EARTH238-2a-Primary Structures Part 1
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Why are primary structures useful
markers; younging indicators
Bedding
Primary layering in sedimentary rock, formed during deposition, manifested by changes in texture, colour, and/or composition
Stratigraphic Facing
Direction to younger strata, direction to the depositional top of beds
Younging directions
same as stratigraphic facing; direction to younger strata; direction which bed gets younger, what way was originally up
Why is bedding the best marker
it is planar and horizontal
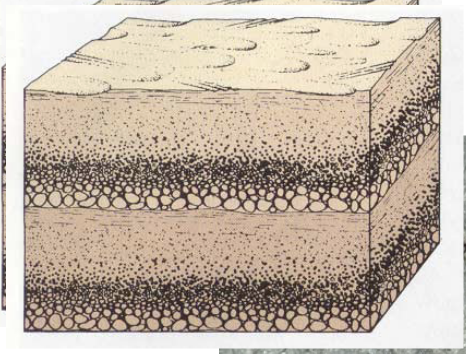
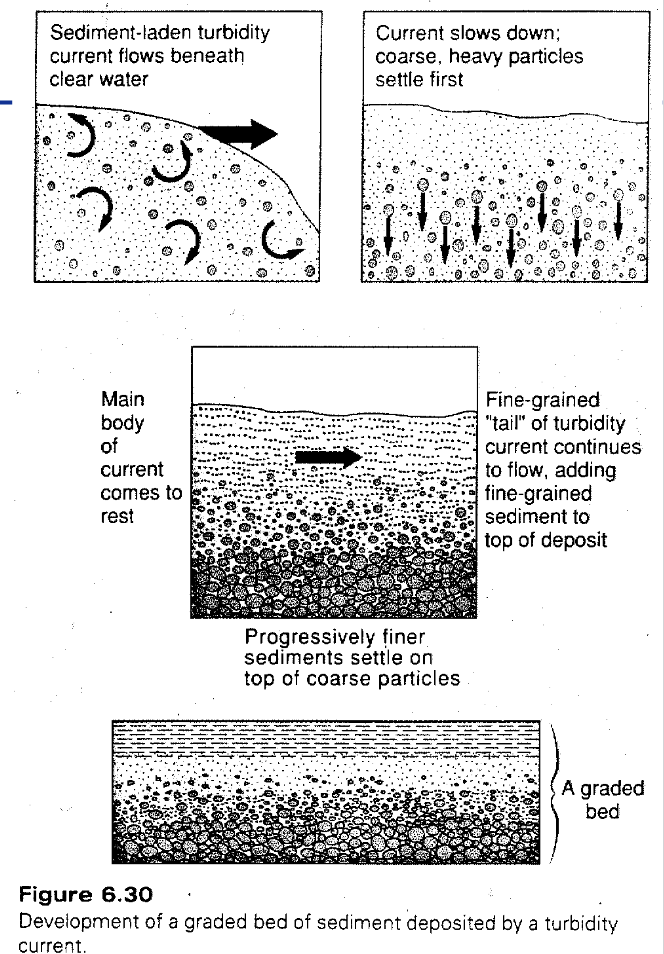
Graded bedding
Systematic variation in grain size within a bed: sediments are coarser grained at base and finer at the top
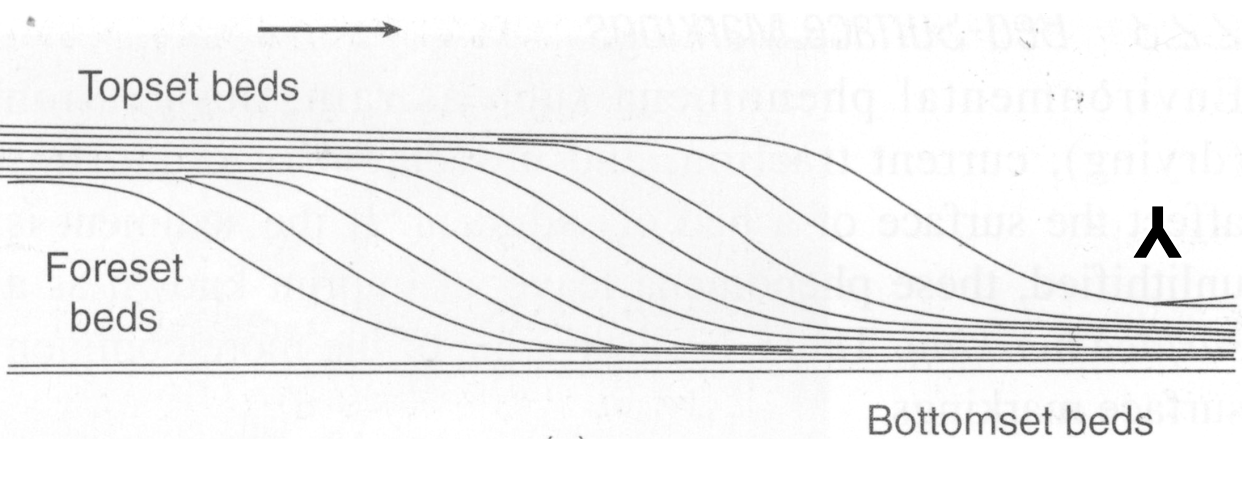
Cross Bedding
surfaces within a thicker, master bed that are oblique to the overall bounding surfaces of the master bed
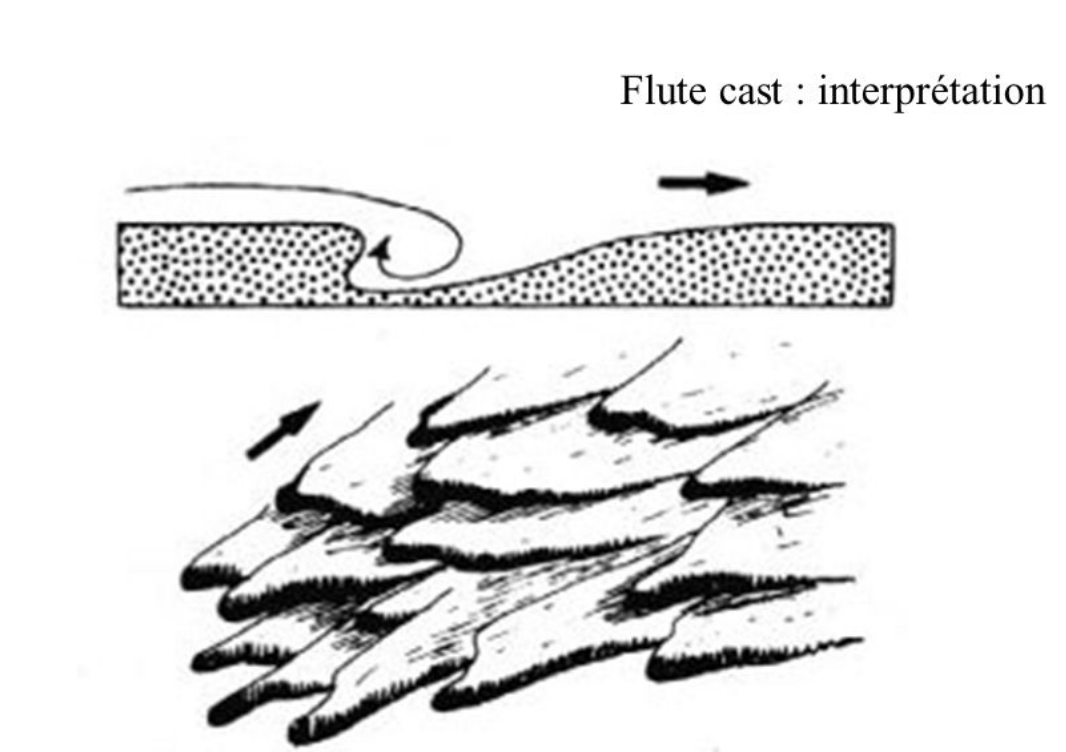
Flute casts
asymmetric troughs formed by vortices (mini-tornadoes) within the fluid that dig into the unconsolidated substrate
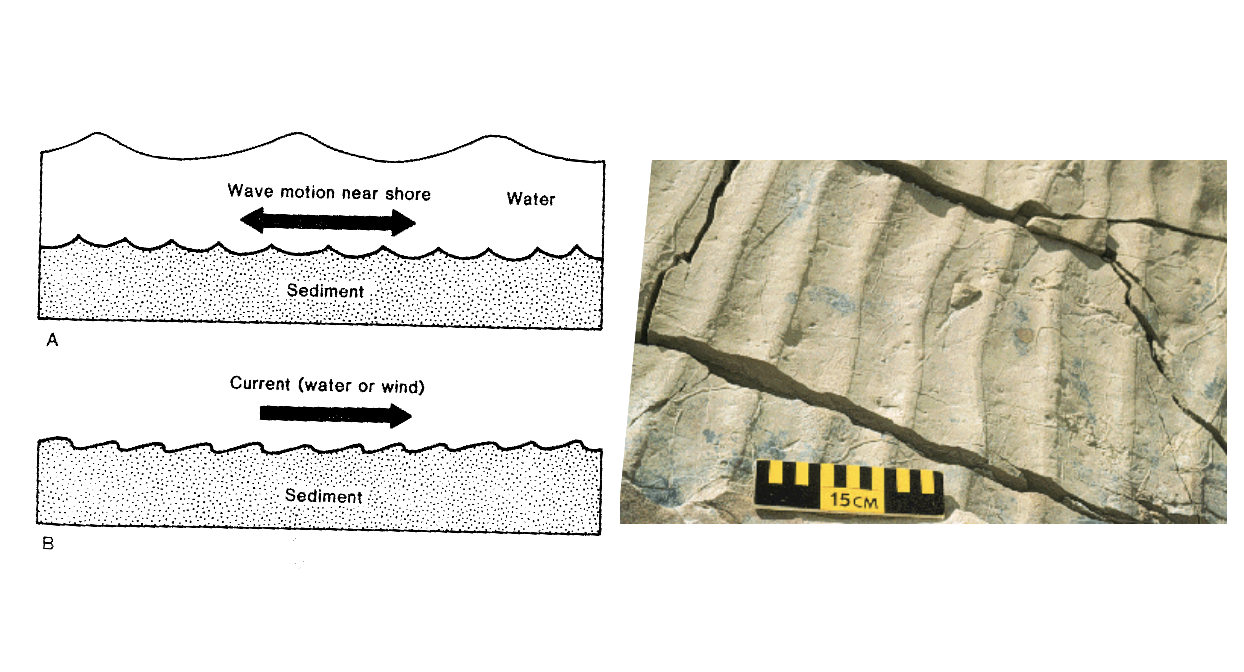
Ripple marks
Ridges and valleys on the surface of a bed formed as a consequence of fluid flow. can be symmetric (flows back and forth) or asymmetric (uniformly flowing)
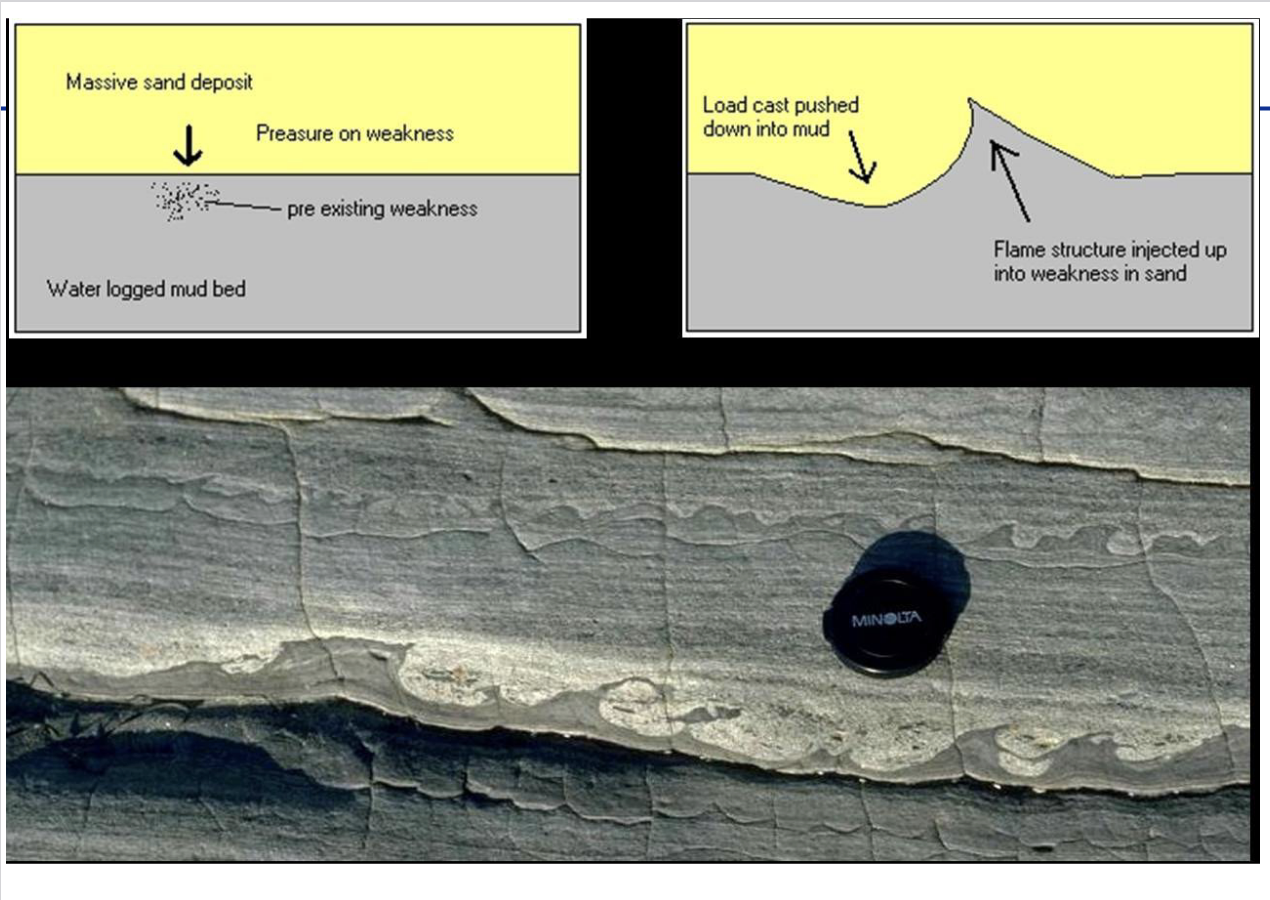
Load Structures
commonly occur at contact b/w sand layer and mud layer
Flames
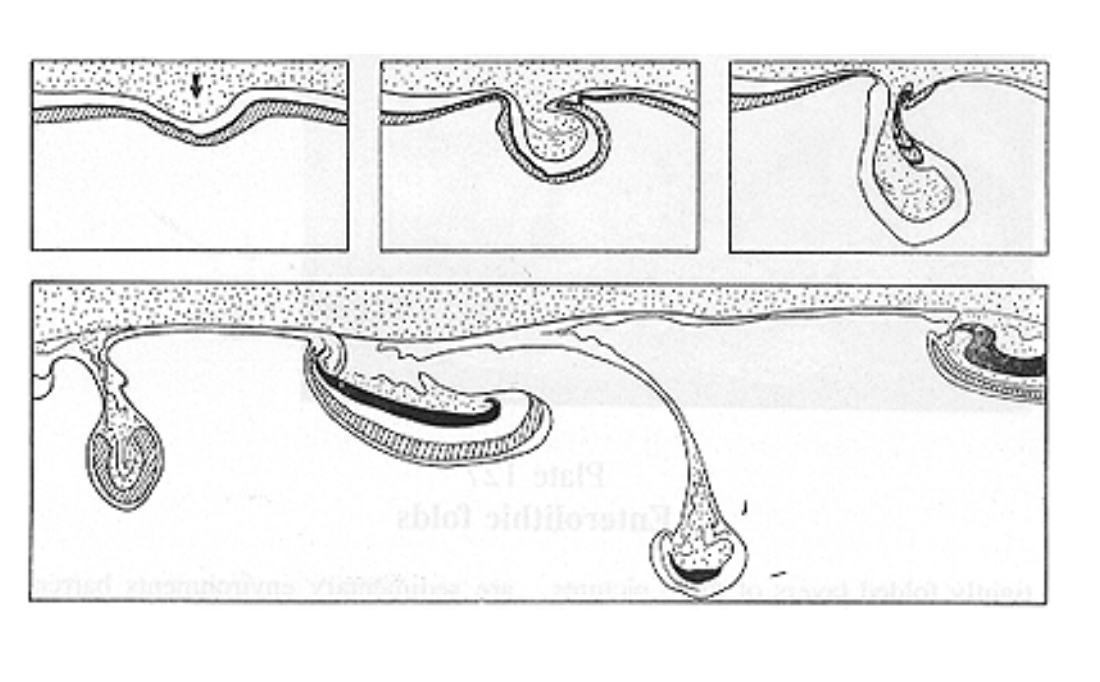
Ball and pillow
Dewatering Structures
sediments oversaturated with water and under pressure; disturbed by an event, water wants to get out