Ovaries, Fallopian tubes & ligaments (copy)
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the pelvic structures?
Ovaries
Uterus
Fallopian tubes
Vagina
Will you see fallopian tubes on ultrasound?
Not unless there is something wrong with them
Peritoneum = _____________
Ligaments
What is the broad ligament?
Peritoneum that drapes over the uterus
The broad ligament divides the pelvic cavity into …
Anterior pelvic cavity
Posterior pelvic cavity
The anterior pelvic cavity contains what structure?
Bladder
The posterior pelvic cavity contains what structure?
Rectum
The broad ligament is divided into _________ broad ligaments?
3
What are the 3 sections of the broad ligament?
Mesovarium
Mesoalpinx
Mesometrium
The broad ligament is not a "________” ligament.
True
The broad ligament houses the?
Fallopian tubes
Round ligament
Ovarian ligament
Vascular structures
Ovaries
What does the mesovarium ligament attach?
The ovary to the posterior wall of the broad ligament
What does the ovarian ligament attach?
The ovary to the lateral wall of the uterus
What does the suspensory ligament attach?
The ovary to the lateral pelvic wall
The suspensory ligament contains what structures?
Ovarian artery and vein
What is the round ligament function?
A pair of paired ligaments providing support for the uterus
What does the round ligament(s) attach?
Connect uterus to the anterolateral pelvic wall (under the broad ligament)
What does the round ligament maintain?
A forward bend of the uterus
What is the cardinal ligament function?
Provides rigid support for the cervix
What is the uterosacral ligament function?
Provides rigid support for the cervix
The ovarian ligament is a ___________________.
Cord within the broad ligament
Ovaries are anchored in place by three ligaments, what are they?
Mesovarium
Ovarian
Suspensory
Why might the position of the ovaries vary?
Pressure from loops of bowel
Expansion of uterus during pregnancy
What are the normal shapes of the ovaries?
Almond shaped
What is the normal size of the ovaries?
3 cm
Ovaries contain > __________________.
1 million primary oocytes (eggs)
Women are born with all their _____, and they slowly lower in number.
Eggs
What is ovarian fossa?
Shallow depressions in the lateral wall
The outer surface of ovaries is __________.
Granulated
The normal ovary can hold numerous _________________.
Ovarian follicles
When the follicle matures, what does it become?
Graafian follicle
How often do follicles turn into a Graafian follicle?
Monthly
What is the process of ovulation?
Release of oocyte from Graafian follicle
What are ovaries function?
It is the sex organ that produces oocytes, estrogen, and progesterone
What do ovaries look like on ultrasound?
Heterogeneous appearance due to anechoic/cystic appearance of follicles
Where do ovaries sit?
Posterolateral to uterus but position is variable and influenced by surrounding structures
Ovaries are supported by ___ ligaments.
3
What is the corpus luteum?
Essential for establishing and maintaining pregnancy in females
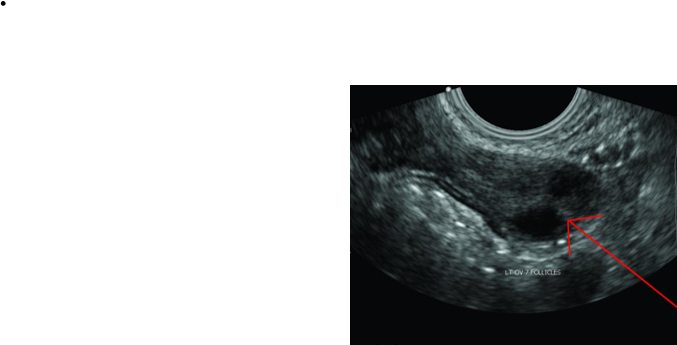
What structure is this, what approach is it scanned through, and what in view?
LT Ovary
Transvaginal
Transverse
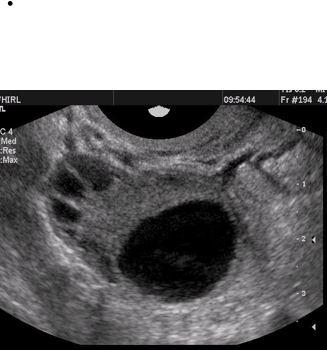
What structure is this, what approach is it scanned through, and what in view?
Ovary
Transvaginal
Transverse
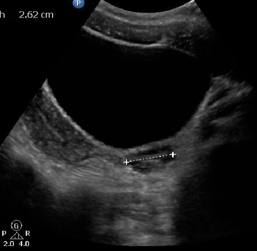
What structure is this, what approach is it scanned through, and what in view?
LT ovary
Transabdominal
Transverse
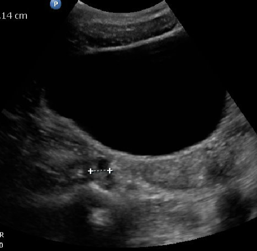
What structure is this, what approach is it scanned through, and what in view?
RT ovary
Transabdominal
Transverse
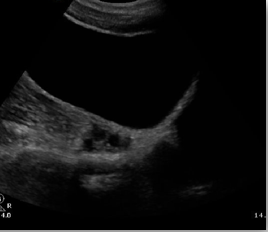
What structure is this, what approach is it scanned through, and what in view?
RT ovary
Transabdominal
Long
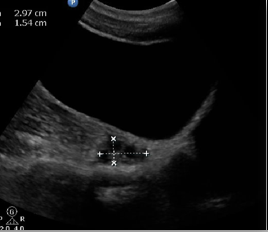
What structure is this, what approach is it scanned through, and what in view?
RT ovary w/ correct measurement
Transabdominal
Long
What size of follicles are considered cysts?
2.5cm or greater
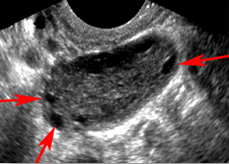
What structure is this, what approach is it scanned through, and what in view?
Ovary
Transvaginal
Long
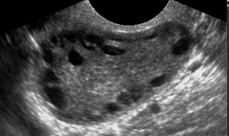
What structure is this, what approach is it scanned through, and what in view?
LT Ovary
Transvaginal
Long
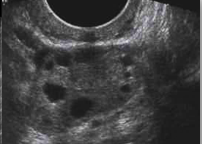
What structure is this, what approach is it scanned through, and what in view?
Ovary
Transvaginal
Long
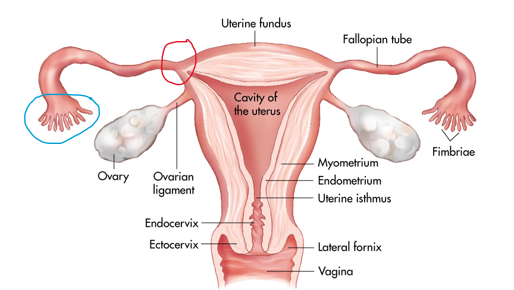
The blue circle represents the _______ portion of the fallopian tube
Disal - opens into the peritoneal cavity
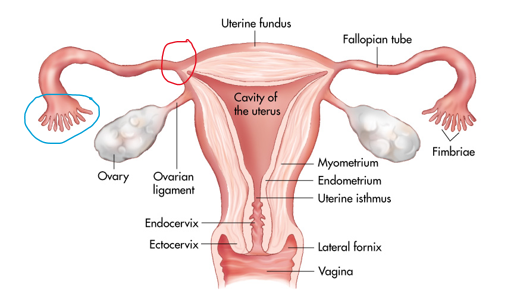
The red circle represents the _______ portion of the fallopian tube
Proximal - opens into the uterine cavity (cavity of uterus)
What is the normal length of the fallopian tubes?
10-12 cm
What is the normal shape of the fallopian tubes?
J-shaped
Where do the fallopian tubes lie?
Superior portion of broad ligament
What kind of connection is there between the ovaries and fallopian tubes?
There is no direct connection
What do the fallopian tubes permit?
Communication between external and internal (pathway for pathogens to enter {infections})
How many segments make up the fallopian tube?
5
What are the 5 segments of the fallopian tubes?
Interstitial
Isthmus
Ampulla
Infundibulum
Fimbriae
What is the interstitial portion of the fallopian tubes?
Located in the cornua of the uterus (proximal)
What is the Isthmus portion of the fallopian tubes?
Proximal part of the tube just outside of the uterus
What is the ampulla portion of the fallopian tubes?
Portion between the Isthmus and the Infundibulum
What is the infundibulum portion of the fallopian tubes?
Funnel-shaped end of the tube near the ovary
What is the fimbriae portion of the fallopian tubes?
Fingerlike extension at the edge of the infundibulum
What is the most common area for ectopic pregnancy’s?
Ampulla