Final Exam ichthyology
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
What is the trend in fishes regarding bones?
Reduction of bones
What are the two primary functions of the skeletal system?
Provides framework and support for the body
What forms a transitional boundary that protects the organism in fishes?
Skin and scales
What are the two types of bone?
Dermal Bone and Endochondral Bone
What is Dermal Bone?
Membrane bone that forms directly through ossification of mesenchyme
What is Endochondral Bone?
Cartilage bone that is initially formed within a cartilaginous matrix and later ossified
What are the three types of jaw suspension?
Amphistylic, Hyostylic, Autostylic
Describe Amphistylic jaw suspension.
Upper jaw attached to cranium by ligaments, little mobility
Describe Hyostylic jaw suspension.
Both jaws suspended from chondrocranium via ligaments, allowing greater jaw mobility
Describe Autostylic jaw suspension.
Palatoquadrate fused to chondrocranium, hyoid arch not involved
What are the four feeding modes?
Grazers, Strainers, Suction feeders, Tube feeders
What do Grazers feed on?
Stationary food like plants and coral
What do Strainers primarily feed on?
Plankton
What characterizes Suction feeders?
Rounded, inferior mouths with thick, fleshy lips
What are Tube feeders adapted for?
Sucking in small food items or feeding in small crevices
What is the function of gill rakers?
Assist in the capture or retention of prey.
What are bony or cartilaginous projections that point inwards and forwards from the inner face of each gill arch?
Gill rakers.
What type of teeth are triangular, blade-like, and used for slashing food items?
Triangular teeth.
What is an example of a fish with triangular teeth?
Requiem sharks, piranhas, and barracudas.
What type of teeth are recurved, conical, and fang-like?
Caniniform teeth.
What is an example of a fish with caniniform teeth?
Cods, snappers, and bowfin.
What type of teeth are numerous, short, and have a rough sandpaper texture?
Cardiform teeth.
What is an example of a fish with cardiform teeth?
Bass, snook, and billfish.
What is the function of the spiral valve in sharks?
To increase absorptive surface area.
How does the gut tract of herbivores differ from that of carnivores?
Herbivores have a long intestine; carnivores have a short intestine.
What are myomeres?
Series of muscle blocks in fish.
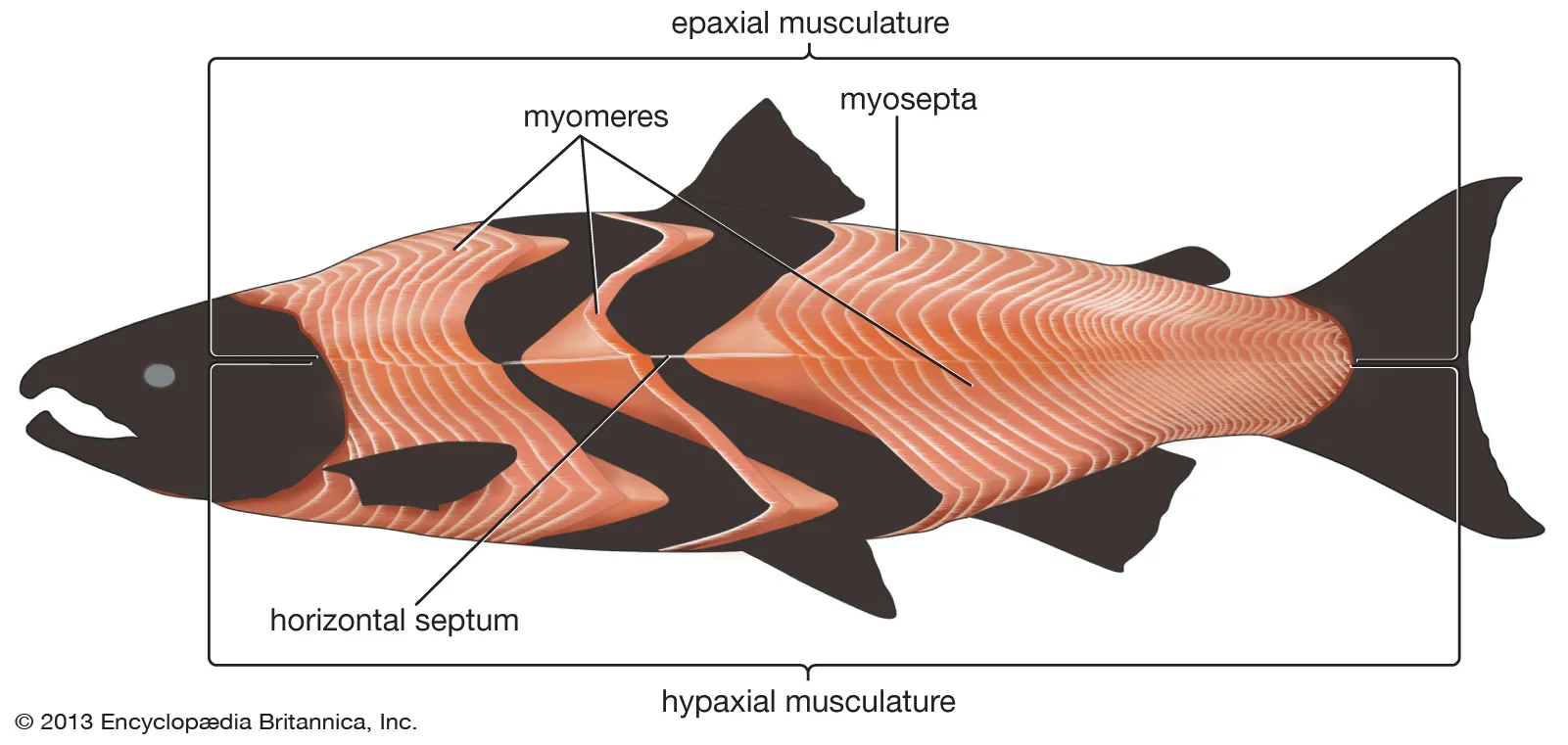
What separates myomeres?
Myosepta.
What are the upper muscles in fish called?
Epaxial muscles.
What are the lower muscles in fish called?
Hypaxial muscles.
What type of muscle is used for short duration burst swimming?
White muscle.
What type of muscle is used for continuous swimming?
Red muscle.
What is the function of the caudal fin?
Propulsion and rudder.
What is the function of dorsal and anal fins?
Undulatory propulsion and prevents roll.
What is the main route of transport of oxygenated blood from gills to the rest of the body?
Dorsal aorta.
What is the major return route of deoxygenated blood?
Postcardinal vein.
What is a holobranch?
A full gill made up of two halves.
What is a hemibranch?
Half a gill, consisting of one half.
What is the importance of countercurrent flow in gills?
It enhances the efficiency of gas exchange.
What are some buoyancy strategies used by fish?
Become benthic, low density compounds, lift generated by swimming, reduction of heavy tissues, swim bladder.
What is the difference between physostomic and physoclistic swim bladders?
Physostomic swim bladders are connected to the gut; physoclistic swim bladders are not.
What is an example of an isotonic fish?
Hagfish.
What type of fish are hypotonic to their environment?
Marine saltwater fish, such as clownfish.
What type of fish are hypertonic to their environment?
Freshwater fish.
What compounds do sharks use to retain salts?
Urea and trimethylamine oxide (TMAO)
What are the main strategies of marine teleosts for osmoregulation?
They drink seawater, have fewer and smaller glomeruli, excrete salts along convoluted tubules, and produce concentrated urine.
What is the problem faced by marine teleosts regarding water?
They lose water through their membranes and must conserve water while excreting excess salts.
How do freshwater teleosts manage osmoregulation?
They have body fluids in greater concentration than surrounding water, take on water, and lose valuable salts.
What is the problem faced by freshwater teleosts?
They need to eliminate excess water and retain salts.
What is the difference between anadromy and catadromy?
Anadromy: adults spawn in freshwater, juveniles move to saltwater; Catadromy: adults spawn at sea, juveniles migrate to freshwater.
What is fecundity in fish?
The number of gametes produced.
What influences the number of eggs produced in fish?
Egg size and number are inversely related; egg number is directly related to female size and influenced by food supply.
What is the difference between oviparous and viviparous reproduction?
Oviparous: egg birth; Viviparous: live birth.
What is iteroparous spawning?
Spawning repeatedly in a lifetime.
What is semelparous spawning?
Spawning once in a lifetime.
What are primary sex characteristics?
Characteristics directly involved in reproduction mechanics, such as brood pouches and claspers.
What are secondary sex characteristics?
Characteristics involved in mate attraction or parental care.
In what geologic period did fish arise?
Silurian period (444-419 million years ago).
What are the four chordate features?
A notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail.
What does neoteny refer to?
Retention of juvenile characteristics in adults, allowing sexual maturity without developing adult features.
What are some characteristics of ostracoderms?
Armored, jawless fish with bony shields and plates, a cartilaginous skeleton, and typically lacking paired fins.
What distinguishes hagfish from lampreys?
Hagfish have a larger mouth opening and are slime-producing scavengers; lampreys can be parasitic and have fewer gill openings.
How have sea lampreys negatively impacted the Great Lakes?
They prey on Lake trout, causing high mortality rates and contributing to population collapses.
When did jaws arise in fish?
Silurian period (444-419 million years ago).
What structure evolved with jaws?
The hyoid arch.
From what did jaws evolve?
Gill arches of ancient jawless fish.
What was the evolutionary significance of jaws and paired fins?
They allowed vertebrates to become mobile predators, expanding their ability to hunt and exploit food sources.
What made placoderms unique?
Bony armor, jaws, live birth, internal fertilization, unique neck joint, and paired fins.
What are some unique adaptations of chondrichthyans?
Flexible cartilage skeleton, advanced sensory systems, and highly developed senses of smell and hearing.
How do torpedinids generate electrical currents?
Using modified muscle cells called electrocytes arranged in columns.
What adaptations does the head shape of Sphyraenidae provide?
Enhanced maneuverability, better chemo- and electroreception, wider field of view, and ability to ram and pin prey.
What are key differentiating characters between sawfish and sawsharks?
Sawfish are rays with gill slits on the underside; sawsharks are true sharks.
Provide an example of a Galeomorph.
Great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) or bull sharks.
Provide an example of a Squalimorph.
Spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) or nurse shark.
Provide an example of a Batimorph.
Manta ray (Manta birostris) or skates.
What food items were paddlefish and sturgeon fished for?
Caviar and white meat.
What kind of larvae do eels, tarpon, bonefish, and ladyfish have?
Leptocephalus, a flat, transparent, and ribbon-like form.
What are examples of anadromous and catadromous fish?
Anadromous: Fresh→ Salt- Chinook Salmon
Catadromous: Salt→ Fresh- American Eel
What are the three characteristics of ostariophysians?
Schrekstoff's substance, Weberian apparatus, and breeding tubercles.
What is the function of the modified vertebrae that touch the swim bladder in catfish and clupeids?
They connect the swim bladder to the inner ear for enhanced hearing.
What groups generate electrical currents and how are they used?
Torpediniformes (to capture prey), Mormyridae (for locating objects and social interactions), Gymnotidae (producing electric pulses), Gymnarchidae (detecting electric fields), and Apteronotidae (producing weak pulses).
What is the evolutionary advantage of spines in Acanthopterygii?
Defense, making it painful for predators to swallow them.
What are the feeding specializations in Acanthopterygii?
Protrusible premaxilla, teeth, jaw and mouth adaptations, pharyngeal modifications, maneuverability, fin position, and strength.
What is the most specious group in freshwater environments in the Eastern US?
Percidae
What is the most specious group in marine environments?
Gobiidae.
How do swordfish and marlin differ morphologically?
Swordfish have a flat, broad bill, tall crescent-shaped dorsal fin, absent pelvic fins, and a robust body. Marlin have a pointier bill, lower longer dorsal fin, present pelvic fins, and a more elongated body.
What is the sequence of eye location during a flounder's development?
Larval stage: bilaterally symmetrical with one eye on each side. Juvenile stage: one eye migrates to the other side. Adult stage: both eyes on the same side.
What are some groups that are hermaphroditic?
Family Serranidae and Sparidae.
What are the dominant carnivores in North America?
Centrarchidae, including sunfish.
What adaptations do Notothenoids have to survive in Antarctic waters?
Production of antifreeze glycoproteins, reduction of skeletal elements, using lipids instead, lack of red blood cells, and colorless blood and flesh.
Provide an example of an Elopomorph.
American eel (Anguilla rostrata).
Provide an example of an Osteoglossomorph.
Arapaima (Arapaima gigas) or Mooneye.
What are the four main cohorts of Teleostei?
Elopomorpha, Osteoglossomorpha, Otocephala, and Euteleostei.
In more highly derived fish, where are the pelvic fins positioned?
Pelvic fins have moved forward on the body, often to a thoracic or jugular position.
Why are coelacanths considered a Lazarus species?
They were thought to be extinct for millions of years.
What is aestivation?
A state of dormancy during hot, dry periods to protect animals from arid conditions.
What is the evolutionary significance of Infraclass Elpistostegalia?
They have paired fins that are leg-like and show similarities to tetrapods.
In what geologic period where the first chondrichthyans
Devonian
Percomorpha
Gar
Otocepehla
Squirrel fish, Anchovy
Cyclosquamata
Lizardfish