fundamentals of neuroscience midterm #1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
neuroscience
study of the nervous system
aspects of human nature considered in neuroscience
curiosity, pain, pleasure, movement, reasoning, learning, memory, emotion, and madness
the society for neuroscience (SfN)
the largest professional society for neuroscientists, it’s official journal is the Journal of Neuroscience
BRAIN Initiative (Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies)
launched by the U.S. gov to revolutionize understanding of the human brain by developing new technologies to map and observe neural circuits
Human Brain Project
a European Union-funded research initative (2013-2023) that aimed to create a digital research infrastructure, know as EBRAINS, to accelerate understanding of the human brain, develop brain-inspired technology, and find new treatments for brain diseases
Brain/MINDS Initiative
Japan’s Brain Mapping by Integraded Neurotechnologies for Disease Studies, a project launched in 2014 to map brain circuits, focusing on marmosets to understand human disorders like dementia and depression
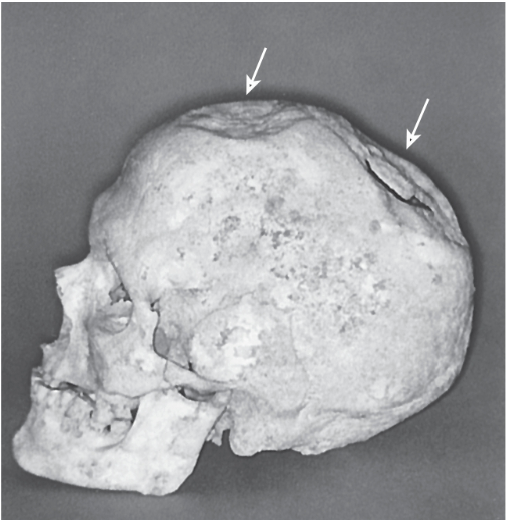
trepanation
an ancient surgical procedure involving drilling or scraping a hole through the human skull to expose the brain’s surface, there is evidence of this over 7000 years ago
ancient Egypt’s thoughts on neuroscience
became aware of many brain damage symptoms
said that “the heart is the seat of soul and memory” (not the head)
ancient Greece view of the brain
suggested a correlation between structure and function
Hippocrates said “the brain is involved in sensation and is the seat of intelligence”
Galen view of the brain (roman empire)
since the cerebrum is soft, it was associated with sensation
since the cerebellum is hard, it was associated with muscle control
ventricles were thought to be hollow cavities in the brain that allowed for fluid to flow and control different things
renaissance to 17th century view of the brain
the fluid-mechanical theory of brain function
Descarte proposed the philosophical mind-brain problem
fluid-mechanical theory of brain function
posits that fluids like cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and interstitial fluid (ISF) are crucial for brain health, acting as a transport system for nutrients, waste removal, and cushioning, with movement driven by pressure gradients an arterial pulsations, influencing everything from cognitive function to neurological diseases like hydrocephalus, dementia, and MS
Descartes
talked about the philosophical mind-brain problem
gray matter
brain tissue rich in neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons
white matter
myelinated nerve fibers (axons) that transmit signals between different brain regions
18th century view of the brain
gross anatomy detailed
bumps (gyri) and grooves (sulci and fissures)
suggested that different bumps may have different functions
19th century view of the brain
nerves were seen as wires there was a new understanding of electrical phenomena and that the nervous system can generate electricity
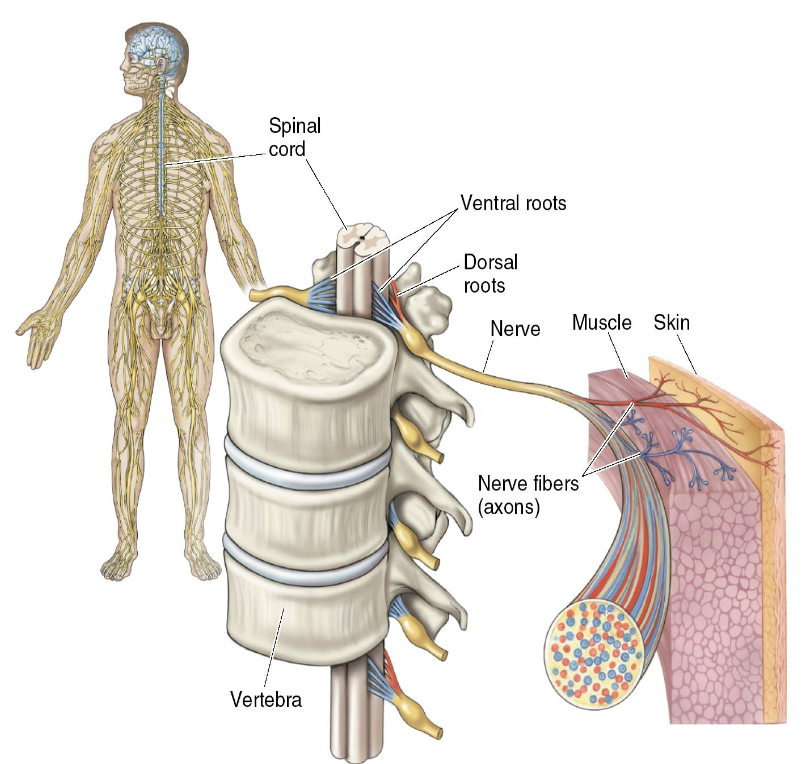
Bell and Magendie (19th century)
said that dorsal and ventral roots carry information in opposite directions
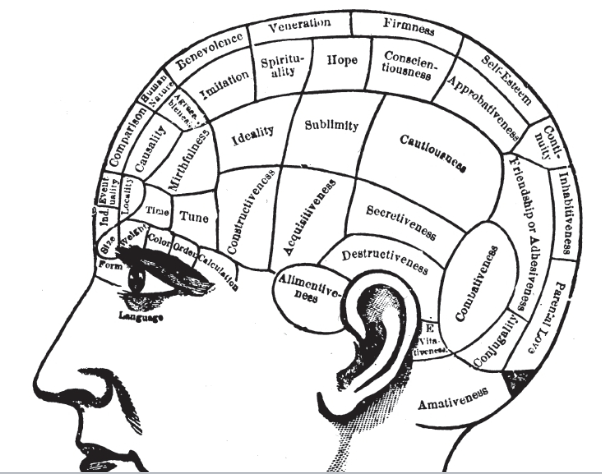
phrenology (19th century)
a popular 19th century pseudoscience claiming that bumps and contours on a person’s skull revealed their character, personality, and mental faculties, championed by Franz J. Gall
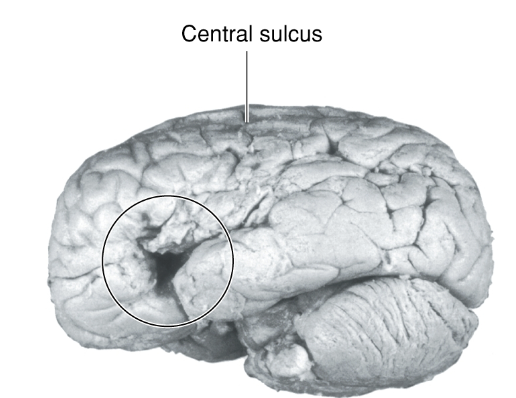
Paul Broca (19th century)
did a lot of work with discovering the localization of function in the brain (research in acquired damage to the from regions of the brain, such as Broca’s area/frontal lobe of the dominant hemisphere)
specifically found the brain region necessary for speech
Charles Darwin (19th century)
pioneered the idea of the evolution of the nervous system
his rationale for animal models was that they evolve from common ancestors and may have common mechanisms
neuron
the basic functional unit of the brain
levels of analysis
molecular neuroscience
cellular neuroscience
systems neuroscience
behavioral neuroscience
cognitive neuroscience (brain activity creates mind)
Alzheimer’s disease
a progressive degenerative disease of the brain, characterized by dementia and always fatal
Autism
a disorder emerging in early childhood characterized by impairments in communication and social interactions, and restricted and repetitive behaviors
Cerebral palsy
a motor disorder caused by damage to the cerebrum before, during, or soon after birth
Depression
a serious disorder of mood, characterized by insomnia, loss of appetite, and feelings of dejection
Epilepsy
a condition characterized by periodic disturbances of brain electrical activity that can lead to seizures, loss of consciousness, and sensory disturbances
Multiple sclerosis
a progressive disease that affects nerve conduction, characterized by episodes of weakness, lack of coordination, and speech disturbance
Parkinson’s disease
a progressive disease of the brain that leads to difficulty in initiating voluntary movement
Schizophrenia
a severe psychotic illness characterized by delusions, hallucinations, and bizarre behavior
Spinal paralysis
a loss of feeling and movement caused by traumatic damage to the spinal cord
Stroke
a loss of brain function caused by disruption of the blood supply, usually leading to permanent sensory motor, or cognitive deficit
neurologist
and M.D. trained to diagnose and treat diseases of the nervous system
psychiatrist
an M.D. trained to diagnose and treat disorders of mood and behavior
neurosurgeon
an M.D. trained to perform surgery on the brain and spinal cord
neuropathologist
an M.D. or Ph.D. trained to recognize the changes in nervous tissue that result from disease
developmental neurobiologist
analyzes the development and maturation of the brain
molecular neurobiologist
uses the genetic material of neurons to understand the structure and function of brain molecules
neuroanatomist
studies the structure of the nervous system
neurochemist
studies the chemistry of the nervous system
neuroethologist
studies the neural basis of species-specific animal behaviors in natural settings
neuropharmacologist
examines the effects of drugs on the nervous system
neurophysioloist
measures the electrical activity of the nervous system
physiological psychologist
studies the biological basis of behavior
psychophysicist
quantitatively measures perceptual abilities