DNS, Time Protocols, , SSH, Security Concepts
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
What is the point of DNS?
Translate human-readable names into computer-readable IP addresses.
you only need to remember cnn.com, not the IP address
What are examples of generic top-level domains?
.com
.org
.net
etc
What are examples of top level country code domains?
.us
.ca
.uk
.ai
etc
DNS Hierarchy
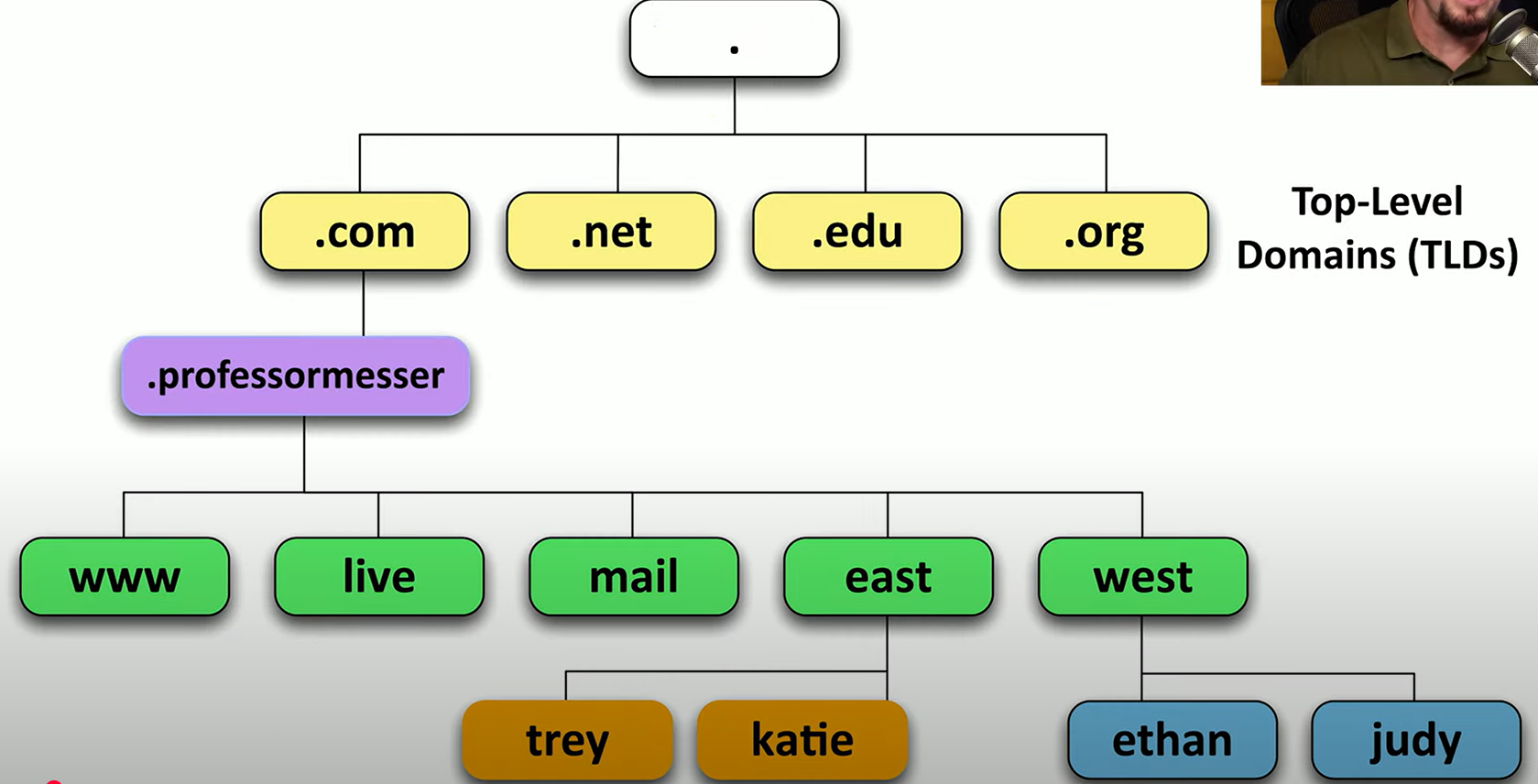
What does FQDN stand for? What is it?
Full Qualified Domain Name
is the complete domain name of a system, including the hostname and all domain levels (e.g., server.example.com
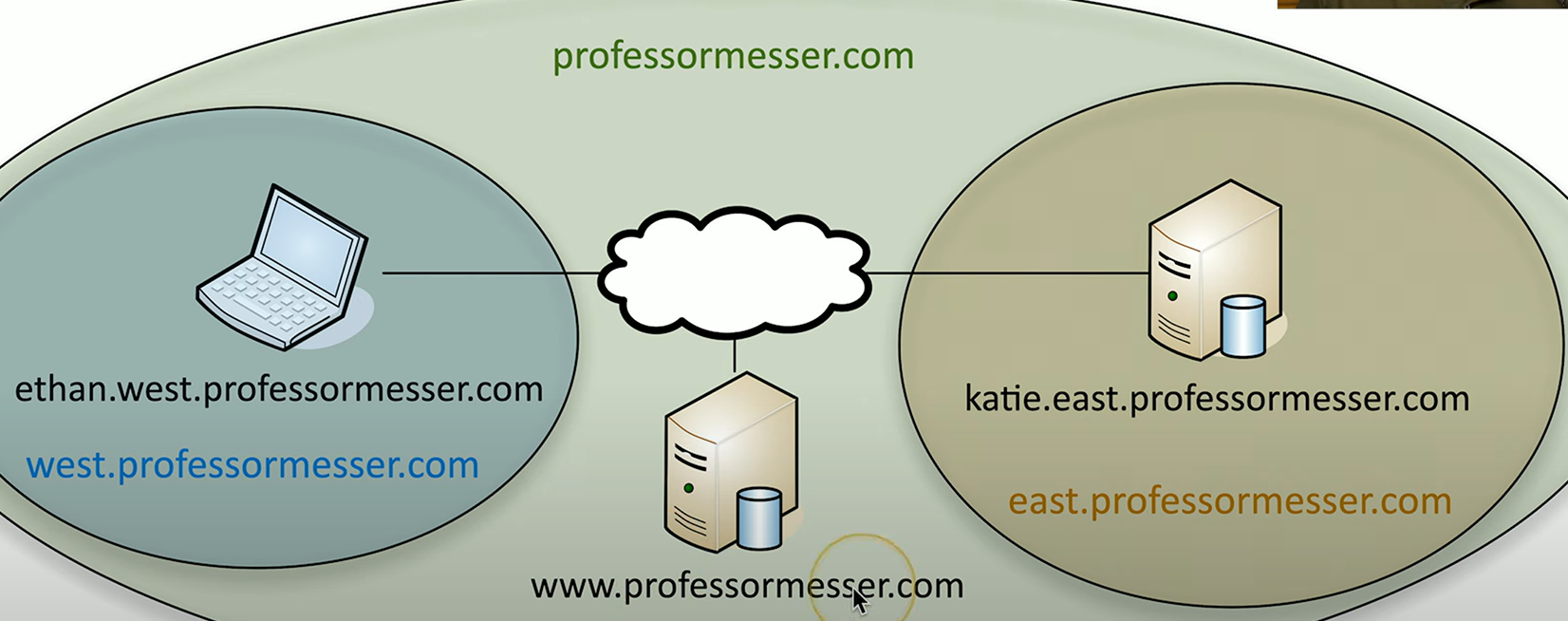
What is a primary DNS server?
main server that holds the authoritative DNS records for a domain and responds to queries with the correct IP address for that domain
What is a secondary DNS server?
is a backup server that holds a copy of the DNS records from the primary DNS server. If the primary server is unavailable, the secondary server can continue to resolve domain names
As a user, can we see and tell the difference between the primary and secondary dns servers?
no, we cannot see updates to the primary/secondary dns servers
What is local name resolution?
Local name resolution is the process of translating a domain name into an IP address within a local network, often using a local DNS server or a hosts fil
What is a forward DNS lookup?
A forward lookup is the process of resolving a domain name (like www.example.com) into its corresponding IP address. It is the most common type of DNS query, where a client requests the IP address associated with a domain name.
What is a reverse DNS lookup?
Reverse DNS (rDNS) is the process of resolving an IP address back into a domain name. It's the opposite of a forward lookup, where instead of querying a domain name for its IP address, you query an IP address to find out which domain name is associated with it.
When you receive the results of a DNS query, those are often provided to you through a server that is caching that information, but occasionally you want information from the primary DNS server for that domain. We refer to that primary device as the ____________
Authoritative Server
What is a nonauthoritative server?
provides cached information from previous queries or forwards requests to authoritative DNS servers to obtain the correct data
What is a challenge that we have with cached information?
TTL time to live configured on the authoritative server
specifies how long a cache is valid
A very long TTL can cause problems if changes are made
What are recursive DNS queries?
when your DNS server asks other servers to find the answer for a domain name, and then sends the final result back to you
Delegates the lookup
allows multiple queries, with minimal traffic
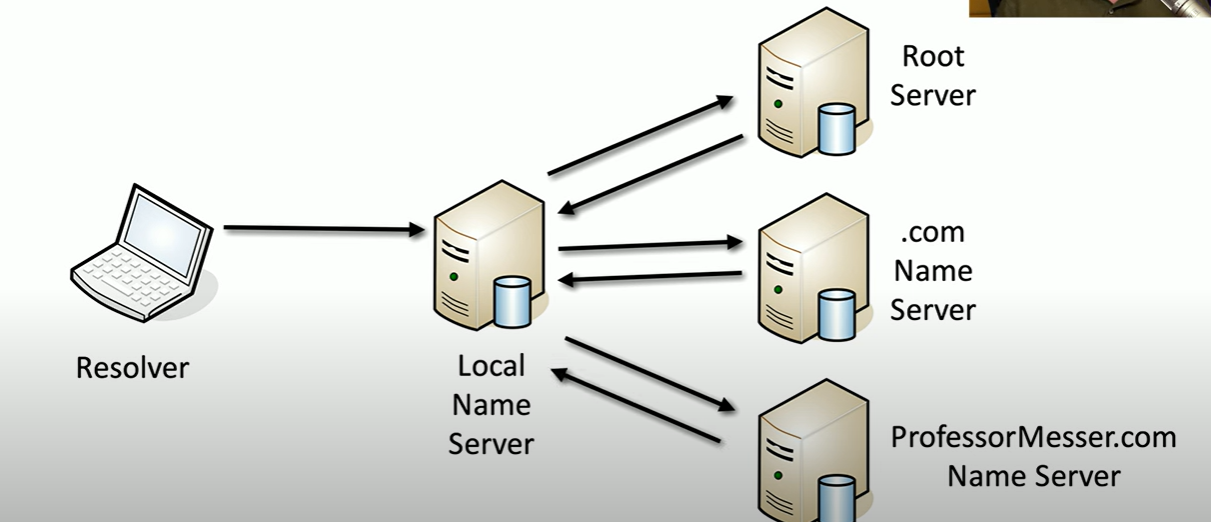
What is a resolver?
The device requesting information
Is DNS information encrypted or sent in the clear?
In the clear, and responses arent authenticated. Which means results are easy to spoof.
What is DNSSEC?
Domain Name Security Extensions
DNS responses from the server are digitally signed
a fake is easily identified
required additional configurations on the DNS server however.
Despite DNSSEC, information sent is still ____________
In the clear
anyone can view the traffic, and there is security/privacy concerns
How do we encrypt DNS information? (DoT)
DNS over TLS (DoT)
Send DNS traffic over tcp/853, but encrypted with TLS/SSL
Looks like a web server communication over tcp/443
some browsers use DoH by default.
What is another method of encrypting DNS info (DoH)
DNS over HTTPS
Send DNS traffic in HTTPS packets
What is are Resource Records (RR) in DNS?
The database records of domain name services
over 30 types of records (IP addresses, certificates, host alias names, etc)

What is an SOA record?
Start of Authority
Describes the DNS zone details
serial number
refresh, retry, and expiry timeframes
Caching duration/TTL
What is the A record or the AAAA?
Defines the IP address of a host
the most popular query
Records marked with “A” are for IPv4
Records marked with “AAAA” are for IPv6

What is CNAME?
Canonical Name Record
maps one domain name to another. It is used to create an alias, so multiple domain names can point to the same website or service

What is the MX record?
Mail Exchanger Record
Determines the host name for the mail server
This isn’t an IP address; its a name
What is the TXT record?
Text Records
Human-readable text information
useful public info
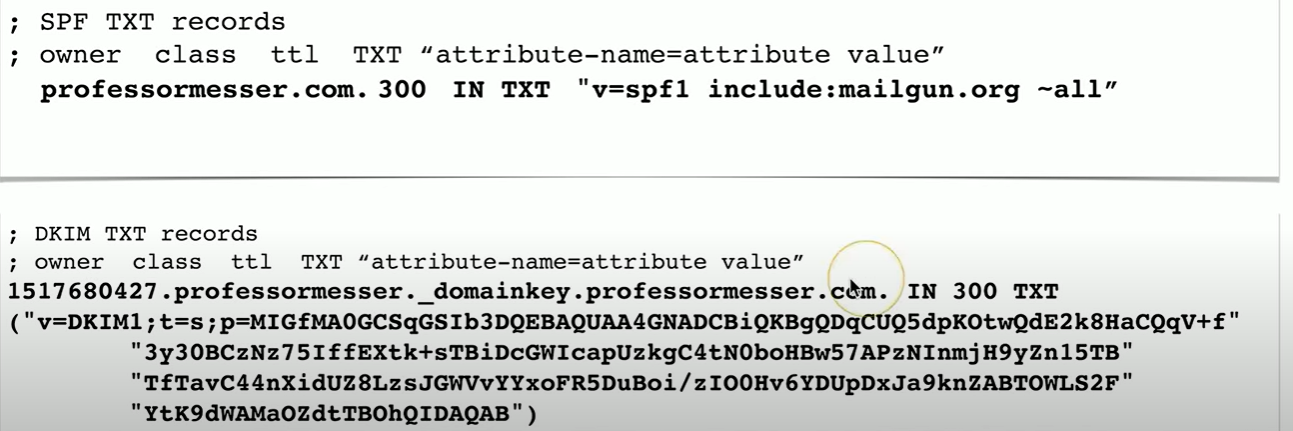
In the TXT record, what is the SPF protocol?
Sender Policy Framework
prevents mail spoofing
mail servers check that incoming mail really did come from an authorized host.
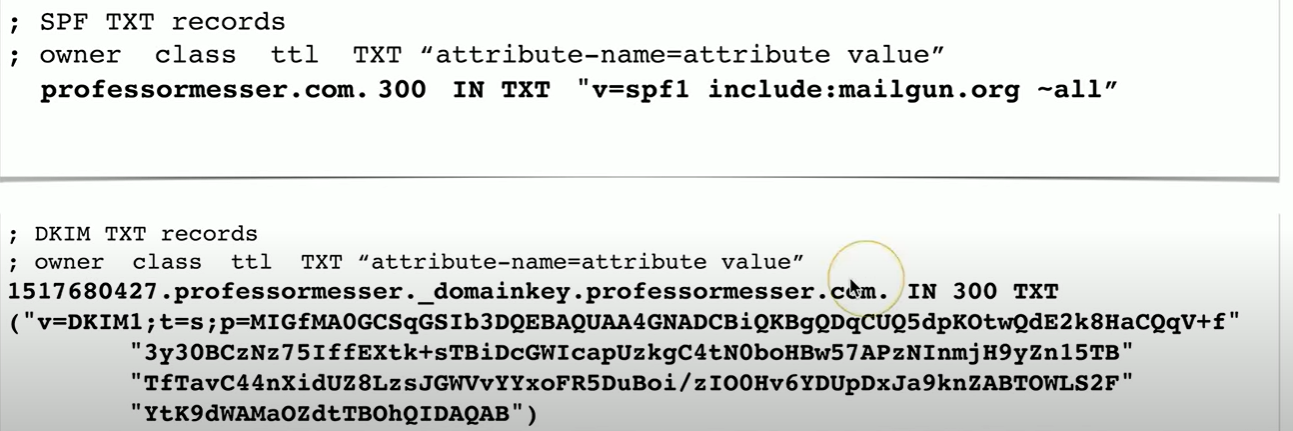
In TXT records, what is DKIM?
Domain Keys Identified Mail
digitally sign your outgoing mail
validated by the mail server, not usually seen by end user
Put public key in the DKIM TXT record
What are Name server records?
DNS records that specify which servers are authoritative for a domain. They tell the internet which DNS servers hold the official records for a domain
if example.com has NS records pointing to ns1.dnsprovider.com and ns2.dnsprovider.com, those servers handle all DNS queries for example.com
What is the PTR record?
Pointer Record
The reverse of an A or AAAA record, a reverse lookuip.
used for reverse DNS lookups, mapping an IP address back to a domain name
if 192.168.1.1 has a PTR record pointing to server.example.com, a reverse lookup on that IP would return server.example.com
What does NTP stand for?
Network Time Protocol
What is NTP?
protocol used to synchronize the clocks of computers and devices over a network. It ensures that all systems have the same accurate time.
log files
outage details
What is an NTP server?
Listens on udp/123, and it is responsible to replying to any time requests from NTP clients.
What is the NTP client?
The party that is requesting time updates from thr NTP server
Does NTP send information encrypted, or in the clear?
In the clear
time of day isnt really a secret…
Can the wrong time be an issue?
yes, for authentication some softwares use time limits, etc and 5 mins off can result in a denial of access
What is NTS?
Network Time Security
provides authentication, so NTP information can be trusted.
What is a NTS-KE server?
Server responsible for authenticating the clients, and making sure that they all have a cookie that can then be used for the NTP query.
first obtain authentication details
Provide cookie to NTP server
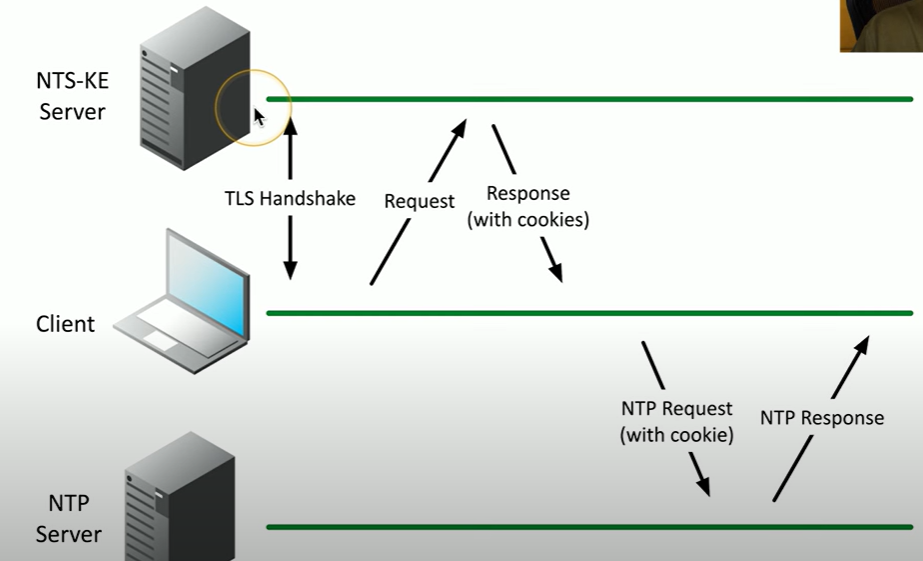
What is a handshake?
a handshake is a process where two devices (like a client and server) exchange signals to establish a connection, agree on parameters, and ensure both are ready to communicate
What is PTP?
Precision Time Protocol
A more precise time protocol, down to the nanosecond
important for finance trading, aerospace etc
hardware-based time sync
How is PTP implemented?
implemented as a specialized hardware, to avoid delays from the operating system and application.
What does VPN stand for?
Virtual Private Network
Ecrypted private data that can traverse a public network.
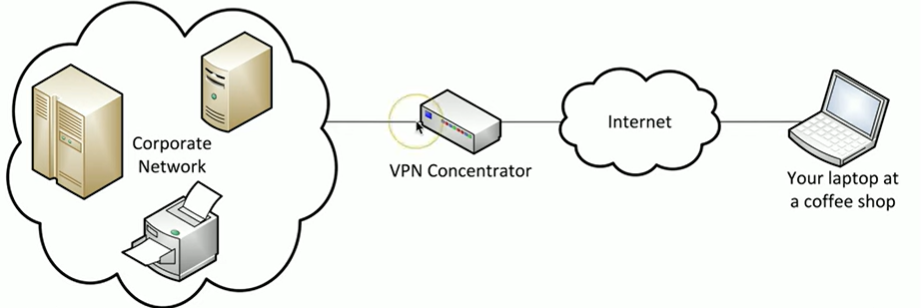
What is a VPN concentrator?
Encryption/decryption access device, often integrated into a firewall
A VPN concentrator is like a secure airport terminal where travelers (remote users) go through security (encryption) before boarding a private airline (VPN tunnel
What is a client-to-site VPN?
Software installed onto the client workstation and that client would be communicating back to a central site.
some software cna be configured as always on
What is a site-to-site VPN?
All the communication between one site to another is encrypted over this VPN tunnel.
Always on or almost always
usually built into an existing firewall
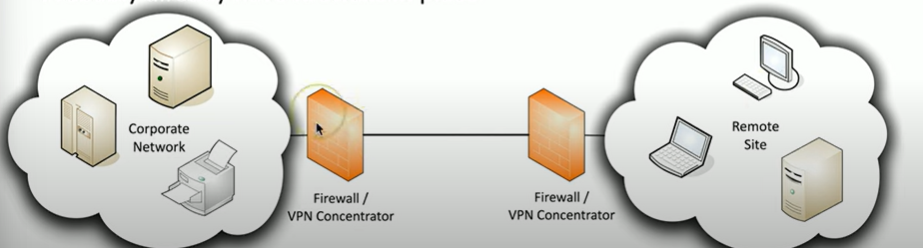
Give an analogy of firewall vs vpn
A firewall is like a security guard at a building entrance, deciding who can enter and who is blocked based on security rules.
A VPN is like a secure tunnel that lets you travel safely through a dangerous area, hiding your identity and protecting your information from prying eyes.
What are clientless VPNs?
Usually runs inside a browser using HTML 5, and allows use to use an API to interact with the browser.
Specifically a web cryptography API (allows a VPN client in the browser
nothing to install
just need a HTML5 compliant browser
What is a Full tunnel?
all of a user's internet traffic through the VPN, the client makes no additional forwarding decisions
What is a split tunnel?
outes only specific traffic through the VPN, while other internet traffic goes directly to its destination, improving speed.
configured in the VPN software
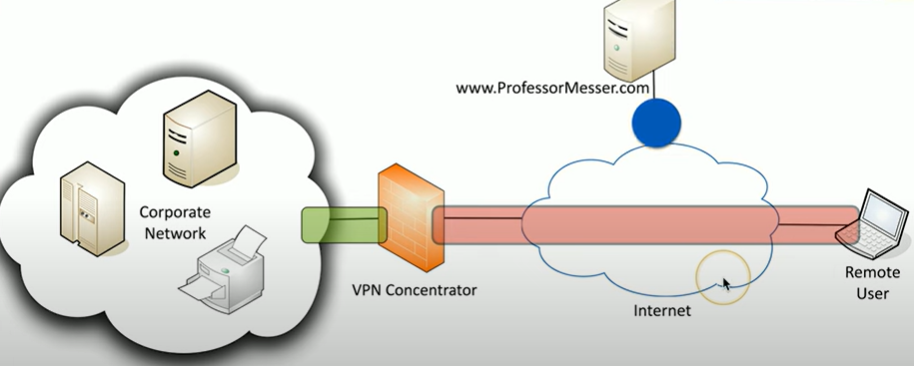
Explain how this traffic would be sent with a full tunnel
remote user info goes to VPN concentrator, info that is bound for professormesser then gets sent back there
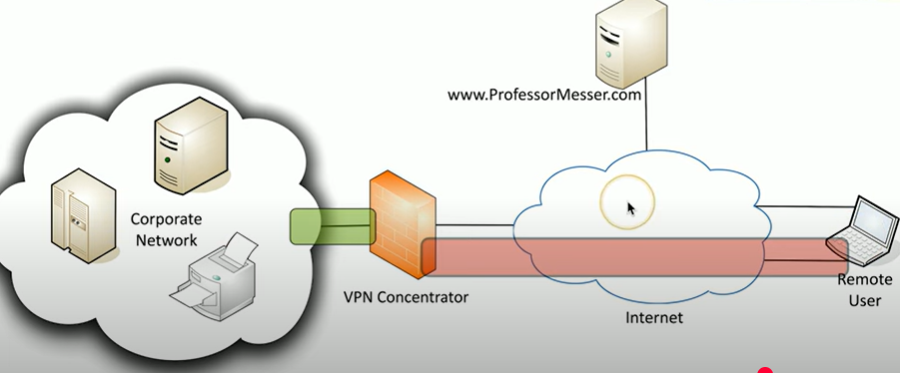
Explain this split tunnel diagram
2 paths, one for VPN traffic, one for nonvpned communication to professormesser.com
What is SSH?
protocol that provides a secure way to remotely access and control devices over an encrypted connection
For encrypted console communication (SSH), what port do we use?
tcp/23
What does GUI stand for?
Graphical user interface
Sometimes you need to share a desktop from a remote location, how do we do this on windows?
Use RDP, aka Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol
clients for Mac OS, Linux, and others
Wha is another option for remote connection?
VNC (Virtual Network Computing)
Similar to RDP, but VNC can be used on many operating systems and many are open source.
What is a more automated way of controlling and managing devices: hundreds of firewalls, routers, switches, servers, etc
Use APIs which can connect and control to devices, using their native languages
If you are in the same phyiscal location of a device, you can use:
a port called console
important if you lose all network connectivity and when all else fails
What is a jump server/box?
A jump server (jump box) is a secure, controlled gateway that administrators use to connect to and manage devices in a protected network, reducing direct exposure to sensitive systems
the jump server allows us to control all the devices in that jump box, which reduces the amount of connections we need.
needs to be highly secure
significant security concern
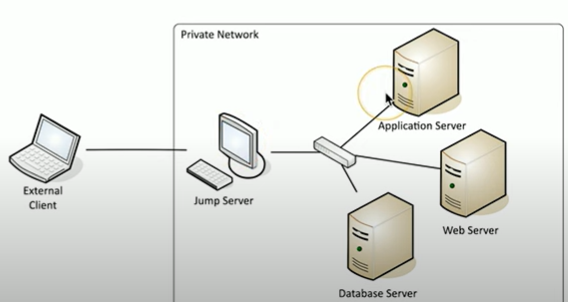
What is in-band management?
In-band management is the practice of managing and configuring network devices or systems over the same network used for regular communication
Assign an IP to a device, and then connect to it using SSH or a webfaced frontend
What is out-of-band management?
allows IT administrators to remotely access and manage devices independently of the primary network, ensuring continuous control even if the main network is down or the operating system is unresponsive
What is Data in Transit?
Data transmitted over the network
also called data in-motion
not much protection as it travels, switches, routers and devices are focused on forwarding data
What are examples of network-based protection?
Firewalls, IPS
What are examples of transport encryption?
TLS: Transport Layer Security
IPsec: Internet Protocol Security
What is data at rest?
The data on a storage device
hard-drives
SSD
Flashdrives
etc
What are some types of data at rest encryption?
Whole disk encryption
Database encryption
File or folder-level encryption
We also apply access controls and authrorization constraints for users to access data.
What does PKI stand for?
Public key infrastructure
What is Public key infrastructure?
framework of hardware, software, policies, and standards that manage digital keys and certificates
create, distribute, manage, store and revoke
What are digital certificates?
an electronic document issued by a Certificate Authority (CA) that verifies the identity of a website, person, or device.
What are certificate authorities
a trusted organization that issues and verifies digital certificates
What are self-signed certificates?
a digital certificate that is signed by its own creator instead of a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), making it useful for internal use
What does IAM stand for?
Identity and Access Management
What is IAM
a framework of policies and technologies that ensures the right individuals have the appropriate access to systems, applications, and data.
data can be located anywhere
many different application users
give the right permissions
What does access control mean?
An entity only gets access to what they need
What is authentication and authorization?
Entities must prove they are who they claim to be
What is identity governance?
Track an entity’s resources access
may be a regulatory requirement
What is the concept of least privilege?
Rights and permissions should be set to the bare miniumum
only need exactly whats needed to complete your objective.
What is RBAC?
Role-based access control
restricts system access based on a user's role, ensuring they only have permissions necessary for their job
etc: a manager needs more access than an analyst
In windows, how do we use RBAC?
We use Groups
shipping
accounting
What are geographic restrictions?
Identify where a user happens to be, and assign rights/permissions based off their location.
Network Locations:
Can sometimes be done over an IP address (IP subnet)
Can be difficult with mobiel devices
What does geolocation mean?
determine a user’s location
GPS: mobile devices, very accurate
802.11 Wireless: less accurate
IP address: not very accurate
What is Geofencing?
is a technology that creates a virtual boundary around a real-world location and triggers actions (like alerts or access controls) when a device enters or exits that area.
Ex. no access if you’re not near the office.
What is identification?
This is who you claim to be, usually your username
What is the triple A framework
Authentication
Authorization
Accounting
What is authentication?
Proveing you are who you say you are
password and other authentication factors
What is authorization?
Based on your indentification and authenication, what access do you have?
What is accounting?
Resources used: Login time, data sent and recieved, logout time.
Gaining access diagram
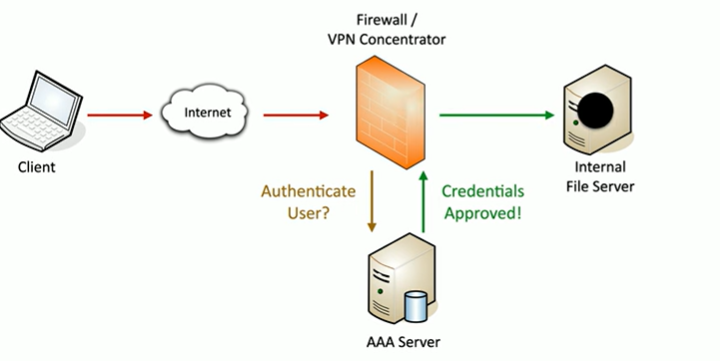
What does SSO stand for? What is it?
Single Sign On
Provides credentials one time
get access to all available or assigned resources
no additional authentication required
24hr expiry usually
ex. logging on in the morning, and then beign good for the day
What does RADIUS stand for?
Remote Authenication Dial-in User Service
What is RADIUS?
is a networking protocol that provides centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) for users accessing a network.
centralized authentication
routers, switches, firewalls
server authentication
Remote VPN access
avaiable on almost aby server operating system
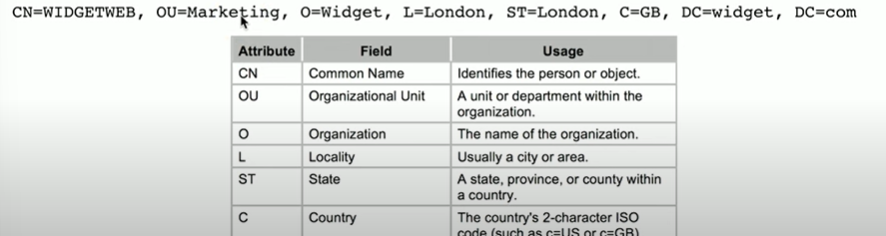
What is LDAP?
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
is a protocol used to access and manage directory services, which store information about users, devices, and other network resources. It allows systems to query, add, modify, and delete data in a directory
like a phone book directory
Uses X.500 distinguished names
What is X.500?
et of ITU standards for directory services that defines how information about users and resources is stored and accessed, and serves as the foundation for LDAP.
What does X.500 allow us to do?
Allows us to add attributes to a user or a device.
Most specific attribute is listed first
What is an X.500 Directory Information Tree?
hierarchical structure of information associated with devices
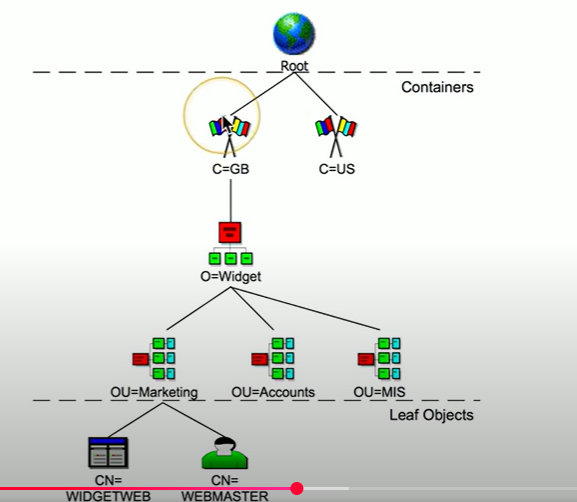
What are container objects in a hierarchical tree?
Country, organization, organizational units
What are leaf objects in a hierarchical tree?
Users, computers, printers, and files
What does SAML stand for?
Security Assertion Markup Language
What is SAML?
Open standard for authentication and authorization
you can authenticate through a 3rd party to gain access
one standard does it all
When you log into BCIT’s portal, SAML lets you access Moodle, email, and student services without logging in again