cman 380 exam 2
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
screening?
process of using clinical tests and/or examinations to identify patients who require additional health-related interventions
testing people who are at risk BUT are asymptomatic
key component of secondary prevention
is a screening diagnostic?
no!
screen a subset of the population who may be at risk
what is USPSTF?
US Preventive Services Task Force
uses clinical research and evidence-based preventative care to recommend screenings
does USPSTF fall under HHS?
No, but HHS supports USPSTF
USPSTF falls under Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (which is under HHS)
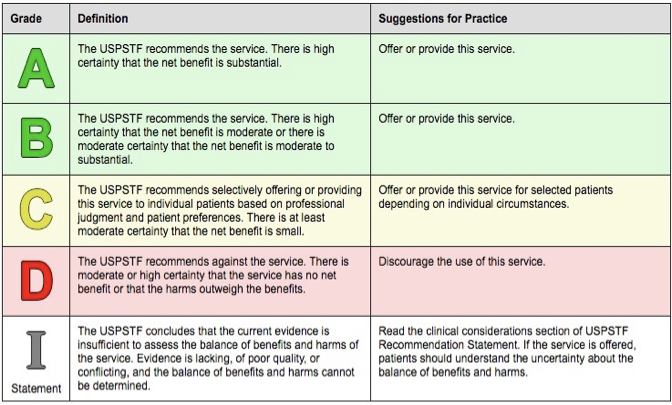
USPSTF grading
a: recommends
b: moderate
c: selectively offering
d: against the service
i: evidence is insufficient
criteria for making a screening program
1.The disease problem is significant and potentially manageable, i.e., you can do something about it once it is identified.
2.The screening technique is valid; i.e., the screening results can be confirmed by other diagnostic procedures.
3.The screen technique is reliable, i.e., it gives a consistent result.
4.There will be a sufficient # of cases to make the screen worthwhile, i.e., the prevalence of the disease is relatively high.
5.The cost is reasonable; i.e., the cost-benefit ratio must be favorable.
6.The screening technique is acceptable; i.e., the public will want to participate.
7.The follow-up services and facilities are adequate. And we have an ethical responsibility to refer persons discovered to have the disease to appropriate sources for care.
***if 1 of 7 is missing, do not test
other factors to consider in selecting a screening tool
cost vs benefit
is it acceptable?
test’s reliability and validity?
easy to administer?
does the test detect at an early stage?
is the treatment for the disease being screened for available?
how to select a screening test?
must be valid & reliable
validity: can correctly distinguish
sensitive: correctly identifies those WITH disease
specific: correctly identifies those W/O disease
reliable: consistent results over time & between examiners
sensitivity example
sensiTivity = sensitive to the Truth
if test has 90% sensitivity, test can correctly identify 90 of 100 people with the disease
other 10 people will appear negative for the disease (false negative)
specificity example
speciFicity = speciFies the False
if a test has 90% specificity, if 100 healthy people are tested then 90 healthy people will be found to be disease free
other 10 people will appear positive for the disease (false positive)
when is sensitivity prioritized?
disease is serious
treatment is effective & available
high risk of infectivity if individuals are not treated
subsequent test (next option) is cheap and low-risk
when is specificity prioritized?
treatment is difficult
subsequent tests is expensive and risky