Map Projections
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Planar (Azimuthal) Projection
Use: A duel Map projection used to show each hemisphere with a primary central focus on the North and South Poles
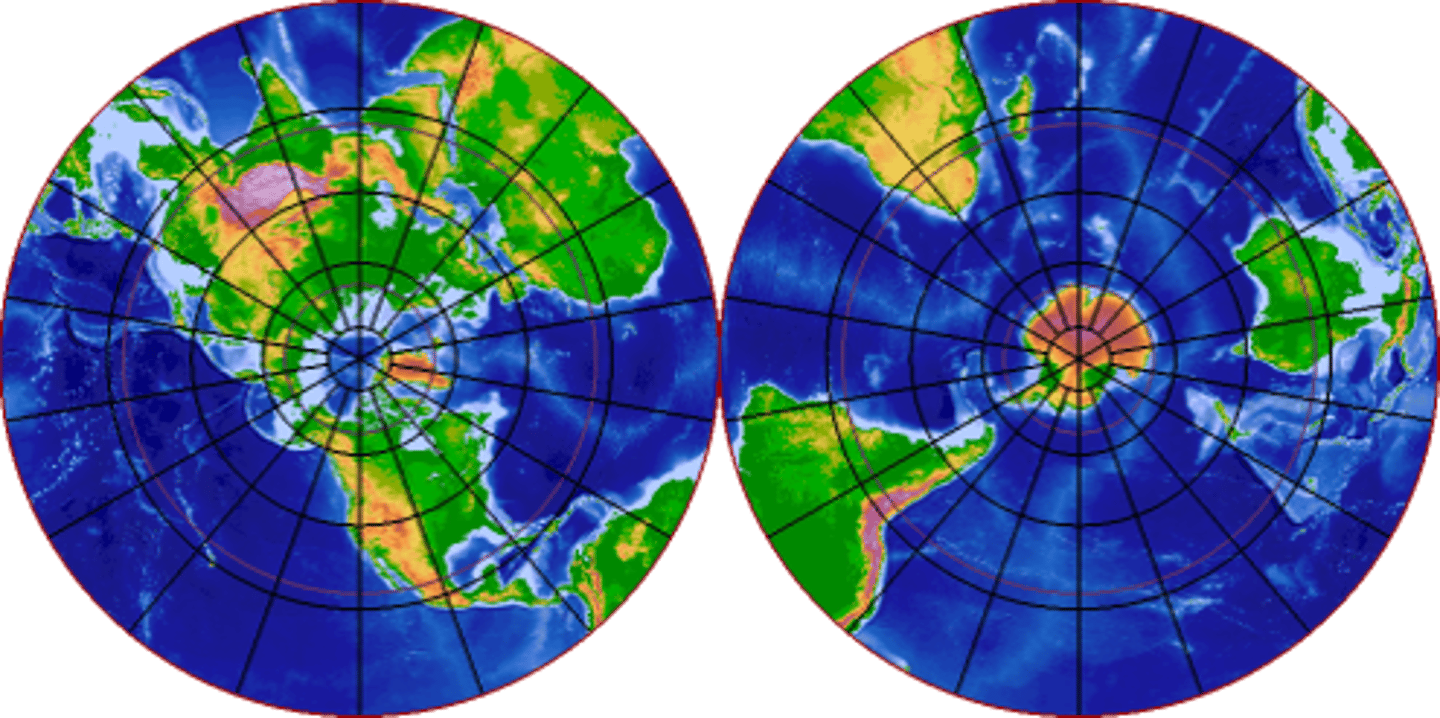
Planar (Azimuthal) Projection
Advantage: Direction from any given central point to any other point on the map is shown accurately
Planar (Azimuthal) Projection
Disadvantage: Size and Shapes become stretched and exaggerated the further from the poles landmasses are located
Planar (Azimuthal) Projection
Disadvantage: Requires two maps as one projection only represents a single hemisphere.
Planar (Azimuthal) Projection
Advantage: Very accurate at its center with no distortion of relative size, shape or direction at either pole
Conic Projection
Use: Aeronautical navigation depicting accurate point to point Great Circle Routes distances.
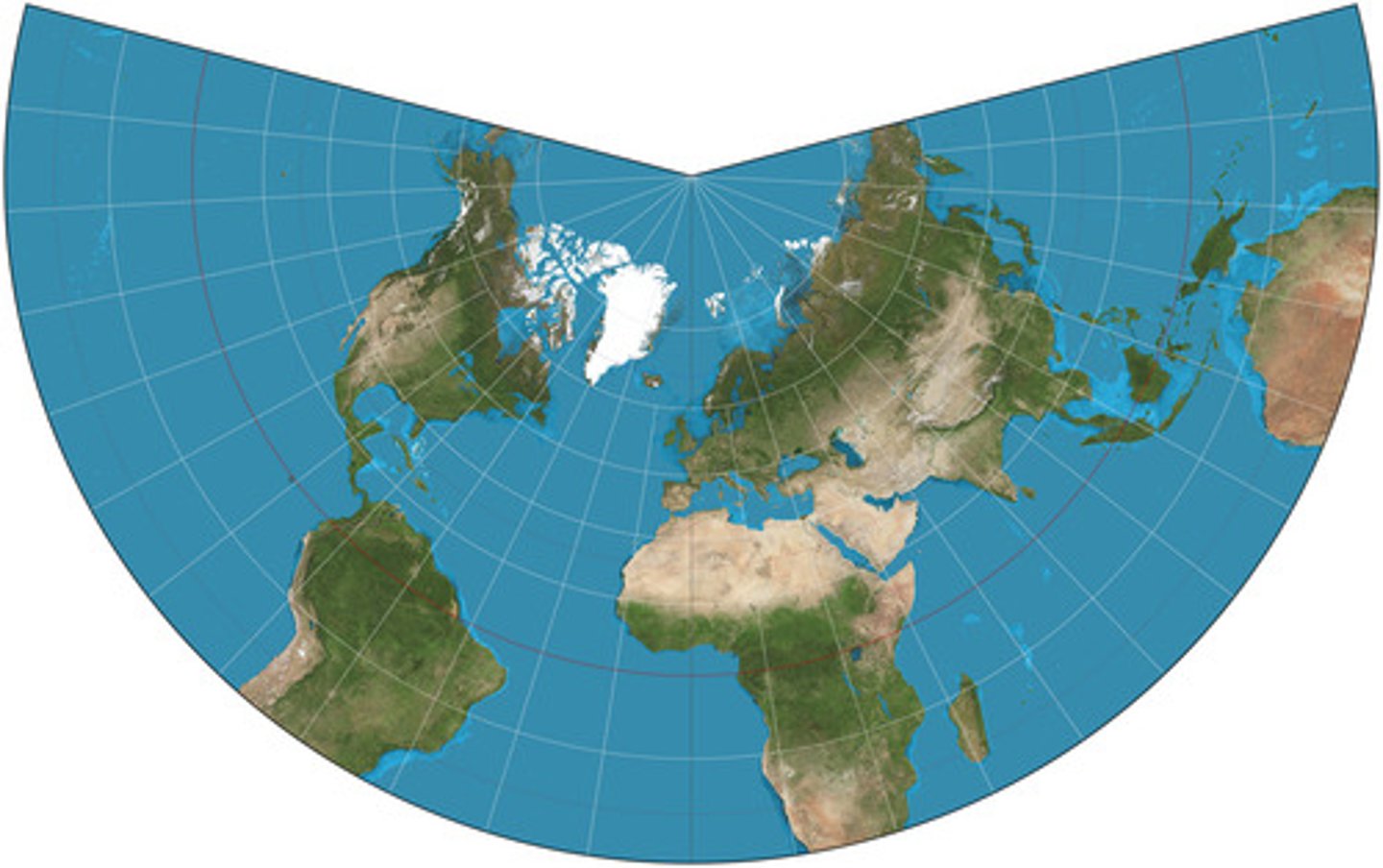
Conic Projection
Advantage: Shows areas elongated in an east-west direction very well
Conic projection
Advantages: Shows distance along the mid-latitude parallels accurately
Conic Projection
Disadvantage: scale becomes distorted at the Poles, further from a reference parallel
Conic Projection
relatively small zone of accuracy
Robinson Projection
Use: A general reference map designed to be appealing to the viewer
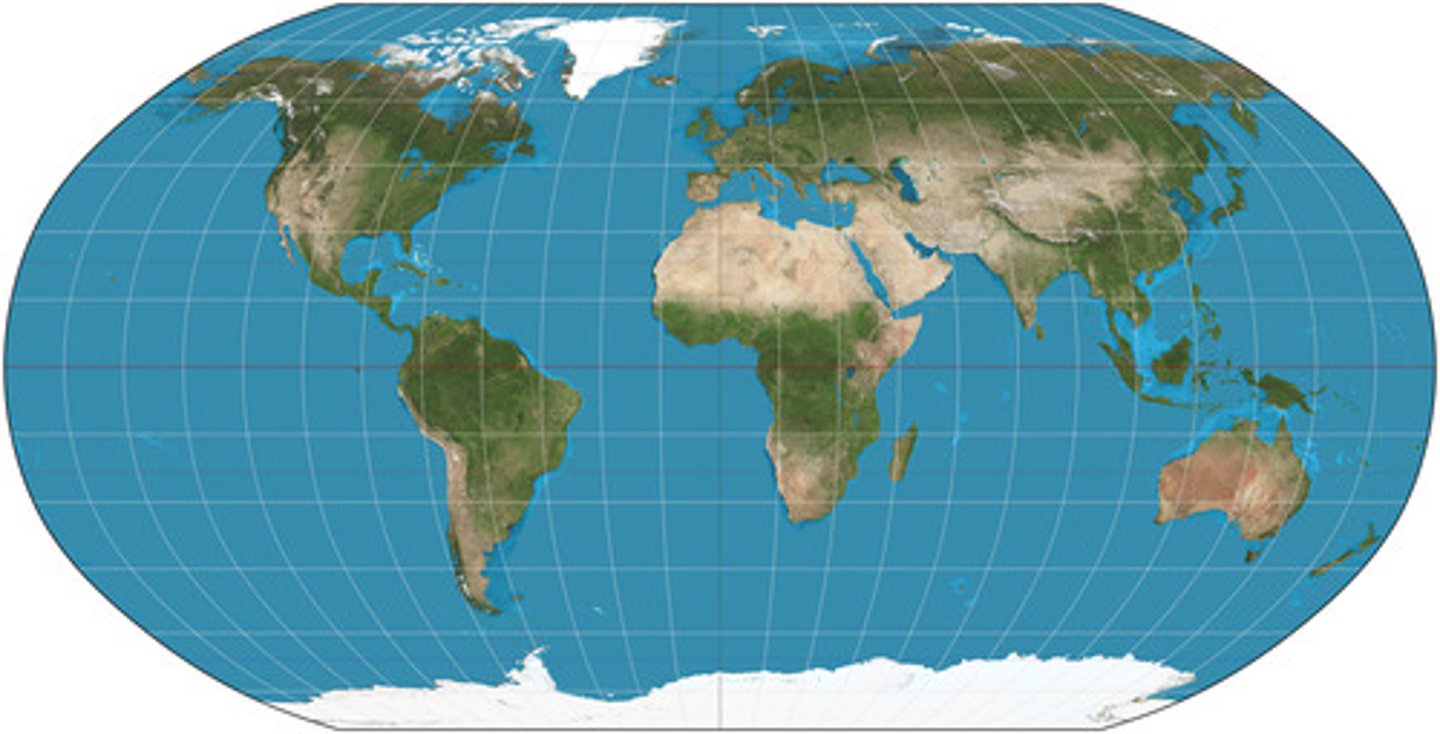
Robinson Projection
Advantage: reduces distortion of area, shape, distance, and direction by balancing these projection error.
Robinson Projection
Advantage: Accurate sizes & shapes on east & west ovular edges of map
Robinson Projection
Disadvantages: Parallels depicted as straight lines at the poles rather than intersecting
Robinson Projection
Disadvantage: North and South Poles appear flat and landmasses are heavily distorted at the poles though not as much as Mercator's Projection.
Goode's Projection
Use: An equal area map designed to accurately display thematic spatial data (densities, resources, ethnicities, religion etc.) by minimizing size and shapes distortion.
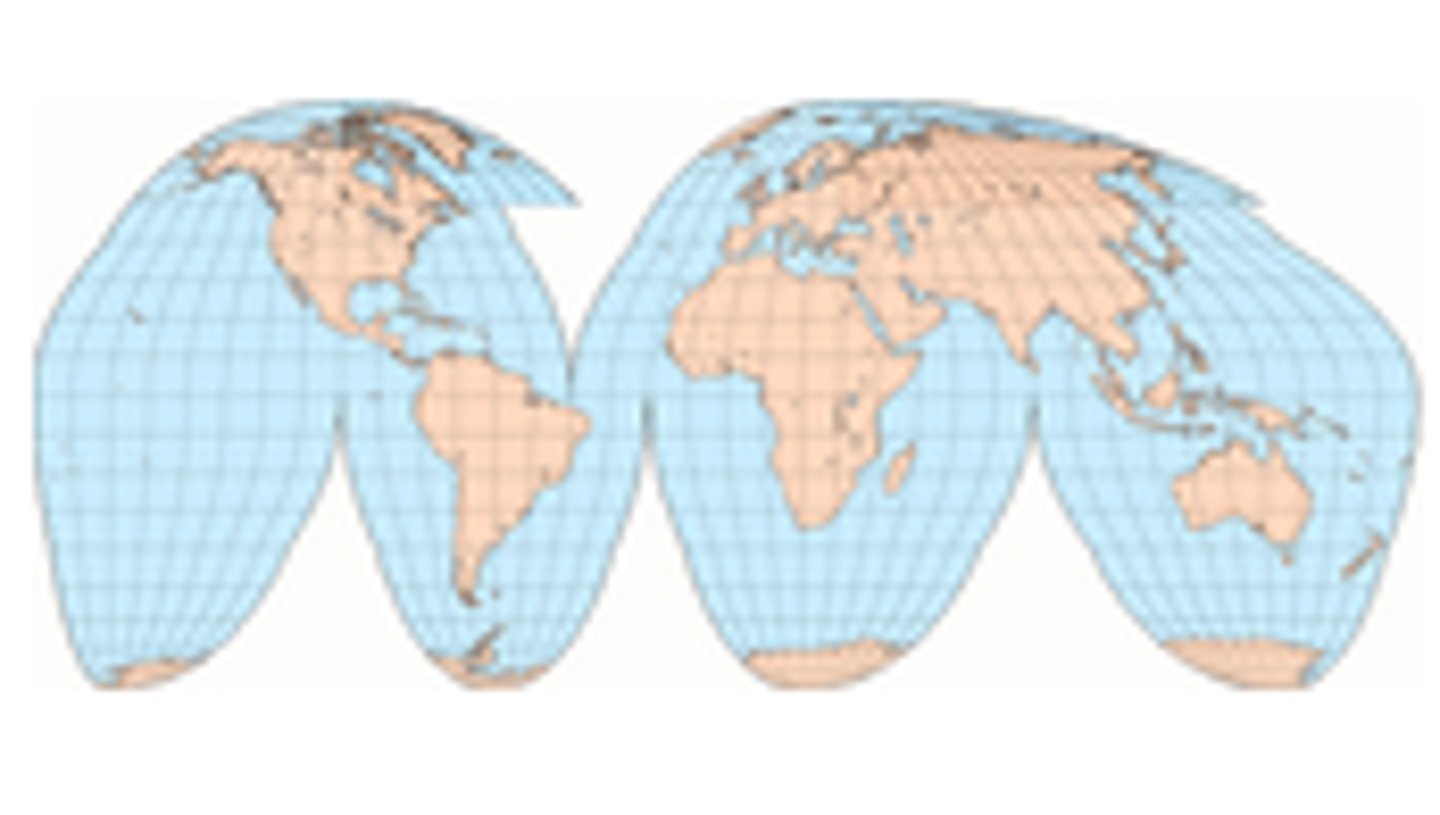
Goode's Projection
Advantage: Reduces distortion in shape of landmasses
Goode's Projection
Advantage: the size of an area on the map is in true proportion to its size on the Earth
Goode's Projection
Disadvantage: Many polar landmasses such as Antarctica and Greenland are divided/interrupted on this projection
Goode's Projection
Disadvantage: The interruptions in oceans distorts our perception of direction and distance.
Gall-Peters Projection
Use: Equal area map created to show the relative sizes of the earth's continents accurately (equal area).
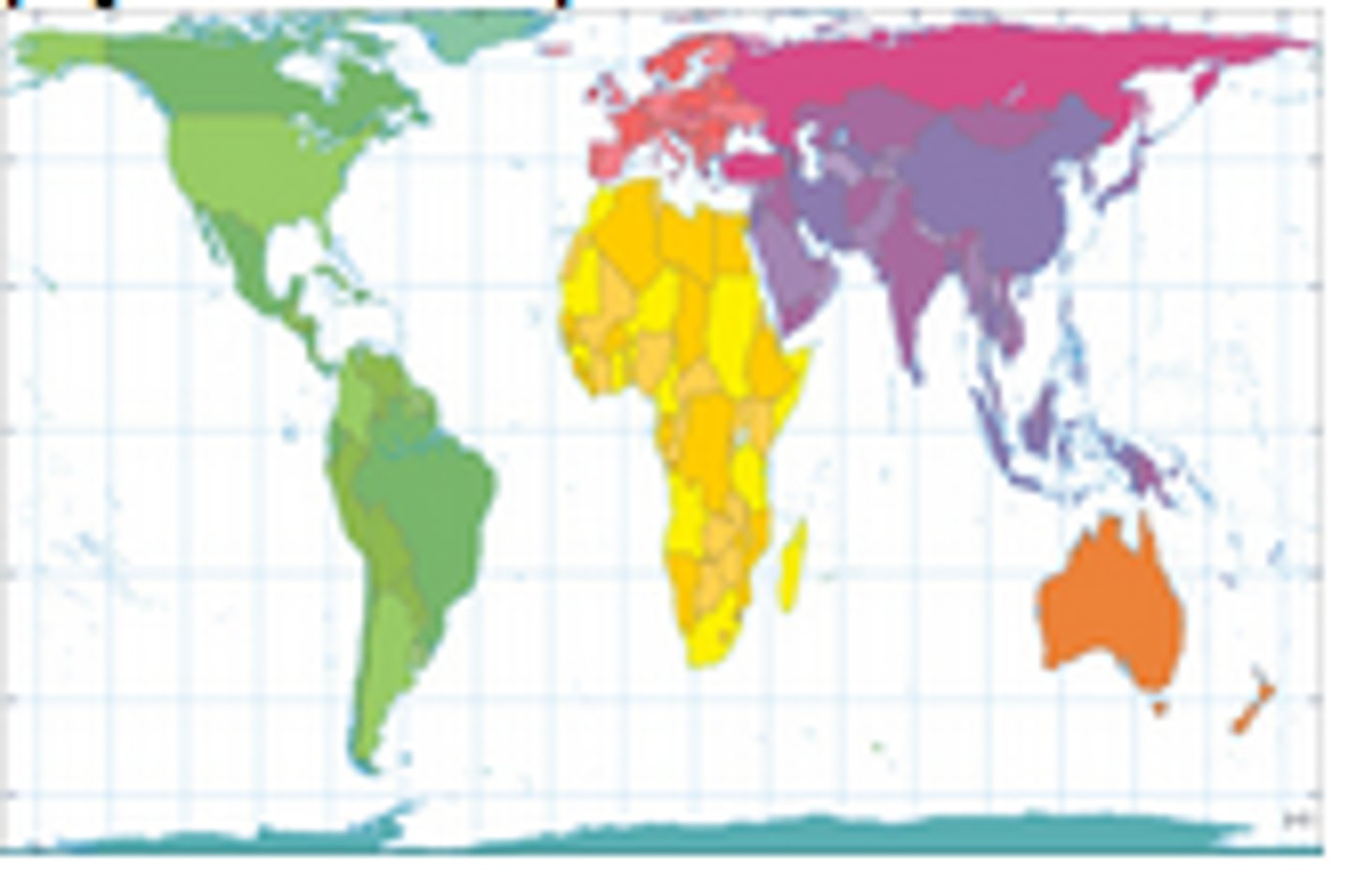
Gall-Peters Projection
Advantage: Accurate sizes of landmasses
Gall-Peters Projection
Disadvantage: Elongated shapes stands out as an obvious factor of distortion.
Gall-Peters Projection
Disadvantage: Aside from accurate relative sizes Projection errors are found in all facets of this projection including, shape, direction, and distance
Mercator Projection
Use: A Map designed for maritime navigation (sea travel)
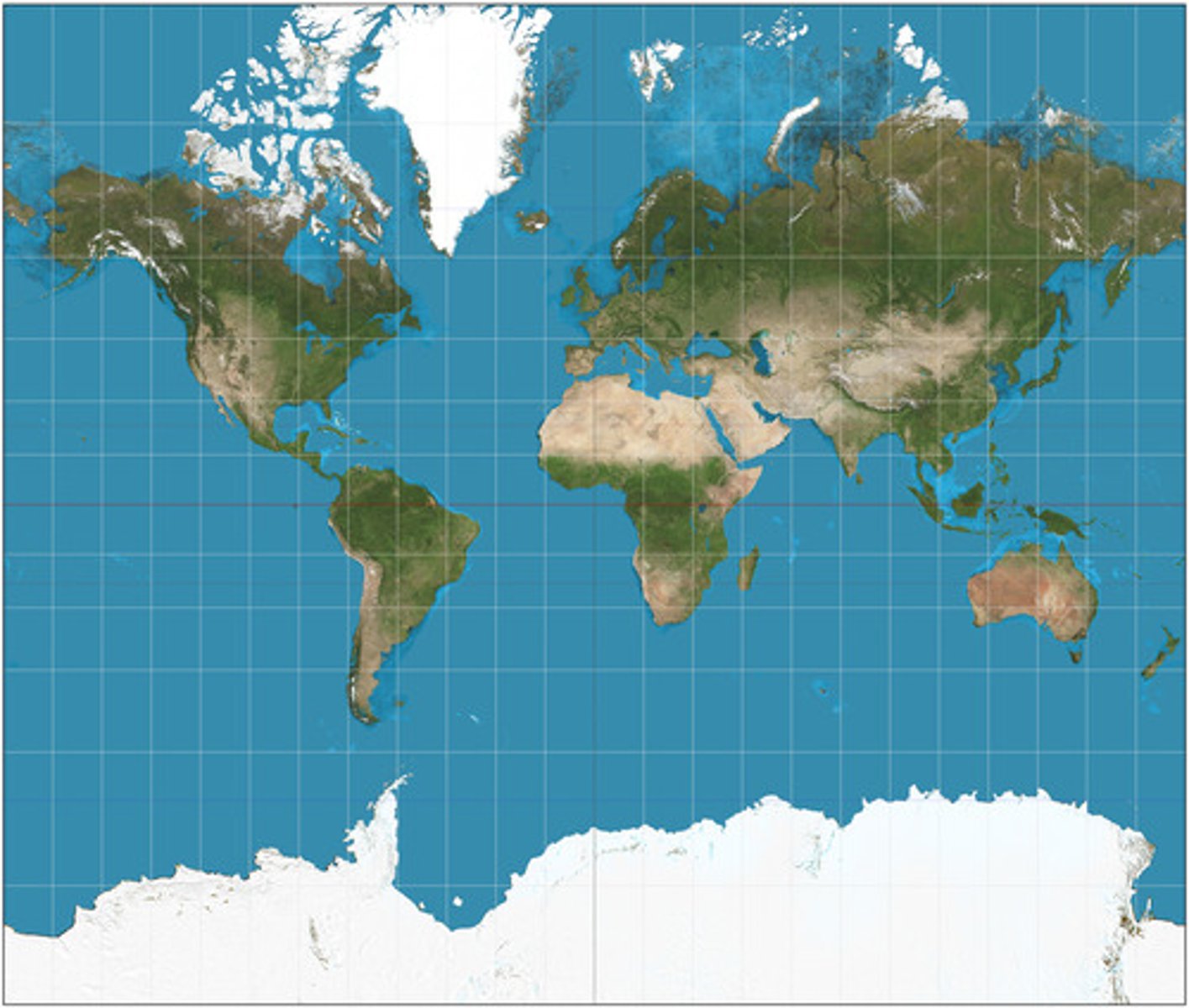
Mercator Projection
Advantage: Displays accurate shapes of landmasses
Mercator Projection
Advantage: Displays True Direction
Mercator Projection
Disadvantage: Extreme distortion of shape at the poles to minimize distortion in the mid and low latitudes
Mercator Projection
Disadvantage: Distance between landmasses are heavily distorted