Biostatistics exam 3 - Multiple Explanatory Variables
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Generalizing linear models
• in a linear model the null hypothesis is β = 0
• so setting β = 0 reduces the equation
Y = α + βX → Y = α'
• α' =constant that equals the grand mean
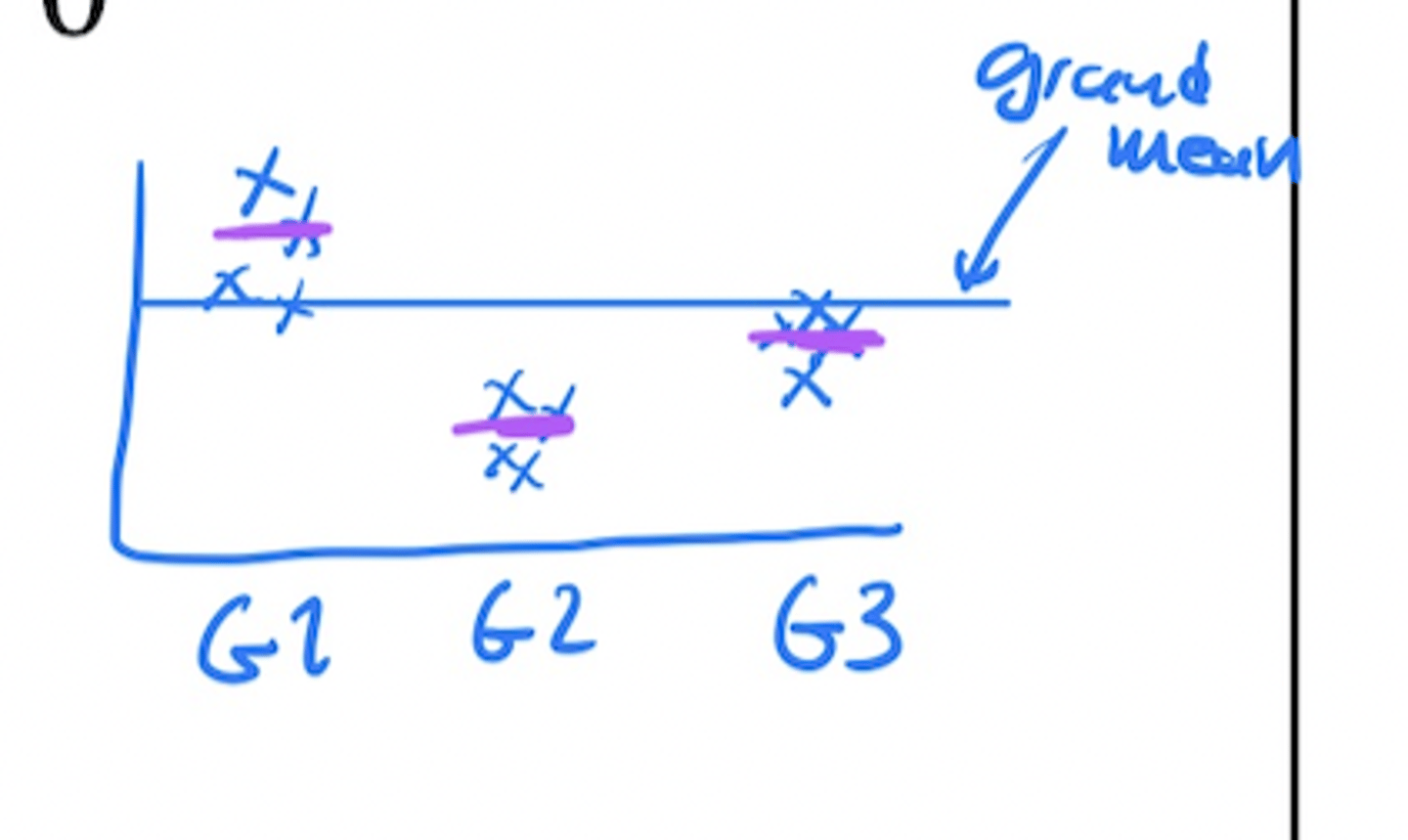
Is ANOVA a linear model?
YES
ANOVA as a linear model (equation)
Linear model: Y = µ + A
• Y: response
• µ: grand mean (constant)
• A: treatment
Example: circadian clock study: shift = constant + treatment
hypotheses for ANOVA linear model
H₀: Y (response) = Grand mean (constant)
Ha: Y (response) = Grand mean (constant) + Treatment
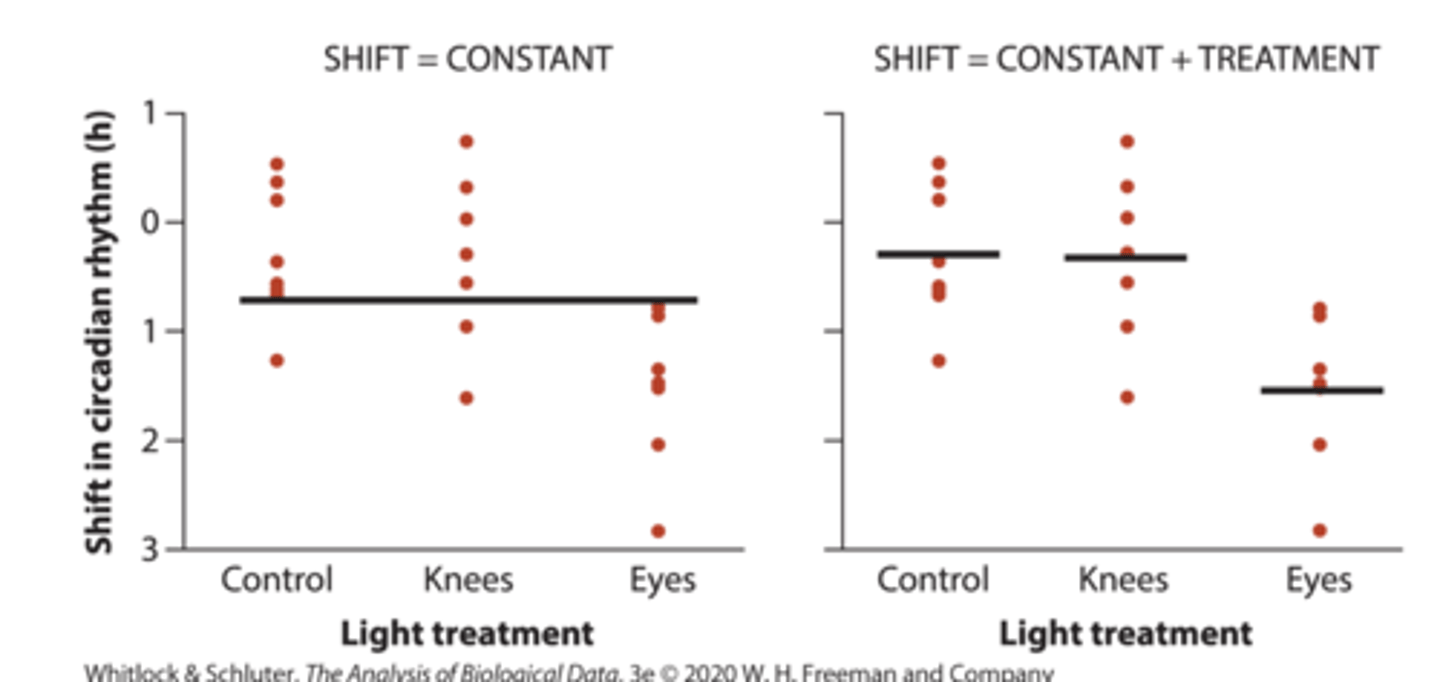
sampling error for ANOVA as a linear model
Even if the hypothesis is true, however, the treatment means will be different due to sampling error thus, the full model with treatment will be a better fit to the data
** F-ratio takes this into account
F-ratio for ANOVA as a linear model
F-ratio is used to test whether including the treatment variable in the data results in a significant Improvement in the fit of the model to the data
• compared with the fit of the null model lacking the treatment variable
ANOVA linear model for multiple explanatory variables (equation)
Response = constant + explanatory
• extending for multiple explanatory variables
Response = constant + exp1 + exp2 +...
• models often include an interaction term
Response = constant + exp1 + exp2 + exp1 * exp2
• design is called a two-way ANOVA or two-factor ANOVA
interaction term
Means that the effects of one variable on the response depends on the value of the second variable
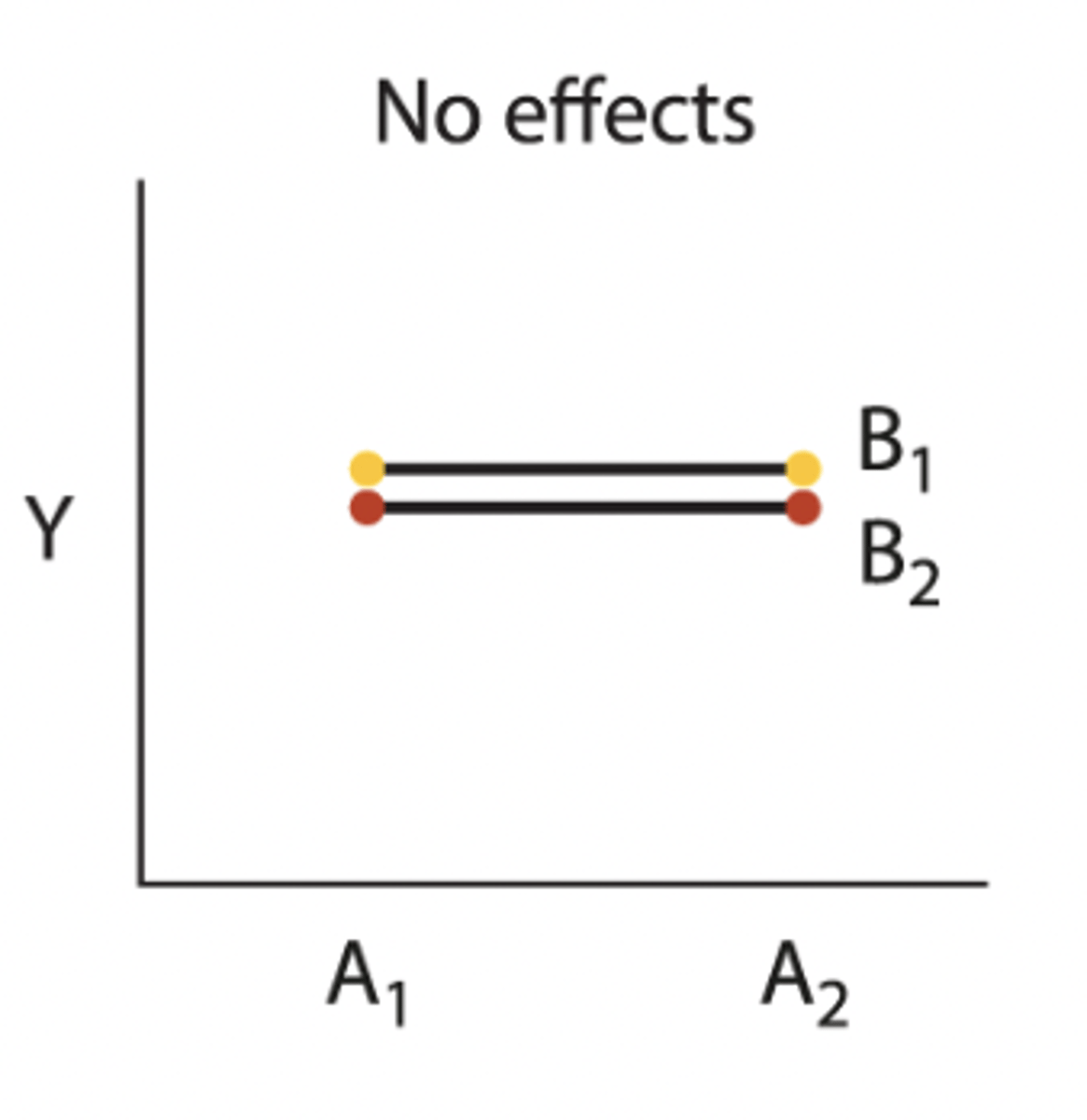
Two - factor outcome (no effect)
• no difference in averages for A or B
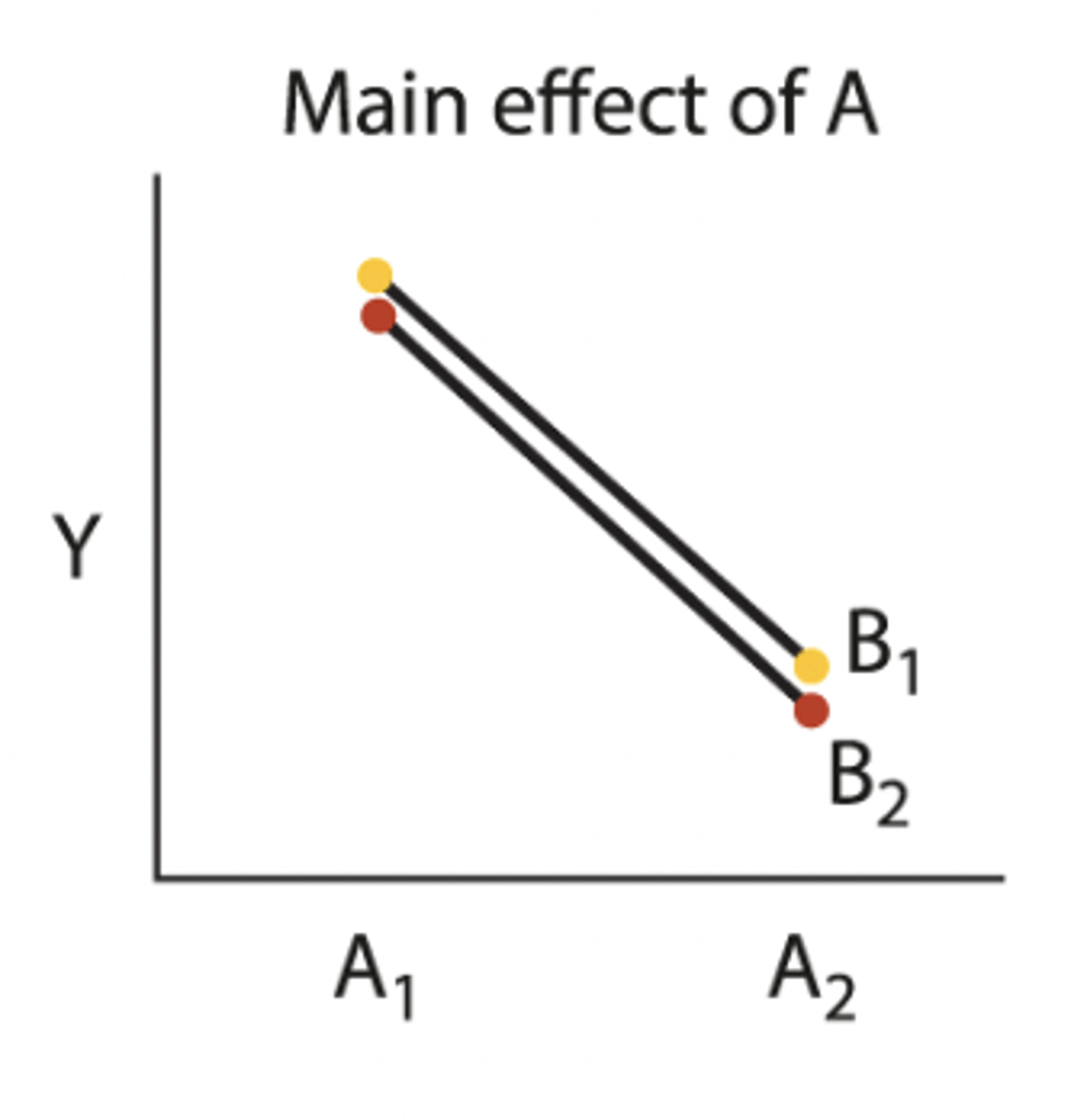
Two - factor outcome (Main effect of A)
• average of A1 and A2 are not the same (A effect)
•average between the two yellow dots is the same as the average between the two red dots (No B effect)
Two - factor outcome (Main effect of B)
• A1 and A2 avg is the same (no effect of A)
• average of two yellow dots will be higher than the average of the two red dots Different Y-ints
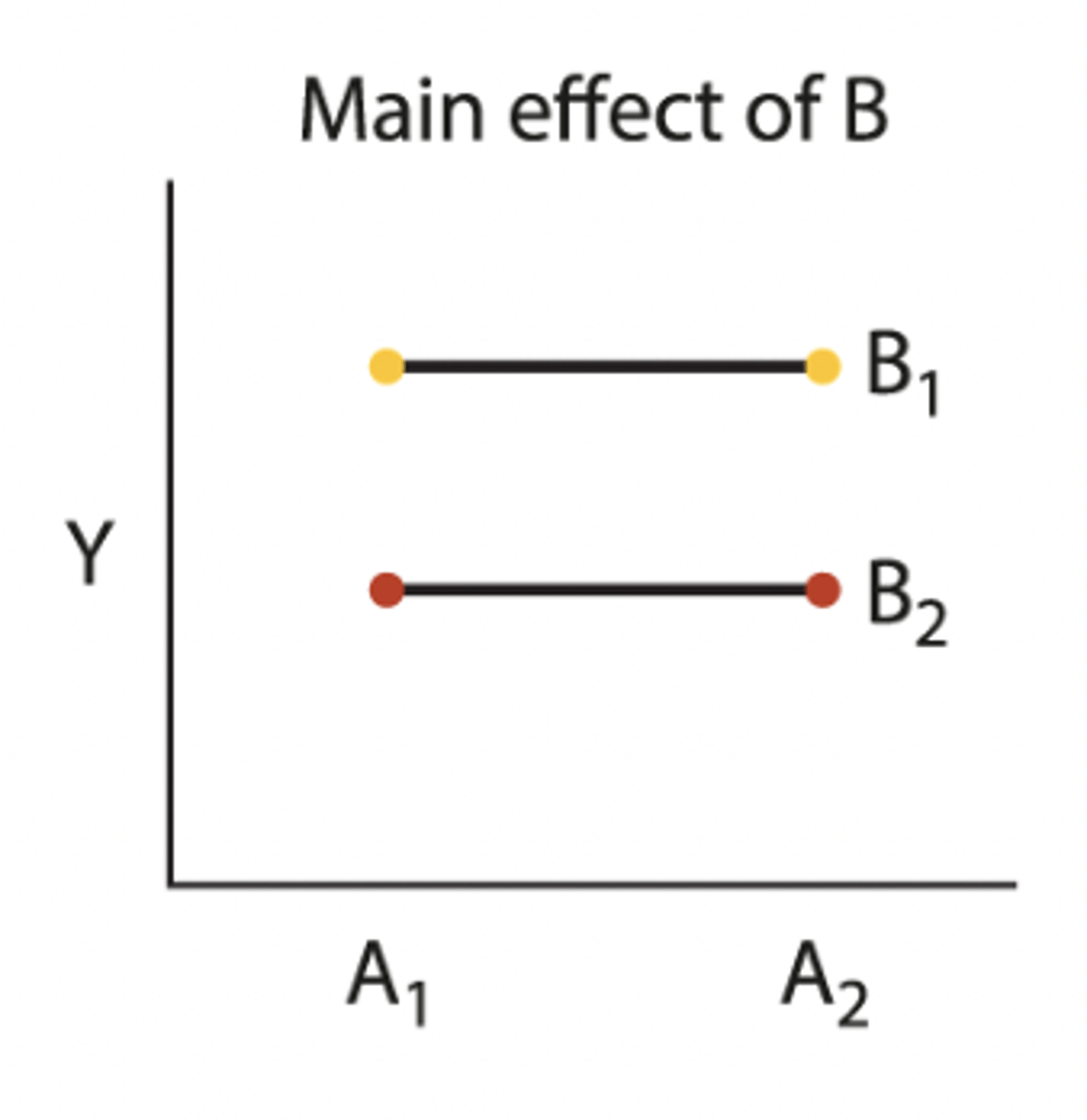
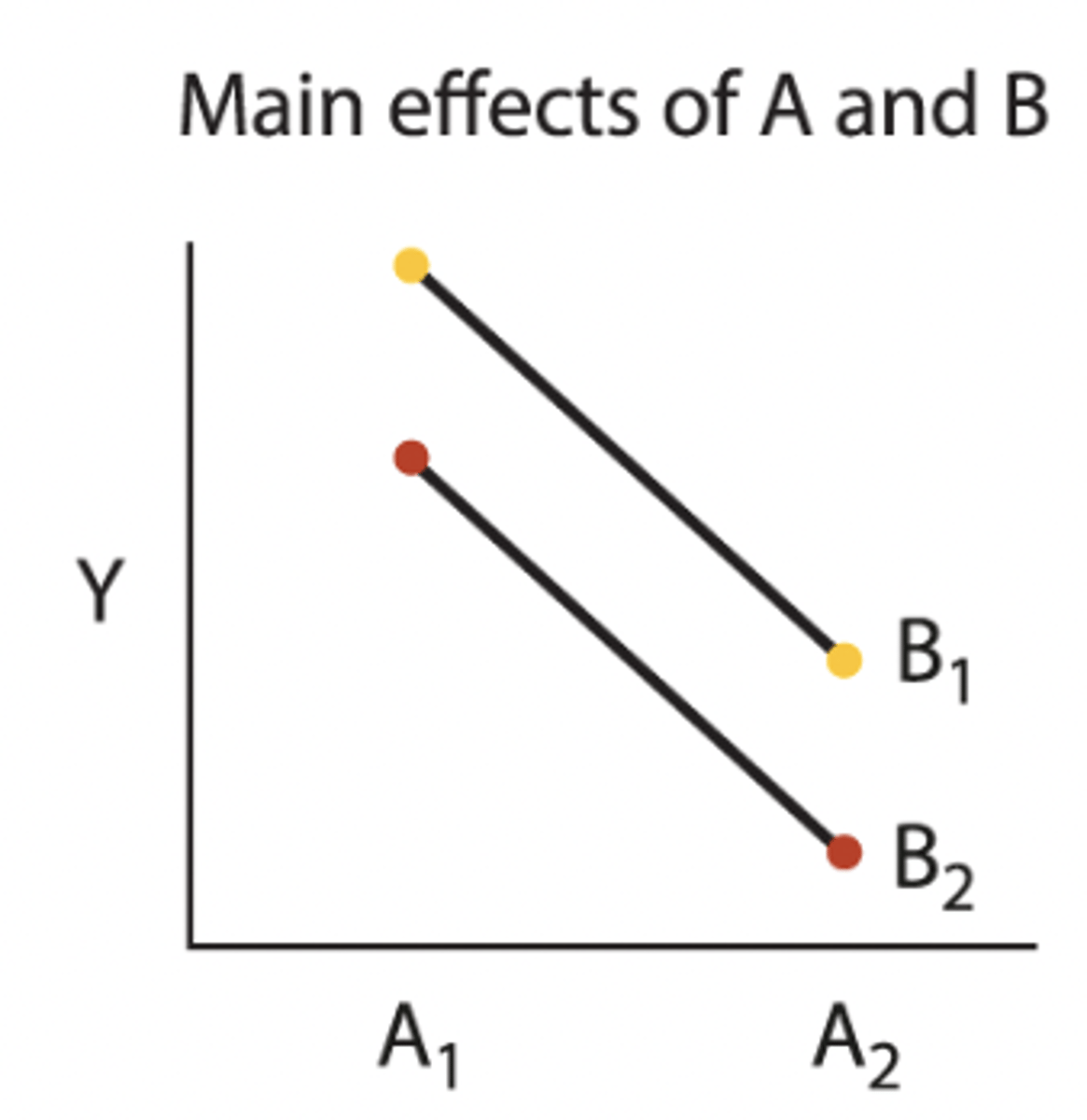
Two - factor outcome (Main effects of A and B)
• A1 and A2 average is not the same (A effect)
• The average of two yellow dots is higher than red, so B has an effect (DIF Y-INT!)
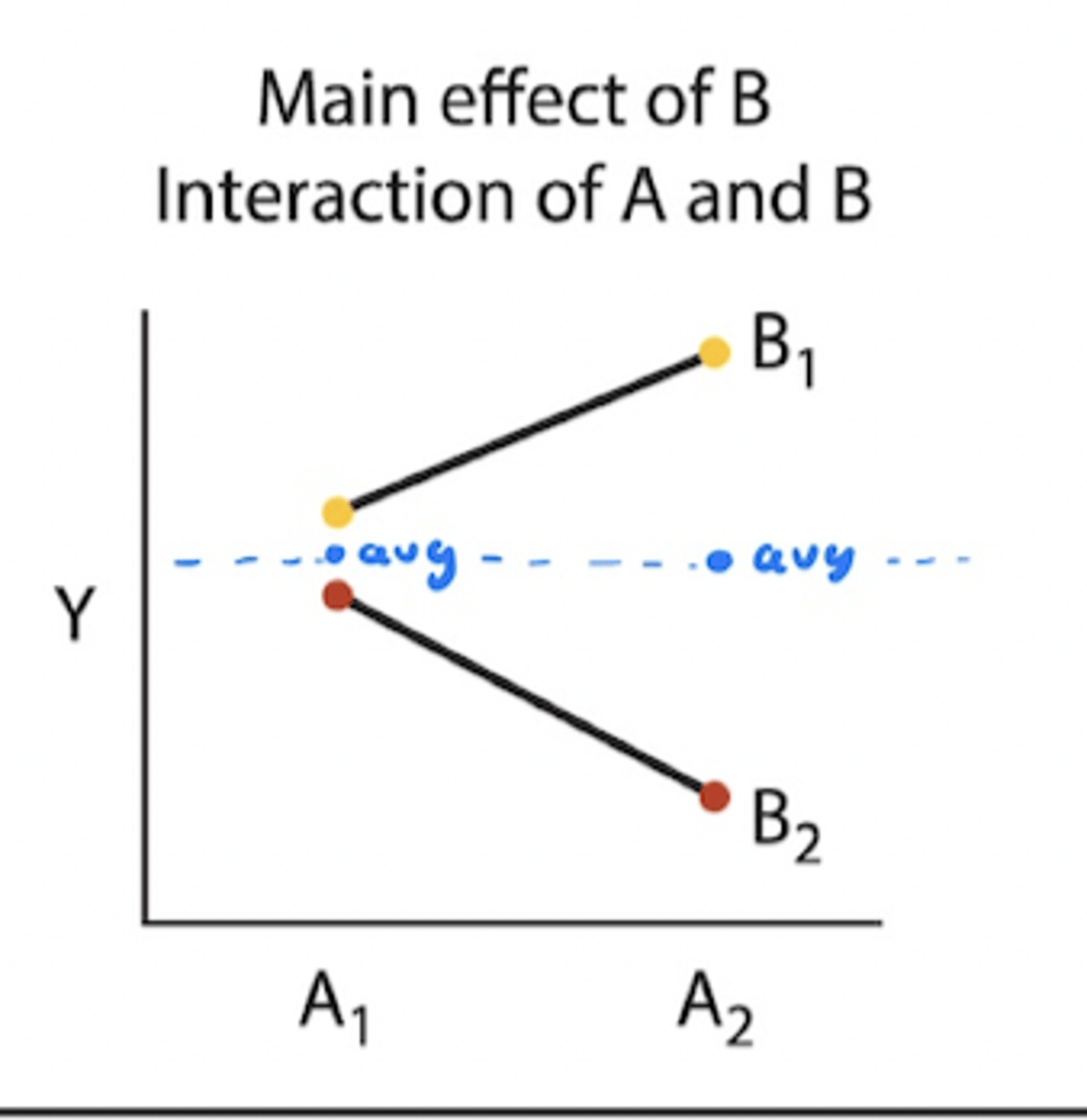
Two - factor outcome (Main effect of B with interaction of A and B)
• A1 and A2 average is the same (No main A effect)
• average of yellow is higher than red (B main effect)
• what happens with B depends on A (diff slopes -> interaction between A and B)
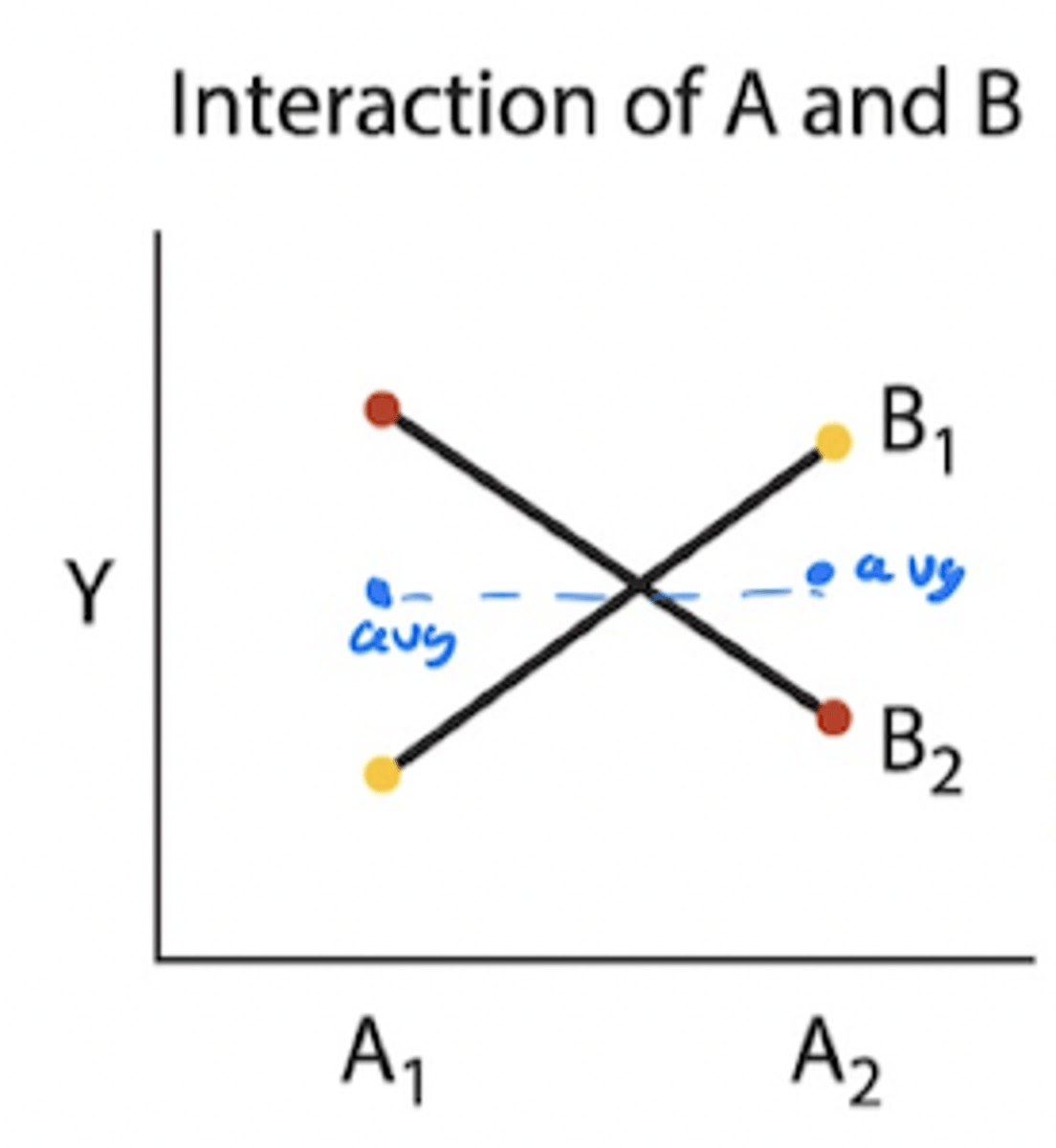
Two - factor outcome (Interaction of A and B)
• different slopes (Intraction)
• average A1 and A2 are the same (No main effect of A)
• average of yellow dots and red dots are the same (no main effect of B)
Assumptions of two-factor ANOVA linear models
• the measurements at every combination of values for the explanatory variables are a random sample from the population of possible measurements
• the measurements for every combination of values for the explanatory variables have a normal distribution in the corresponding population
• the variance of the response variable is the same for all combinations of explanatory variables