Lecture 7 Mutation and Genetic Variation
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
gene
fundamental unit of heredity, often codes for proteins
locus
specific place on the chromosome where a gene is located (physical location)
allele
variant forms of a gene, or variant nucleotide sequences at a particular locus
pyrimidines
cytosine or thymine
purine
adenine or guanine
codons
amino acids coded by triplets of nucleotides
mutation
any alteration in nucleotide sequence of a genome
ultimate source of genetic variation and the raw material on which natural selection acts
result of errors in DNA replication or repair of damage by chemical mutagens or UV radiation
must occur in germline (progenitors of gametes) to be transmitted to offspring a permanent change in the DNA sequence of an organism.
types of mutations
point mutation
insertion/deletion
chromosome inversions
gene duplication
point mutations
Alteration of a single base in a DNA sequence
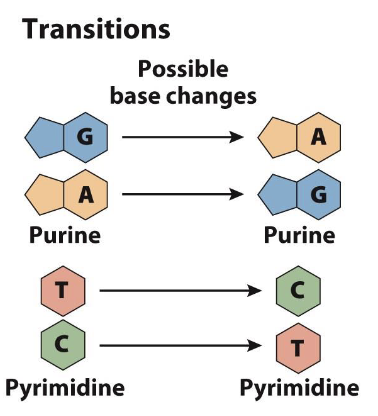
Transition → changing between purines (A to G or G to A) or pyrimidines (C to T or T to C)
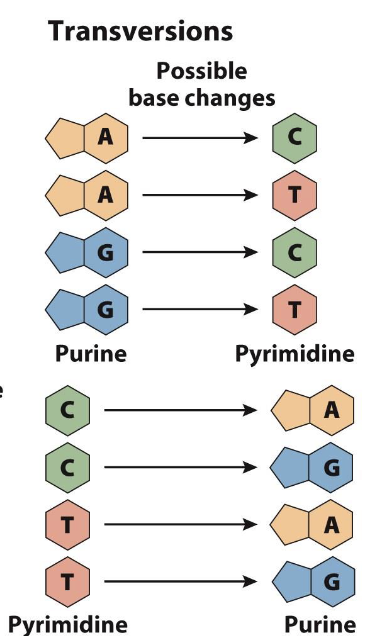
Transversion → changing between purines to pyrimidines or pyrimidines to purines (A to C or T; G to C or T; C to A or G; T to A or G)
transition
changing between purines (A to G or G to A) or pyrimidines (C to T or T to C)
more frequent than transversions (~2x)
transversions
changing between purines to pyrimidines or pyrimidines to purines (A to C or T; G to C or T; C to A or G; T to A or G)
what are consequences of point mutations?
missense mutation — nonsynonymous replacement
nonsense mutation
silent (synonymous) mutation
missense (nonsynonymous replacement) mutation
results in an amino acid change (almost all changes happen at first and second codon positions)
synonymous (silent) mutation
does not result in an amino acid change — still get the same amino acid sequence
nonsense mutation
new codon is a stop codon; there is premature termination of translation
sickle cell is an example of _______
point mutation
insertion/deletion mutations (indels)
“daughter” DNA has a different number of base pairs in a particular region than the “parental” DNA
caused by errors in DNA replication, often in repetitive sequences
In order to maintain alignment and conserve the things that are being conserved → you need to add gaps or insert things to keep it aligned
what are consequences of insertion/deletion mutations?
can result in a frameshift mutation, insertion/deletion of amino acids in the protein, and/or premature stop codons (nonsense mutations)
chromosome inversions
a region of DNA that has been flipped so that the genes are in reverse order
after breakage, the segment can detach, flip, and reanneal
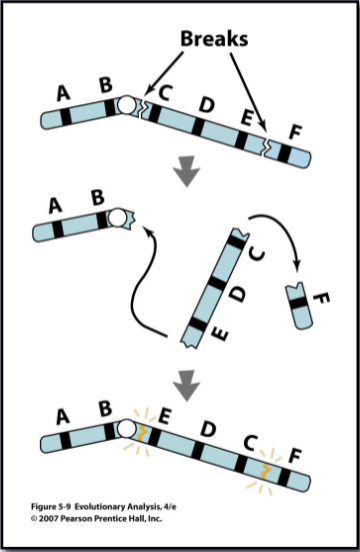
what can induce chromosomal breaks?
oxygen radicals, gamma-irradiation, chemicals
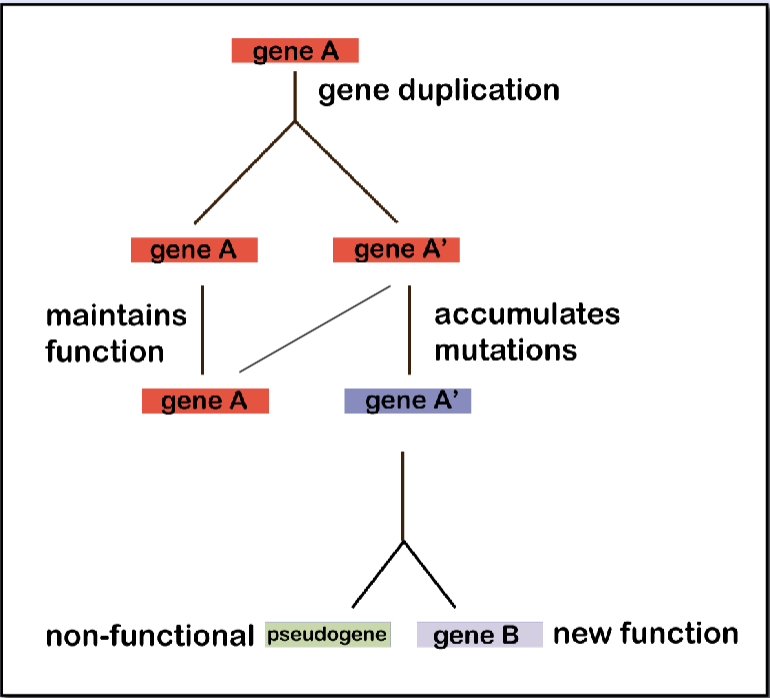
gene duplication
generation of an extra copy of a locus
most duplicated genes are generated via unequal crossing over
what are the fates of duplicated genes?
mutations can be accumulated, which can lead to gain or loss of function of the gene