2.2 Biological Molecules
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
why is water a good solvent?
because it is polar
explain the polarity of water
delta positive H atom
delta negative O atom
they can form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules
high specific heat capacity
hydrogen bonds mean water molecules are able to absorb a lot of energy, so a lot is overcome bonds between the molecules
why does high specific heat capacity make water useful?
it is a good habitat:
water doesn't experience rapid temperature changes
temperature is likely to be more stable than on land
high latent heat of evaporation
a lot of energy is needed to overcome hydrogen bonds and evaporate water
why does high latent heat of evaporation make water useful?
water can be used as a coolant when we overheat
sweating removes energy from the body and cools the skin surface down
water very cohesive
water is very cohesive, flows easily and great for transporting water up plant stems
cohesion
attraction between molecules of same type
lower density when solid
water freezes + becomes solid
H2O molecules held further apart in ice than liquid (lattice shape)
ice is less dense than water
why is lower density when solid useful?
ice is less dense than water, so it floats to the surface and forms an insulating layer over water, preventing water below it freezing
aquatic animals do not freeze
water - good solvent
ionic substances can be dissolved in solution
polar ends of water molecule attracted to ions + surround ions
why is being a good solvent important for water?
allows important ions to dissolve in the blood and transport around body
surface is habitat for small invertebrates
due to surface tension
small invertebrates can live on surface of water
condensation reaction
any reaction joining 2 molecules, forming a bond and forming a water molecule
hydrolysis reaction
reaction breaking a chemical bond between 2 molecules, using a water molecule
name 3 common sugar monomers
glucose
galactose
fructose
what do monosaccharides make up?
larger carbohydrates/polymers
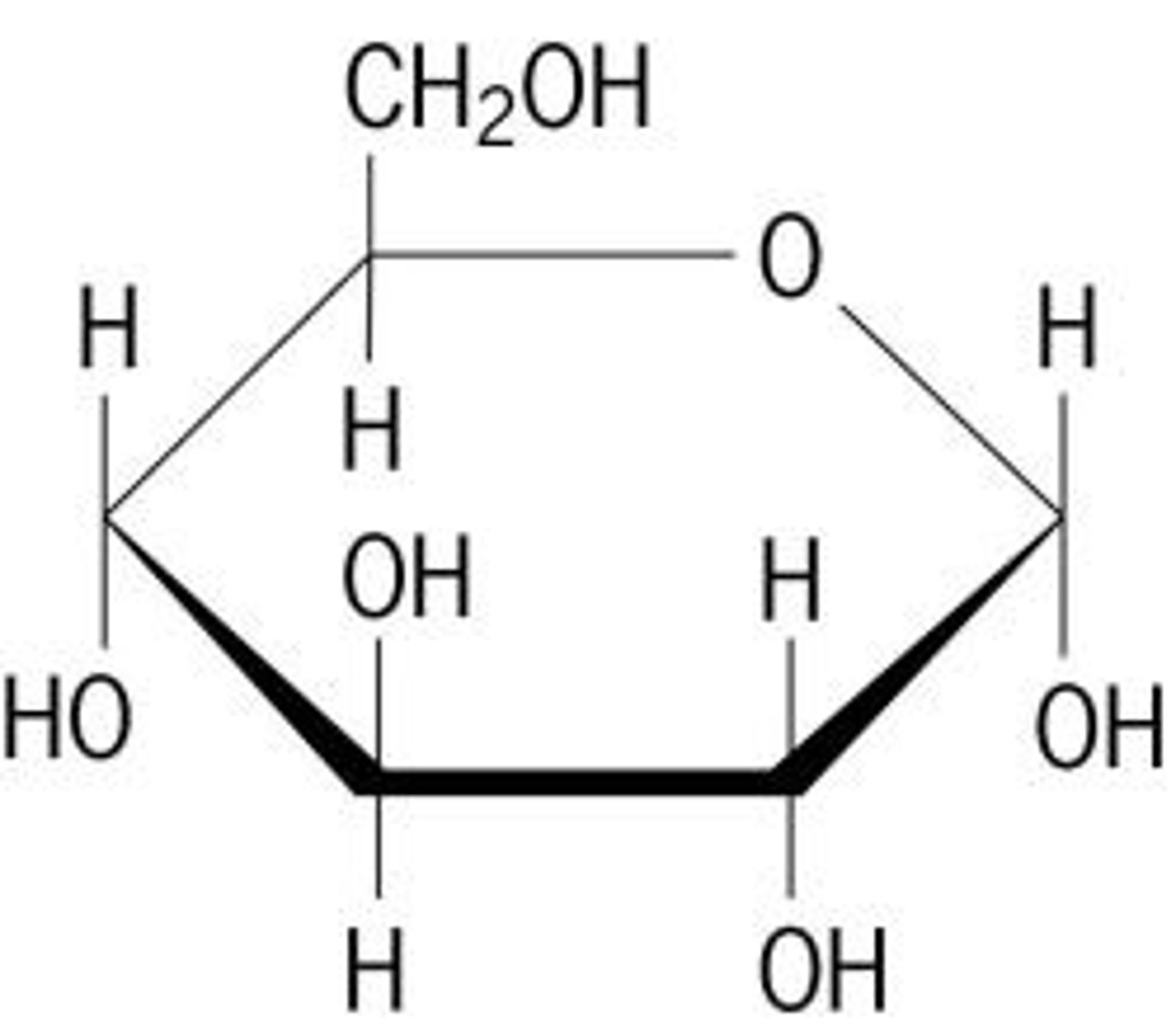
2 isomers of glucose
alpha and beta
ABBA
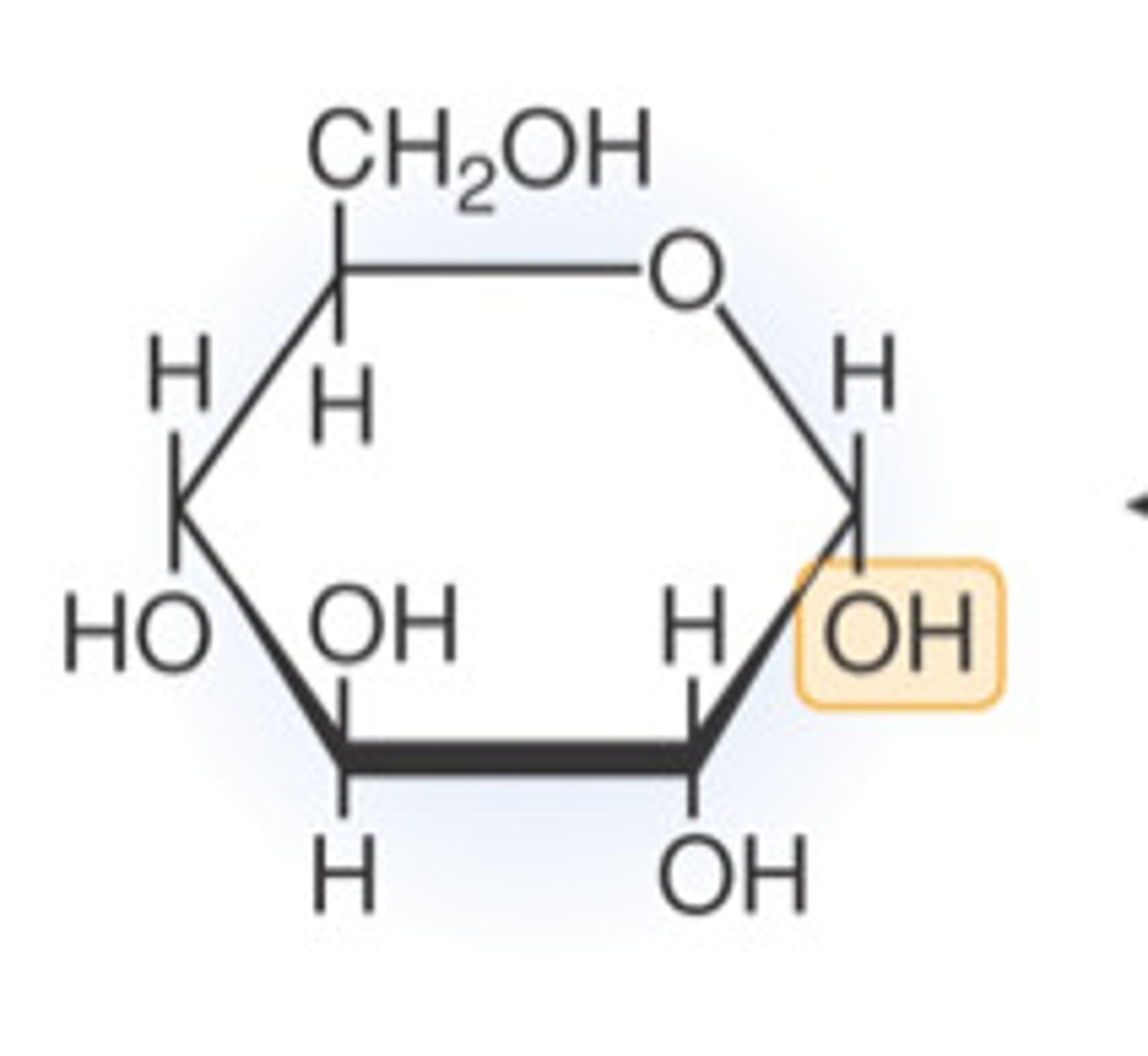
alpha-glucose
OH below
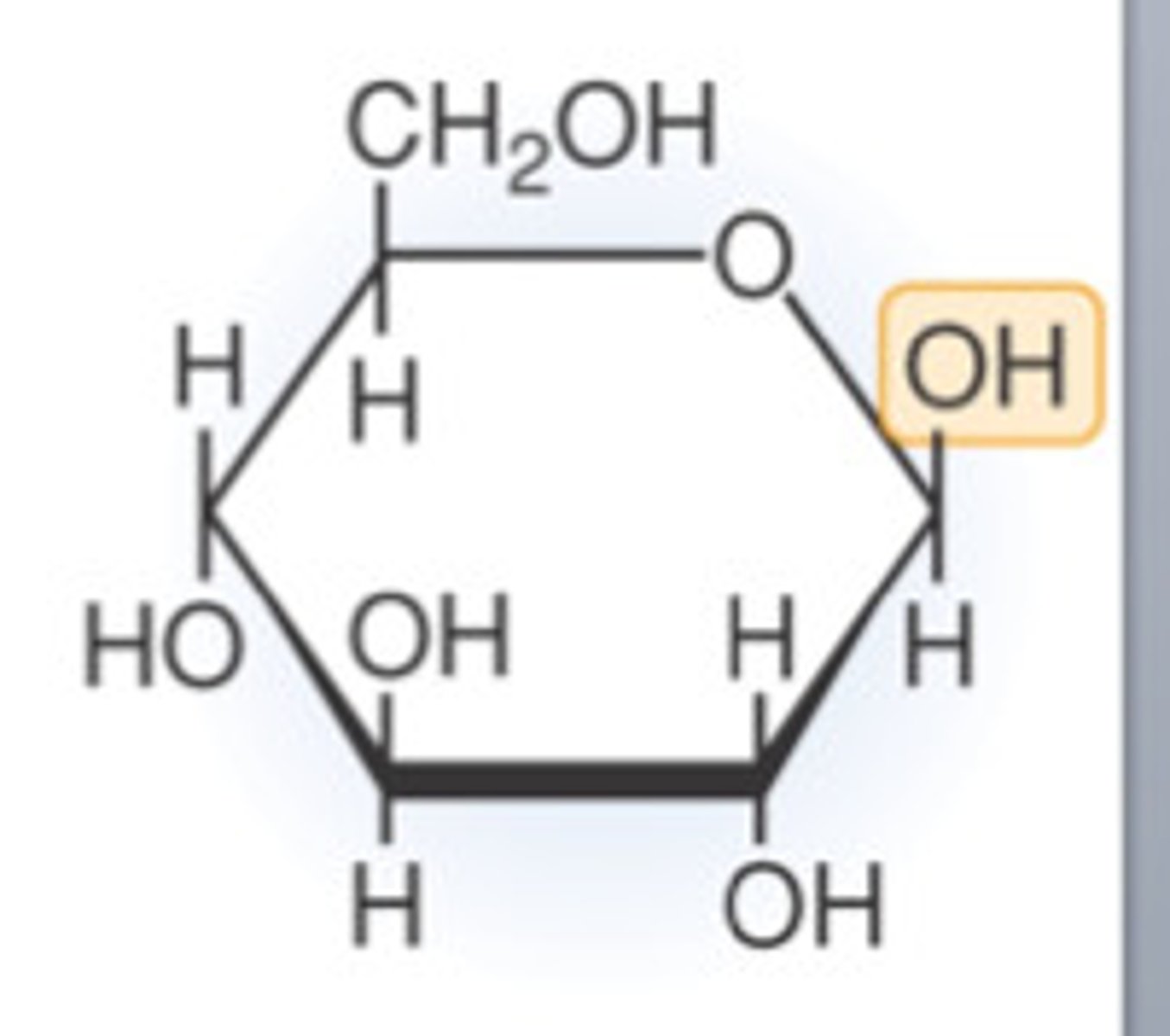
beta-glucose
OH above
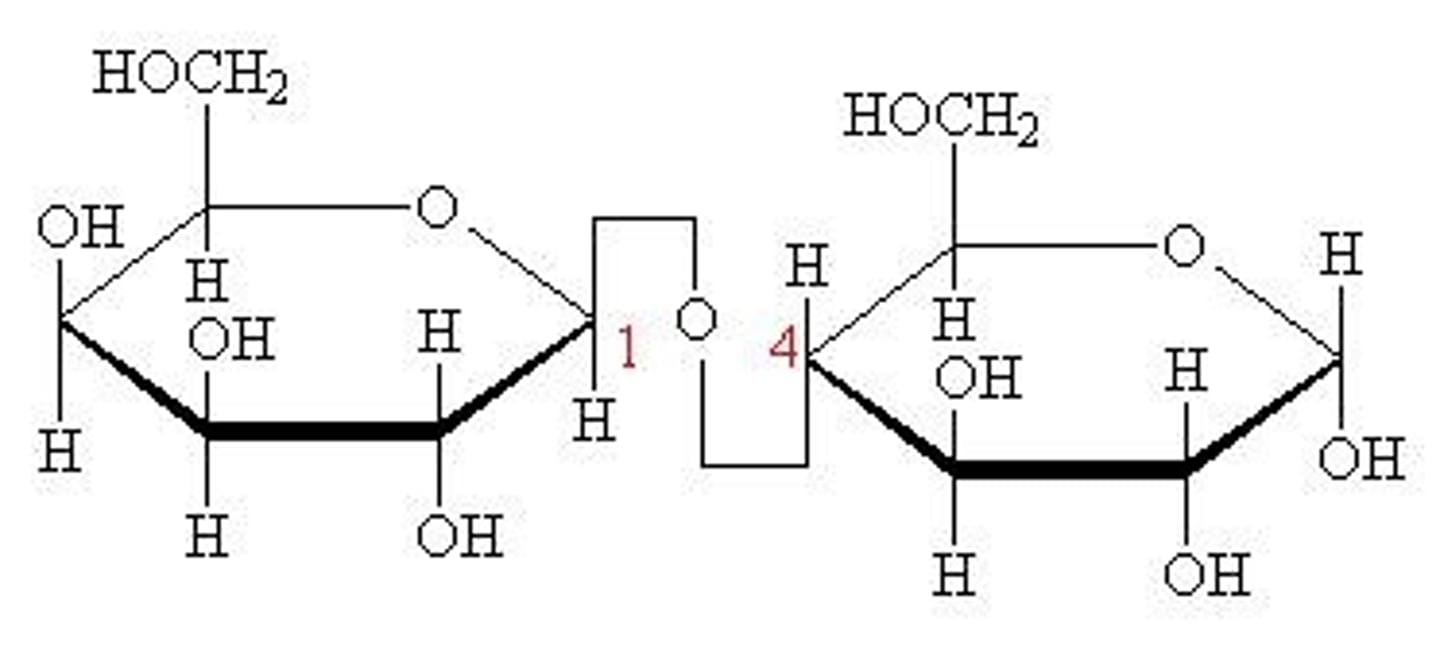
what bond is formed + what is released during a condensation reaction?
glycosidic bond
strong bond
release of H2O molecule
what are 2 bonded monosaccharides called?
disaccharides
name 3 common disaccharides
maltose
sucrose
lactose
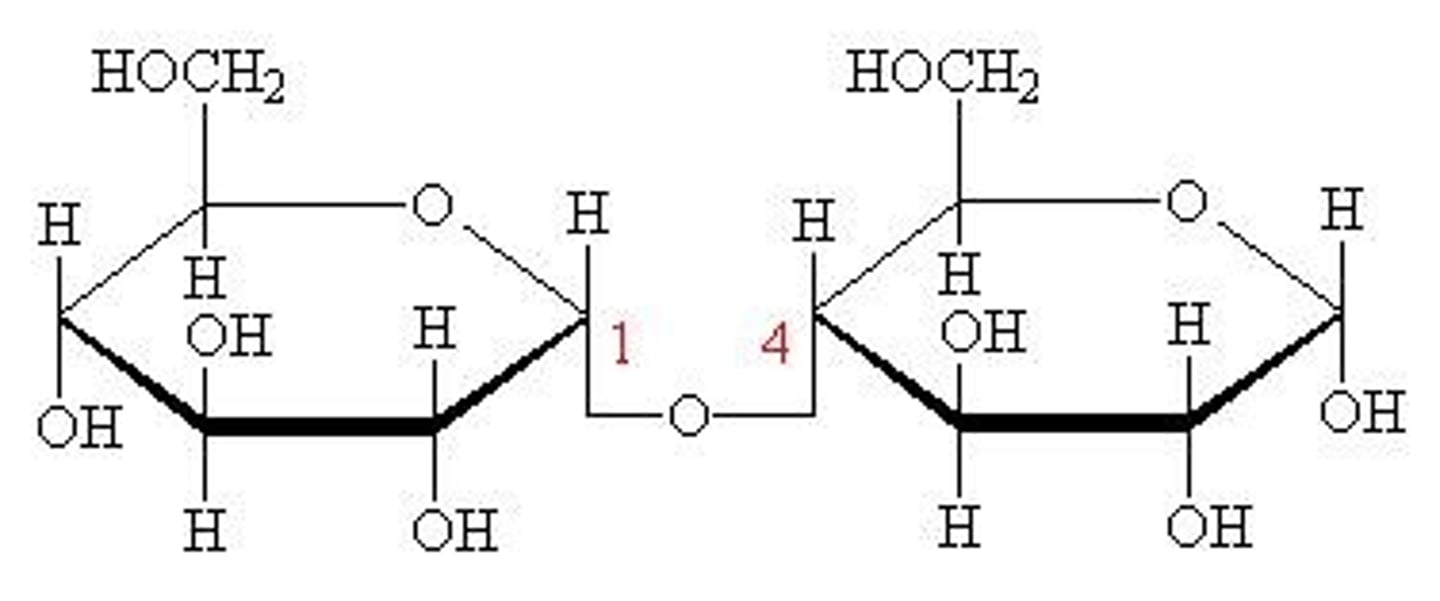
maltose
glucose + glucose
beer brewing
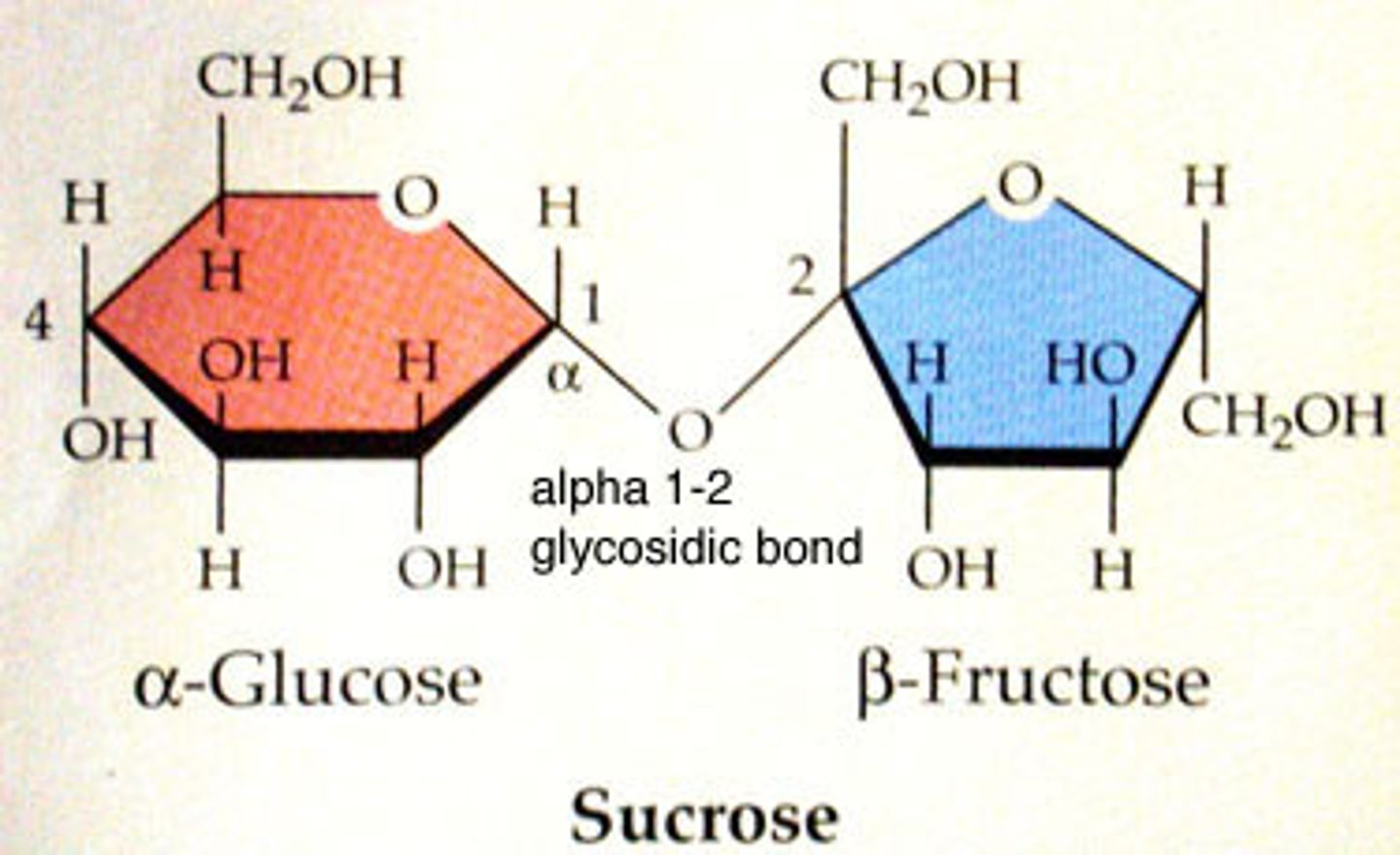
sucrose
glucose + fructose
common in plants, main transport of sugar
lactose
galactose + glucose
found is mammalian milk
3 elements in carbohydrates
C, H, O
properties of starch
insoluble in water
2 forms - amylose/amylopectin
main energy storage in plants + in food
when broken down = releases glucose for respiration
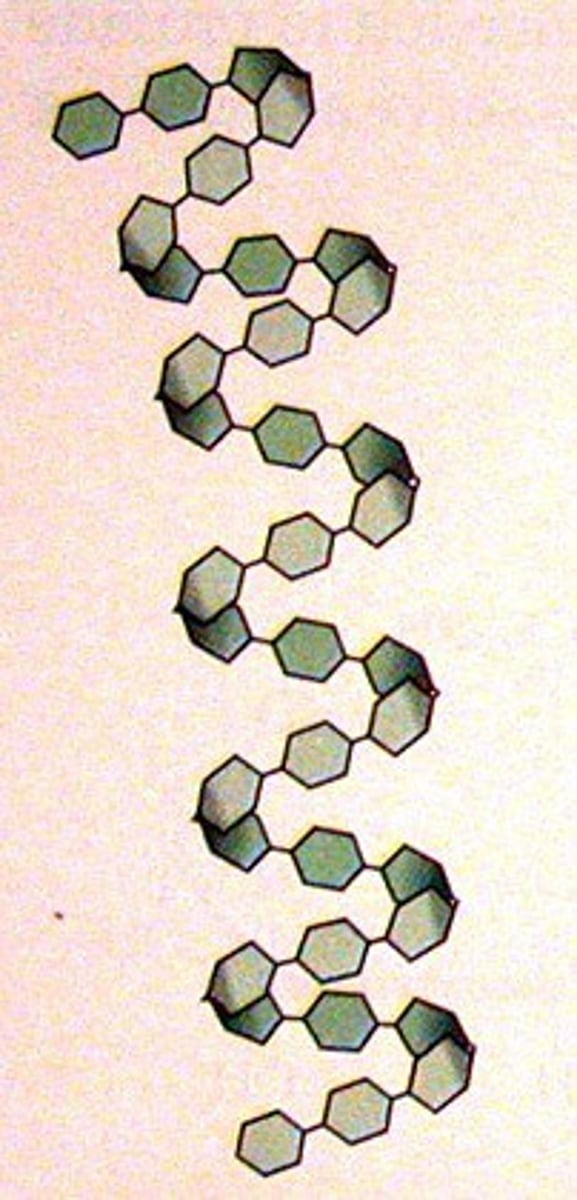
amylose
unbranched chain of alpha-glucose
helical
compact + helical is good for storage (a lot of glucose)
1,4 glycosidic bonds
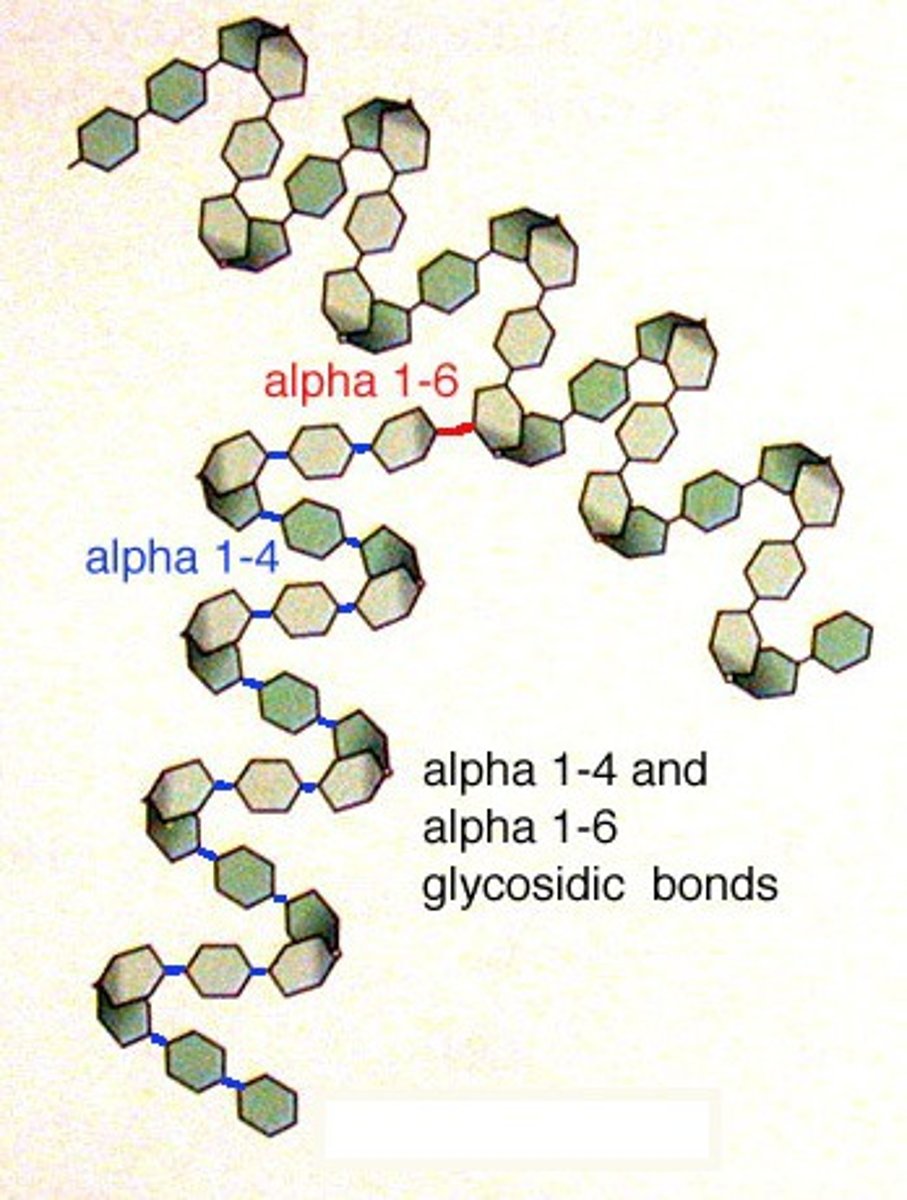
amylopectin
branched chain of alpha-glucose
exposed branches
branches make it easier to release glucose = quickly releases energy for respiration
1-4, 1-6 glycosidic bonds
glycogen
animal-found polysaccharide of alpha-glucose
stored in liver + muscles
insoluble in water
broken into glucose in liver, releases into blood
many branches = easy access for enzymes
branches = compact
cellulose
unbranched chains of beta-glucose
regular, straight chain
cellulose fibres (microfibrils) are strong, due to hydrogen bonds between chains
cellulose = strength + great structural support
structure of a phospholipid
hydrophilic head (phosphate group)
hydrophobic tail
(2 fatty acid tails)
head + tail are joined by glycerol molecule
polarity of phospholipids
hydrophilic heads attach to H2O molecules
outside bilayer
hydrophobic tails not attracted to H2O molecules
inside bilayer
what is the phospholipid bilayer?
cell membrane
centre of bilayer = hydrophobic (water-soluble substances cannot easily pass)
barrier to water-soluble substances
triglycerides
1 glycerol molecule
ester covalent bond to 3 fatty acids
condensation between acid group of fatty acid + 1 hydroxyl OH groups (of glycerol molecules)
functions of lipids in organisms
source of energy (respiration = energy)
energy storage (adipose cells)
membranes (phospholipid bilayer)
insulation (visceral fat)
protection (waxy surface of plant = won't dry out)
hormones (e.g. steroid hormones)
saturated lipid
only single C bonds
straight chain
more H atoms
solid at room temp
higher melting point
animal lipid
unsaturated lipid
at least 1 double C=C bond
not straight (contains a kink due to C=C bond)
less H atoms
liquid at room temp
lower melting point
plant lipid
primary structure
amino acid sequence, held together by peptide bonds
secondary structure
hydrogen bonds between amino acid groups
H bonds cause polypeptide to twist + forms alpha-helix coil OR beta-pleated sheet
tertiary structure
interactions between R groups = form disulfide bonds
ionic bonds between R groups
hydrogen bonds between some R groups
hydrophobic R groups clump together (hydrophilic R groups left on outside) - affects folding of protein
hormones must fit receptors
enzymes must have complementary active site
-------
3D shape of protein
Coiling in secondary structure brings R groups together so they interact
Globular or fibrous
quaternary structure
2+ polypeptides bound together (final protein - e.g. haemoglobin/collagen)
solubility of globular proteins + 3 examples
soluble in water
haemoglobin
amylase
insulin
solubility of fibrous proteins + 3 examples
insoluble in water
collagen
keratin
elastin
haemoglobin
globular protein
carries O2 around blood in RBCS
conjugated protein - protein attached to prosthetic group (non-protein)
each of 4 polypeptide chains = has a prosthetic group
haem group - contains iron (O2 binds to Fe)
which protein type are most enzymes?
globular
amylase
globular
enzyme catalysing reaction break down of starch into glucose in digestion
single chain of amino acids
secondary structure: contains BOTH alpha helix and beta pleated sheet sections
insulin
globular
hormone secreted by pancreas (regulates blood glucose levels, by changing solubility)
can be transported in blood to tissues needing it
2 polypeptide chains held by disulfide bonds
multiple molecules bond = form large structure
collagen
fibrous
found in animal connective tissue (bone, skin, muscle)
very strong molecule
minerals can bind to it = high rigidity
keratin
fibrous
found in external animal structures (skin, hair, feathers, horns)
can be very flexible or hard/tough
elastin
fibrous
found in elastic connective tissue (skin, large blood vessels, some ligaments)
elastic = allows tissues to return to original shape after stretching
calcium
Ca 2+
nerve impulse transmission
muscle contraction
sodium
Na +
nerve impulse transmission
kidney function
potassium
K +
nerve impulse transmission
stomatal opening
activates enzymes for photosynthesis
hydrogen
H +
catalysing reactions (e.g. respiration, photosynthesis)
pH determination
ammonium
NH4 +1
production of nitrate ions by bacteria
nitrate
NO3 -
nitrogen supply to plants
for amino acid + protein formation
chloride
Cl -
balance positive charge of Na + K ions in cells
phosphate
PO4 3-
cell membrane formation
nucleic acid + ATP formation
bone formation
hydroxide
OH -
catalysis of reactions
pH determination
glucose
monosaccharide
main sugar used in respiration
absorbed and transported in bloodstream to cells
polymers of glucose
polymers: starch, glycogen, cellulose, starch
galactose
monosaccharide
mainly in our diets as lactose disaccharide
fructose
monosaccharide
sugar naturally found in fruit, honey, vegetables
condensation
a reaction joining 2 molecules together, where water molecule is released as a byproduct, as they react
water molecule is formed by loss of H atom from one molecule and loss of OH hydroxyl group from other molecule = water H2O
hydrolysis
the chemical breakdown of a compound due to the addition of water
this occurs during digestion
3 elements found in carbohydrates
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
usually ratio of C : 2H : O
xylem vessel
one-way transport of water + minerals in plants
no end walls between cells, long and hollow continuous tube
thick walls, stuffed with lignin (dead cells)
phloem vessel
two-way flow of transport of water + food
cells have end walls with perforations (alive cells)
what is sucrose used for in plants?
as a transport medium, for sugar in plants
what is glucose used for in plants?
aerobic respiration, at the mitochondria
how is glucose stored in plant cells?
stored as cellulose, in cell walls
name 3 monosaccharides
glucose, galactose, fructose
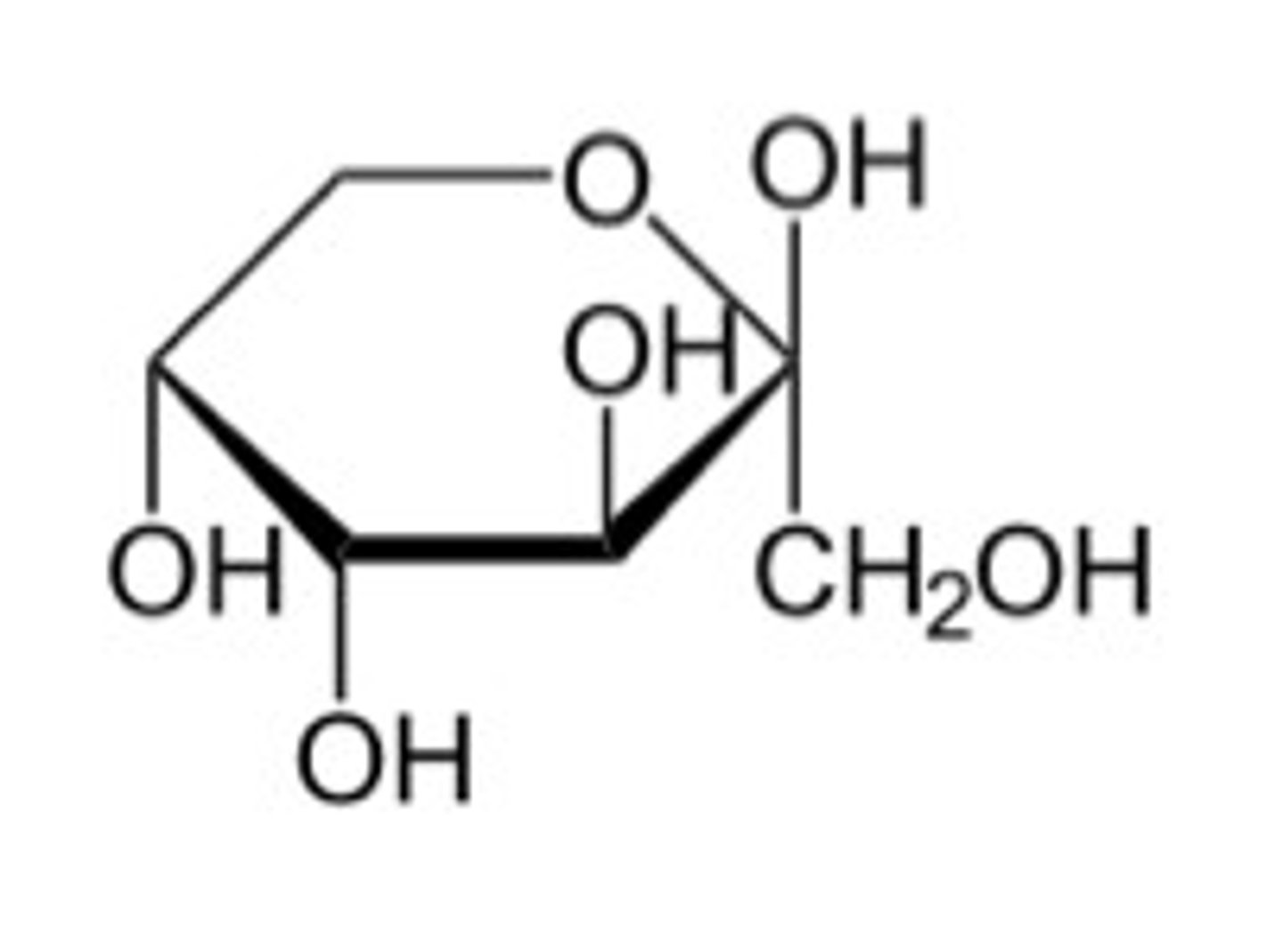
draw a beta glucose structure
image
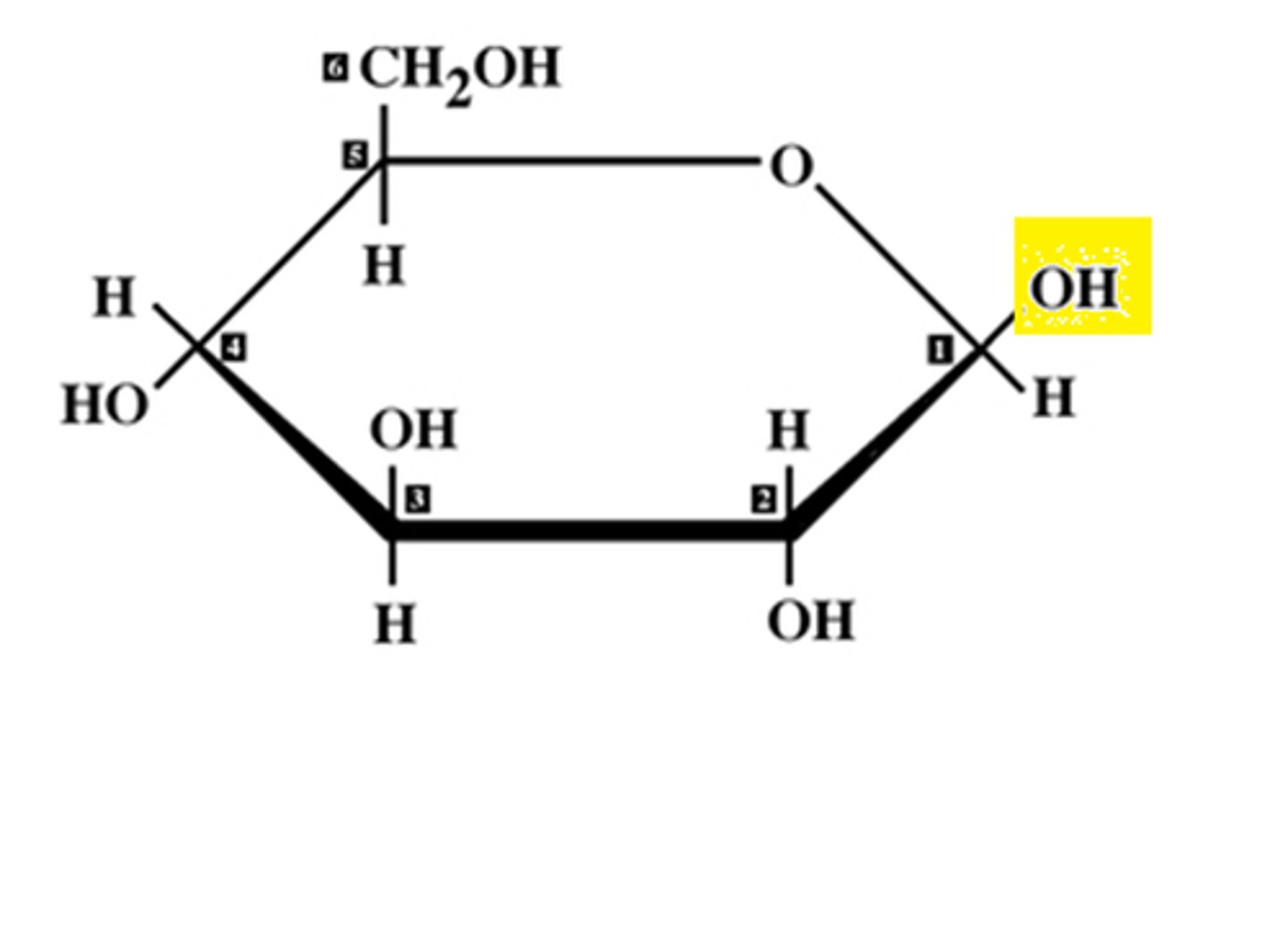
draw an alpha glucose structure
image
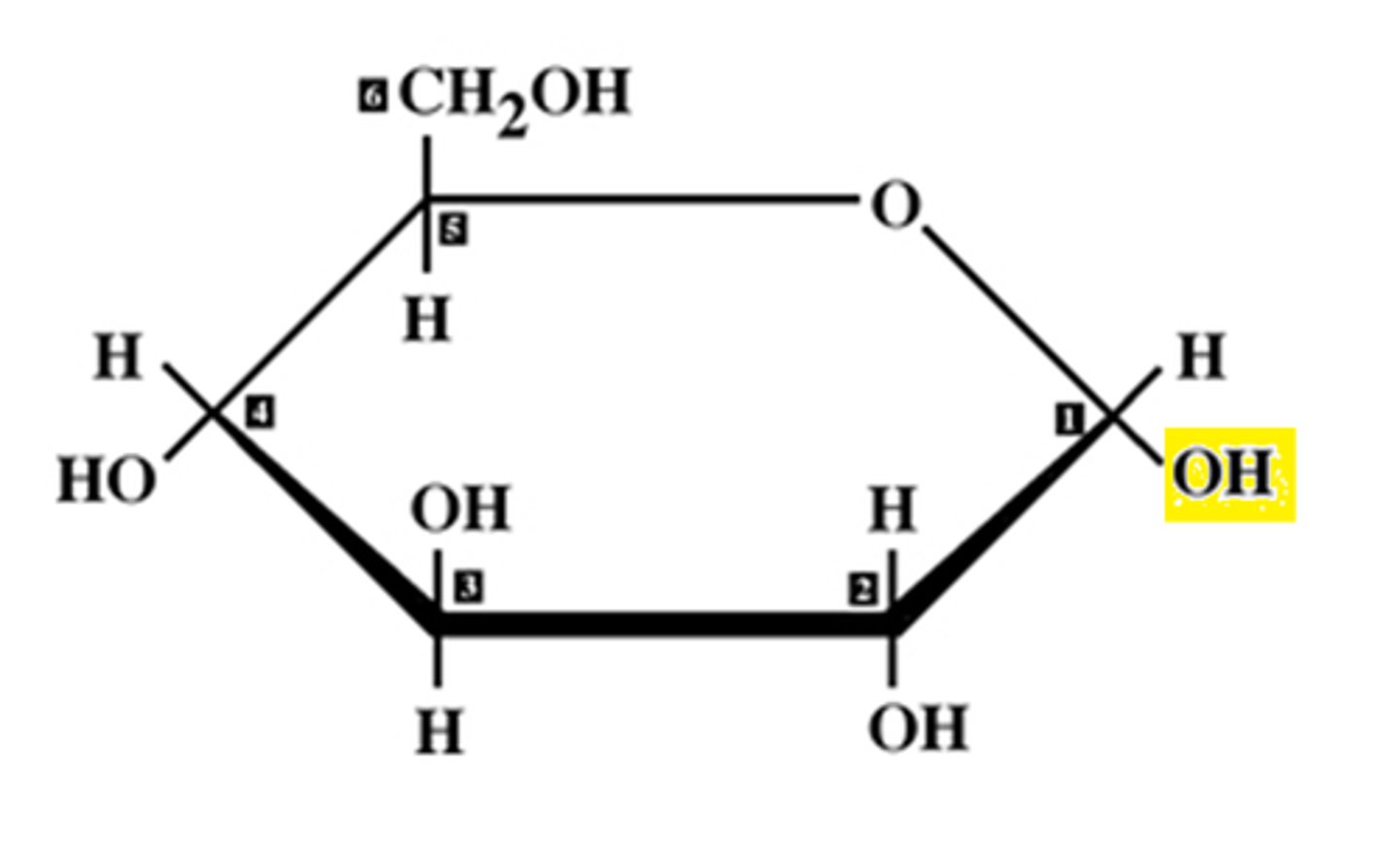
what are the monosaccharides for lactose?
galactose + glucose
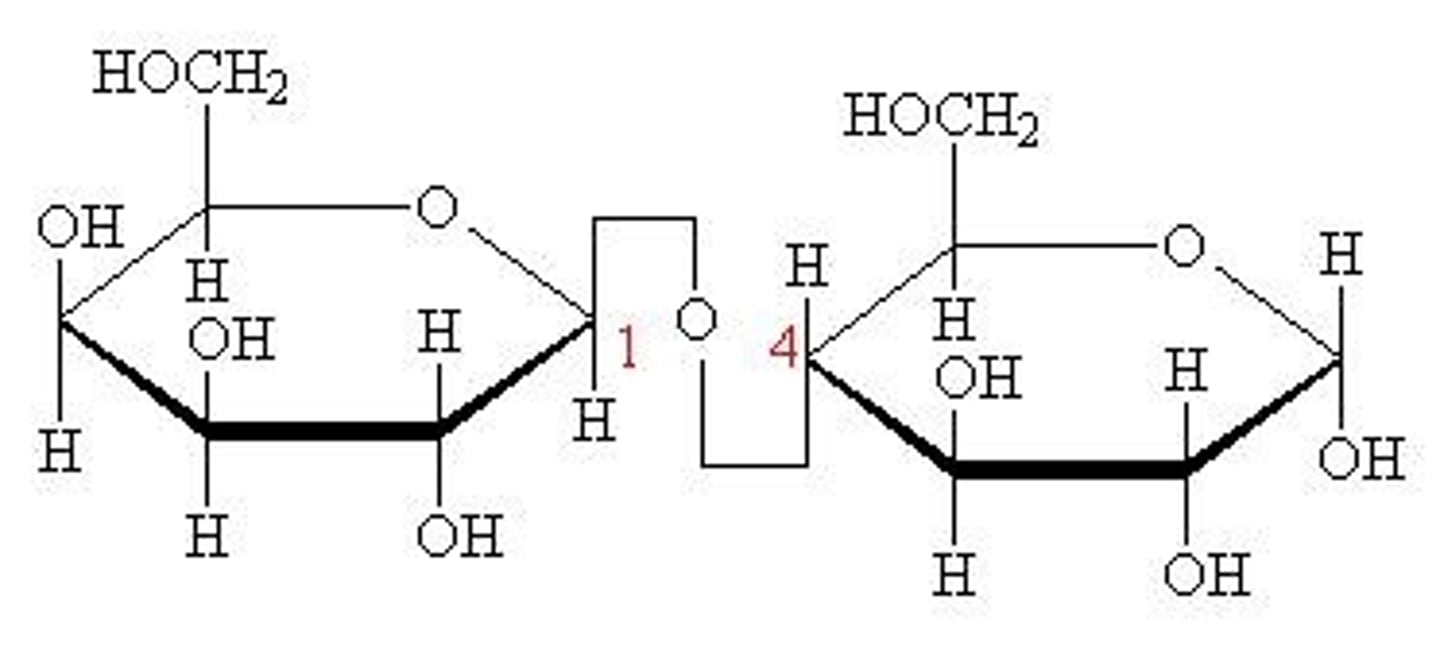
what are the monosaccharides for maltose?
glucose + glucose
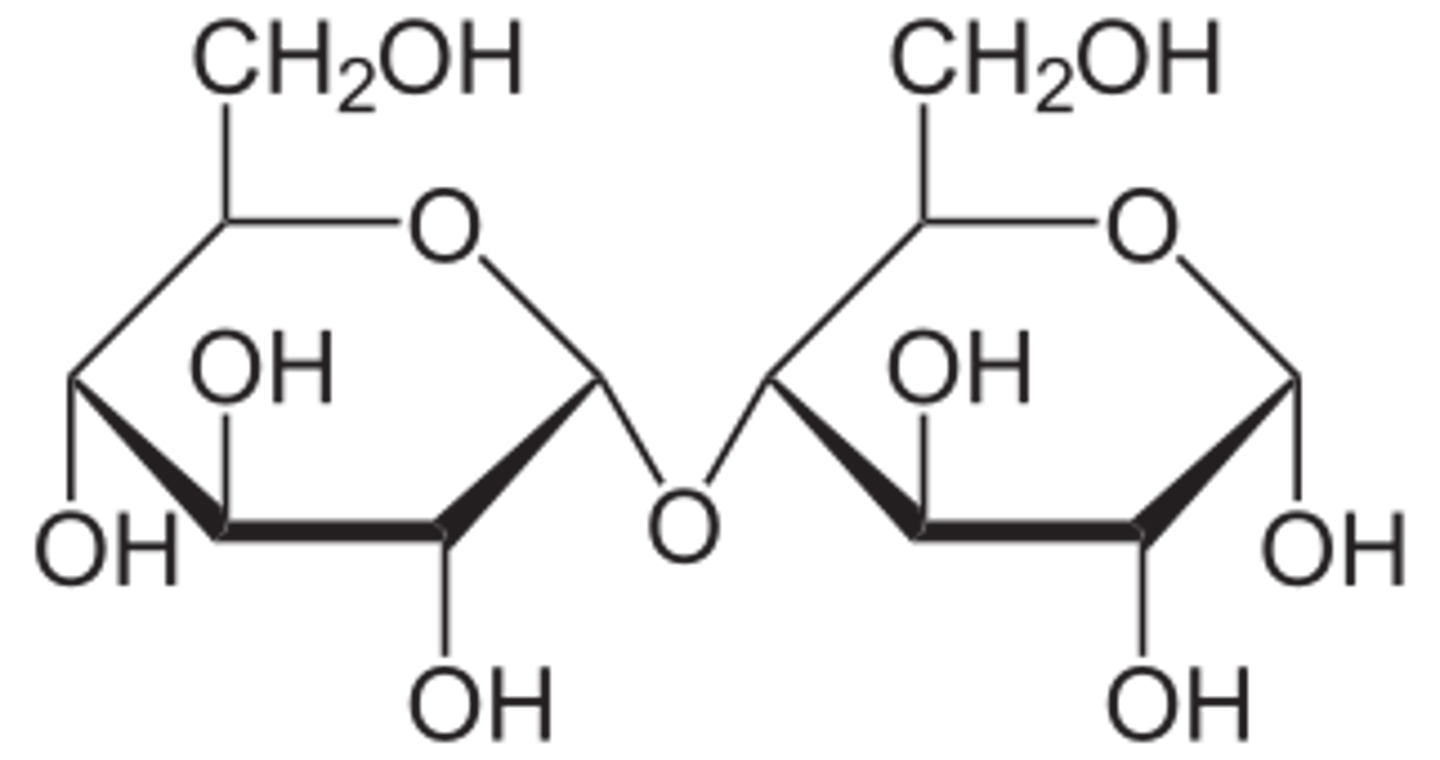
what are the monosaccharides for sucrose?
fructose + glucose
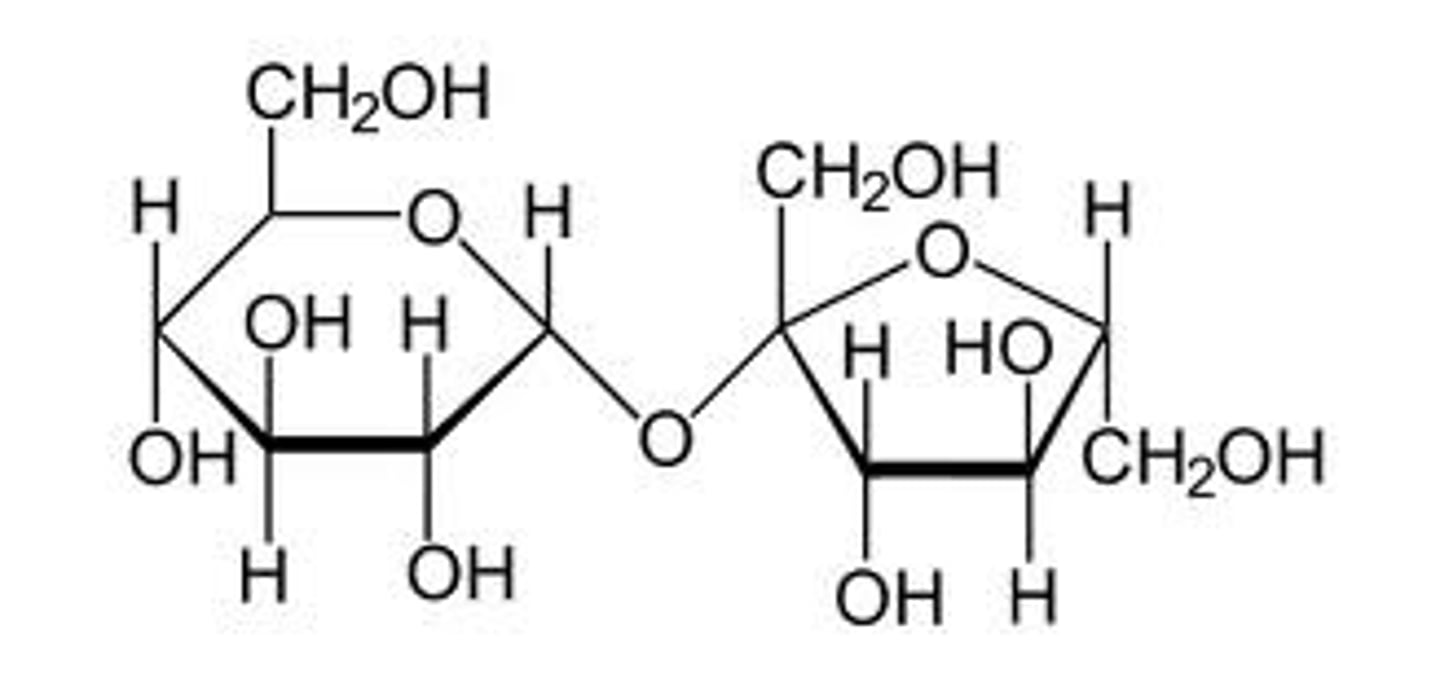
aerobic respiration equation
glucose + oxygen > carbon dioxide + water + ATP
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 > 6 CO2 + 6 H2) + ATP
calculating Rf value
distance travelled by sample/distance travelled by solvent
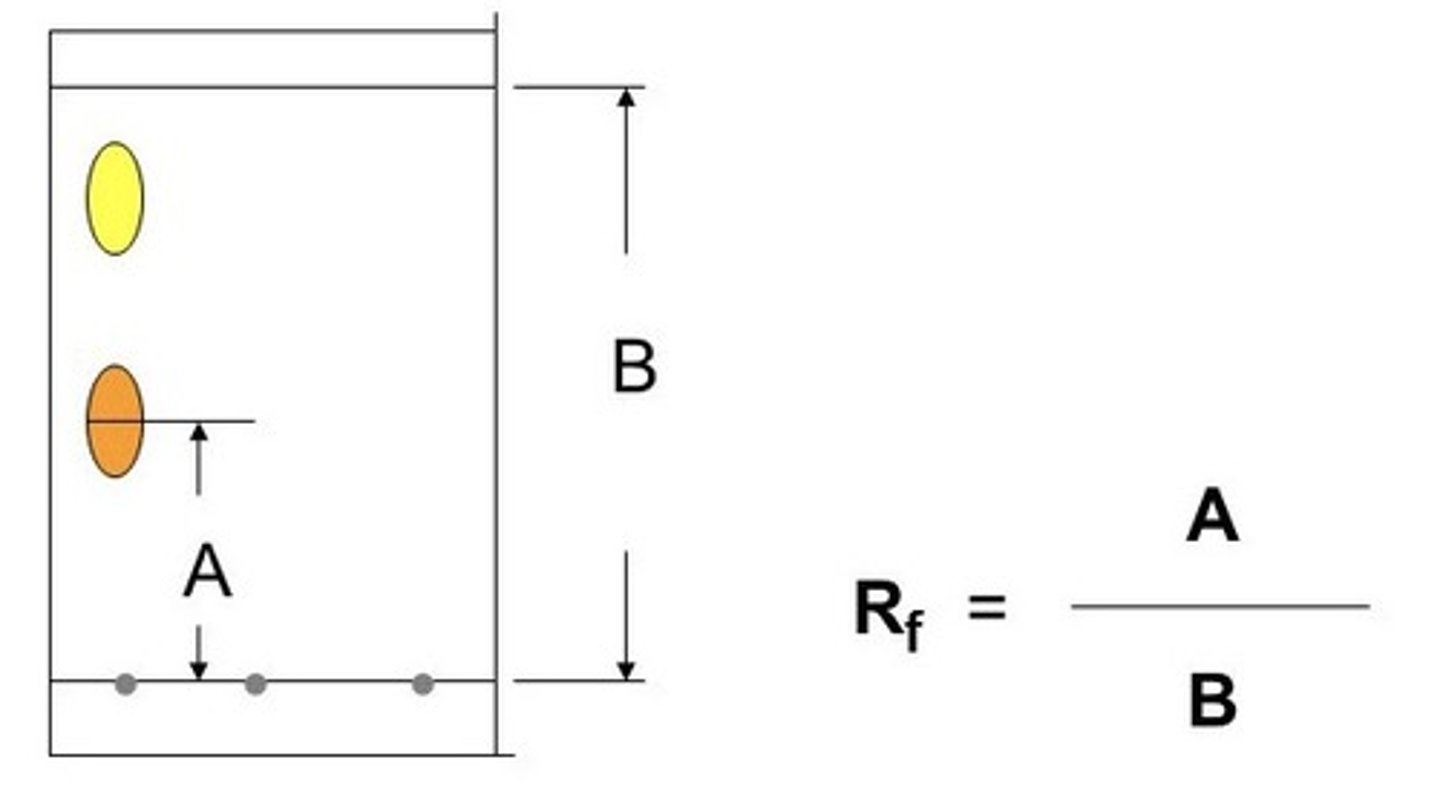
chromatography steps
1) draw pencil line near bottom of chroma. paper
2) place concentrated spot of amino acid mixture onto line
3) roll up paper into cylinder
4) stand up cylinder in the beaker containing solvent
5) cover beaker with lid, to prevent evaporation
6) when solvent reaches the top of the paper
7) remove it from beaker
leave paper to dry
spray with ninhydrin solution
amino acids = purple
8) calculate Rf value of amino acid