AP BIO COMPLETE SET
1/985
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
986 Terms
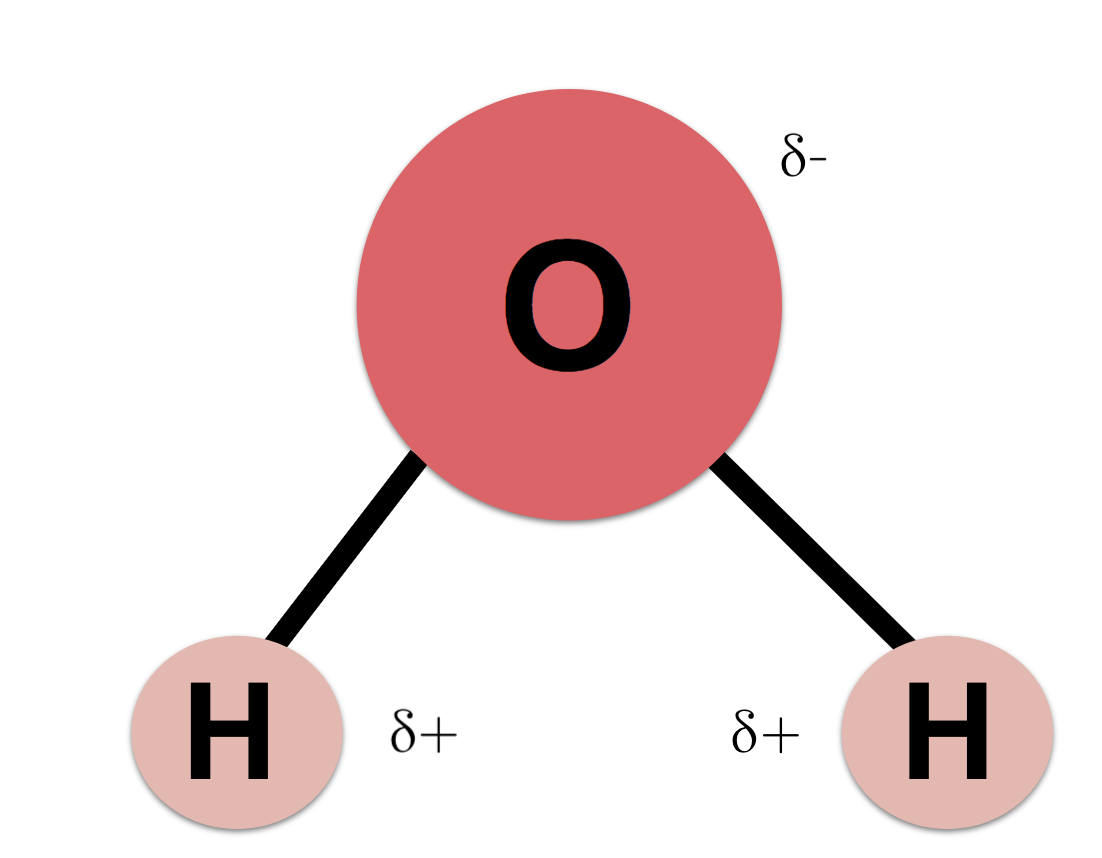
What is water composed of?
2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen
What type of bond is between hydrogen and oxygen (in water)?
polar covalent bond
What type of bond forms between water molecules?
hydrogen bond
covalent bonds
when 2 or more atoms share electrons
hydrogen bonds
when a partially positive hydrogen atom forms an electrostatic attraction to a negative atom in another molecule; weaker bond
ionic bonds
attraction between oppositely charged atoms
Which end of water is negative? positive?
oxygen is negative, hydrogen is positive
polar molecule
when the atoms share electrons unequally - leads to partially negative and positive ends
nonpolar molecule
electrons shared equally
What are the 6 properties of water?
surface tension, capillary action, high specific heat, evaporative cooling, density, “universal” solvent
cohesion
hydrogen bond between the same molecules
surface tension
when water tends to form more hydrogen bonds (cohesion) toward the surface, allowing denser objects to rest on top of it
adhesion
hydrogen bond between different molecules
capillary action
combination of adhesion and cohesion allows water to flow in narrow spaces without any outside force
example of capillary action
water transport in plants through the xylem
high specific heat
water’s ability to withstand dramatic changes in temperature; important for homeostasis
evaporative cooling
when water evaporates, it creates a cooling effect
density
when water turns into ice, its hydrogen bonds between molecules become rigid and arrange themselves into a crystal lattice, making it less dense than water
Why is the property of ice and its density important?
allows for life in bodies of water in the winter
universal solvent
water can dissolve a lot of substances
hydrophilic
molecules that dissolve in water (ionic/polar)
hydrophobic
molecules that don’t dissolve in water (nonionic/nonpolar)
What happens when water reacts with soap?
surface tension goes down
What happens when water reacts with salt?
surface tension goes up
What happens when water reacts with sugar?
surface tension goes down
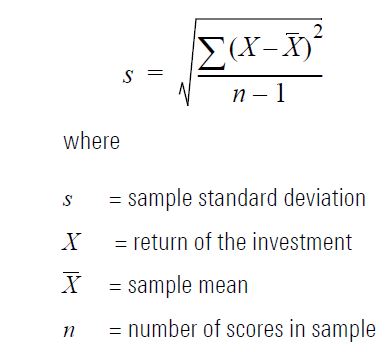
standard deviation
how spread out the data is from the mean
normal distribution
68% data within 1 SD, 95% within 2 SD, 99% within 3 SD
standard deviation formula
standard error of the mean
used to determine the precision/accuracy of the mean
SEM formula
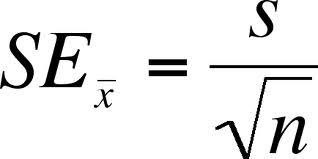
error bars
±2 SEMS
How do we get smaller error bars?
large sample size, small variation
How do we get larger error bars?
small sample size, large variation
What does it mean if error bars overlap?
not significant, fail to reject the null hypothesis
What does it mean if error bars don’t overlap
probably significant; reject the null hypothesis
null hypothesis
predicts no relationship between variables
alternate hypothesis
predicts relationship between variables
independent variable
factor being changed
dependent variable
factor being affected by independent variable
constant variable
factor kept consistent for all groups
experimental group
group exposed to the independent variable to test it
control group
group not exposed to the independent variable
positive control
expected to produce a result
negative control
expected to produce no result
what are the components you need to include when graphing?
title, labels for axes (including units), scale, key (if necessary)
What does pH stand for?
power of hydrogen
What is a neutral pH?
7
What is a strong acid?
0-3
What is a weak acid?
4-6
What is a weak alkaline/base?
8-10
What is a strong alkaline/base?
11-14
What scale is the pH scale based on?
a logarithmic scale
buffer
substance that minimizes pH change
What’s an example of a buffer in our bodies?
carbonic acid (H2CO3)
What type of bond forms between water molecules?
hydrogen bond
structure of water
in addition to picture, polar covalent bond in between hydrogen and oxygen
What are the 6 properties of water?
surface tension, capillary action, high specific heat, evaporative cooling, density, “universal” solvent
cohesion
hydrogen bond between the same molecules
surface tension
when water tends to form more hydrogen bonds (cohesion) toward the surface, allowing denser objects to rest on top of it
adhesion
hydrogen bond between different molecules
capillary action
combination of adhesion and cohesion allows water to flow in narrow spaces without any outside force
high specific heat
water’s ability to withstand dramatic changes in temperature; important for homeostasis
evaporative cooling
when water evaporates, it creates a cooling effect
density
when water turns into ice, its hydrogen bonds between molecules become rigid and arrange themselves into a crystal lattice, making it less dense than water
universal solvent
water can dissolve a lot of substances
organic
contains carbon
inorganic
has no carbon
macromolecule
large complex molecules that are essential for life
monomer
small units
polymer
made up of repeating monomers connected by covalent bonds
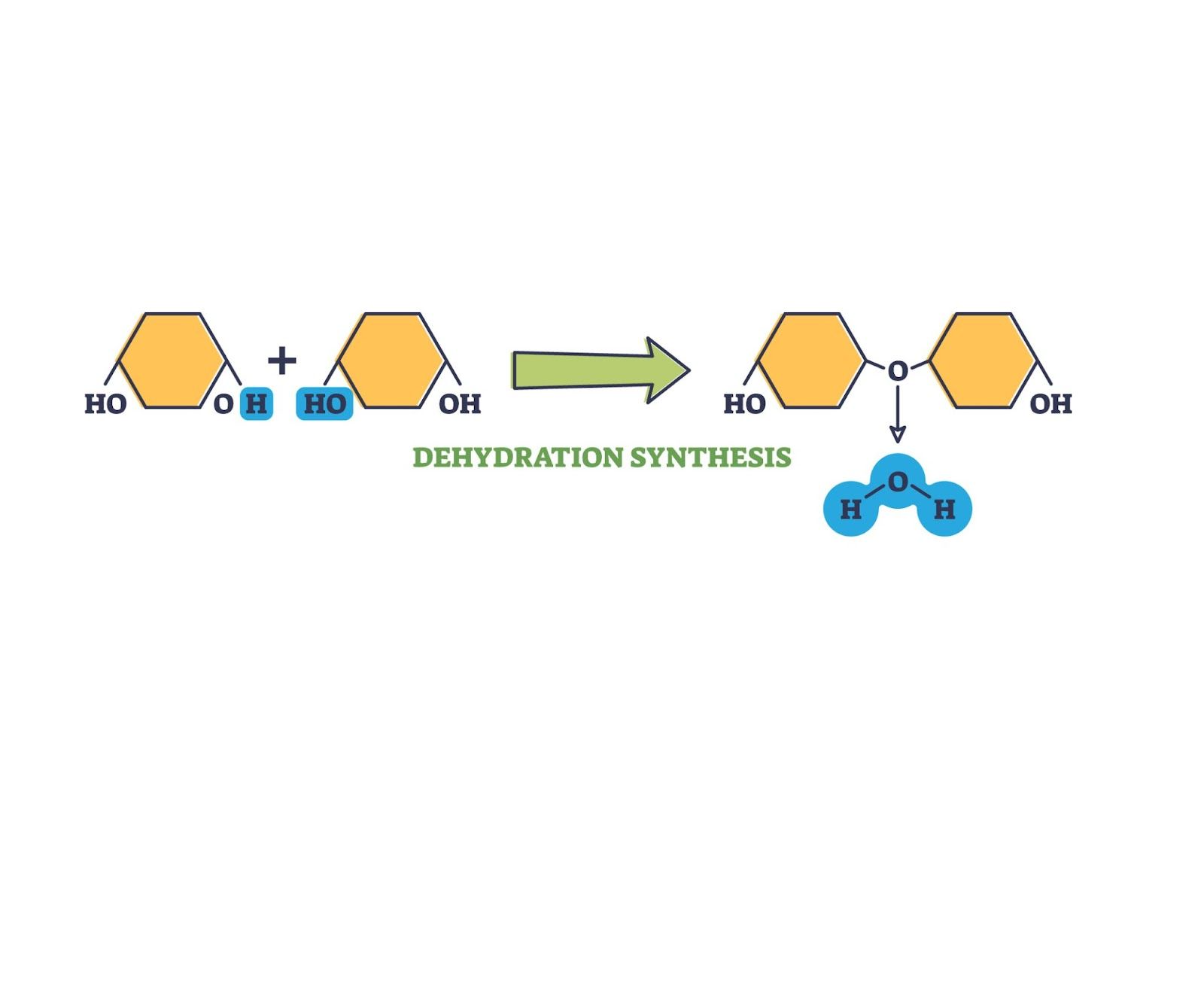
dehydration synthesis
in a catabolic reaction, water is released to create covalent bonds
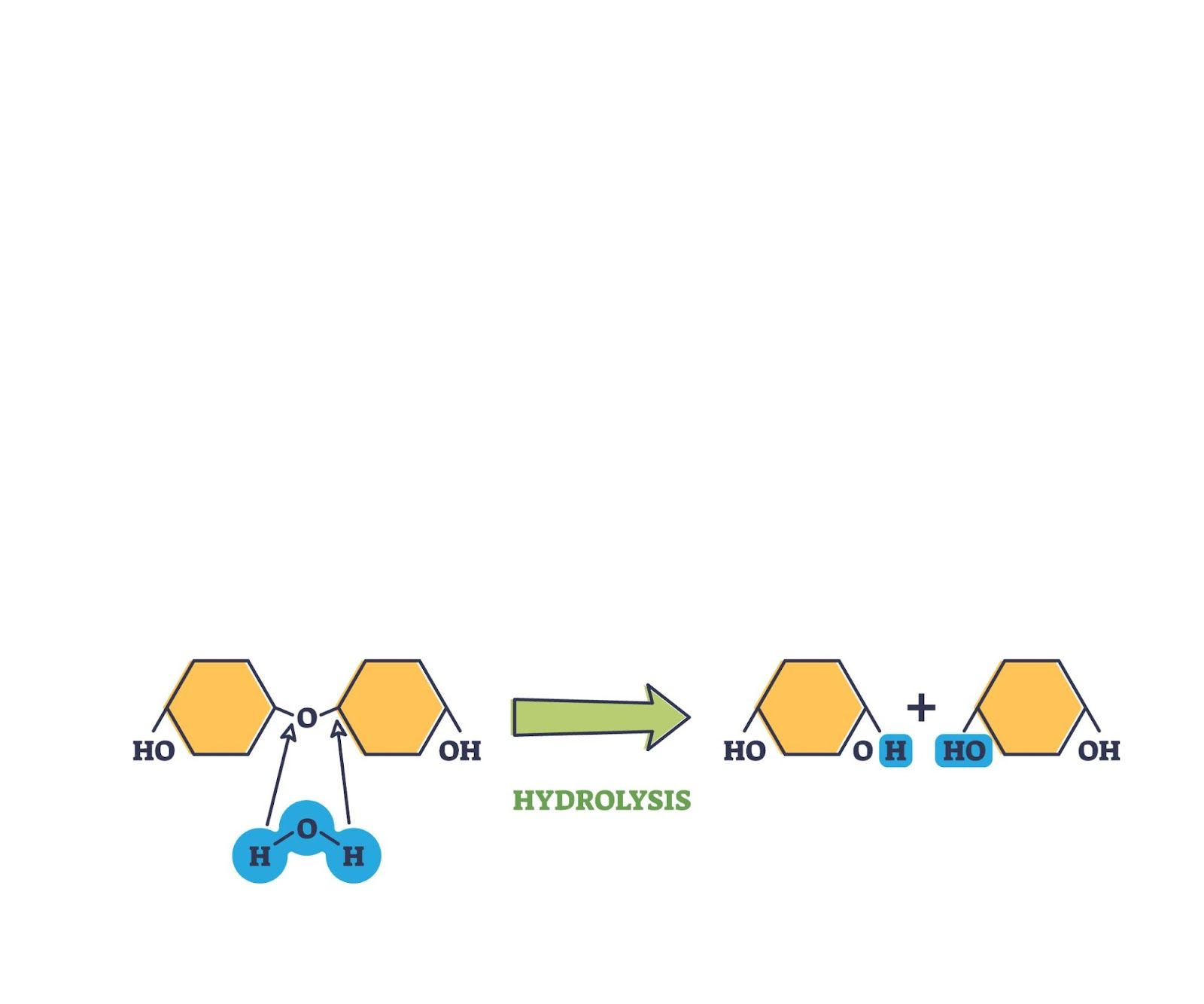
hydrolysis
in an anabolic reaction, water is used to break down covalent bonds
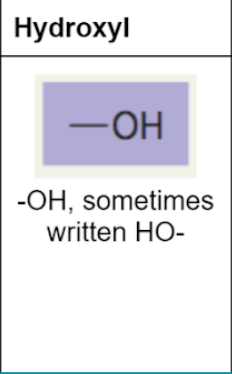
hydroxl group
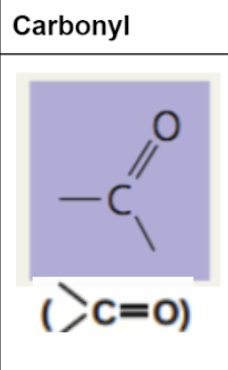
carbonyl group
carboxyl group
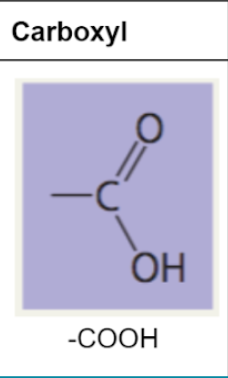
amino group
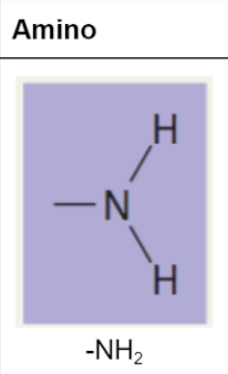
sulfhydryl group
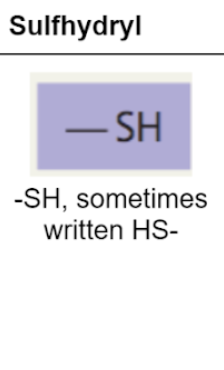
phosphate group
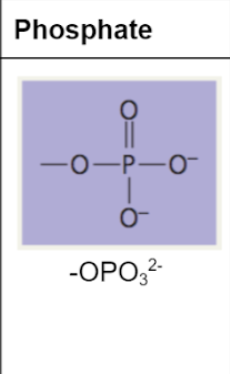
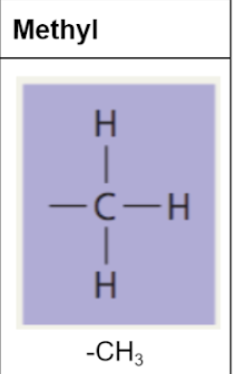
methyl group
only functional group that is non-polar
carbohydrate elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (CHO)
function of a carbohydrate
provides energy, energy storage, structure
structure of a carbohydrate
linear, ring, or branched forms
monosaccharide
simple carb, monomer of a carbohydrate
what type of bond connects monosaccharides?
glycosidic bond
examples of a monosaccharide
glucose, fructose, galactose
disaccharide
simple carb, two connected monosaccharides
examples of a dissacharide
sucrose (G + F), lactose (G + L), maltose (G + G)
polysaccharide
complex carb, 3+ connected monosaccharides
energy polysaccharides
starch (stored form of glucose in plants), glycogen (stored form of glucose in animals)
structural polysaccharides
cellulose (cell wall in plants), chitin (cell wall in fungi and exoskeletons in arthropods), peptidoglycan (cell wall in bacteria)
isomer
molecules with the same atoms but different arrangment of those atoms
What’s the atomic ratio of carbohydrates?
1:2:1 (C:H:O)
elements in lipids
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, sometimes phosphate (CHOP)
monomer of a lipid
fatty acids + glycerol
Lipids are not ______. Why?
true polymers; monomer is made up of two smaller components
what type of bond connects glycerol to a fatty acid?
ester
function of a triglyceride
longterm energy storage
structure of a triglyceride
1 glycerol connected to 3 fatty acids
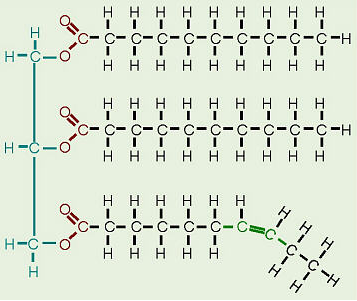
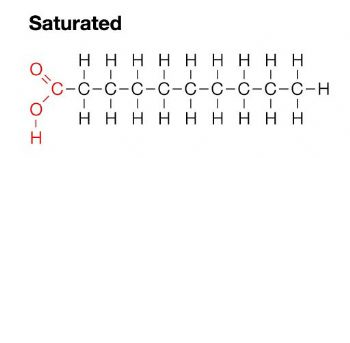
saturated fat
all single bonds between carbons; solid at room temp; unhealthy fat
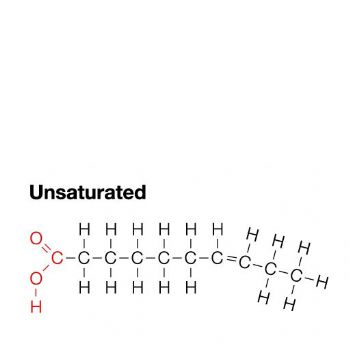
unsaturated fat
1 or more double bonds; liquid at room temp; healthy fat