4 - Neuropeptides and Neurotransmitters
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
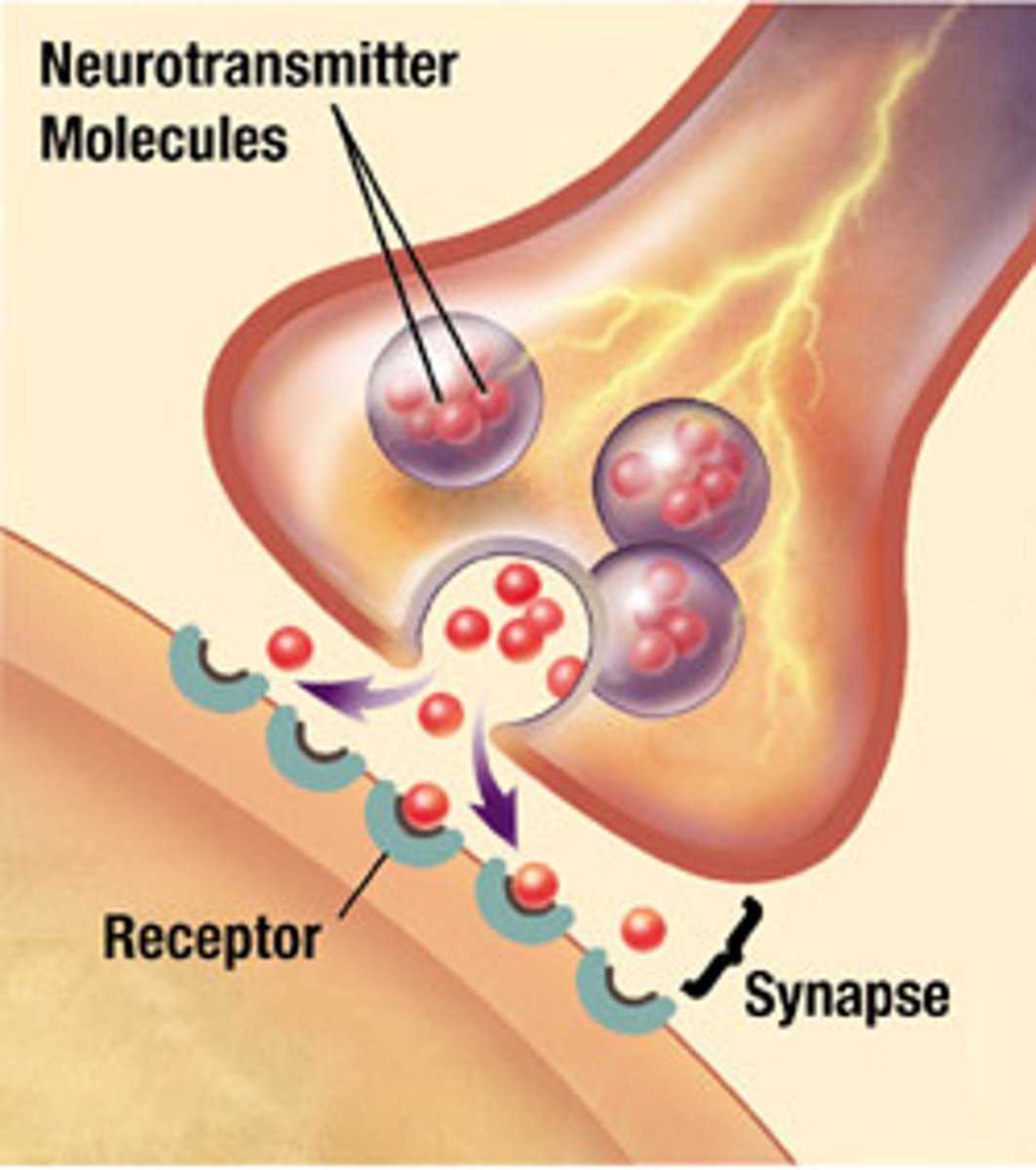
synapses
located at the END of an axon, sites where transmission of the action potential "message" is relayed to effector cells
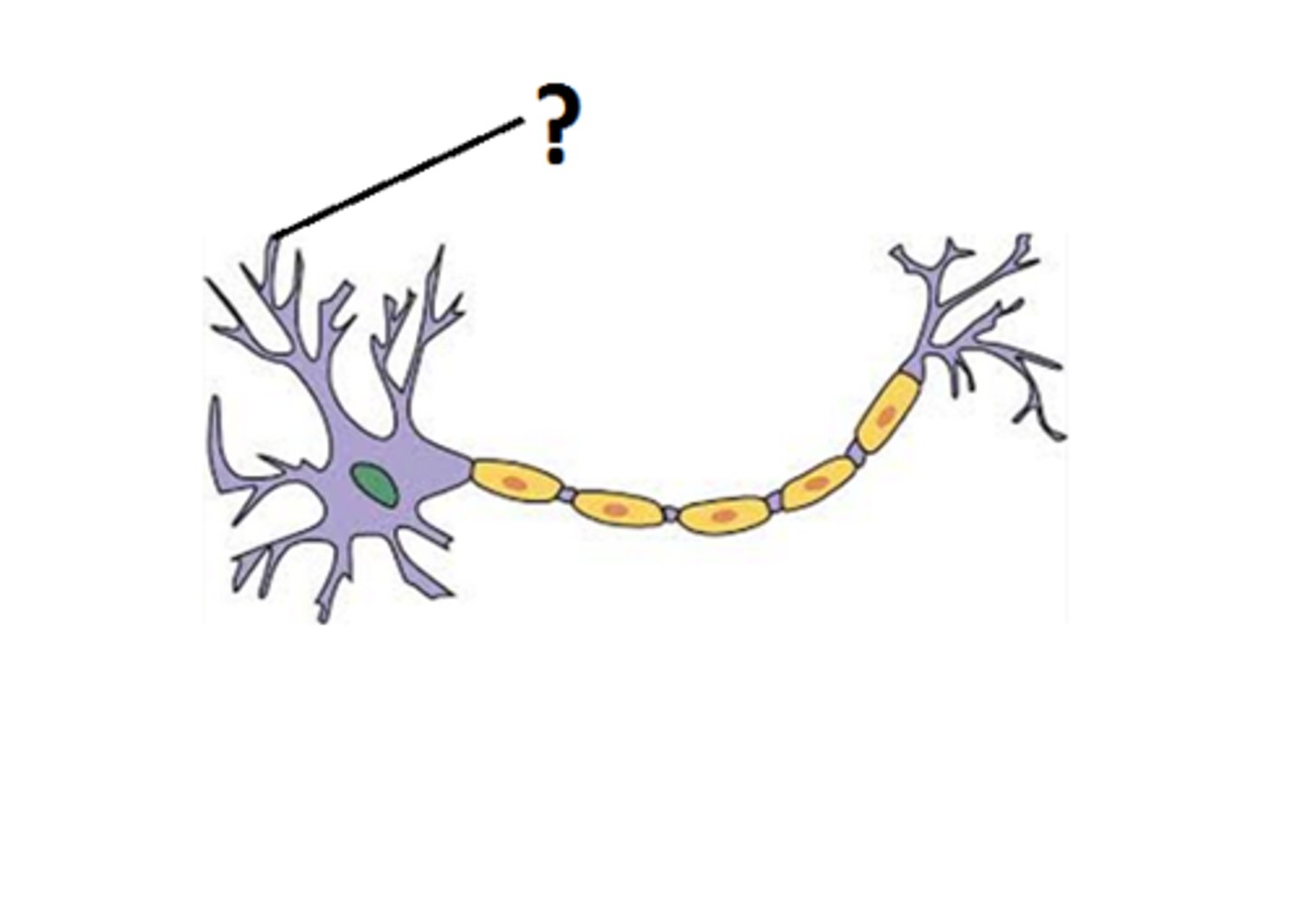
dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
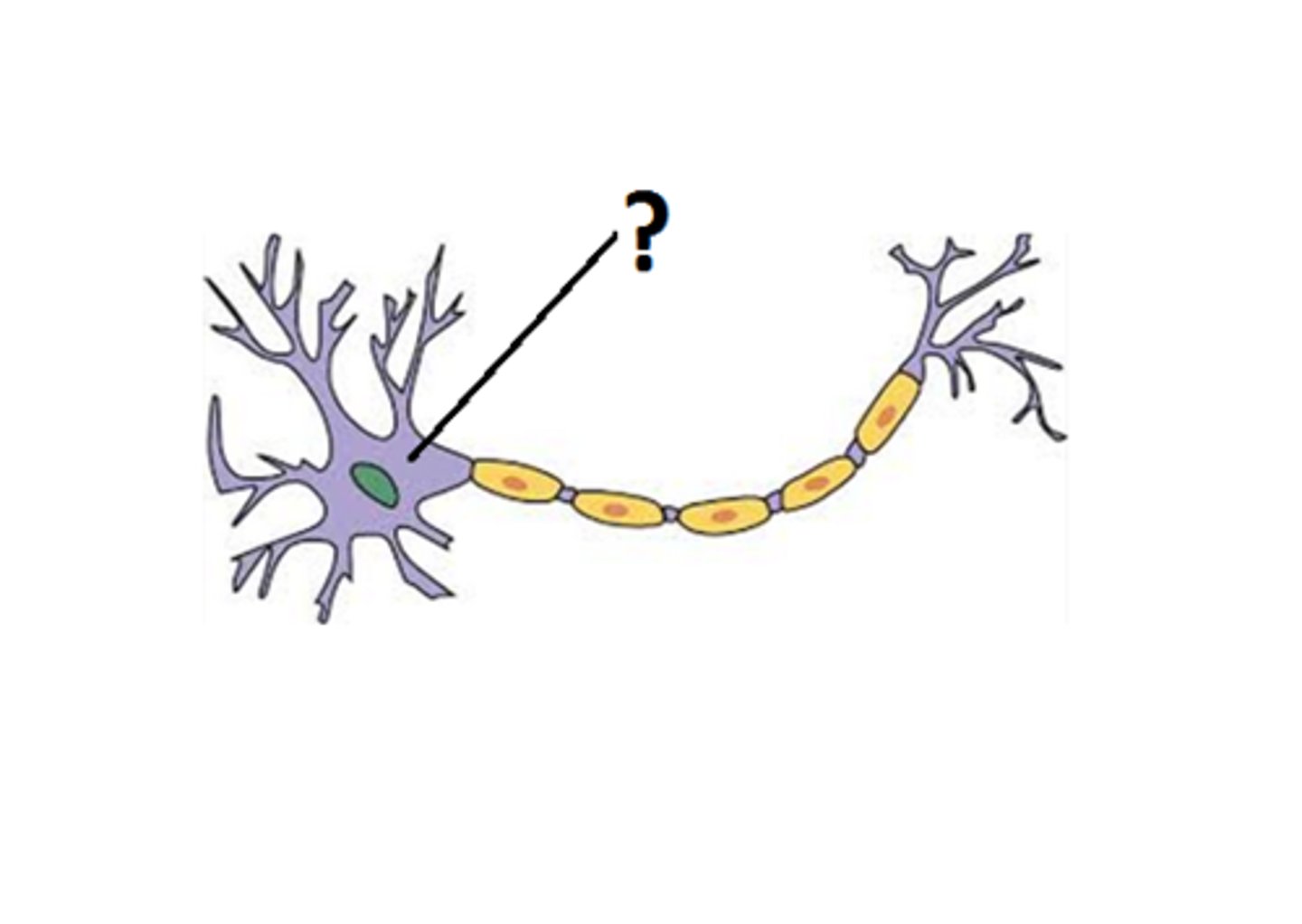
cell body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus, integrates incoming signals and generates outgoing signal to axon
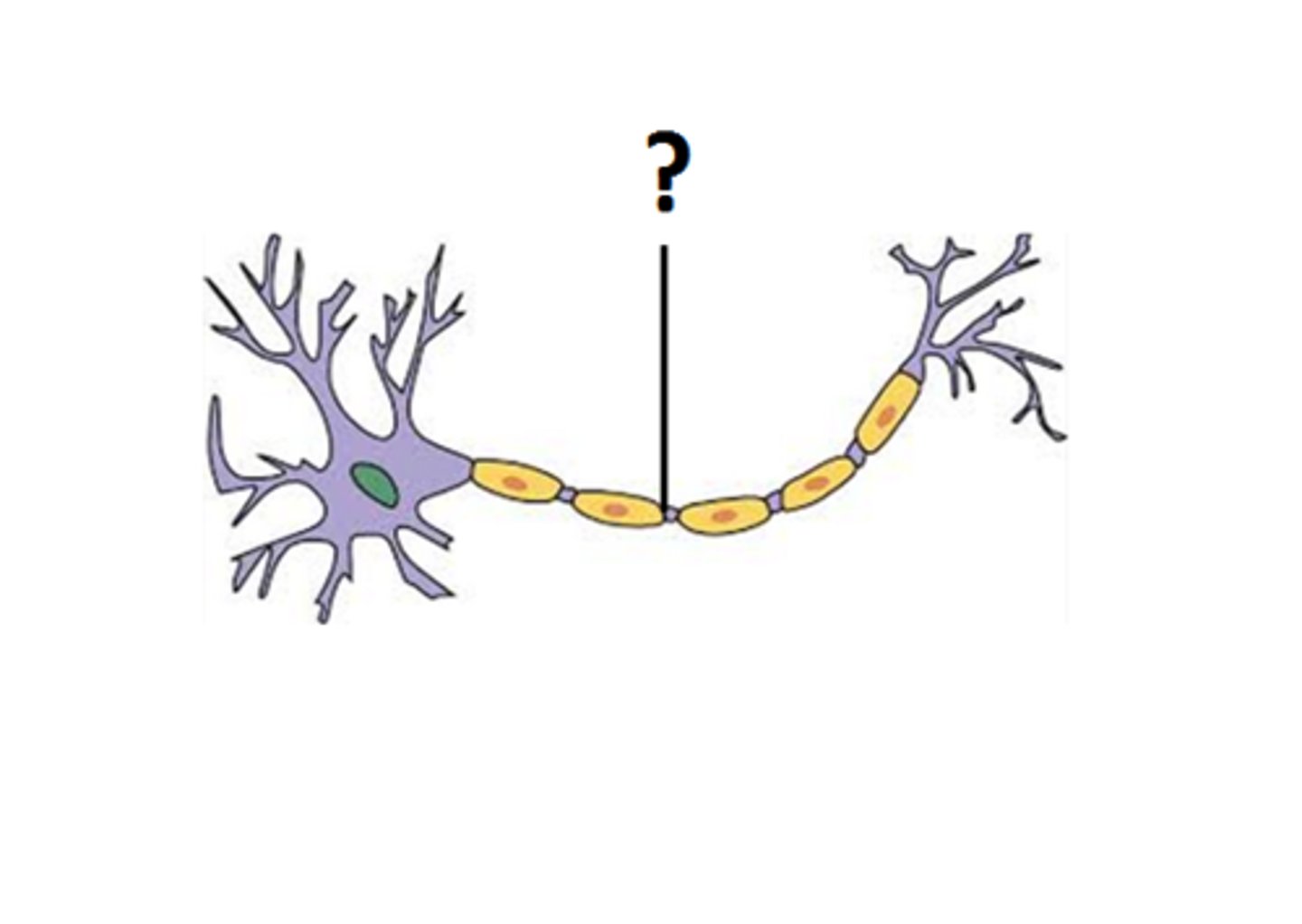
axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
neuromuscular junction
synapse to muscle cell signal
neuroglandular synapses
synapse to gland (endocrine) cells
neuropeptides = prolonged
neurotransmitters = short acting
main difference between neuropeptide and neurotransmitters
neuropeptide
act on multiple receptor proteins, aka GPCRs (G-Protein-coupled receptors) performing prolonged action
opioid peptides
type of neuropeptide, controls pain modulation and reward
pituitary peptides
type of neuropeptide, controls hormonal control
gut-brain peptides
type of neuropeptide, regulates appetite and digestion
tachykinins
type of neuropeptide, responsible for sensory processing and pain transmission
insulin like peptides
type of neuropeptides, controls metabolism regulation
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons, producing short-term response
exitatory
type of neurotransmitters, increasing likelihood of action potential (stronger signal response)
inhibitory
type of neurotransmitter, decreasing the likelihood of action potential
modulatory
type of neurotransmitter, influences multiple neurons