Lecture 12: Otitis Externa/Media
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Otitis Externa
inflammation of the ear canal
Otitis Media
inflammation of the bulla
Otitis Interna
inflammation of the canaliculi and/or cochlea
Inflammation of the ear is a ? not a disease
clinical sign
What are predisposing factors to otitis?
- anatomy/conformation (stenosis, hair)
- excessive moisture and humidity (swimming, climate)
- excessive cerumen production
- inappropriate treatment (q-tip trauma, plucking, over cleaning)
- obstructive ear disease (neoplasia, polyp, FB)
- systemic disease (immune suppression such as FIV, FeLV, neoplasia, debilitation)
What are primary factors for otitis?
disease that causes inflammation - foreign bodies, allergies, autoimmune disease, endocrinopathies, and parasitic disease
Otodectes cynotis?
ear mite - non-borrowing psoroptid mite
- 50% of OE in cats
What is characteristic of Otodectes cynotis?
- survives on the skin surface
- protected by thick, brown crust
- feeds on lymph and blood
What age of animals is Otodectes cynotis commonly seen in?
<1 year
Otobius megnini?
spinous ear tick found in the SW U.S. - larvae and nymphs induce inflammation and drops to the ground as an adult
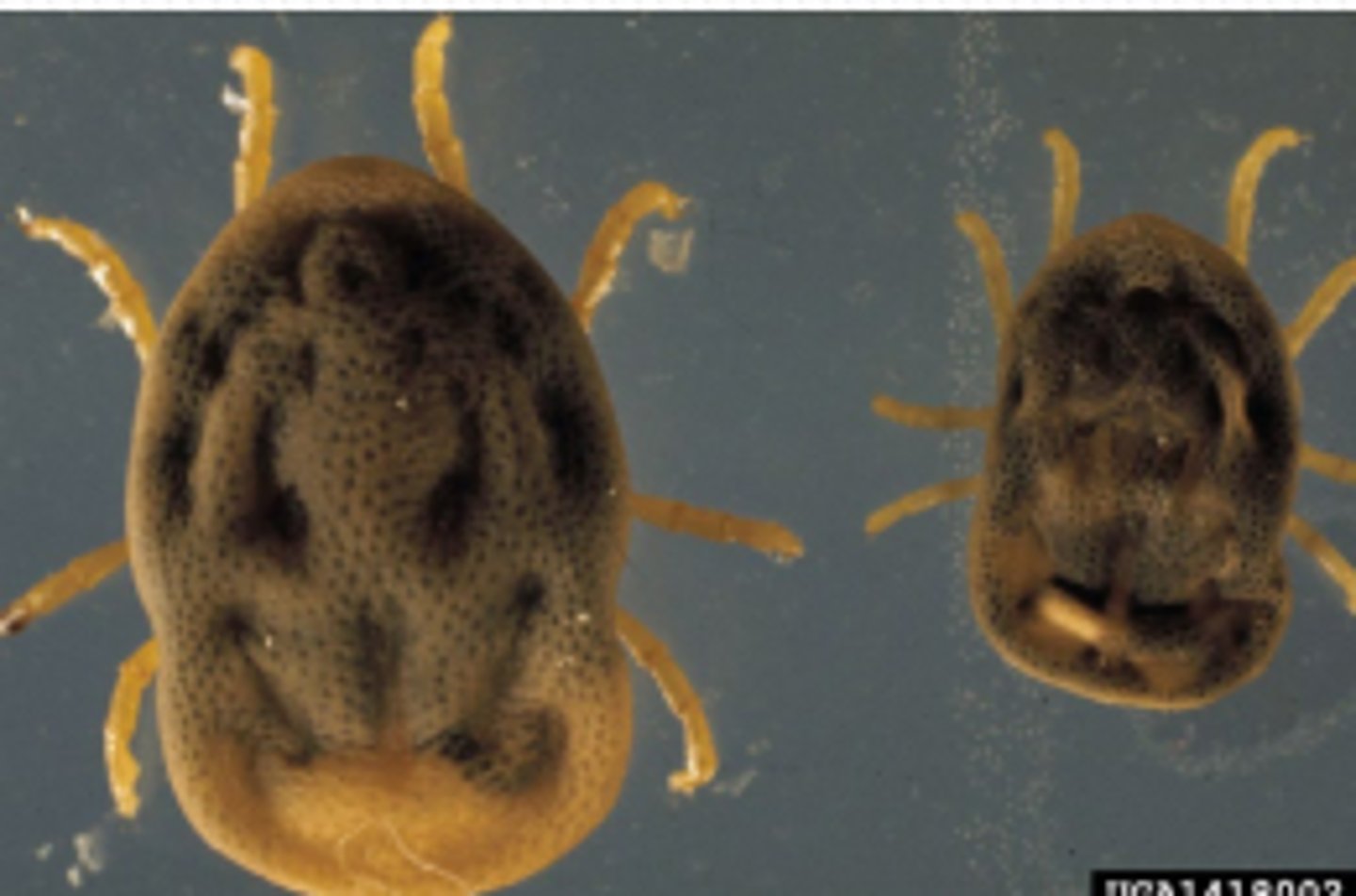

Eutrombicula alfreddugesi?
chiggers - bite causes irritation and variable pruritis, red in color with head the size of a pin
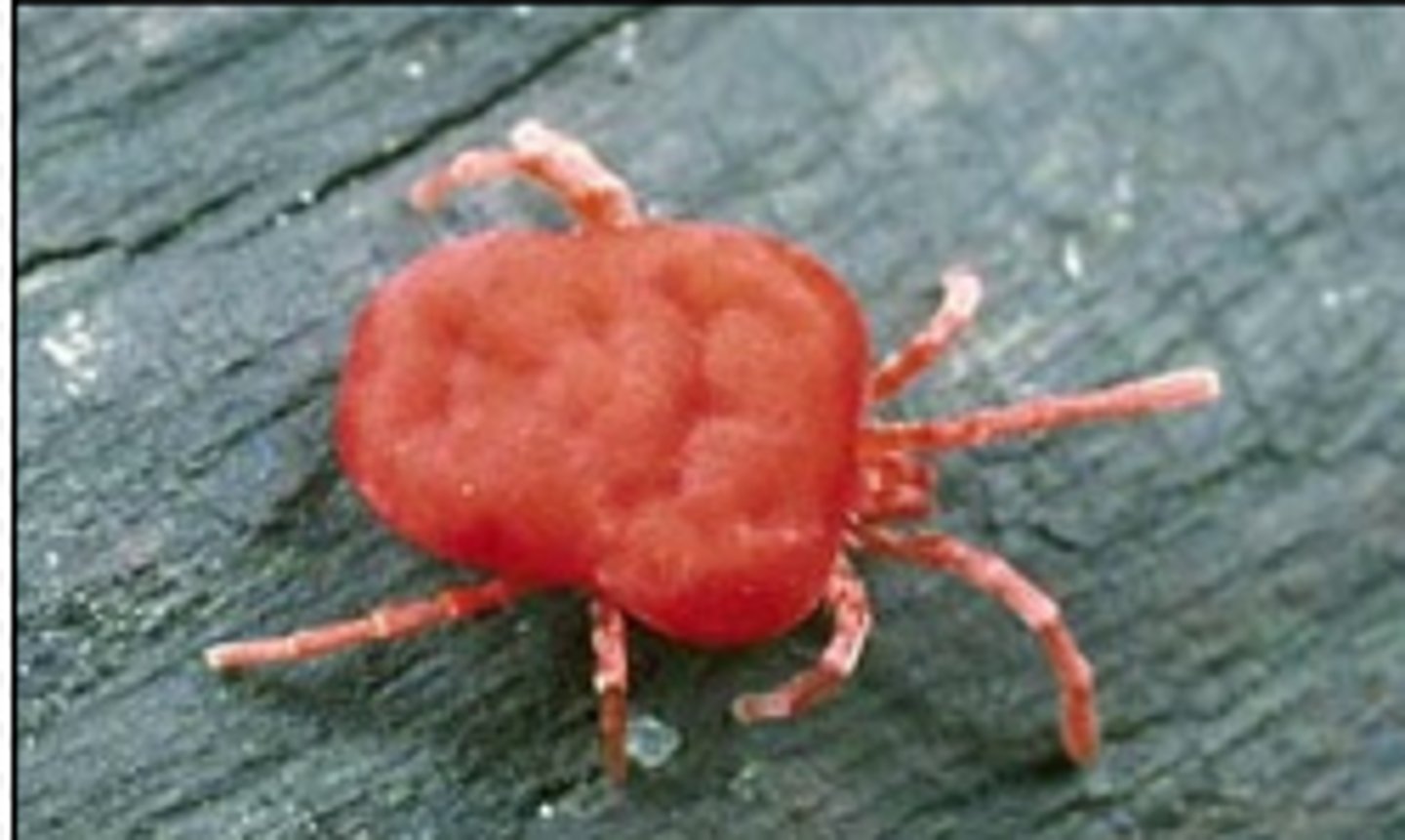

When is Eutrombicula alfreddugesi common?
seasonally - late summer/fall, contact with woods and fields
Otodemodicosis?
- in cats (D. cati)
- ceruminous OE
What is Otodemodicosis associated with?
immunosuppressive disease - FeLV, FIV, neoplasia, and diabetes
Sarcoptes scabei var canis?
canine scabies - usually found on the ear tips but may also be associated with OE
What is characteristic of Sarcoptes scabei var canis?
female burrows into the epidermis and lays eggs --> thick, yellow crust and severe pruritis - low # of mites found
Notoedres cati?
feline scabies
What is characteristic of Notoedres cati?
- affects the medial proximal pinnae, face, eyelids, neck, feet, and perineum
- female mites burrow
- intense pruritis
- highly contagious
- abundant # of mites
What are potential foreign bodies associated with otitis?
plant awns (barley), insect, sand, and dry medications
What clinical signs are associated with foreign body associated otitis?
tx?
acute/chronic unilateral otitis
remove FB, topical abx
Are intraluminal tumors more common in dogs or cats?
cats
What is characteristic of intraluminal tumors?
obstructive lesions with ulceration and necrosis
What are common malignant intraluminal tumors found in cats?
ceruminous gland adenocarcinoma, SCC, and MCT
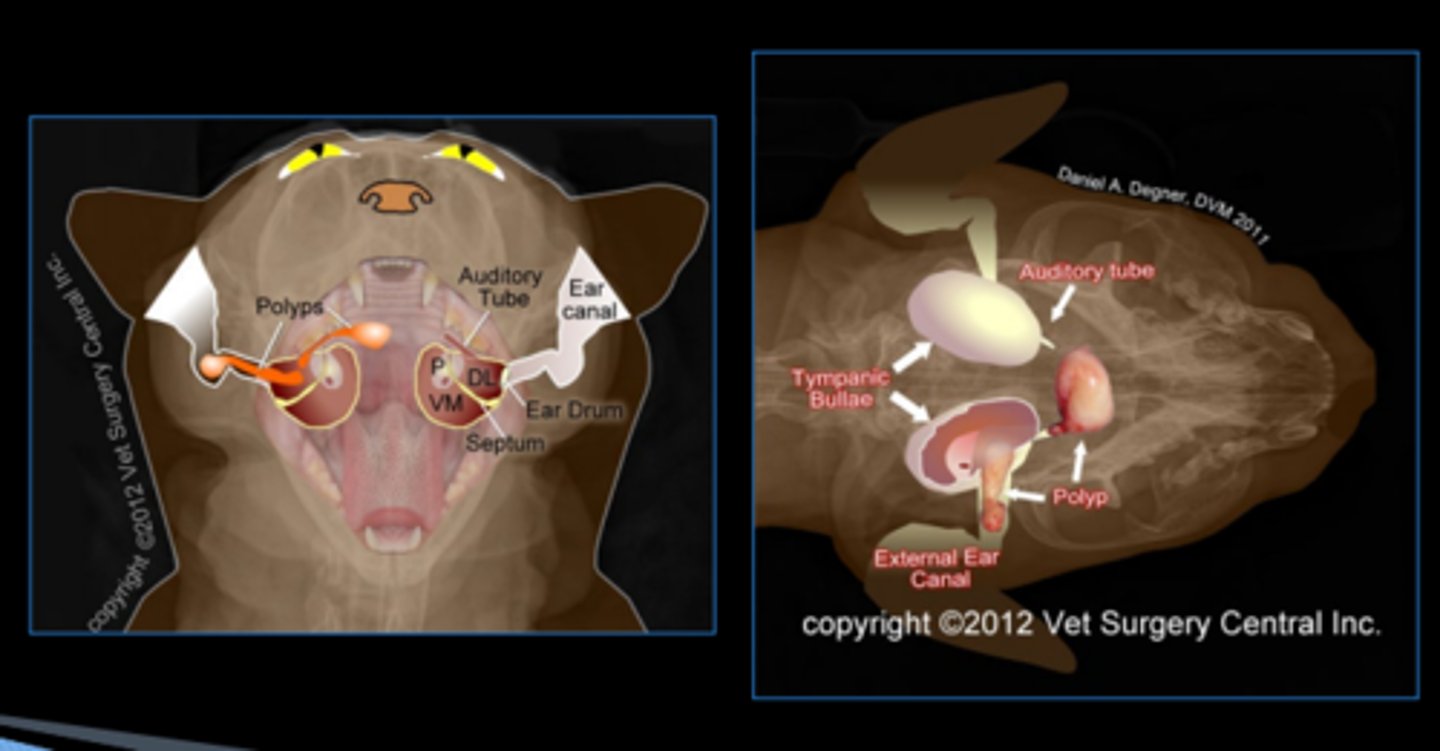
What are the causes of nasopharyngeal polyps?
congenital, bacterial, and calicivirus
What are the clinical signs associated with nasopharyngeal polyps?
treatment?
chronic uni/bilateral otitis, mass in the ear canal, and head tilt
surgery
Apocrine Cystomatosis?
cysts of apocrine glands
What are the clinical signs associated with apocrine cystomatosis?
- adult animals
- solitary, well-circumscribed, smooth, bluish swelling on the concave surface of the pinna or vertical ear canal
- can be uni/bilateral
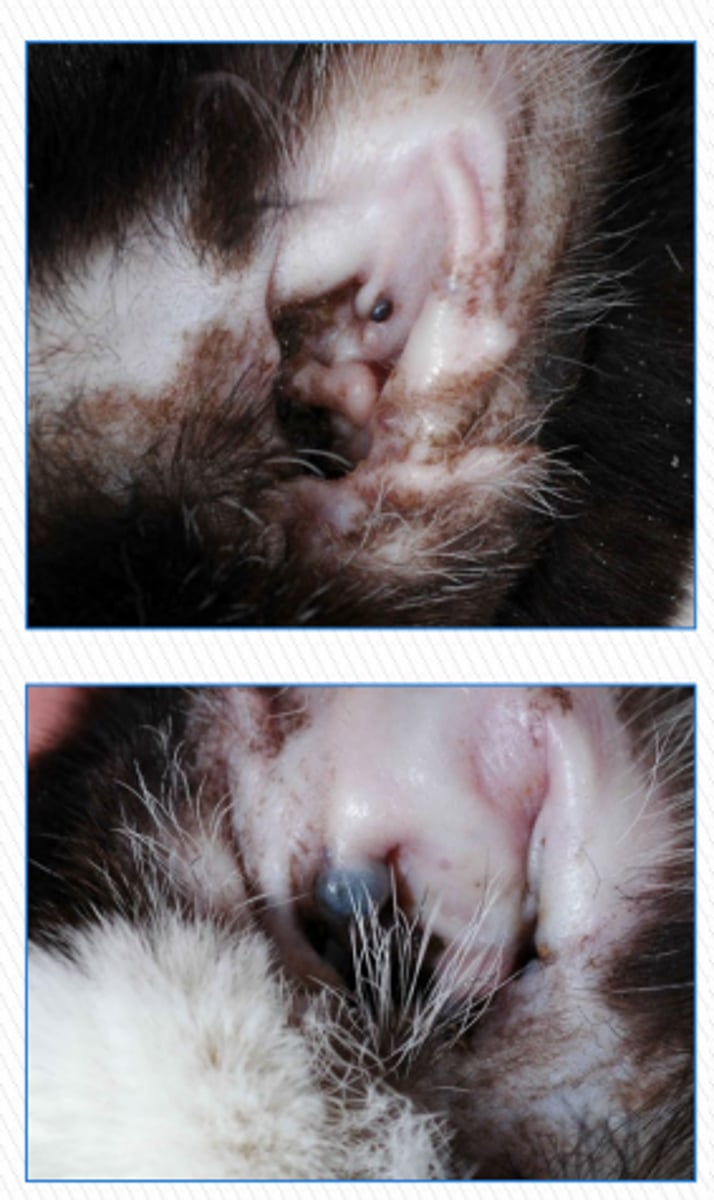
How is apocrine cystomatosis treated?
benign neglect or surgery
What allergies are causative agents of otitis?
food allergy, atopic dermatitis, and contact allergy
What clinical signs are associated with allergic otitis?
tx?
chronic bilateral otitis and dermatitis
treat allergy/infection
What is associated with atopic dermatitis induced otitis?
erythema and inflammation in the pinnae, vertical ear canal, or entire ear canal (chronicity)
What percentage of food allergic dogs have OE?
80%
is Contact allergy common?
tx?
no
- Neomycin/gentamycin, Miconazole 1%, Propylene glycol
What disorders of keratinization can cause OE?
primary idiopathic seborrhea
hypothyroidism
sex hormone imbalance
lipid related conditions
What is characteristic of Primary Idiopathic Seborrhea induced OE?
- increased cerumen production
- altered cerumen composition --> delayed desquamification and stenosis
--> calcifying OE/OM (Cocker Spaniels)
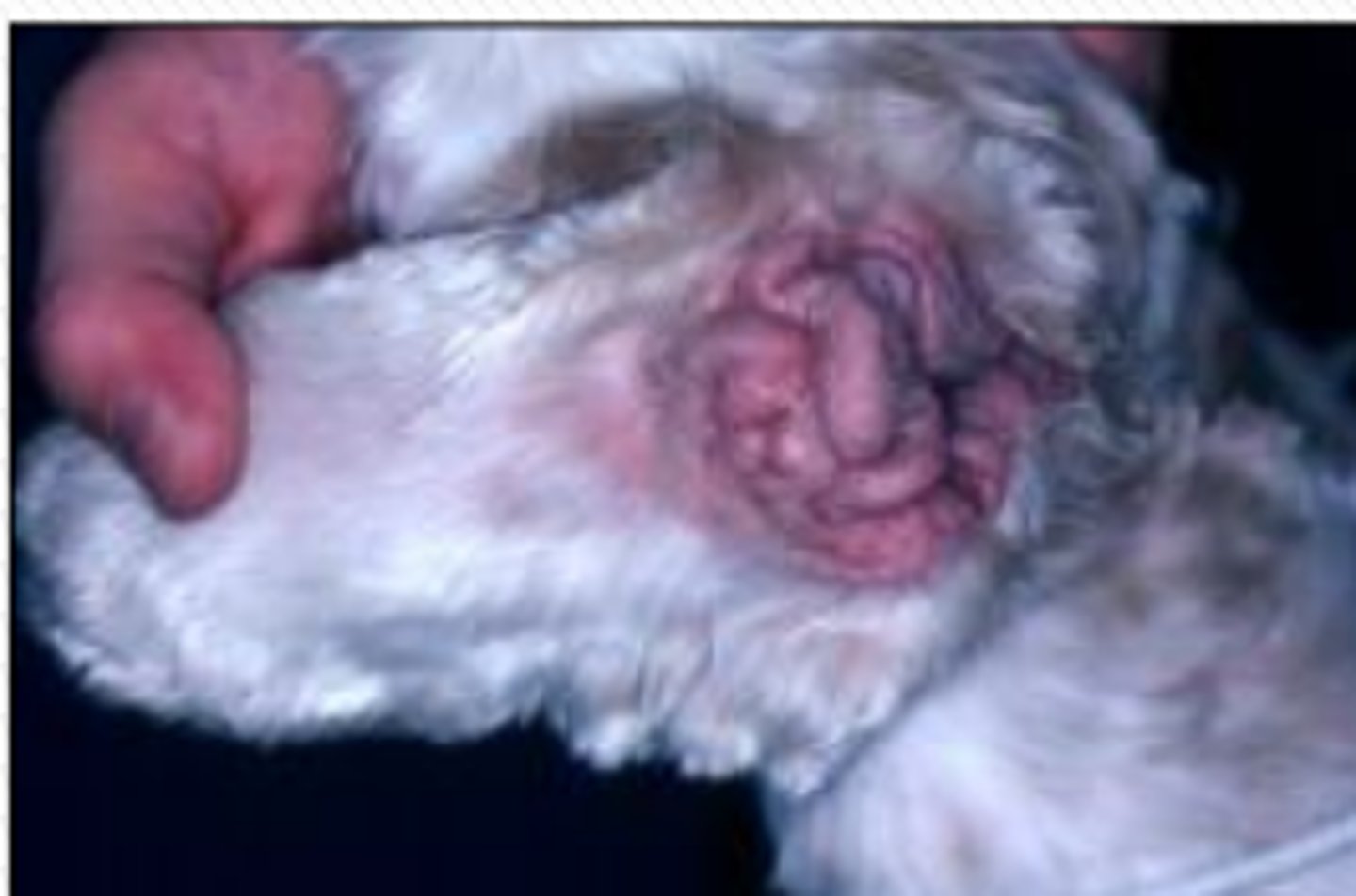
How do endocrinopathies cause OE (Hypothyroidism & sex hormone imbalance)?
increased mucin deposition in the dermis --> hyperplasia/hyperkeratosis of the epidermis and altered fatty acid production
What clinical signs are associated with endocrinopathy induced OE?
tx?
chronic bilateral otitis and dermatitis
Hormone supplement & surgery
What autoimmune diseases cause OE?
pemphigus foliaceus
pemphigus erythematous
systemic lupus erythematous
Juvenile Cellulitis?
- Puppies-3-16 old
- Vesiculopustular disease
- Purulent otitis with head & facial lesions
- unknown etiology
Secondary Factors of Otitis
infection secondary to the inflammatory process - bacteria/yeast
What is the most common bacteria associated with otitis?
S. pseudintermedius
What are the most common yeast associated with otitis?
Malassezia pachydermatis
Candida albicans
What is the influence of bacteria/yeast on otitis?
perpetuating factors - cause the otitis to persist leading to otitis media, mineralization, and hyperplasia of the ear canal
NOT responsible for the otitis!!
What pathological changes are associated with perpetuating factors of OE?
epidermal: hyperkeratosis, hyperplasia, and epithelial folds
dermal: edema and fibrosis
adnexal: ceruminal gland hyperplasia/hypertrophy
lumen stenosis and calcification
What tympanic membrane changes are seen with perpetuating OE?
increased opacity, dilation, and diverticulum
What changes are associated with otitis media due to perpetuating OE?
epithelial changes, purulent accumulation, caseation, cholesteatoma (skin growth), proliferation, and destructive osteomyelitis
What are the common clinical signs associated with OE?
odor, head shaking, discharge, pruritis, aural hematoma, head tilt, pain, and erythema
What are the common clinical signs associated with chronic OE?
edema, lichenification, hyperpigmentation, excoriations, and mineralizations
What are the causes of otitis media?
extension of otitis externa #1, ascending infection via the eustachian tube, and hematogenous spread
Why is diagnosis of otitis media difficult?
1. ear canal filled with debris/exudate
2. stenotic
3. painful and difficult to examine
4. inability to visualize the TM
What neurological signs are associated with otitis media?
facial nerve paralysis, KCS, and Horner's syndrome
What peripheral vestibular signs are associated with otitis media?
head tilt, nystagmus, ataxia/loss of balance, and +/- nausea and vomiting
What diagnostic tools are used for otitis?
ear cytology, video-oscopy, diagnostic imaging, biopsy, and culture and sensitivity
What is characteristic of video-otoscopy?
performed under GA to visualize the tympanic membrane
What is video-otoscopy useful for?
deep ear flushing, myringotomy, and performing biopsy
What are the goals of a deep ear flush?
1. remove the exudate to allow for visualization of the TM, unmask a foreign body or tumor, and remove purulent discharge so medication can work
2. perform myringotomy (incision is made in the tympanic membrane (eardrum) to drain fluid or collect samples from the middle ear)
3. collect culture/flush of the middle ear
What medications are inactivated by the purulent discharge in the ear associated with otitis?
Gentamicin and Polymyxin B
What equipment is needed to perform a deep ear flush?
8" Fr red rubber catheter, 12cc syringe, warm saline, an otoscope (handheld or video), and cotton tip applicators
How is a deep ear flush performed?
1. withdraw 2-12cc of warm sterile saline
2. instill gently into the ear
3. massage the ear canal gently
4. withdraw the saline and exudate
5. continue until the ear is clear of exudate
6. attempt to pass the catheter into the middle ear canal
What is the video-otoscope helpful in performing?
unblinded myringotomy, biopsy, and polypectomy
Myringotomy
surgical rupture of the TM
What are the purposes of a myringotomy?
diagnostic - collect material for culture or PCR
therapeutic - flushing of the bulla and permanent opening
What should be done after a deep ear flush?
instill antibiotics and administer steroids
What is the benefit of steroid administration post deep ear flush?
decrease inflammation and stenosis and increase comfort/owner's ability to treat
What steroids can be used?
oral prednisone or triamcinolone or topical dexamethasone
What are potential complications associated with deep ear flush?
iatrogenic rupture of the TM, pain, Horner's syndrome, facial paralysis, KCS, vestibular signs, and deafness
horner's syndrome?
Ptosis of eyelids
Miosis
Hypohydrosis of the face
Redness of the conjunctiva
reduced hearing
What are the advantages of performing a biopsy?
identify the mass and best treatment choice/prognosis
What are the disadvantages of performing a biopsy?
small samples and low sensitivity/specificity
What is diagnostic imaging (x-rays/MRI/CT) useful in evaluating?
neoplasia, otitis media, and calcification of the ear canal
What are the advantages of performing a CT?
better definition, very sensitive/specific, and quick
What is the advantage of performing a MRI?
better for soft tissue structures
When is culture and sensitivity beneficial?
otitis media and identification of appropriate systemic antibiotics
summary of treatment options?
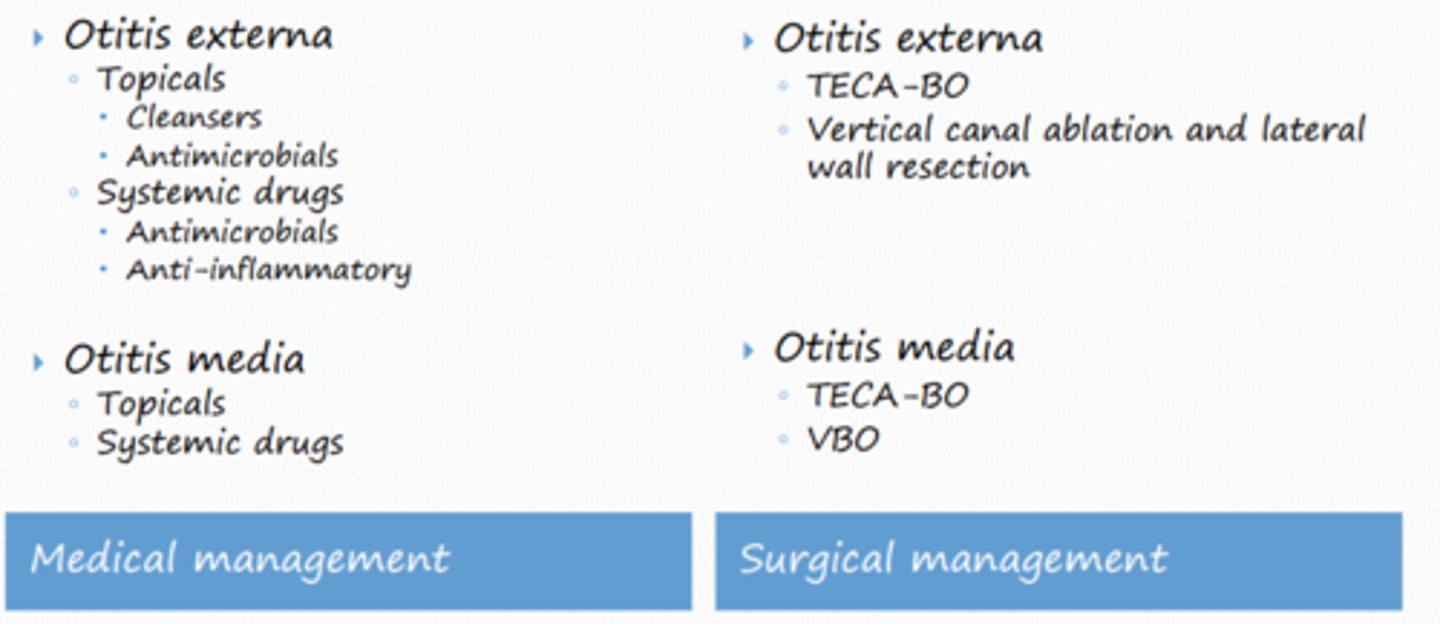
What are the goals of treatment for otitis?
1. treat primary cause
2. treat perpetuating factors
3. use topical medications
4. use weekly flushes
Which systemic medication is more useful by itself when treating otitis, antimicrobials or glucocorticoids?
glucocorticoids
How should an ear cleanser be used?
weekly/biweekly with cotton balls for application
What ear cleansers inhibit microorganisms?
Tris-EDTA, chlorhexidine, ketoconazole, and acetic acid

What ear cleansers are ceruminolytic?
squalene and propylene glycol
Ceruminolytics?
used to soften impacted material prior to deep flushing - can be irritating and potentially ototoxic
Acidifying Agents
dry the ear canal to make it less habitable for microbes
What are the components of Tris-EDTA?
alkalizing and chelating agents
Chelating Agents
disrupt cell membrane of bacteria and enhances antibiotic therapy
What antibiotics can be combined with Tris-EDTA?
aminoglycosides and fluoroquinolones
What aminoglycosides are used for otitis?
Neomycin (Tresaderm), Gentamycin (Otomax/Mometomax), Tobramycin, and Amikacin
What is important to remember about aminoglycosides?
inactivated by low pH or debris
When should systemic antibiotics be used for otitis?
otitis media and extremely severe/chronic otitis externa
ALWAYS WITH TOPICALS
(pred)
What is the minimum length of treatment for otitis media?
6-8 weeks of topical and systemic antimicrobials
What are the common causative rod-shaped agents of otitis media?
Pseudomonas spp., Cornyebacterium spp., E. coli, and P. mirabilis
What systemic antibiotics should be used for rod-shaped bacteria?
Enrofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, or Marbofloxacin
What systemic antifungals are useful for Malassezia associated otitis media?
ketoconazole (not cats), itraconazole, and fluconazole
follow up appointments?
- recheck 2w
- comfort should be improving
- complications include resistance, new organisms, contact hypersensitivity, O non-compliant