Urinalysis Microscope Slides
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Urine, CSF, Body Fluid, Stool
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
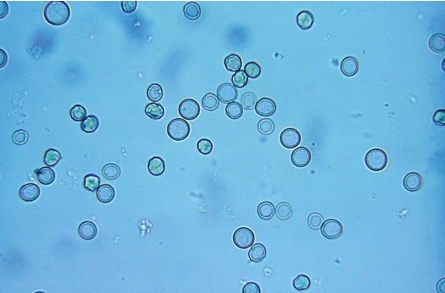
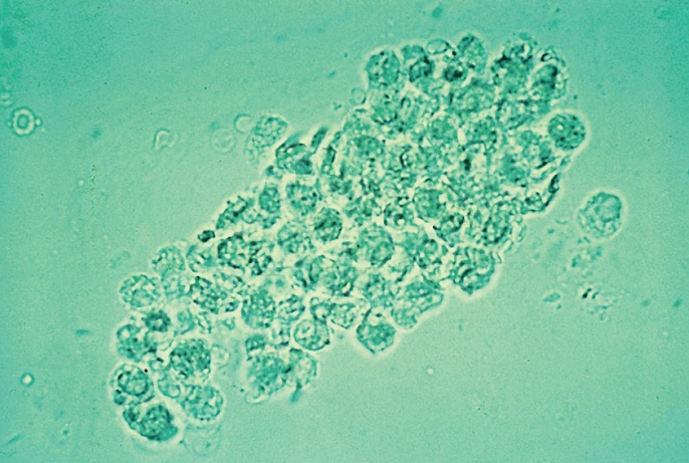
RBC
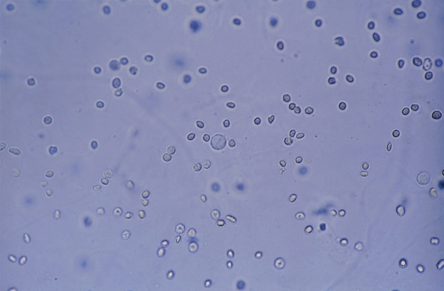
RBC-lower magnification
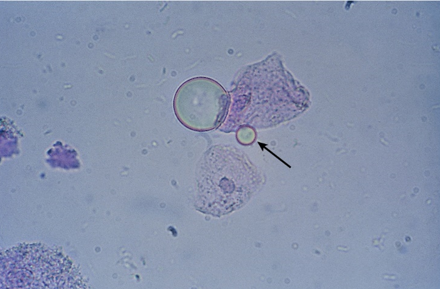
Air Bubble
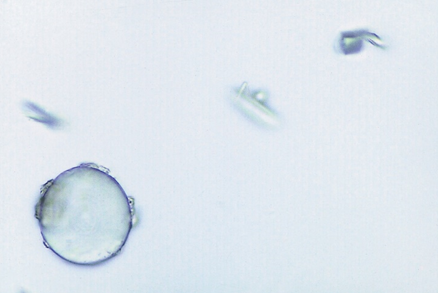
Oil Droplets
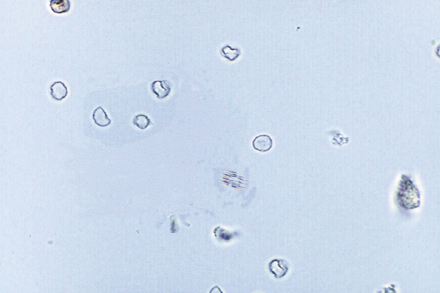
Dysmorphic RBCs
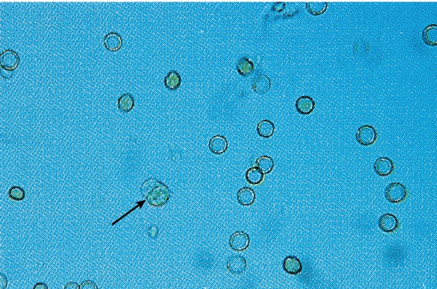
cell arrow pointing at
WBC
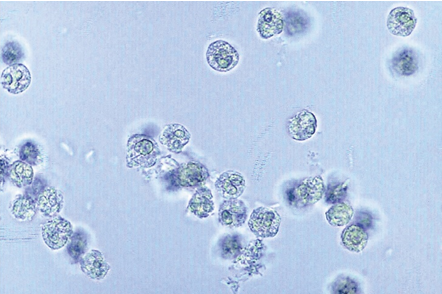
WBC-high contrast
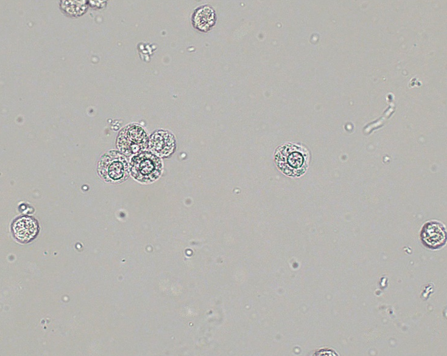
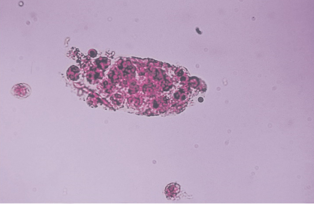
Glitter cell
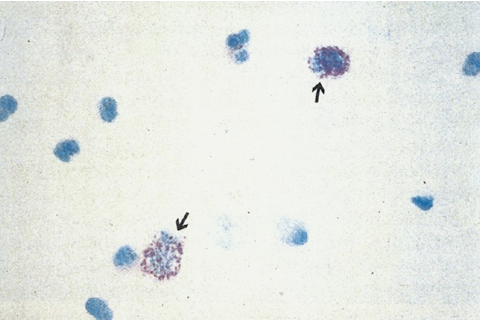
Eosinophils
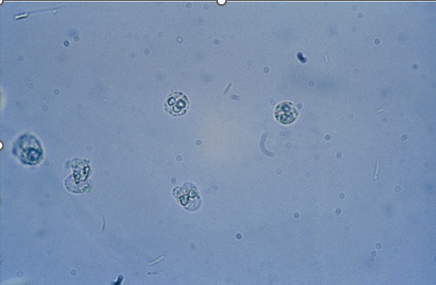
Mononuclear cells
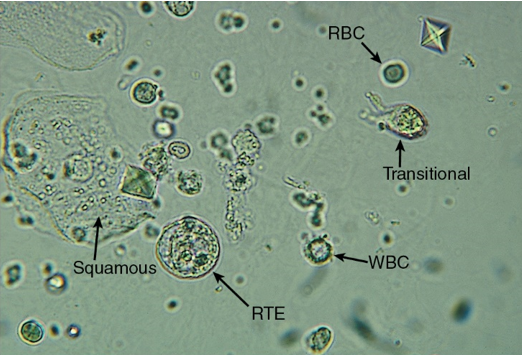
Epithelial Cells
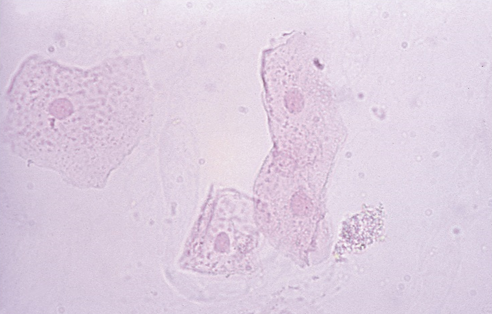
Squamous Epithelial Cells
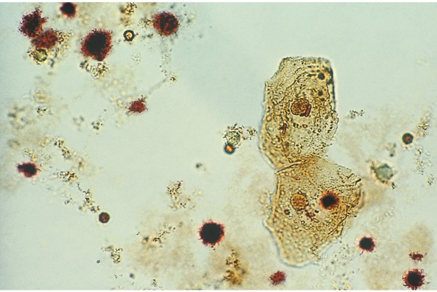
Squamous Epithelial Cells-stained
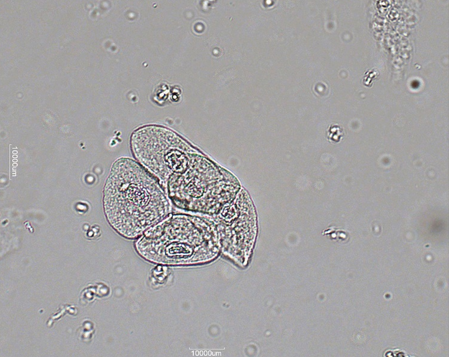
Transitional Epithelial
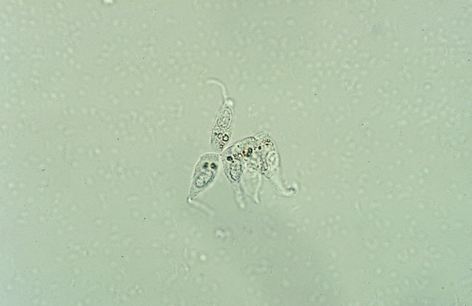
Transitional Epithelial- caudate
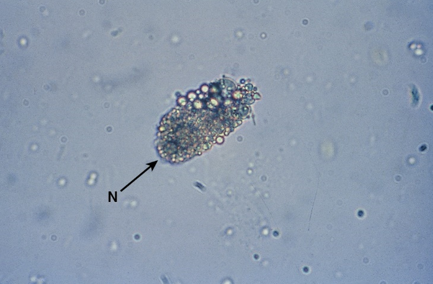
RTE-PCT
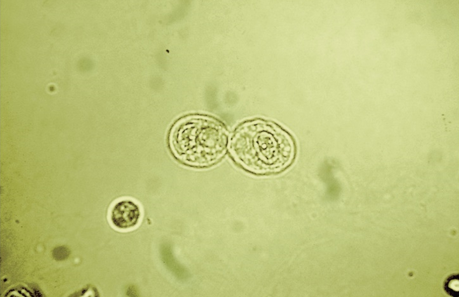
RTE-DCT
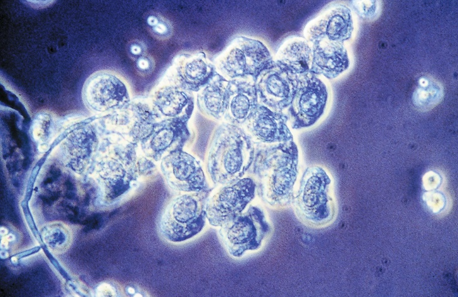
RTE-Collecting Duct
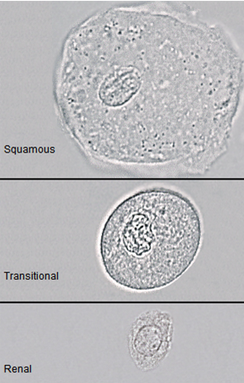
These are all
Epithelial cells
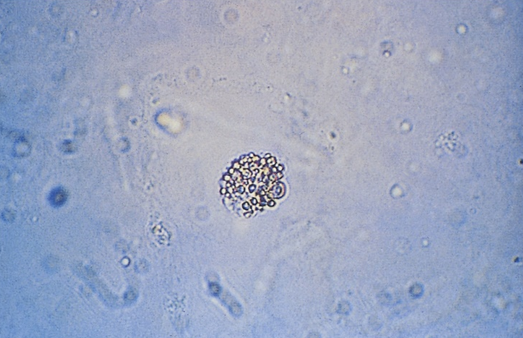
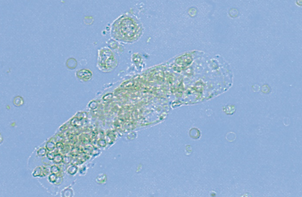
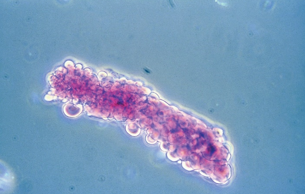
Oval Fat Bodies

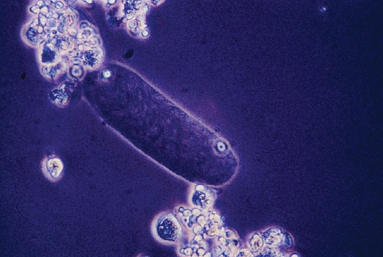
Bacteria
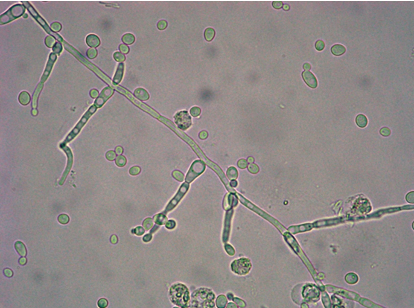
Yeast-branched
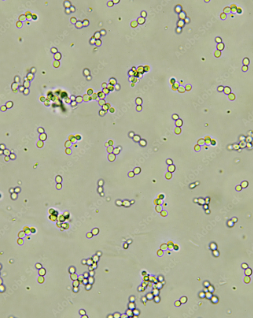
Yeast-budding
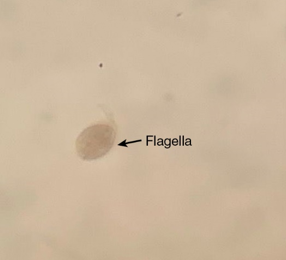
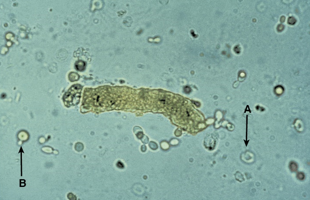
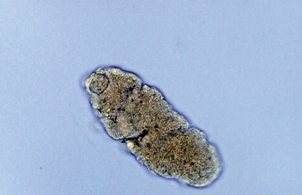
Parasite
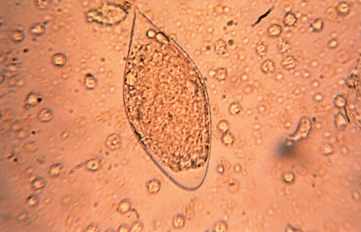
Parasite w/o flagella
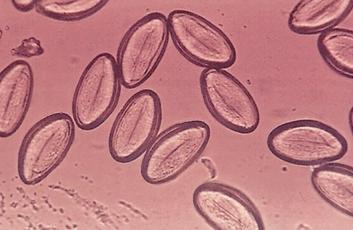
Parasite-high contrast
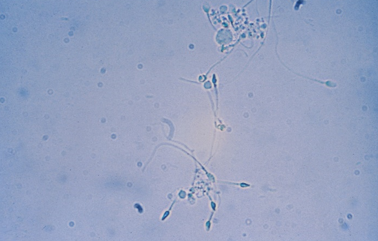
Spermatozoa
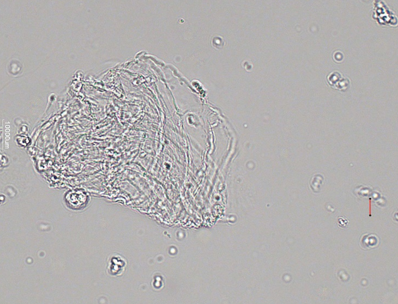
Mucus-High contrast
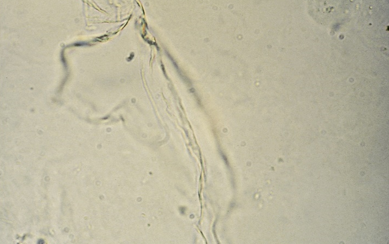
Mucus 2
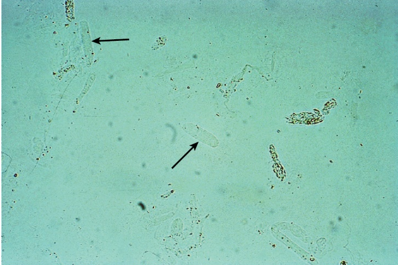
what the arrow is pointing at
Hyaline casts
Hyaline casts-dark light
RBC casts-fresh
RBC cast-stained
ignore arrows
RBC casts-degraded with free cells
RBC casts-degraded with no free cells
WBC cast-stained
WBC cast
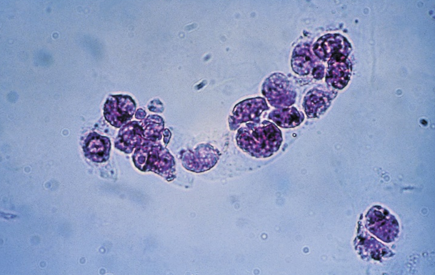
Epithelial Cell Casts-stained
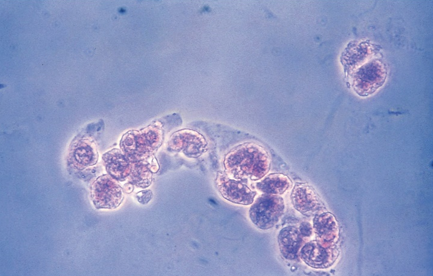
Identify the urine sediment element shown and what perspective it is in
Epithelial Cell Casts-high contrast
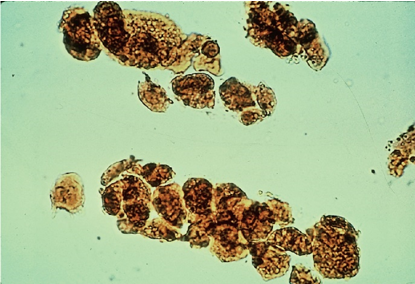
Epithelial Cell Casts- bilirubin stain
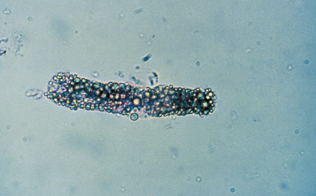
Fatty casts
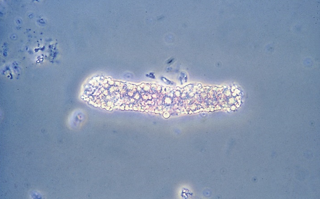
Identify the urine sediment element shown and what perspective it is in
Fatty casts-phase contrast
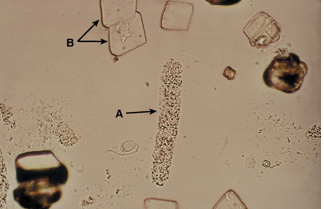
what A is pointing at
Granular Casts
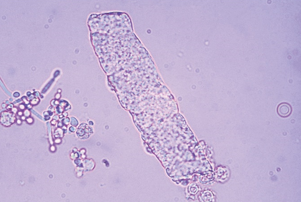
Waxy casts
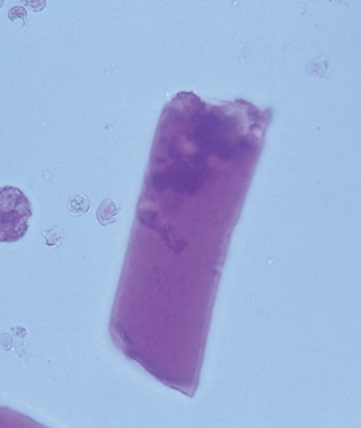
Waxy casts-stained
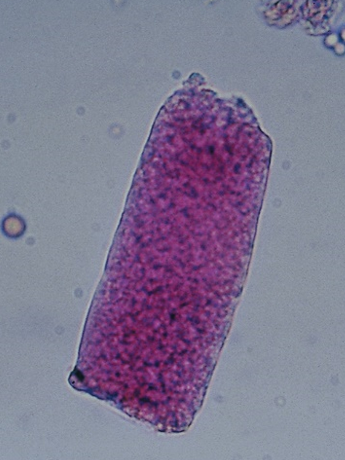
broad casts-stained
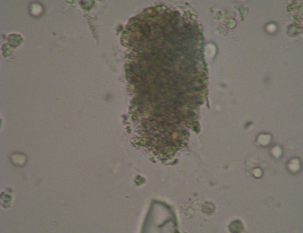
broad casts
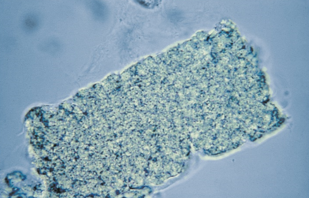
Identify the urine sediment element shown and what perspective it is in
broad casts-phase contrast
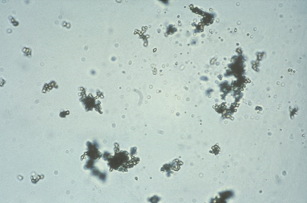
Amorphous urates
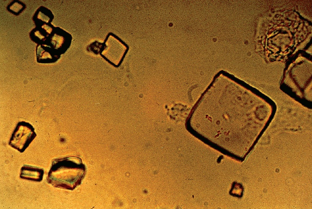
Uric acid crystals

Identify the urine sediment element shown and what perspective it is in
Uric acid crystals-polarized

Sodium urates
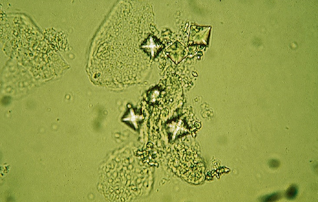
Dihydrate calcium oxalate
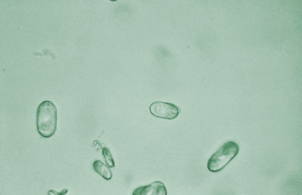
Monohydrate calcium oxalate
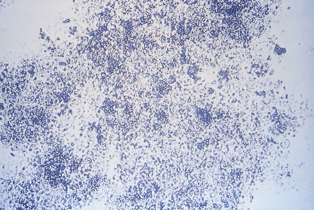
Amorphous phosphates
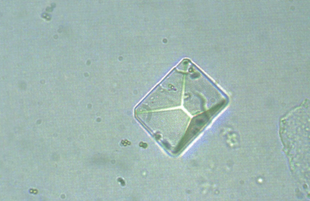
Triple phosphate

Calcium phosphate
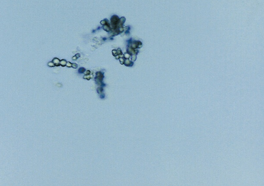
Calcium carbonate
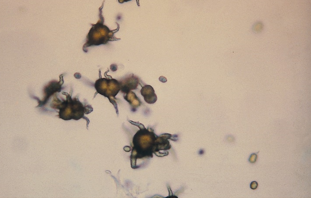
Ammonium biurate
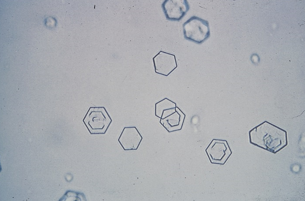
Cystine crystals
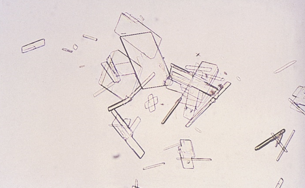
Cholesterol Crystals

Identify the urine sediment element shown and what perspective it is in
Cholesterol Crystals-polarized
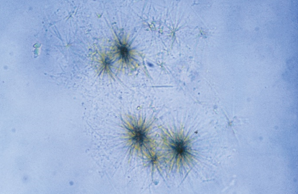
Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Tyrosine crystals
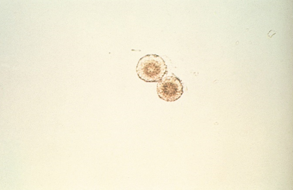
Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Leucine crystals
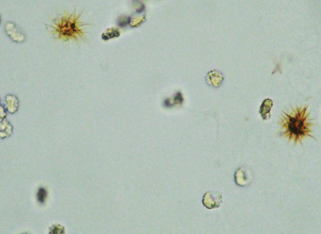
spikey rust orange
Bilirubin crystals
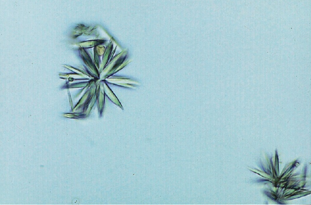
Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Sulfonamide Crystals-phase conteast
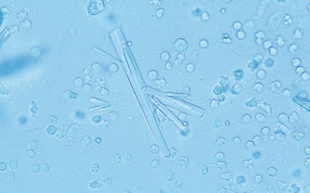
Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Sulfonamide Crystals
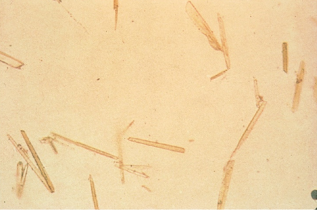
Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Ampicillin Crystals
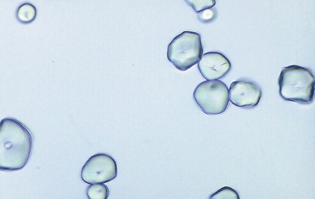
Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Artifact-granules

Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Artifact-fiber piece
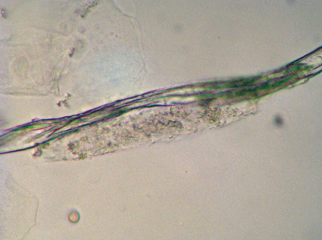
Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Cast like artifact
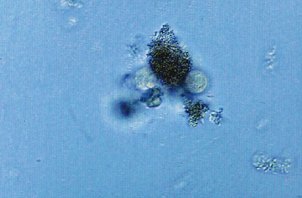
Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Artifact
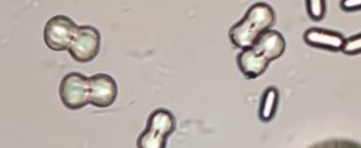
calcium carbonate-higher magnification
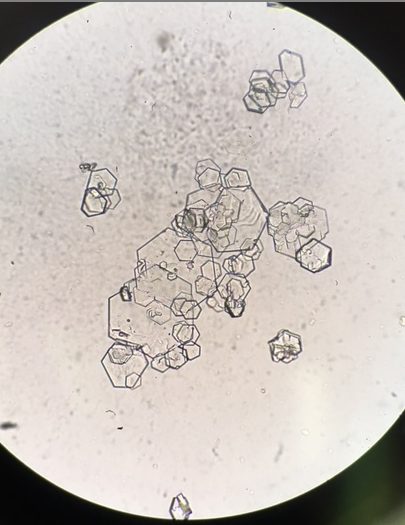
Cystine crystals
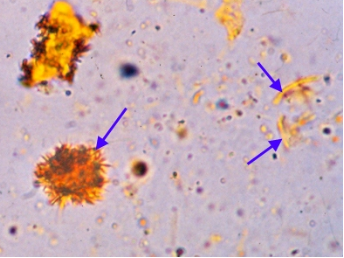
yellow clumped needles or granule-like crystals
Bilirubin crystals
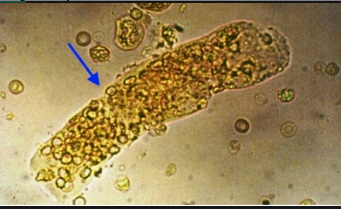
What type of cast is shown in the illustration?
RBC cast
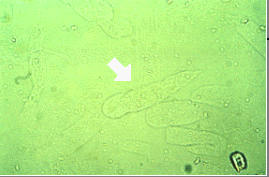
Identify the urine sediment element shown by the arrow.
Cylindroid
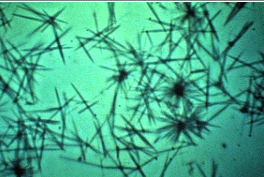
Identify the urine sediment elements present in this illustration:
Tyrosine crystals
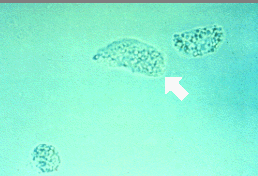
Identify the urine sediment element shown:
Oval fat bodies
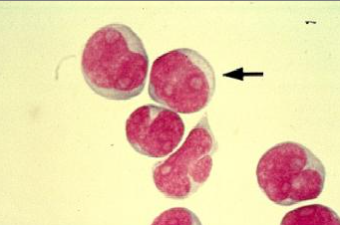
CSF stained smear shows cells that may indicate what condition?
Allergic reaction
Bacterial meningitis
Leukemia with CNS involvement
Viral meningitis
Leukemia with CNS involvement
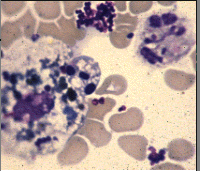
The predominant cells seen on the CSF smear are indicative of:
Normal cytocentrifuged smear
Viral meningitis
Bacterial meningitis
Fungal infection
Bacterial meningitis
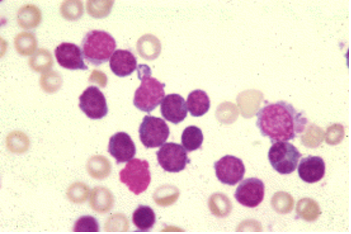
The predominant cell seen in this CSF are from a twelve-year old female exhibiting fever, lethargy, and a stiff neck. The WBC count on the sample was 2000/microliter. The findings most likely indicate:
Normal cytocentrifuged smear
Viral meningitis
Bacterial meningitis
Alzheimer’s disease
Viral meningitis
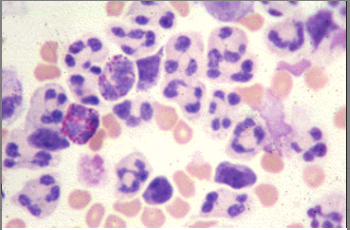
A cloudy CSF sample has a white count of over 1000 WBC/uL. Large number of these cells seen in cytocentrifuged smear is suggestive of:
Viral meningitis
Bacterial meningitis
Fungal infection
Malarial infection
Bacterial meningitis
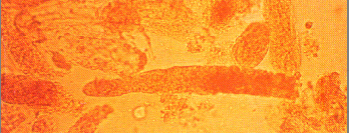
Identify the urine sediment elements present in this illustration:
WBC casts
Hyaline casts
Waxy casts
Fine granular casts
Fine granular casts
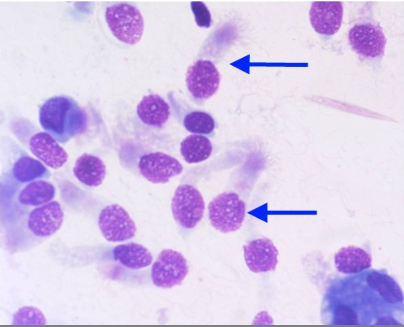
After suspecting that his patient may have lung disease, the physician sends a bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) to the laboratory for examination. What is the cell type noted by the arrows in this cytospin sample?
Lymphocytes
Mesothelial cells
Macrophages
Bronchial lining cells
Bronchial lining cells
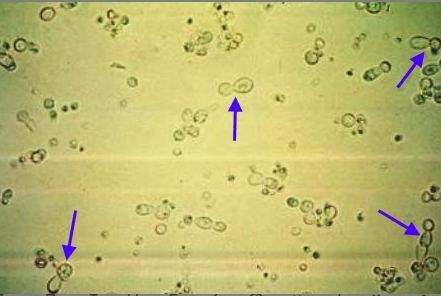
Identify the majority of cells present in this urine slide (arrows indicated)
Yeast

Cholesterol crystals
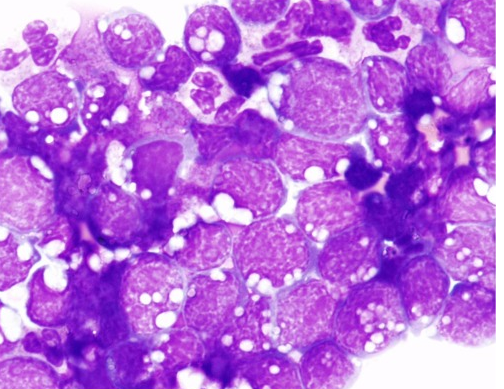
Prominent vacuolation involving the cytoplasm of abnormal lymphoblast-like cells seen in the peritoneal body fluid preparation shown is a distinctive feature of which disease?
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Burkitt Lymphoma
Hairy Cell Leukemia
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Burkitt Lymphoma
Upon centrifugation, a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) sample supernatant exhibited xanthochromia. The image is a Wright-Giemsa stained smear that was made from that CSF sample. What condition is probably related to these macroscopic and microscopic findings?
Previous subarachnoid hemorrhage
Traumatic tap
Leukemia
This is a normal microscopic finding for a CSF specimen
Previous subarachnoid hemorrhage
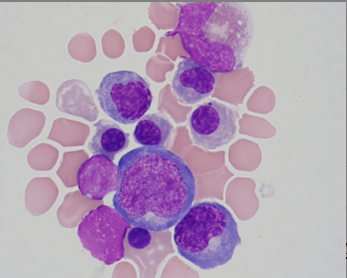
The image is a stained smear of cerebrospinal fluid. Which of the following statements is true about the cells shown at the right?
Their numbers are increased when the patient has leukemia.
Their numbers are increased when the patient has multiple sclerosis.
They line the arachnoid space.
They are capable of engulfing red cells.
They line the arachnoid space.
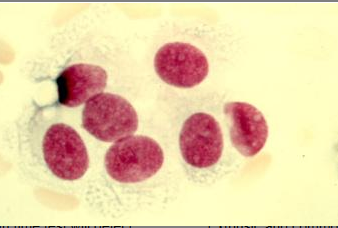
Identify the predominant nucleated cell in this cerebrospinal fluid cytospin differential.
Nucleated red blood cells (NRBCs)
Neutrophils
Metamyelocyte
Tumor cells
Nucleated red blood cells (NRBCs)
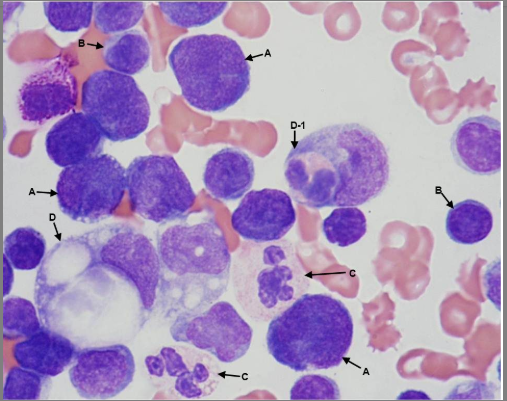
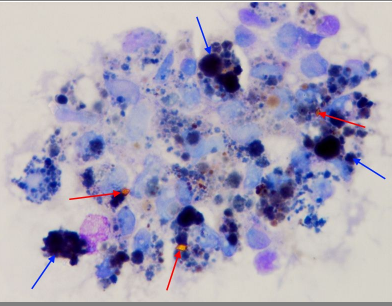
Select from the choices below the best report that reflects this pleural fluid cytospin image from a patient with refractory non-hodgkin lymphoma:
Lymphoma cells, mesothelial cells, macrophages, neutrophils
lymphocytes, Lymphoma cells, macrophages, neutrophils, hemophaocytosis
mesothelial cells, macrophages, neutrophils, hemophaocytosis
neutrophils, hemophaocytosis, mesothelial cells, Lymphoma cells, macrophages,
a: lymphoma cells, b: Lymphocytes, c: Neutrophils, d: macrophages, d-1: hemophagocytosis
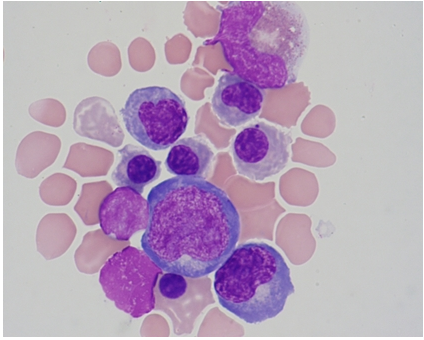
Identify the predominant nucleated cell in this cerebrospinal fluid cytospin differential.
Nucleated RBCs
Neutrophils
Metamyelocte
Tumor cells
Nucleated RBCs
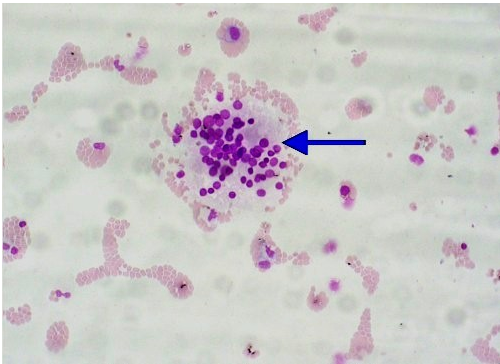
What is the ID of this cellular clump found in CSF?
Cartilage Cell
Tumor Cell clump
Ependymal clump
Lymphoblast clump
Ependymal clump
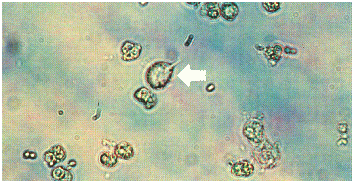
Trichomonas
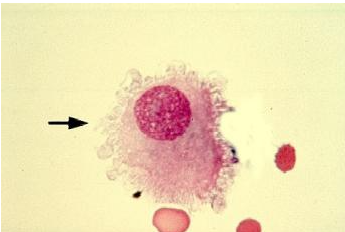
A CSF sample was cytocentrifuged and the smear was stained. Which is true about the cell in the image?
Increased numbers of this cell is seen in patients with bacterial meningitis
It lines the arachnoid space (CNS)
It is a monocyte
It is a malignant cell
It lines the arachnoid space (CNS)
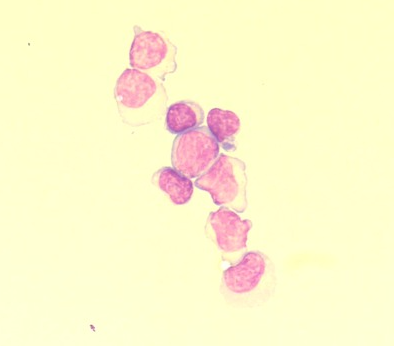
Which cells should be identified in the CSF report for the cytospin field shown?
Monocytes
Blast cells
Lymphocytes
Plasma cells
Lymphocytes
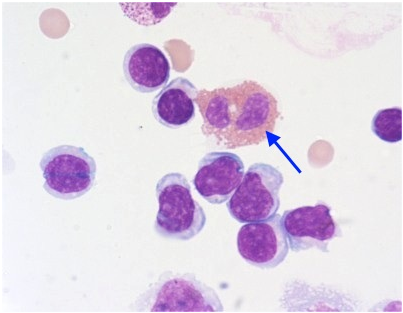
CSF cytospin slide, what is the blood cell indicated in the photo?
Segmented neutrophil
Monocyte
Eosinophil
Macrophage
Eosinophil
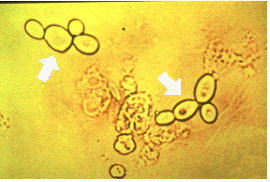
The elements indicated by the arrows are more likely to be seen in patients with which condition?
Bacterial infection
Nephrotic syndrome
Diabetes
Renal failure
Diabetes
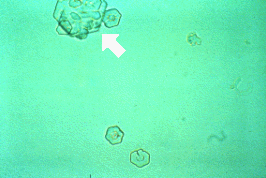
cystine crystals