bioe 3
5.0(3)Studied by 44 people
Card Sorting
1/165
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:52 AM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
1
New cards
4 kinds of intellectual property
trademarks
copyrights
trade secrets
patents
copyrights
trade secrets
patents
2
New cards
what is a trademark
any word, name, symbol, or device or any combo thereof and used to identify goods and distinguish them from those manufactured and sold by others ex: google, apple
3
New cards
what is a copyright?
an exclusive legal right to print, publish, perform, film, or record material
4
New cards
what is a trade secret?
secret device or technique used especially in a trade
5
New cards
what is a patent?
a patent is a claim(s) of invention.
it permits its owner to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention
it permits its owner to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention
6
New cards
types of patents
utility patent
design patent
plant patent
provisional patent
design patent
plant patent
provisional patent
7
New cards
utility patent
a utility patent is obtained for processes
(chemical, mechanical, or electrical procedures), machines, articles of manufacturing, and compositions of matter.
(chemical, mechanical, or electrical procedures), machines, articles of manufacturing, and compositions of matter.
8
New cards
design patent
is obtained for an invention of a new, original and ornamental design for an article of manufacture. Design patent protection extends only to an item’s appearance, not its functional aspects
9
New cards
plant patent
is granted for a distinct and new variety of a cultivated asexually reproduced plant.
10
New cards
provisional patent
contains a specification sufficient detail to allow one skilled in the art to practice the invention. A provisional is a preliminary action to provide the inventor 12 months to develop the full patent claims
11
New cards
process for patents (4 steps)
1) it must fall into one of the statutory classes:
processes, machines, manufactures (objects made by humans or machines), compositions of matter
2) it must be useful
3) it must be novel
4) it must not be obvious to a person w/ ordinary skill in the art to which the subject matter pertains
processes, machines, manufactures (objects made by humans or machines), compositions of matter
2) it must be useful
3) it must be novel
4) it must not be obvious to a person w/ ordinary skill in the art to which the subject matter pertains
12
New cards
what goes into a patent?
claims (from uspto.gov)
13
New cards
two types of claims for patents
independent claims and dependent claims
14
New cards
independent claims
is a standalone claim that contains all the limitations necessary to define an invention.
15
New cards
dependent claims
must refer to a claim previously set forth and must further limit that claim.
16
New cards
who can file a patent application?
must be filed in the name of the inventor(s). However, patents can be assigned to others.
~ assignee
~ assignee
17
New cards
assignee
the legal owner of a patent (unless you’re an entrepreneur, usually your employer
18
New cards
who is an inventor
an inventor must take creative contributions to the invention
19
New cards
if you want to patent... (do's)
~ maintain a lab notebook
~ make progress on "completing" the invention
~ seek professional assistance
~ make progress on "completing" the invention
~ seek professional assistance
20
New cards
if you want to patent... (dont)
~ publish an article that would enable others to practice the invention; you have 1 yr to file an application after an article has been published
~ sell or offer for sell anything based upon the invention or accept a purchase order
~ explain your invention to anyone without a confidentiality agreement ( Non-disclosure agreement)
~ sell or offer for sell anything based upon the invention or accept a purchase order
~ explain your invention to anyone without a confidentiality agreement ( Non-disclosure agreement)
21
New cards
how long do you have protection?
20 years from the earliest filing to which the patent claims 'priority'
22
New cards
'priority'
sometimes one files ‘follow-on’ or derivative patents, these usually expand or specialize the originals claims, therefore, they usually link back to the original patent in terms of their protection and lifespan
23
New cards
filing rules
~ US patent rights have historically been granted on the basis of ‘first to invent’
~ The US patent law has recently been updated and will be on a ‘first to file’ basis going forward, generally consistent with
international practice
~ The US patent law has recently been updated and will be on a ‘first to file’ basis going forward, generally consistent with
international practice
24
New cards
what is the value of intellectual property?
depends on how you utilize your patent protection
~ exclusion of others
~ give your business exclusivity
~ licensing rights to others for consideration
~ exclusion of others
~ give your business exclusivity
~ licensing rights to others for consideration
25
New cards
license
a legal document granting rights to intellectual property and/or material in exchange for good and valuable consideration
26
New cards
rights to the invention
rights can be restricted to:
~ type of license
~ field of use
~ a period of time
~ a territory
~ type of license
~ field of use
~ a period of time
~ a territory
27
New cards
what goes into a license?
a royalty and a grant of the right to prohibit others from practicing the technology
28
New cards
how does IP impact me as a researcher in a large company
researcher in a large company
~ May be called upon to build a better mouse trap. (i.e. find a way around a competitors patent)
~ Named as inventor but all rights assigned to the company as a condition of employment
~ May be called upon to build a better mouse trap. (i.e. find a way around a competitors patent)
~ Named as inventor but all rights assigned to the company as a condition of employment
29
New cards
how does IP impact me as a product manager/ marketing
~ may work with all types of Intellectual Property in the marketing of a product
~ need to be aware of competitor's products that may infringe
~ need to be aware of competitor's products that may infringe
30
New cards
how does IP impact me as a an entrepreneur
~ excludes others
~ creates value
~ can be costly to protect
~ creates value
~ can be costly to protect
31
New cards
used for wound closure
sutures, tissue adhesives/ sealants
32
New cards
goals of wound closure (5)
• Accelerate healing and reduce scarring
• Reduce the opportunity for infection
• Restore mechanical strength to wounded tissue during healing
• Reduce blood loss-hemostasis
• Minimize the formation of adhesions -internal wound closure
• Reduce the opportunity for infection
• Restore mechanical strength to wounded tissue during healing
• Reduce blood loss-hemostasis
• Minimize the formation of adhesions -internal wound closure
33
New cards
general procedures (dermal)
• General wound cleaning
– PVP-iodine (betadine)
• Local anesthesia (sutures / staples-not required for most adhesives)
• Irrigation-sterile water or saline
• Debridement if necessary
– Remove foreign material
– Create sharp wound edges
– Can accelerate healing and improve cosmetic
outcome
• Approximate wound edges and close via
selected method
– PVP-iodine (betadine)
• Local anesthesia (sutures / staples-not required for most adhesives)
• Irrigation-sterile water or saline
• Debridement if necessary
– Remove foreign material
– Create sharp wound edges
– Can accelerate healing and improve cosmetic
outcome
• Approximate wound edges and close via
selected method
34
New cards
suture applications
• Closure of surgical incisions (dermal / internal)
• Securing medical devices to patient tissue (permanent implant)
• Re-connection of tissues separated by injury (permanent implant)
– tendon
– peripheral nerve
• Securing medical devices to patient tissue (permanent implant)
• Re-connection of tissues separated by injury (permanent implant)
– tendon
– peripheral nerve
35
New cards
2 types of suture materials
absorbable and non-absorbable
36
New cards
absorbable
for wounds, 2-3 months
~ cagut: (isolated from sheep or bovine intestine) commonly treated with chromium trioxide-reduces absorption rate 40 to 75 days, reduces tissue reaction
~ polyglycolic acid (PGA) and poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA)
~ cagut: (isolated from sheep or bovine intestine) commonly treated with chromium trioxide-reduces absorption rate 40 to 75 days, reduces tissue reaction
~ polyglycolic acid (PGA) and poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA)
37
New cards
Non-absorbable
implants and wounds
~ cotton, silk, PET, polypropylene
~ cotton, silk, PET, polypropylene
38
New cards
hydrogel
~ cross-linked network of water soluble polymers
~ once cross-linked MW essentially goes to infinity
~ due to cross-linking the hydrogel is insoluble
fun fact
~ once cross-linked MW essentially goes to infinity
~ due to cross-linking the hydrogel is insoluble
fun fact
39
New cards
why are hydrogels good?
the human body is 70% water and the high water content of hydrogels provides mech properties similar to many soft tissues
40
New cards
primary applications of hydrogels
contact lens, intraocular lens, tissue sealants, tissue engineering
41
New cards
making hydrogels
cross-linking mechanisms
~ physical, ionic, covalent
~ step growth
~ free radical polymerization
~ physical, ionic, covalent
~ step growth
~ free radical polymerization
42
New cards
adhesives
A substance capable of holding materials together in a functional manner
43
New cards
sealant
A material applied to a joint in paste or liquid form that hardens or cures in place, forming a barrier against gas or liquid entry-particularly blood leakage
44
New cards
purpose of surgical adhesives/ sealants
• Rapid wound closure
• Improved prevention of blood loss
• Minimizing deformation of tissue (reduce scarring)
• Closure of mechanically weak tissues that are difficult to suture (liver, kidney, spleen)
• Improved prevention of blood loss
• Minimizing deformation of tissue (reduce scarring)
• Closure of mechanically weak tissues that are difficult to suture (liver, kidney, spleen)
45
New cards
in situ forming
liquid to solid transformation occurs during application (in situ
polymerization of liquid monomers)
polymerization of liquid monomers)
46
New cards
cure time
how long liquid-solid transformation requires
47
New cards
shelf life
how long can it be stably stored as a
monomer without premature polymerization
monomer without premature polymerization
48
New cards
key characteristics of surgical adhesives/ sealants (6)
~ in situ forming
~ cure time
~ shelf life
~ tissue bond strength
~ flexible - minimize irritation
~ easily sterilized
~ cure time
~ shelf life
~ tissue bond strength
~ flexible - minimize irritation
~ easily sterilized
49
New cards
failure mechanisms
adhesive failure, cohesive failure, substrate failure
50
New cards
adhesive failure
failure occurs at the tissue/material interface
51
New cards
cohesive failure
failure occurs within the substance of the adhesive
52
New cards
substrate failure
failure of the tissue substrate
53
New cards
type of adhesive
cyanoacrylate
54
New cards
cyanoacrylate
~ superglue and other chem variations
~ degradation is proportional to length of chain
~ rapid degradation is toxic
~ octyl cyanoacrylates are approved for topical use in humans
~ degradation is proportional to length of chain
~ rapid degradation is toxic
~ octyl cyanoacrylates are approved for topical use in humans
55
New cards
cyanoacrylate polymerization
initiated by water and amine groups present on proteins in the tissue
~ bc the tissue initiates the polymerization, it is chemically bonded to the adhesive, providing exceptional bond strength
~ bc the tissue initiates the polymerization, it is chemically bonded to the adhesive, providing exceptional bond strength
56
New cards
application of dermal cyanoacrylate adhesive
• Use proper good wound care practices
• Appose wound edges tightly
• DO NOT GET ADHESIVE IN THE WOUND!!!
• Appose wound edges tightly
• DO NOT GET ADHESIVE IN THE WOUND!!!
57
New cards
5 types of sealants (all hydrogels)
– Fibrin glue
– BioGlue
– ProGel
– DuraSeal
– FocalSeal
– BioGlue
– ProGel
– DuraSeal
– FocalSeal
58
New cards
clinical considerations
• Source of proteins-human
• Possible disease transmission (viruses)
• Such risk is considered minuscule
• Proteins are purified from pooled batches of human blood
• Two commercial products
– Hemaseel-Hemacure
– Tisseel-Baxter Healthcare
• Possible disease transmission (viruses)
• Such risk is considered minuscule
• Proteins are purified from pooled batches of human blood
• Two commercial products
– Hemaseel-Hemacure
– Tisseel-Baxter Healthcare
59
New cards
bioglue
• Composed of two solutions-bovine serum albumin (BSA) and glutaraldehyde
** challenge with using BSA clinically is that it is xenogenic
intended use: sealing suture lines in vascular implants
** challenge with using BSA clinically is that it is xenogenic
intended use: sealing suture lines in vascular implants
60
New cards
challenge of crosslinking chemistry for bioglue
cures too fast, glutaraldehyde is toxic
61
New cards
double barrel syringe
allows two highly reactive solutions to be stored separately and stably in one device
62
New cards
static mixer
the coiled piece of metal in the syringe tip-allows mixing of two solutions without agitation
63
New cards
xeno-free
does not contain any animal-derived products
64
New cards
in the US, total cardiovascular disease mortality is what rank in leading cause of death
#1
65
New cards
how many americans die each day from cardiovascular disease (on average)
2,500
66
New cards
what does the heart do
~ pump using transport medium (blood)
~ propels substances to body cells (oxygen, nutrients, wastes, etc)
~ propels substances to body cells (oxygen, nutrients, wastes, etc)
67
New cards
circulatory system is made up of these 2 sub circuits
systemic circuit and pulmonary circuit
68
New cards
systemic circuit
– Blood vessels that carry the functional blood supply to and from all body tissues
– Left side of the heart
– Left side of the heart
69
New cards
pulmonary circuit
- Blood vessels carry blood to and from lungs
- Right side of the heart
- Right side of the heart
70
New cards
capillaries
-microscopically small blood vessels between arteries and veins where oxygen diffuses to surrounding tissue
71
New cards
blood-oxygen transport
~ red blood cells transport hemoglobin
• Hemoglobin reversibly binds oxygen
• Lungs-high levels of oxygen, oxygen binds to hemoglobin
• Capillaries-low levels of oxygen, oxygen dissociates from
hemoglobin and diffuses into surrounding tissue
• Hemoglobin reversibly binds oxygen
• Lungs-high levels of oxygen, oxygen binds to hemoglobin
• Capillaries-low levels of oxygen, oxygen dissociates from
hemoglobin and diffuses into surrounding tissue
72
New cards
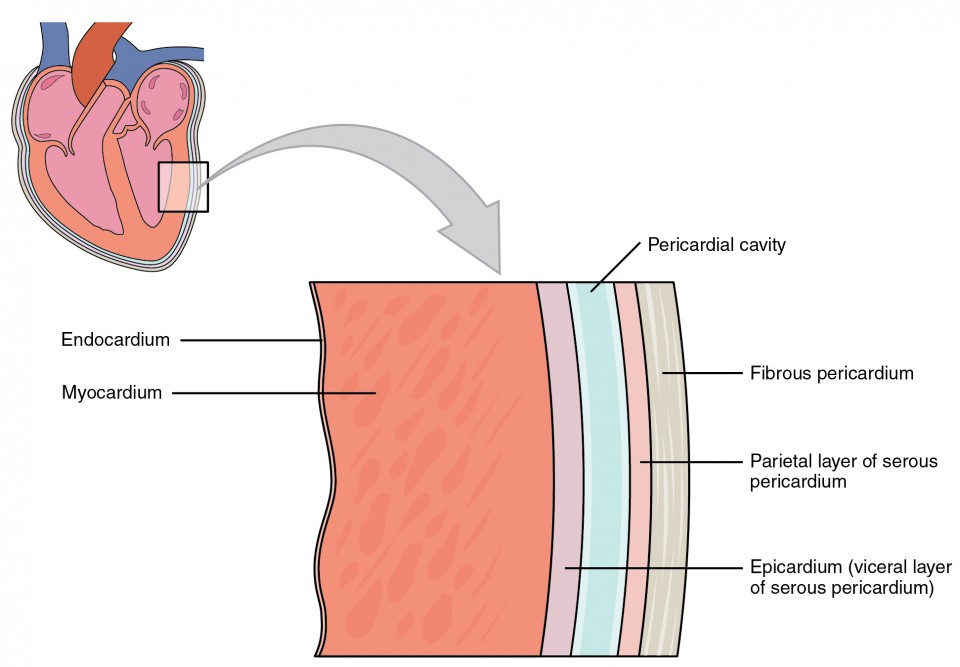
structure of the heart wall
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium (together they make up the heart wall)
73
New cards
endocardium-endothelial cells
provide a “perfect” blood contacting surface that does not initiate coagulation
74
New cards
myocardium
composed of cardiac myoblasts (cardiomyocytes)
75
New cards
cardiomyocytes
- contraction and relaxation
76
New cards
chambers of the heart
4 chambers
~ 2 atriums
~ 2 ventricles
~ 2 atriums
~ 2 ventricles
77
New cards
atriums
– Receiving chambers
– Relatively small, thin-walled chambers
– Blood only pushed to ventricles
– Relatively small, thin-walled chambers
– Blood only pushed to ventricles
78
New cards
ventricles
- Discharging chambers
- Make up most volume of the heart
- Make up most volume of the heart
79
New cards
the 4 chambers and their functions
- Right atrium (Blood from body)
- Right ventricle (Blood to lungs via the pulmonary artery)
- Left atrium (Blood from lungs via the pulmonary vein)
- Left ventricle (Blood to body via the aorta) – walls 3X’s as
thick as right ventricle
- Right ventricle (Blood to lungs via the pulmonary artery)
- Left atrium (Blood from lungs via the pulmonary vein)
- Left ventricle (Blood to body via the aorta) – walls 3X’s as
thick as right ventricle
80
New cards
cardiac cycle (long answer)
~ pumping action in a rhythmic sequence
~ atrial diastole - the atrium is relaxed, allowing blood from the body/lungs to fill the atrium
~ as the atria fill with blood, the pressure rises, forcing the tricuspid and mitral valves to open -> this allows blood to fill diastole ventricles
~ then the atria contracts (systole), filling the ventricles to capacity ** the atrial kick accounts for 30% of cardiac output
~ pressure in the atria and ventricles equalize and the tricuspid and mitral valves begin to close
~ then the ventricles contract (systole) causing ventricular pressure to rise and the aortic and pulmonic valves to open
~ atrial diastole - the atrium is relaxed, allowing blood from the body/lungs to fill the atrium
~ as the atria fill with blood, the pressure rises, forcing the tricuspid and mitral valves to open -> this allows blood to fill diastole ventricles
~ then the atria contracts (systole), filling the ventricles to capacity ** the atrial kick accounts for 30% of cardiac output
~ pressure in the atria and ventricles equalize and the tricuspid and mitral valves begin to close
~ then the ventricles contract (systole) causing ventricular pressure to rise and the aortic and pulmonic valves to open
81
New cards
blood pressure
systolic blood pressure over diastolic bp
ex: bp is 120 over 80
ex: bp is 120 over 80
82
New cards
systolic pressure
Maximum pressure achieved during ventricular contraction
83
New cards
diastolic pressure
Lowest pressure that remains in the arteries before the next ventricular contraction
84
New cards
heart valves - function
~ blood flow only occurs in 1 direction
~ valves direct blood flow and prevent back flow
~ valves direct blood flow and prevent back flow
85
New cards
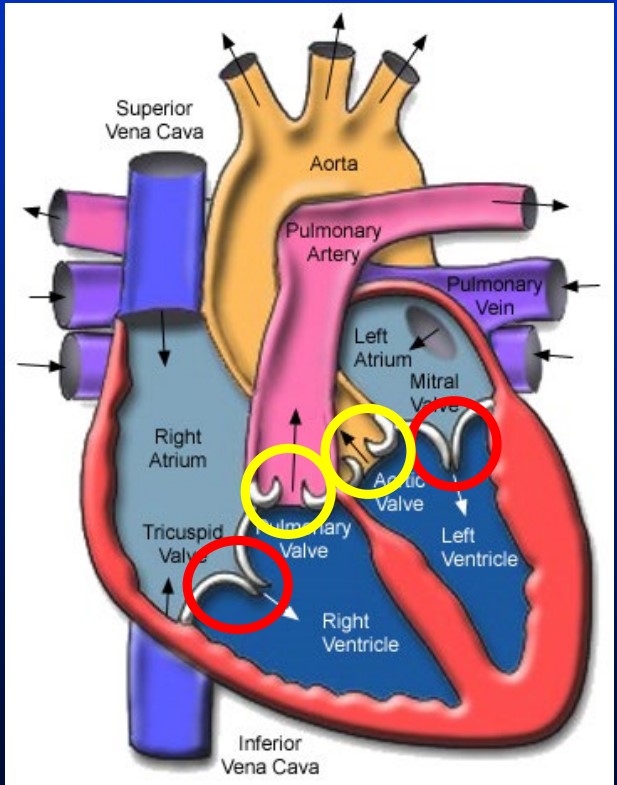
valve locations
• Atrioventricular valves
• Semilunar valves
• Semilunar valves
86
New cards
2 Atrioventricular valves
tricuspid and mitral
87
New cards
2 semilunar valves
aortic and pulmonary
88
New cards
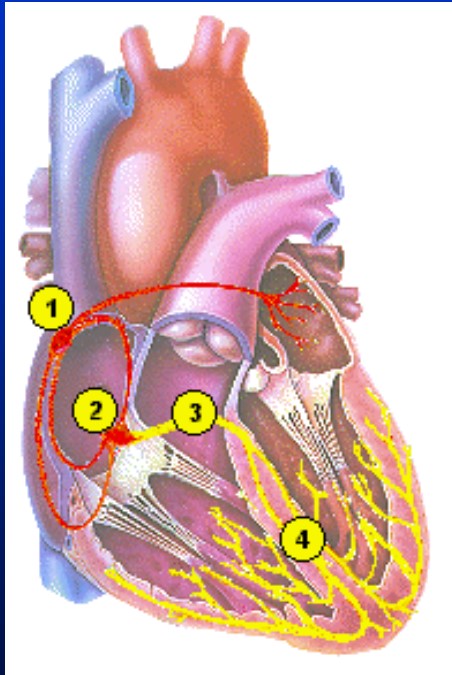
electrical regulation of the heart
• A. Autorhythmicity
• B. Pathway of stimulation
– 1. Sinoatrial node
– 2. Atrioventricular node
– 3. Bundle of His
– 4. Purkinje fibers
• B. Pathway of stimulation
– 1. Sinoatrial node
– 2. Atrioventricular node
– 3. Bundle of His
– 4. Purkinje fibers
89
New cards
SA node
signal generator
~ Basal heart rate is influenced by the nervous and endocrine systems
~ Basal heart rate is influenced by the nervous and endocrine systems
90
New cards
resting membrane potential
Voltage across the cell membrane due to asymmetrical distribution of cations produced by Na/K pump
91
New cards
depolarization
transient reversal of resting membrane potential due to opening of membrane ion channels
** depolarization of muscle triggers contraction **
** depolarization of muscle triggers contraction **
92
New cards
cardiac action potential
a brief change in voltage (membrane potential) across the cell membrane of heart cells
93
New cards
cardiac conduction
• SA nodes generates a periodic, automatic electrical impulse (action potential)
• Travels down the atrial intranodal and intraatrial pathways
• Slows at the AV node allowing the atria to contract and empty
• Travels through common AV bundle to Purkinje fibers causing ventricular contraction
• Travels down the atrial intranodal and intraatrial pathways
• Slows at the AV node allowing the atria to contract and empty
• Travels through common AV bundle to Purkinje fibers causing ventricular contraction
94
New cards
monitoring cardiac conduction
~ ECG or EKG - electrocardiogram
• Heart is in fluid
• Fluid transmits electrical activity from the source to the surface of body
• Electrodes placed on skin surface measure direction and magnitude of current flow
• EKG-2-dimensional representation of this electrical activity
• Heart is in fluid
• Fluid transmits electrical activity from the source to the surface of body
• Electrodes placed on skin surface measure direction and magnitude of current flow
• EKG-2-dimensional representation of this electrical activity
95
New cards
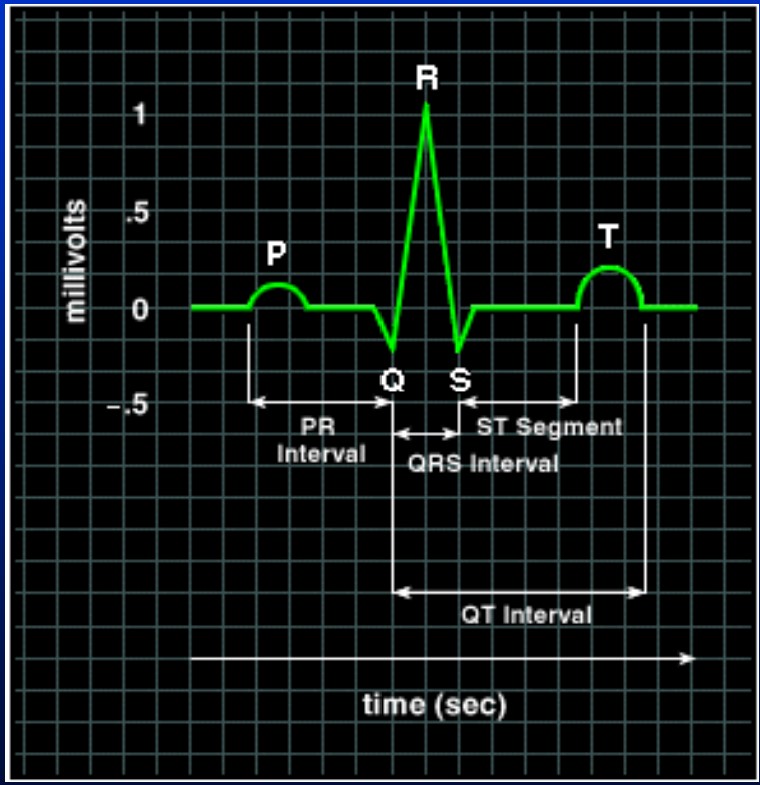
normal EKG (w/ pic)
P: atrial depolarization
P-R: SA to AV
QRS: ventricular depolarization
T: ventricular repolarization
P-R: SA to AV
QRS: ventricular depolarization
T: ventricular repolarization
96
New cards
what causes heart failure #sad
~ insufficient oxygen & nutrients are supplied (usually from a blockage/ occlusion)
~ hypoxia leads to cardiomyocyte death
~ repaired by fibroblasts and scar tissue
~ lack contractile properties of cardiomyocytes
~ decrease the mechanical function of the heart as a pump
~ hypoxia leads to cardiomyocyte death
~ repaired by fibroblasts and scar tissue
~ lack contractile properties of cardiomyocytes
~ decrease the mechanical function of the heart as a pump
97
New cards
heart failure (cause, symptoms, consequence)
~ root cause is vascular pathology
~ symptoms: heart attack (AKA myocardial infarction)
~ consequence: permanent damage to the cardiac muscle
~ symptoms: heart attack (AKA myocardial infarction)
~ consequence: permanent damage to the cardiac muscle
98
New cards
Cardiomyocytes
the muscle cells of the heart-are considered post-mitotic (incapable of cell division)
99
New cards
heart failure solutions for a partially damaged heart
prosthetic ventricles such as ventricular assist devices (VADs)
100
New cards
heart failure solutions for a severely damaged heart
~ transplant
~ prosthetic heart (temporary)
~ prosthetic heart (temporary)