BIOL20 - Autonomic + Somatic Nervous System
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Somatic nervous system
sensory + motor neurons
sensory - touch, pain, temp, proprioception, sight, hearing, taste, smell, equilibrium
motor- SKM
Autonomic NS
sensory received from organs, blood vessels, muscles, NS
Somatic v. Autonomic Motor division
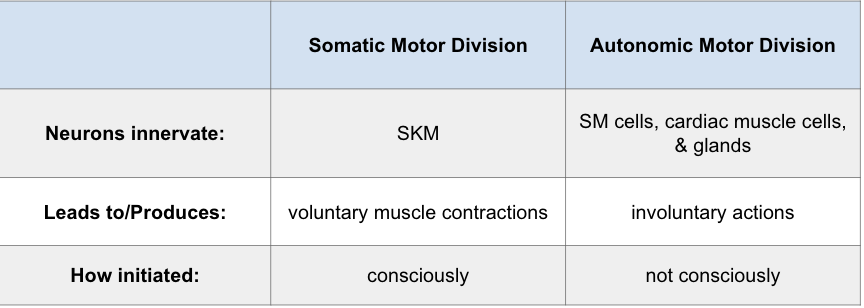
Main differences between Somatic and Autonomic
ANS motor neurons DO NOT directly innervate target
have preganglionic and postganglionic neurons
SNS - axon of a single, myelinated somatic motor neuron extends from CNS to SKM fiber it innervates
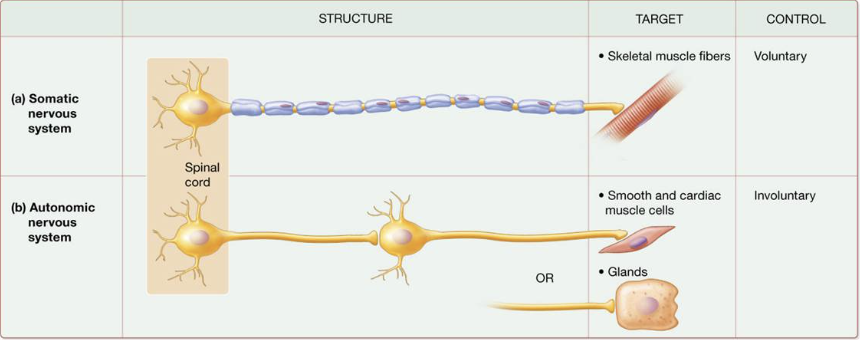
Preganglionic neuron
initial efferent neuron
cell body in CNS
all axons release ACh
Postganglionic neuron
cell body in autonomic ganglion in PNS
axons travel → target cells
release either ACh or norepinephrine
trigger specific changes → inhibit/excite responses
Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways
2 neurons in series
preganglionic neuron:
cell body → CNS
axon → autonomic ganglion
myelinated
postganglionic neuron:
unmyelinated
axon extends from ganglion → effector
Autonomic NS includes which 2 divisions
Sympathetic + Parasympathetic
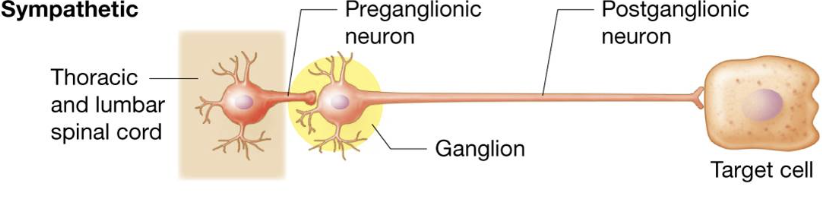
Sympathetic NS axon lengths
Preganglionic sympathetic axon: short
Postganglionic sympathetic axon: longggg
thoracolumbar
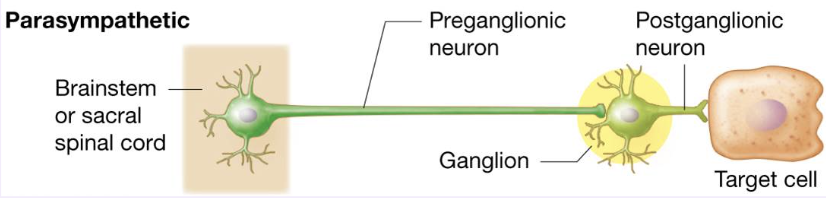
Parasympathetic NS axon lengths
Preganglionic sympathetic axon: longggg
Postganglionic sympathetic axon: short
craniosacral
Sympathetic preganglionic neuron
cell bodies are part of
→ lateral horns of grey matter
→ 1 2 thoracic + first 2/3 lumbar segments
Sympathetic trunk ganglia
anterior + lateral to vertebral column
How preganglionic axons connect with postganglionic axons neurons in the sympathetic trunk ganglia
axon synapses w/ postganglionic neuron
axon goes up or down a trunk
axon continues w/out synapsing (directly to target)
axon continues w/out synapsing through → sympathetic trunk gang → adrenal medullae
Pathways from sympathetic trunk
spinal nerves: postganglionic axons leave trunk via gray ramus communicans
innervates top part of body
cephalic periarterial nerve: superior part of neck, innervate blood vessels in/out of our head
sympathetic nerves: innervate heart + lungs
splanchnic nerves: pass through trunk forming a splanchnic nerve → prevertebral ganglion
Parasympathetic division
in nuclei of 4 cranial nerves ( III, VII, IX, X), in brain stem, and in lateral grey matter of sacral segments of spinal cord
Where are cell bodies of the Parasympathetic outflow located?
nuclei of brain stem + lateral grey matter of sacral spinal cord segments
Cranial parasympathetic outflow
extends from the brain stem in 4 cranial nerves
Sacral parasympathetic outflow
extends from 2nd through 4th sacral spinal nerves
2 major types of sympathetic ganglia
Sympathetic trunk ganglia: lie in a vertical row on either side of the vertebral column
Prevertebral ganglia: lie anterior to the vertebral column and close to the large abdominal arteries
Abdominal + Pelvic Plexuses
named after the artery
celiac (solar) plexus
superior mesenteric plexus
inferior mesenteric plexus
renal plexus
hypogastric plexus
What are ANS neurons characterized by?
the neurotransmitters they produce and release
Cholinergic neurons
release ACh
Adrenergic neurons
release Norepinephrine (noradrenalin)
Sympathetic receptor classes - postganglionic
Adrenergic receptors
Cholinergic receptors
Adrenergic receptors
bind to epinephrine + norepinephrine
2 types:
alpha adrenergic
alpha-1: walls of blood vessels, pupil dilation, ejaculation
alpha-2: presynaptic neurons, release ACh
beta adrenergic
beta-1: in p.mb of cardiac muscle cells, kidney cells, adipose cells
beta-2: in p.mb of SM
beta-3: in SM cells of digestive tracts walls
Cholinergic receptors
bind to ACh
2 types
Muscarinic receptors: on sweat glands in skin
Nicotinic receptors: in p.mb of all postganglionic neurons, w/in sym ganglia + adrenal medullae
Sensation
conscious + subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment
Components of sensation
stimulation of the sensory receptor
→ transduction of stimulus
→ generation of nerve impulses (transmission)
→ integration of sensory input
Classification of Sensory Receptors
General senses - somatic and visceral
Special senses
Somatic sensory
tactile, thermal, pain, proprioceptive sensations
Visceral
provide info abt conditions within internal organs
Special senses
smell, taste, vision, hearing, equilibrium, balance
Types of sensory receptors
free nerve endings
encapsulated nerve endings
separate cells
Free nerve endings
pain + thermoreceptors
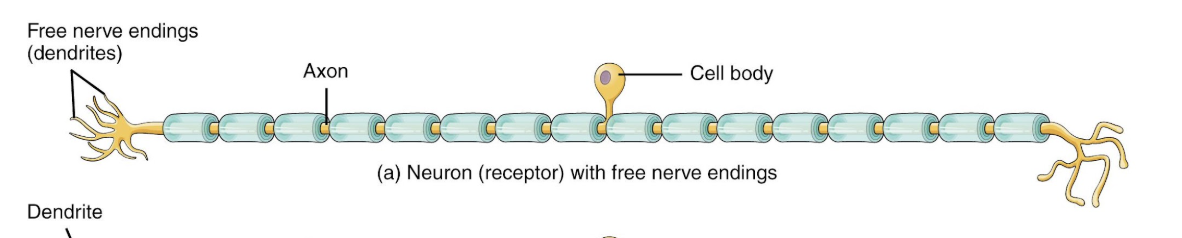
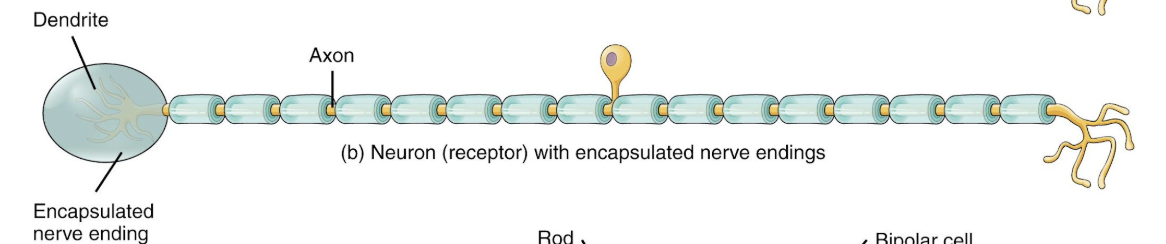
Encapsulated nerve endings
pacinian corpuscles, Meissner’s corpuscles
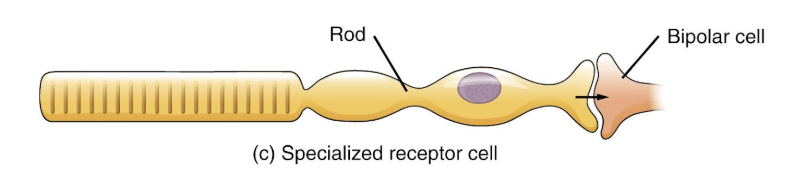
Separate cells
hair cells, photoreceptors, and gustatory receptor cells
Classification of sensory receptors based on location
exteroceptors: at/near body surface
Interoceptros: inside body (blood vessels, viscera, NS)
proprioceptors: muscles, tendons, joints, inner ear
Photoreceptors
specific to the retina
Chemoreceptors
smell, taste, O2, CO2 (pH)
Osmoreceptors
osmotic pressure (type of chemoreceptor)
Baroreceptor
pressure (type of mechanoreceptor)
Proprioceptors
type of mechanoreceptor
Sensory receptor adaptation
decrease in potentials during a maintained, constant stimulus
*desensitizes body
Rapidly adapting receptors
receptors that detect pressure, touch, and smell
Slowly adapting receptors
receptors that detect pain, body position, and chemical composition of blood
Somatic Sensations
sensory receptors in skin, muscles, tendons, and joints
uneven distribution of receptors
4 modalities: tactile, thermal, pain, and proprioceptive
Tactile sensation
touch, pressure, vibration, itch, tickle
in skin → Meissner corpuscles, hair root plexuses, Merkel discs, Ruffini corpuscles, Pacinian corpuscles, free nerve endings
Proprioceptive sensations
slow adaptation
weight discrimination
3 types: muscle spindles, tendon organs, and joint kinesthetic receptors
Somatic sensory pathways
carry info from somatic sensory receptors to the primary somatosensory area in the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum
first order neurons
second order neurons
third order neurons
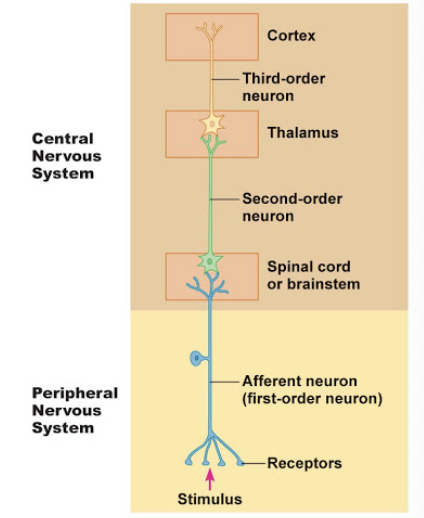
First-order neurons
impulses from somatic receptors → brain stem / spinal cord
Second-order neurons
impulses from brain stem + spinal cord → thalamus
Third-order neurons
impulses from the thalamus → primary somatosensory area of cortex on same side
Somatic sensory impulses ascend to the cerebral cortex along three general pathways
posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway
anterolateral (spinothalamic) pathway
trigeminothalamic pathway
What is the primary somatosensory area?
Postcentral gyrus (both parietal lobes)
each region receives info from different part of body on the opposite side
each point of body maps to a specific region in the primary motor area
Lower motor neurons (LMNs)
nerves that extend out of the brain stem + spinal cord
innervate SKM of face + head via cranial nerves
innervate SKM of limb + trunk via spinal
Somatic motor pathways provide input into LMNs → Four distinct circuits of Somatic Motor Pathways
local circuit neurons
upper motor neurons
basal nuclei neurons
cerebellar neurons
Local circuit neurons
located close to LMNs in the brainstem + spinal cord
Upper motor neurons (UMNs)
input to both lower circuit neurons + LMNs
Basal Nuclei neurons
assist mvmt by indirectly providing input to UMNs
Cerebellar neurons
assist mvmt via control of activity of UMNs
UMNs extend to LMNs via:
Direct motor pathways: delivers signals to LMNs from cerebral cortex
Indirect motor pathways: deliver signals to LMNs from motor centers in basal nuclei, cerebellum, cerebral cortex
Primary Motor Area
Precentral gyrus