Pharmacotherapy Benign Prostate Hyperplasia
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
The prostate is a __________________ gland.
heart shaped
Where is the prostate gland located?
Below the bladder and surrounding the urethra.
What is the normal adult prostate weight?
15-20 grams
What are the three types of tissue in the prostate?
- epithelial
- stromal (contain alpha-1 receptors)
- capsule (contain alpha-1 receptors)
What are the two major functions of the prostate?
1) Secreting fluids that contribute to seminal fluid.
2) Secreting fluids with antibacterial effects.
How is BPH defined?
A proliferative process of both epithelial and stromal cells in the prostate; a benign neoplasm.
Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) the most common benign neoplasm in men?
Yes
How does BPH prevalence vary with age?
50% of men have BPH by age 60 and 90% by age 80.
Impact of BPH on quality of life
- patients may have to limit fluids before bedtime
- patients may have to avoid places without toilets
- patients may have to limit fluids before travel
- patients may not get enough sleep
- patients may not be able to drive more than 2 hours
- patients may have to avoid theaters, movies, church, etc.
- patients may have to avoid outdoor sports
What is the major risk factor for BPH?
Age.
Besides age, what is another known risk factors for BPH?
Family history
What are possible risk factors for BPH?
- obesity
- hypertension
- low HDL
- diabetes
- high insulin levels
What causes the symptoms of BPH (lower urinary tract symptoms or LUTS)?
Enlarged prostate tissue and contraction of the prostate capsule.
How does testosterone contribute to BPH?
Testosterone, the primary androgen in males, is converted by 5-alpha reductase to DHT, which binds androgen receptors, promoting prostate growth.
What is the static component of BPH pathophysiology?
Enlarged prostate tissue that physically blocks the bladder neck, obstructing urine outflow due to DHT effects; causes obstructive symptoms.
What is the dynamic component of BPH pathophysiology?
Contraction of the prostate gland that narrows the urethral lumen due to excessive alpha-adrenergic tone; causes irritative symptoms.
What are obstructive symptoms of BPH?
- weak urine stream
- incomplete bladder emptying
- dribbling
- hesitancy
- need to strain to urinate
What are irritative symptoms of BPH?
Urgency, frequency, and nocturia due to excessive alpha receptor stimulation and detrusor involvement.
What are complications of untreated BPH?
- acute urinary retention
- UTI
- bladder stones
- bladder damage
- renal impairment
- hematuria
What are key components of BPH diagnosis?
- History and physical: digital rectal exam, International Prostate Symptom Score - IPSS) - Laboratory studies: urinalysis,Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) testing
Is BUN/serum creatinine needed during initial assessment of BPH?
No
What are IPSS score ranges for BPH symptom severity?
- 0-7 mild
- 8-19 moderate
- ≥20 severe
What is the main goal of BPH therapy?
Improve symptoms.
What are secondary goals of BPH therapy?
Halt disease progression and prevent complications.
What factors are most important in choosing therapy?
Quality of life and patient preference.
What are the treatment options for BPH?
- lifestyle modifications
- alpha-adrenergic antagonists
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors
- PDE-5 inhibitors
- combination therapy
- phytotherapy
- surgery
- minimally invasive therapy
What lifestyle modifications help BPH?
- fluid restriction at night
- avoid caffeine/alcohol/drugs that worsen symptoms
- scheduled voiding
- smoking cessation
- increased physical activity
Name some alpha-1 adrenergic antagonists used for BPH.
- Terazosin
- Doxazosin
- Alfuzosin
- Tamsulosin
- Silodosin
How do alpha blockers work?
Relax smooth muscle tone and resistance in the prostate and bladder neck.
What are the three alpha-1 receptor subtypes?
- alpha-1a
- alpha-1b
- alpha-1d
Which alpha-1 receptor subtype predominates in the prostate?
Alpha-1a (≈80% of receptors).
Terazosin dosing
1 mg, 2 mg, 5 mg, and 10 mg.
Doxazosin dosing
1 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg, and 8 mg
Tamsulosin dosing
0.4 mg and 0.8 mg
Alfuzosin dosing
10 mg
Silodosin dosing
8 mg
Which alpha 1 blockers require titration?
Terazosin, Doxazosin, and Tamsulosin.
Which alpha blockers are uroselective?
Alfuzosin (functionally), Tamsulosin (1a=1d>1b), and Silodosin (1a>1d>1b).
What are common adverse effects of alpha blockers?
- fatigue
- orthostatic hypotension (dizziness, vertigo, syncope, sexual dysfunction)
- edema
- retrograde ejaculation
- rhinitis
- dyspnea
- headache
- angina
- floppy iris syndrome
- QT prolongation (Alfuzosin)
Which alpha blockers can interact with antihypertensives to cause additive hypotension?
Doxazosin and Terazosin.
What drug decreases clearance of Tamsulosin?
Cimetidine.
Alpha blockers are contraindicated with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors such as:
Ketoconazole, Itraconazole, and Ritonavir.
What are benefits of alpha blocker therapy?
- rapid improvement of urinary flow
- reduced LUTS
- similar efficacy across agents
- modest sexual side effects (except Tamsulosin)
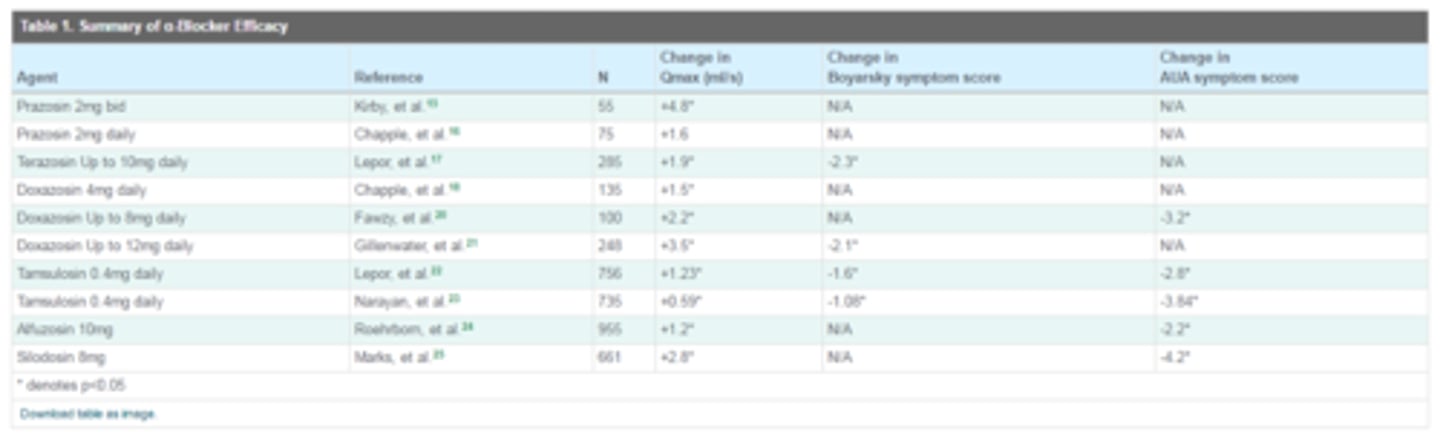
Studies show an increase in _______________ and a decrease in ___________________ for patients on alpha blocker therapy.
QMax (maximum urinary flow rate); symptom scores
Name two 5-alpha reductase inhibitors used in BPH.
Finasteride (Proscar®) and Dutasteride (Avodart®).
Mechanism of action of 5-ARIs:
- Dutasteride inhibits 5AR1 and 5AR2 to block the conversion of testosterone to DHT which in excessive levels causes BPH
- Finasteride inhibits 5AR2 to block the conversion of testosterone to DHT which in excessive levels causes BPH
What do 5-alpha reductase inhibitors do?
- reduce prostate size
- slow disease progression of BPH
- decrease surgery need
- lower PSA by ~50%.
When are 5-ARIs ideal?
For patients with large prostates (>40 g).
How long does it take 5-ARIs to reduce symptoms?
6-12 months.
What are key differences between Finasteride and Dutasteride?
- Finasteride inhibits type II 5 alpha reductase while Dutasteride inhibits types I and II.
- Finasteride lowers DHT by ≈ 70% while Dutasteride lowers it by ≈ 90%.
- Finasteride lowers prostate size by ≈ 20-30% while Dutasteride lowers it by ≈ 15-26%
What are the typical doses of Finasteride and Dutasteride?
- Finasteride 5 mg QD
- Dutasteride 0.5 mg QD
What are common adverse effects of 5-ARIs?
- erectile dysfunction (8%)
- decreased libido (6.4%)
- ejaculatory dysfunction (0.8%)
- gynecomastia and breast tenderness (0.5%)
Outcomes of 5ARI use:
- increased Qmax
- decreased symptom scores
- decrease the size of the prostate
What is combination therapy in BPH?
Use of an alpha antagonist with a 5-ARI for dual action.
What benefits does combination therapy provide?
- reduced clinical progression
- improved LUTS and urine flow
What trial supports combination therapy?
MTOPS trial (placebo vs finasteride 5 mg vs doxazosin 4 mg or 8 mg vs combination).
Outcomes of combination therapy in BPH:
- increased Qmax
- decreased symptom scores
- decreased prostate size
What does the AUA recommend regarding combination therapy?
It should be used in patients with moderate-to-severe symptoms, prostate > 40 g, higher PSA, and advanced age.
What is the mechanism of anticholinergics in BPH?
Block acetylcholine at detrusor muscle junctions, inhibiting detrusor contractions and reducing LUTS.
Name common anticholinergics used for BPH.
- Fesoterodine (Toviaz)
- Oxybutynin ER (Ditropan XL)
- Solifenacin (Vesicare)
- Tolterodine ER (Detrol LA)
What are side effects of anticholinergics?
Dry mouth/eyes, constipation, and blurred vision.
What is Mirabegron (Myrbetriq)?
A beta-3 adrenergic receptor agonist that relaxes bladder muscles and causes less anticholinergic effects.
What adverse effect can Mirabegron cause?
Hypertension
Name some phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors.
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
- Vardenafil (Levitra)
- Avanafil (Stendra)
Which PDE-5 inhibitor is FDA-approved for BPH treatment?
Tadalafil (Cialis)
Name common phytotherapy agents for BPH.
- Saw palmetto (Serenoa repens)
- African plum (Pygeum africanum)
- pumpkin (Cucurbitae peponis semen)
- South African star grass (Hypoxis rooperi)
- stinging nettle (Urtica dioica)
What is surgery considered as for BPH treatment?
The gold standard (TURP) because it offers the most reliable and immediate subjective and objective improvement.
Surgery indicated for BPH in patients who also have:
- renal insufficiency
- urinary retention
- recurrent UTI
- bladder stones
- hydronephrosis
- past voice residual (PVR) > 500 mL.
Past void residual (PVR)
the amount of urine left in the bladder after the patient voids
What are types of surgery for BPH?
- Open prostatectomy
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
- Minimally invasive options (TUNA, TUMT, laser, TUIP, Rezum, ethanol injection, and Urolift)