9.8 - Control of heart rate in mammals
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is the equation to calculate cardiac output?
Cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate
What is cardiac output?
The volume of blood the heart pumps through the circulatory system in one minute
What is stroke volume?
The volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle with each beat of the heart
Describe the autonomic nervous system mean
It is self-governing & controls involuntary (subconscious) activities of internal muscles & glands
It has two divisions: sympathetic & parasympathetic
Compare the sympathetic & parasympathetic nervous systems
Sympathetic ‘fight or flight’:
Helps the body prepare for a perceived threat
inhibition of digestive & immune systems (i.e. diverting blood to muscles)
pupil dilation & increased heart rate
expansion of the lungs
Parasympathetic ‘rest & digest’:
Effects largely mirror opposites of sympathetic system (i.e. antagonistic → bring about opposite effects)
stimulation of digestive & immune systems
decreased pupil size & heart rate
contraction of the lungs
The cardiac centre can send impulses to the SAN of the heart. What do impulses through sympathetic neurons release?
Noradrenaline at the SAN, causing the heart rate to increase
The cardiac centre can send impulses to the SAN of the heart. What do impulses through parasympathetic neurons release?
Acetylcholine at the SAN, causing the heart rate to decrease
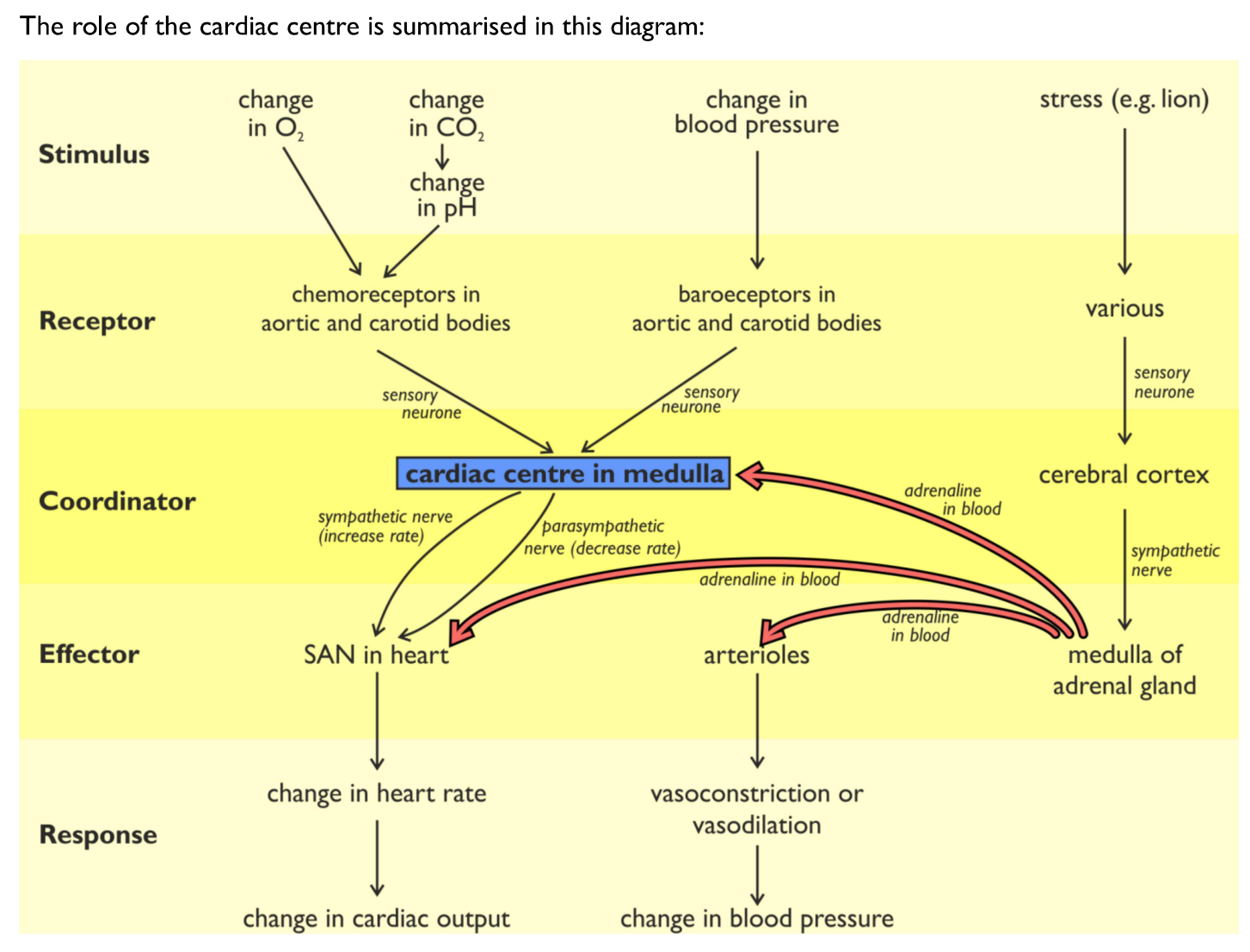
Where in the brain is the cardiac control centre located & name the two types of receptors that send information to the cardiac control centre?
Medulla oblongata:
baroreceptors
chemoreceptors
Which type of receptor is found in the aorta & carotid arteries & is sensitive to pressure changes?
Baroreceptors
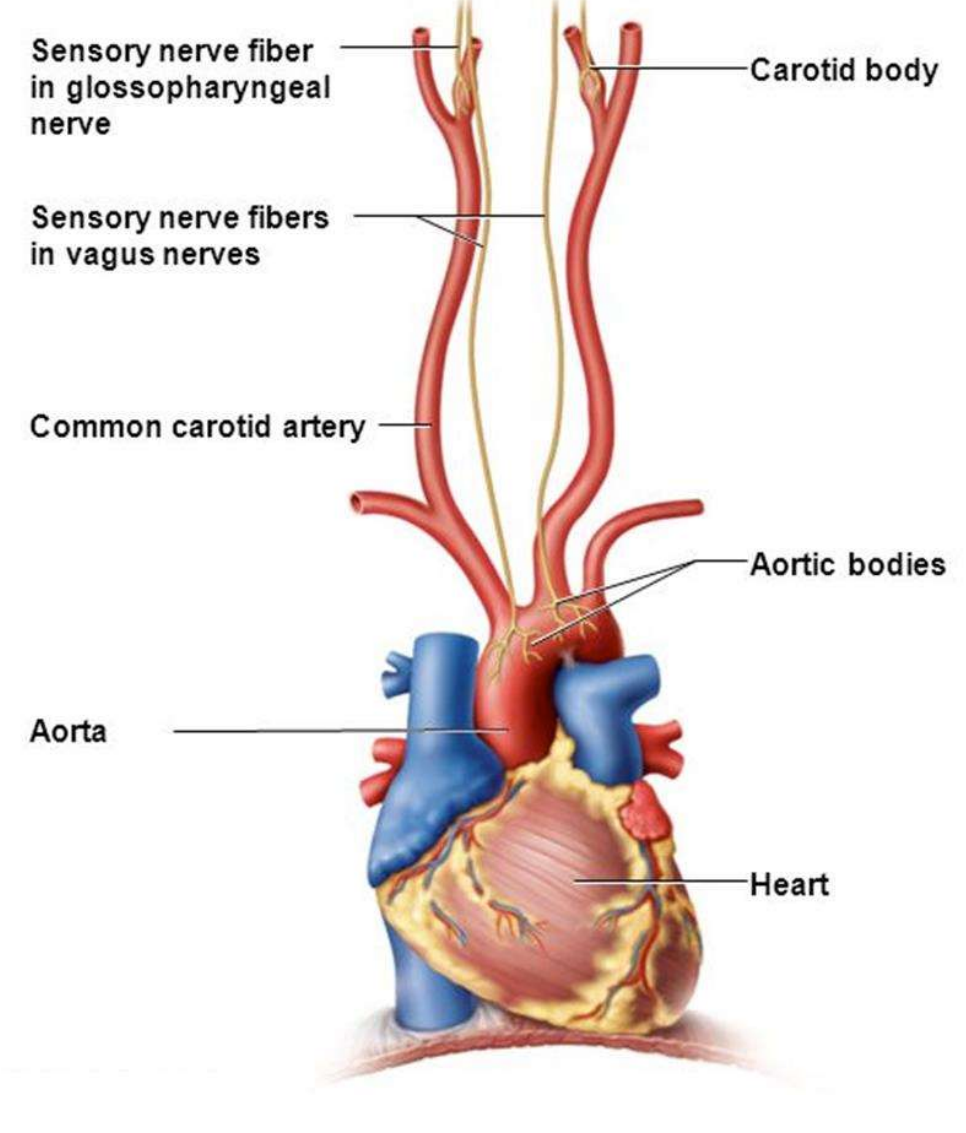
Which type of receptor is found in the walls of the carotid arteries & aorta & are sensitive to levels of blood carbon dioxide?
Chemoreceptors
Describe what the baroreceptors do in response to an increase in blood pressure above normal
When blood pressure rises above normal, the baroreceptors are stretched
They send more nerve impulses to the centre in the medulla that decreases heart rate
This centre sends impulses via the parasympathetic nervous system to the SAN of the heart, which decreases the rate at which the heart beats & causes vasodilation (widening of blood vessels)
Both of these effects lower blood pressure
Describe what the baroreceptors do in response to a decrease in blood pressure below normal
When blood pressure falls below normal, the baroreceptors stretch less
They send more nerve impulses to the centre of the medulla that increases heart rate
This centre sends impulses via the sympathetic nervous system to the SAN of the heart, which increases the rate at which the heart beats & causes vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels)
Both of these effects raise blood pressure
Describe what the chemoreceptors do in response to an increase in CO₂ levels above normal
Increased muscular/metabolic activity (e.g. exercise)
More CO₂ is produced in the tissues from increased respiration
Carbon dioxide is an acidic gas → more CO₂ means a lower pH
Chemoreceptors in the carotid arteries & aorta detect this change & increase the frequency of nerve impulses that are sent to the centre of the medulla that increases heart rate
The centre in the medulla increases the frequency of nerve impulses to the SAN via sympathetic nervous system
The SAN increases heart rate
Increased blood flow removes CO₂ more quickly from the blood
CO₂ levels return to normal → chemoreceptors reduce the frequency of impulses to the medulla
How does the autonomic nervous system increase heart rate?
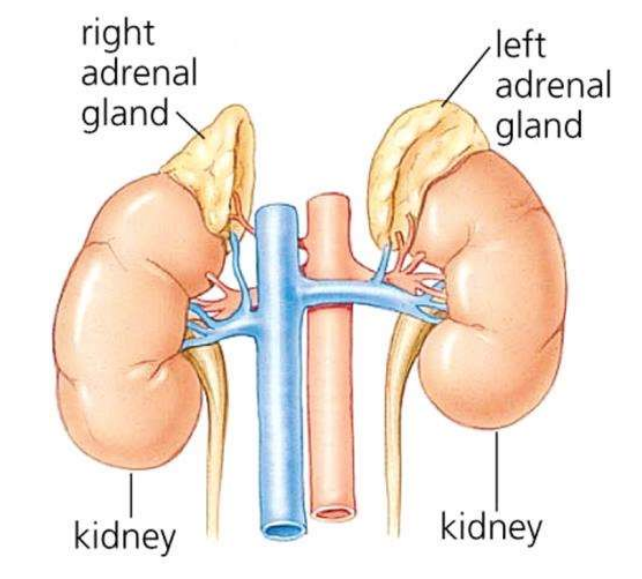
In times of stress, the sympathetic nervous system stimulates the release of adrenaline from the adrenal glands
Adrenaline stimulates the cardiac centre in the brain, increasing the impulses in the sympathetic neurons supplying the heart & SAN to increase heart rate