) <--> 2CO2 (g)
What is the equilibrium constant, K, for this reaction?
2SO2 (g) + 2CO2 (g) <--> 2SO3 (g) + 2CO (g)

B
Consider the reaction:
X2 (g) + 2Y(g) <--> 2Z (g).
12.00 moles of Z are placed in an evacuated 2.00-liter flask. After the reactants and products reach equilibrium, the flask contains 6.00 moles of Y.
What is the equilibrium constant, K, for the reaction?
(A) 0.333
(B) 0.667
(C) 1.50
(D) 3.00
A
Phosgene decomposes into carbon monoxide and elemental chlorine. If the initial concentration of COCl2 (g) is 0.50 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of CO (g)?
COCl2 (g) <--> CO (g) + Cl2 (g)
Ke = 6.6 x 10^-8
(A) 1.8 x 10^-4 M
(B) 9.1 x 10^-5 M
(C) 1.7 x 10^-8 M
(D) 6.6 x 10^-8 M
C
BrCl (g) is in equilibrium with Br2 (g) and Cl2 (g) at 25 degrees C:
2BrCl (g) <--> Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
Kp = 0.130
Initially, in a closed container at 25 degrees C, BrCl (g) has a partial pressure of 0.400 atm and Br2 (g) and Cl2 (g) each have partial pressures of 0.800 atm. What is the partial pressure of BrCl (g) once the system reaches equilibrium?
(A) 0.419 atm
(B) 0.781 atm
(C) 1.16 atm
(D) 1.21 atm
B
Which will drive the equlibrium to form more Cu (s)?
(A) remove CO (g)
(B) remove CO2 (g)
(C) add a catalyst
(D) increase the volume of the container
B
Which set represents a conjugate acid/base pair?
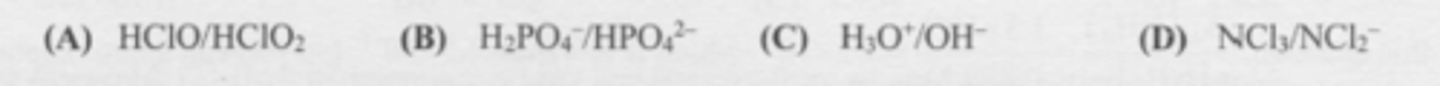
C
What is the pH of a 0.820 M aqueous NH3 solution?
Kb (NH3) = 1.8 x 10^-5
(A) 2.42
(B) 9.25
(C) 11.58
(D) 13.91
C
Which acid is the weakest in aqueous solution?
(A) acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5)
(B) formic acid (Ka = 1.8 x 10^-4)
(C) hydrocyanic acid (Ka = 6.2 x 10^-10)
(D) nitrous acid (Ka = 4.5 x 10^-4)
A
Which anion is the most basic?

D
What is Kb of F-?
Ka of HF is 6.8 x 10^-4
(A) 6.8 x 10^10
(B) 1.5 x 10^3
(C) 6.8 x 10^-4
(D) 1.5 x 10^-11
A
Which substance will dissolve in water to produce an acidic solution?
(A) FeCl3
(B) Na2O
(C) NAC2H3O2
(D) NH3
C
An acetate buffer contains equal volumes of 0.35 M HC2H3O2
pKa = 4.74
and 0.55 M NaC2H3O2.
What is the pH of the buffer?
(A) 4.54
(B) 4.74
(C) 4.94
(D) 7.00
B
What volume (in mL) of 0.150 M NaOH (aq) is required to neutralize 25.0 mL of 0.100 M H2SO4 (aq)?
(A) 16.7 mL
(B) 33.3 mL
(C) 66.7 mL
(D) 75.0 mL
C
What is the Ksp expression for MgCO3 in water?

C
Given the two reactions:
Cr(OH)3 (s) <--> Cr^3+ (aq) + 3OH^- (aq)
Ksp = 1.6 x 10^-30
Cr^3+ (aq) + 4OH^- (aq) <--> [Cr(OH)4]^- (aq)
Kf = 8.0 x 10^29
What is the value of K for the reaction?
Cr(OH)3 (s) + OH^- (aq) <--> [Cr(OH)4]^- (aq)
(A) -8 x 10^29
(B) 2.0 x 10^-60
(C) 1.3 x 10^0
(D) 5.0 x 10^59
D
What is the solubility product constant, Ksp, of Mg(OH)2 if its molar solubility in water is 1.6 x 10^-4 mol/L?
(A) 2.6 x 10^-8
(B) 1.6 x 10^-11
(C) 1.0 x 10^-12
(D) 4.1 x 10^-12
B
Which compound has the highest molar solubility?
(A) AgI, Ksp = 8.52 x 10^-17
(B) BaCO3, Ksp = 2.58 x 10^-9
(C) Fe(OH)3, Ksp = 2.79 x 10^-39
(D) ZnS, Ksp = 3.00 x 10^-23
D
A solution contains 0.002 M Pb^2+ and 0.002 M ag^+. What happens when NaCl (s) is added to bring the chloride ion concentration to 0.01 M?
Ksp PbCl2 = 1.2 x 10^-5
Ksp AgCl = 1.8 x 10^-10
(A) Neither PbCl2 nor AgCl will precipitate.
(B) Both PbCl2 and AgCl precipitate.
(C) Only PbCl2 precipitates.
(D) Only AgCl precipitates.
C
A sample of "hard" water contains about 2.0 x 10^-2 mol of Ca^2+ ions per liter. What is the maximum concentration of fluoride ion that could be present in hard water? Assume fluoride is the only anion present that will precipitate calcium ion.
Ksp of CaF2 (s) at 25 degrees C = 4.0 x 10^-11
(A) 2.0 x 10^-9 M
(B) 2.2 x 10^-5 M
(C) 4.4 x 10^-5 M
(D) 2.0 x 10^-2 M
D
What will change the value of Ksp for silver azide (AgN3)?
(A) Adding water to the solution.
(B) Adding silver ions to the solution.
(C) Removing azide ions from the solution.
(D) Increasing the temperature of the solution.
A
When comparing Q and Ksp of an unsaturated solution, _______.
(A) Q < Ksp
(B) Q = Ksp
(C) Q > Ksp
(D) Q = Ksp = 0
A
Of the four listed compounds, three have correct values for molar entropy, S`, associated with them. For which species is the entropy value incorrect at 298 K?
(A) Ca (s) // S` = 202
(B) Br2 (l) // S` = 152
(C) CO2 (g) // S` = 214
(D) AlCl3 (s) // S` = 109
C
Which change is likely to be accompanied by an increase in entropy?
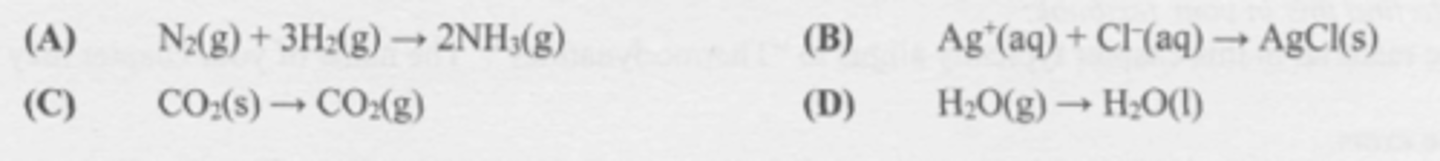
A
For this reaction at 25 degrees C,
Delta H` = -184 kJ/mol
Delta S` = -236 J/mol K.
CH3COCH3 (g) + 4Oz (g) --> 3CO2 (g) + 3H2O (l)
What is the value of Delta G` for this reaction?
(A) -1784 kJ/mol
(B) -1848 kJ/mol
(C) -1924 kJ/mol
(D) 68500 kJ/mol
D
When NH4NO3 dissolves in water, the temperature of the solution decreases. What describes the enthalpy and entropy changes of the system and which change drives the process?
(A) Delta H = (-) and Delta S = (-) and the process is driven by the enthalpy change.
(B) Delta H = (-) and Delta S = (+) and the process is driven by the enthalpy change.
(C) Delta H = (+) and Delta S = (-) and the process is driven by the entropy change.
(D) Delta H = (+) and Delta S = (+) and the process is driven by the entropy change.
C
What is the free energy change for the formation of one mole of ammonia from its elements under standard conditions?
2NH3 (g) --> N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Delta G` = 33.0 kJ/mol
(A) -66.0 kJ/mol
(B) -33.0 kJ/mol
(C) -16.5 kJ/mol
(D) 66 kJ/mol
B
Calculate the standard Gibbs free energy change at 298 K for the reaction:
FeO4 (s) + 4CO (g) <--> 3Fe (s) + 4CO2 (g)
Delta G` CO (g) = -137.2 kJ/mol
Delta G` CO2 (g) = -394.4 kJ/mol
Delta G` Fe3O4 (s) = -1014 kJ/mol
(A) -757 kJ/mol
(B) -14.8 kJ/mol
(C) 14.8 kJ/mol
(D) 757 kJ/mol
B
An equilibrium mixture of I2 (g), Cl2 (g), and ICl (g) at 298 K has partial pressures oof 0.0100 atm, 0.0100 atm, and 0.0900 atm, respectively. What is Delta G` at 298 K for the reaction:
I2 (g) + Cl2 (g) <--> 2ICl (g)
(A) -16.9 kJ/mol
(B) -10.9 kJ/mol
(C) 10.9 kJ/mol
(D) 16.9 kJ/mol
B
Which statement is correct for the reaction below under standard conditions?
2Cl2 (g) + 2NO (g) --> N2 (g) + 2Cl2O (g)
Delta H` = -22.0 kJ/mol
(A) The reaction is spontaneous at all temperatures.
(B) The reaction is spontaneous only at low temperatures.
(C) The reaction is spontaneous only at high temperatures.
(D) The reaction is not spontaneous at any temperature.
C
For a reaction where K > 1 at all temperatures, which statement(s) must be true?
(A) Only I
(B) Only III
(C) Both I and II
(D) Both I and III
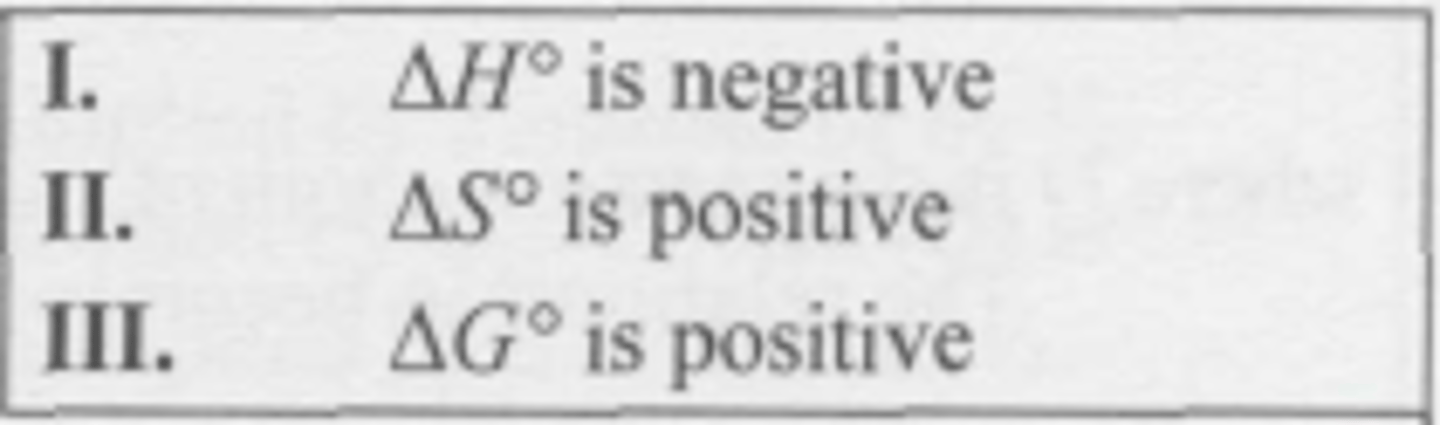
C
What is the coefficient for the nitrate ion (NO2^-) when the redox reaction is balanced in basic solution?
MnO4^- (aq) + NO2^- (aq) -> MnO2 (s) + NO3^- (aq)
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
C
A spontaneous electrochemical cell is set up as shown. Which statement is true?
Sn^(2+) + 2e^(-) --> Sn
E` = -0.136 V
Fe^(3+) + 3e^(-) --> Fe
E` = -0.036 V
(A) The tin electrode is the cathode and electrons move from left to right.
(B) The tin electrode is the cathode and electrons move from right to left.
(C) The tin electrode is the anode and electrons move from left to right.
(D) The tin electrode is the anode and electrons move from right to left.
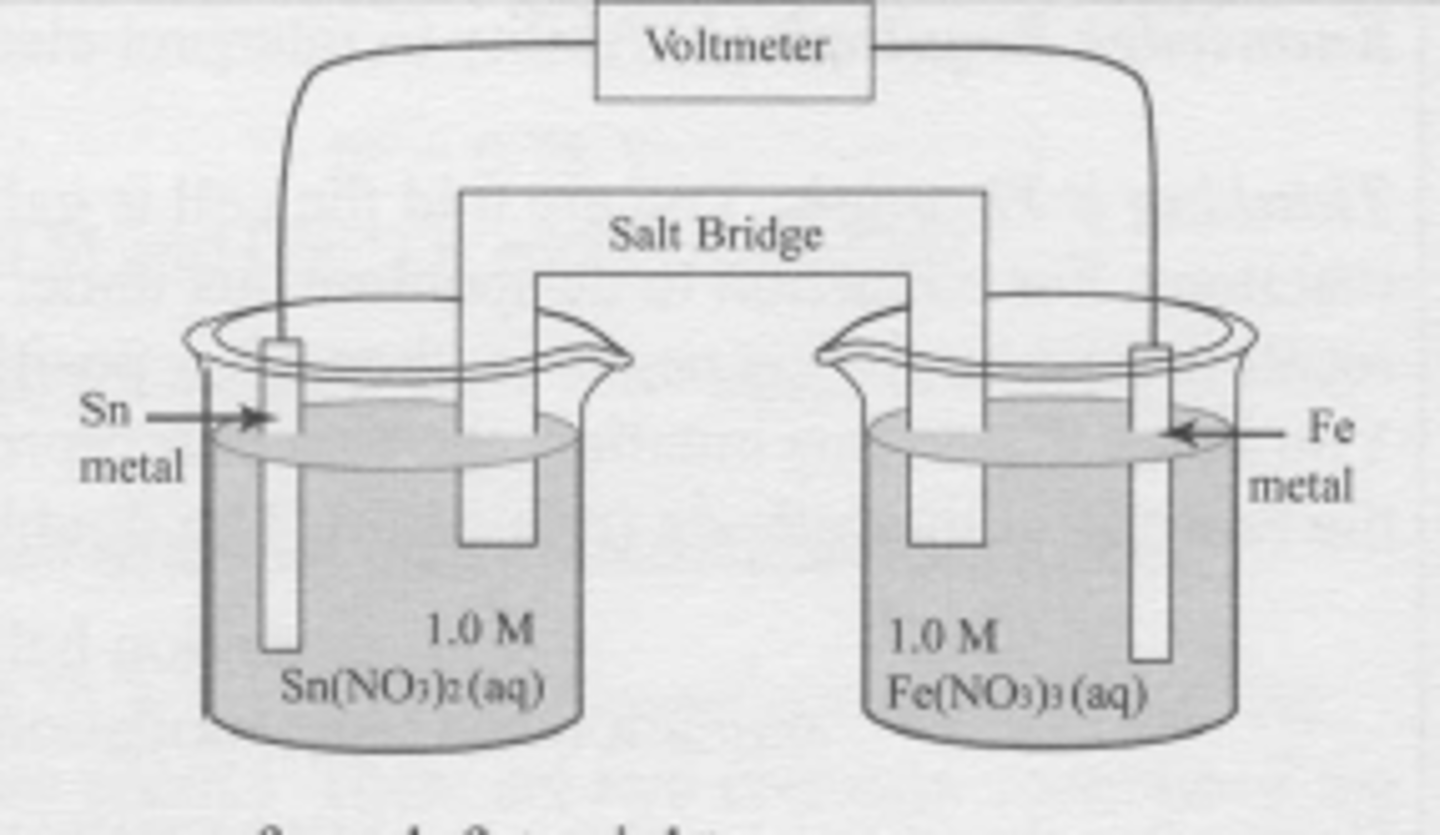
B
Given the standard reduction potentials at 25 degrees C, what is the standard cell potential of a
Ni (s) | Ni^(2+) (aq) || Ag^(+) (aq) | Ag (s) galvanic cell?
(A) 0.56 V
(B) 1.02 V
(C) 1.35 V
(D) 1.81 V

B
An oxidation-reduction reaction in which 3 electrons are transferred has a Delta G` = 18.55 kJ/mol at 25 degrees C. What is the value of E`?
(A) 0.192 V
(B) -0.064 V
(C) -0.192 V
(D) -0.577 V
B
Consider the reaction.
Cu^(2+) (aq) + Fe (s) --> Cu (s) + Fe^(2+) (aq)
E` = 0.78 V
What is the value of E when [Cu^(2+)] is equal to 0.040 M and [Fe^(2+)] is equal to 0.40 M?
(A) 0.72 V
(B) 0.75 V
(C) 0.81 V
(D) 0.84 V
A
What half-reaction occurs at the annode during the electrolysis of molten sodium iodide?
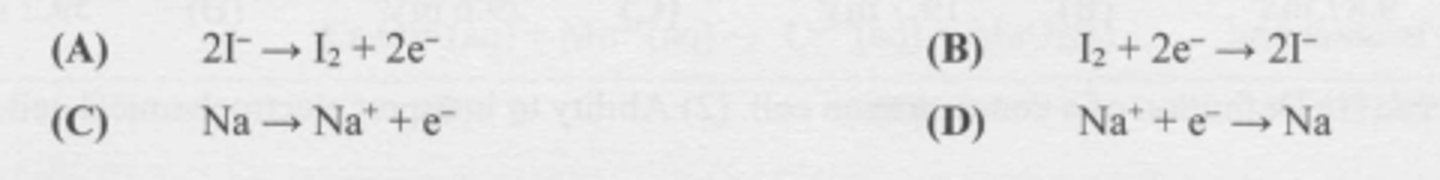
B
How many minutes are required to plate 2.08 g of copper at a constant flow of 1.26 A?
Cu^(2+) (aq) + 2e^(-) --> Cu (s)
Molar Mass Cu = 63.5 g/mol
1 faraday (F) = 96500 C
(A) 41.8 min
(B) 83.6 min
(C) 133 min
(D) 5016 min
B
For the concentration cell
Fe (s) | Fe^(3+) (aq), 0.100 M || Fe^(3+), 1.00 M | Fe (s)
what is Ecell at 25 degrees C (in mV)?
(A) 9.87 mV
(B) 19.7 mV
(C) 29.6 mV
(D) 59.2 mV
B
What is the missing particle in the nuclear equation?
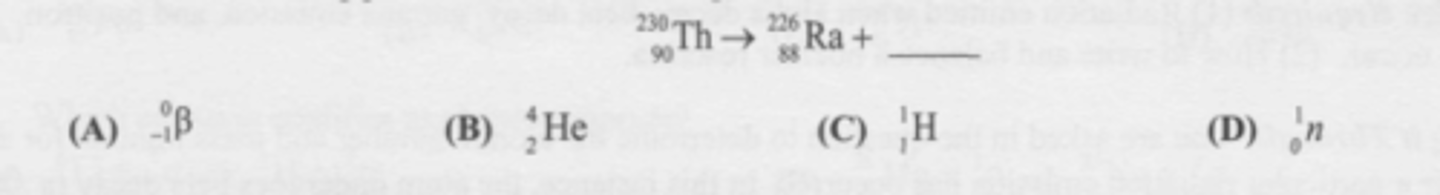
C

A
An atom of the element of atomic number 53 and mass number 131 undergoes beta decay. The residual atom after this change has an atomic number of _____ and a mass number of _____.
(A) 54, 131
(B) 53, 131
(C) 53, 131
(D) 51, 127