1.1. neurology
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1.1. neurology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
GLIAL CELLS are found in both
CNS
PNS
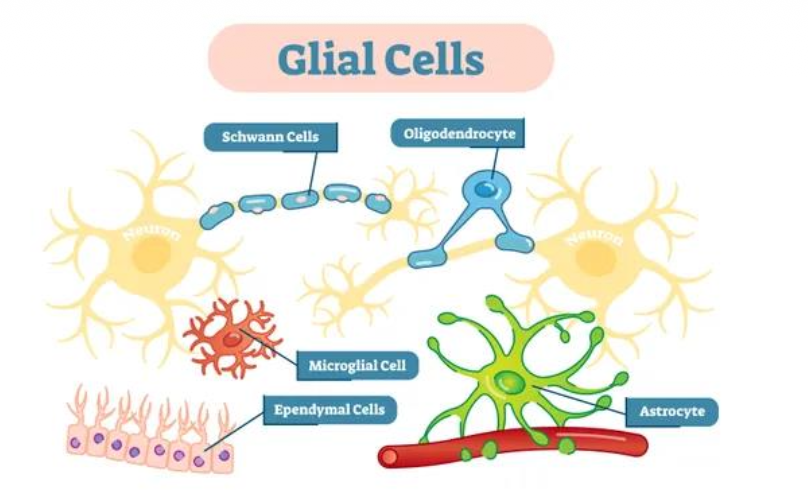
Glial cells in PNS
Schwann cells
Satellite cells
Glial cells in CNS
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Ependymal cells
Microglia
Glial cells support inn
Physical support of neurons (glia: glue in Greek)
Metabolic support
Modulation of neuronal communication
Myelinization of axons
Tissue repairing
Defense
Astrocytes maintains
Chemical environment for neuronal signaling
Neuronal survival & tissue repairing
Neuronal survival & tissue repairing
Astrocytes release substances (trophic factors, cytokines) for nervous tissue maintenance & repair.
Role of Astrocytes
Nutrition role
Synapse modulation role
Protective role
Nutrition role
Provide neurons with glucose, lactate & other metabolites
Remove waste metabolites or cell debris from the area.
Synapse modulation
Astrocytes participate in the communication between neurons
Release of gliotransmitters (e.g. ATP)
Re-uptake of neurotransmitters (glutamate)
Regulation of extracellular levels of Ca2+ and K+ (critical for the synapses & the transmission of the electrical impulse)
Protective role
Provide physical support to neurons
Surrounds the capillaries & blood vessels, creating the blood-brain-barrier (BBB)
Regulates the diffusion of certain molecules, drugs & nutrients from the blood to the extracellular space.
Astrocytes induce the formation of
tight junctions
The tight junctions of astrocytes are found in
Between endothelial (blood vessel) cells → preventing substances (toxins & microorganisms) to pass
BBB dysfunction lead to
permeability compromised → disease
→
* Leakage of non-specific molecules from blood into brain
* Infections
* Inflammation
Main causes of BBB dysfunction
Ischemia/reperfusion (Hypoxia / hypoglycemia)
Osmotic shock
Inflammatory processes
Diseases related to BBB dysfunctions
Multiple sclerosis, epilepsy, stroke, Alzheimer’s disease
Parkinson disease
In Parkinson’s disease, dopaminergic neurons are lost → dopamine concentration in the striatum are too low →
Inability to initiate spontaneous movements
Treatment used for Parkinson disease
L-DOPA (because of dopamine itself cannot cross the BBB)
L-DOPA
Dopamine precursor
Crosses the BBB through an aminoacidic transporter
Uptaken by neurons & converted to dopamine
Compensating the dopamine deficiency
Oligodendrocytes
Glial cells that create the myelin sheath around several neuronal axons in the CNS
Myelin sheath
Lipidic cover that supports & insulates the axon
Node of Ranvier
Axon areas without myelin sheath.
Accelerates impulse travelling through the axon
Impairment of oligodrendrocytes can lead to
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis occurs due to
Demyelination caused by autoimmune attack.
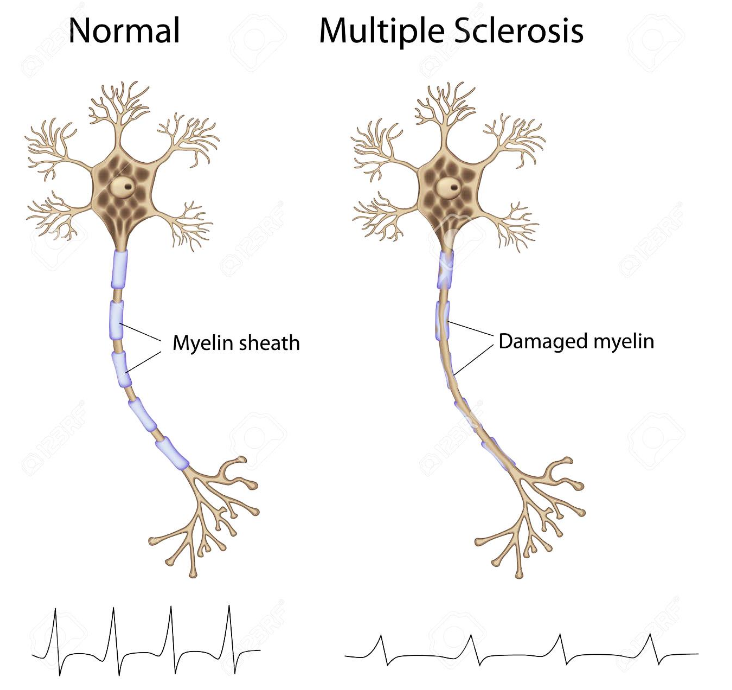
Loss of myelin sheath impairs
Impulse transmission
Symptoms of MS
Fatigue, muscle spams, vision problems, numbness, balance problems, pain, depression
Microglia
Resident immune cells in the CNS
Response to pathogens (virus, bacteria) & damage
Functional states of Microglia
Nurturer
Sentinel
Activated/warrior
Nurturer
Clears debris, promotes tissue repair, supports survival of neurons & restores homeostasis.
Sentinel
Scan the microenvironment.
High motility.
Activated/warrior
Responds to damage.
Supports neurons (cytokines) & maintain the microenvironment (phagocytosis), causes inflammation.
Microglia
Mediate neuroinflammatory processes
Neuroinflammatory processes release of
Release of cytokines can produce local inflammation
Microglia participate in the
remodelling & pruning of the dendritic tree (learning & memory process)
Microoglia are activated in the response to
Brain damage
Ependymal cells
Specialized polar cells that form the ventricle walls (choroid plexus)
Ependymal cells participate in the
Formation of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) & its circulation
Ependymal cells can act as
Precursors of brain cells
The choroid plexus consists of
Modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries & loose connective tissue.
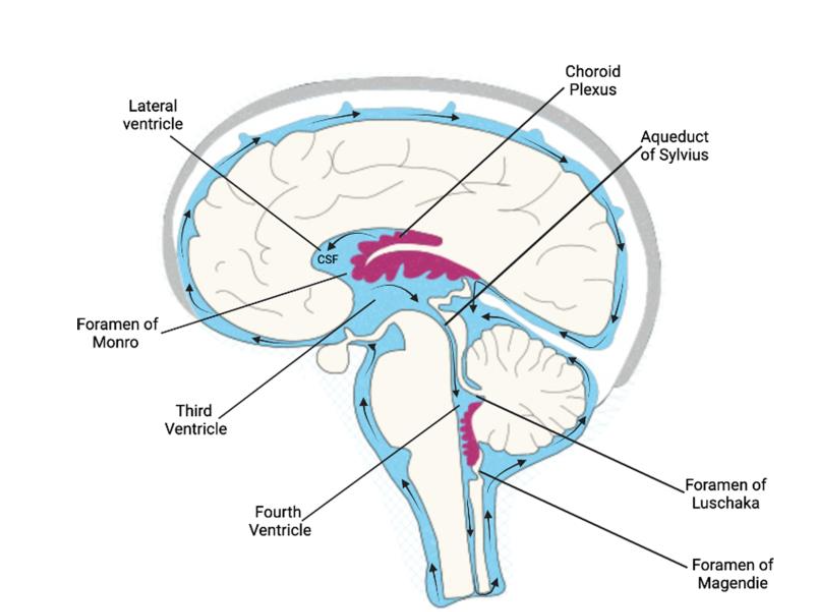
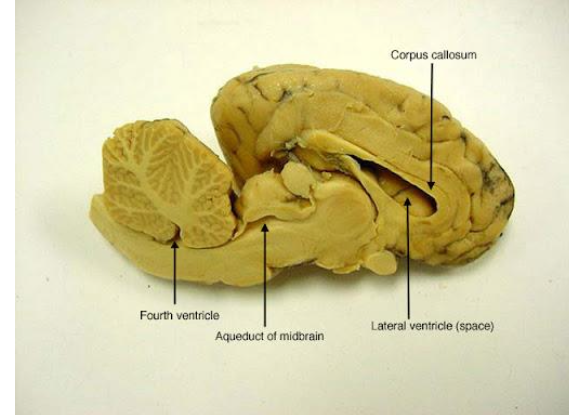
VENTRICLES
Interconnected cavities inside the brain
Connected with the spinal cord
Filled with CSF
V1 & V2
Lateral ventricles
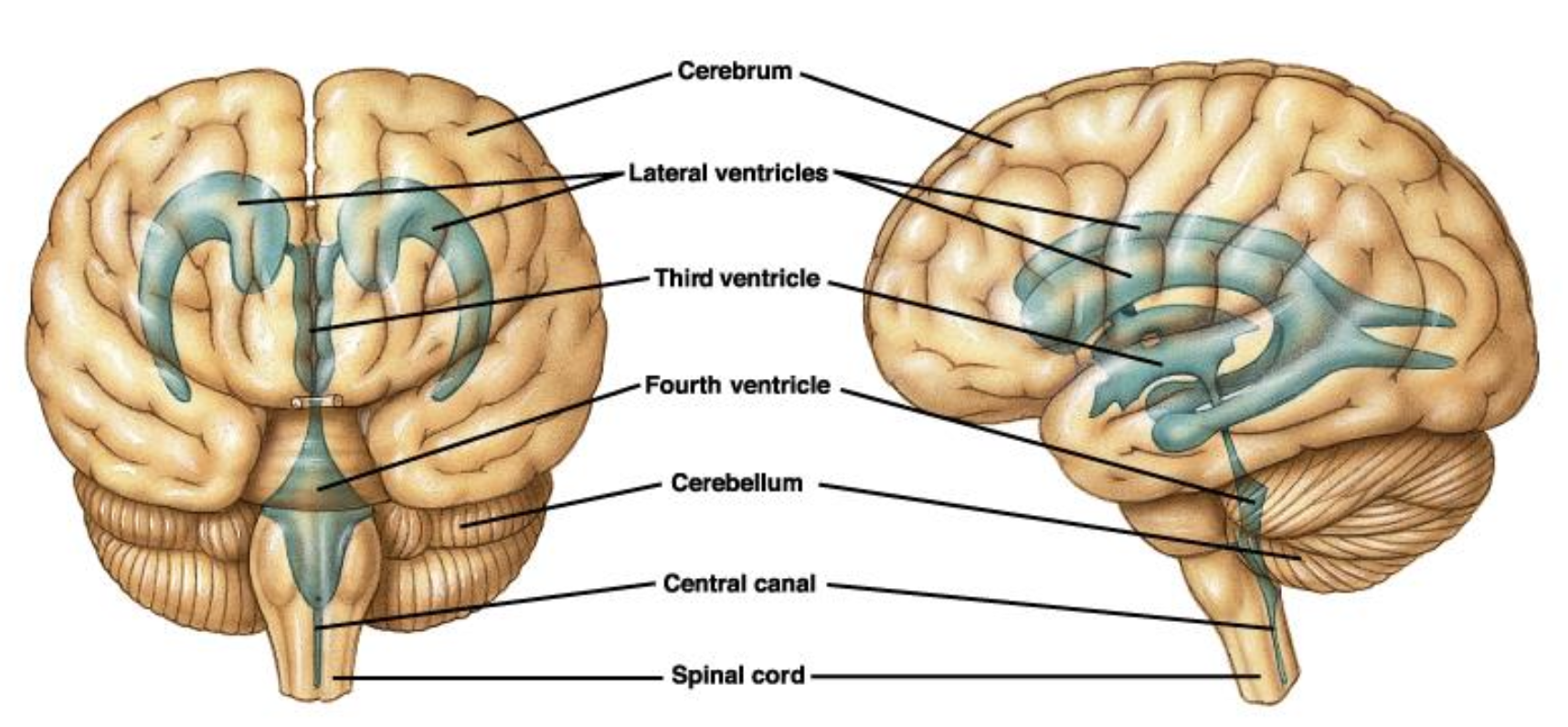
V3 & V4
Descendant ventricles
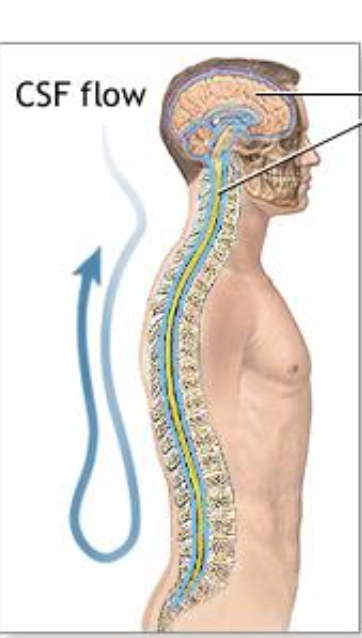
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID
Saline solution that fills the ventricle system.
CBF is secreted by the
choroid plexus
CBF is absorbed to the blood by the
Arachnoid granulations
The role of CEREBROSPINAL FLUID
Mechanical support
Nutrient distribution
Elimination of waste from the CNS
Mechanical support CSF
cushioning
regulates pressure
Nutrient distribution CSF
oxygen & glucose
waste recollection
The flow rate of CSF through CNS is sufficient to
Replenish the entire CSF volume approximately three times a day
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID composition
Several salts (help control pressure & nerve function) & glucose (provides energy for brain cells)
Low proteins (keeps the fluid thin & clear)
No cells (no blood cells or other cells)
Alterations in CSF compositions can lead to
symptom of pathologies development (CNS infections, demyelization or tumors)
RADIAL GLIA
special support cells in the developing brain
scaffolding or guide rails for the brain
RADIAL GLIA & ependymal cells together could have
behave as stem cells that can produce new neurons.
Adult neurogenesis
described only in
→ subventricular zone (SVZ)
→ granular zone (GZ) of the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus
Adults hippocampal neurogenesis drops in patients with
Alzheimers disease
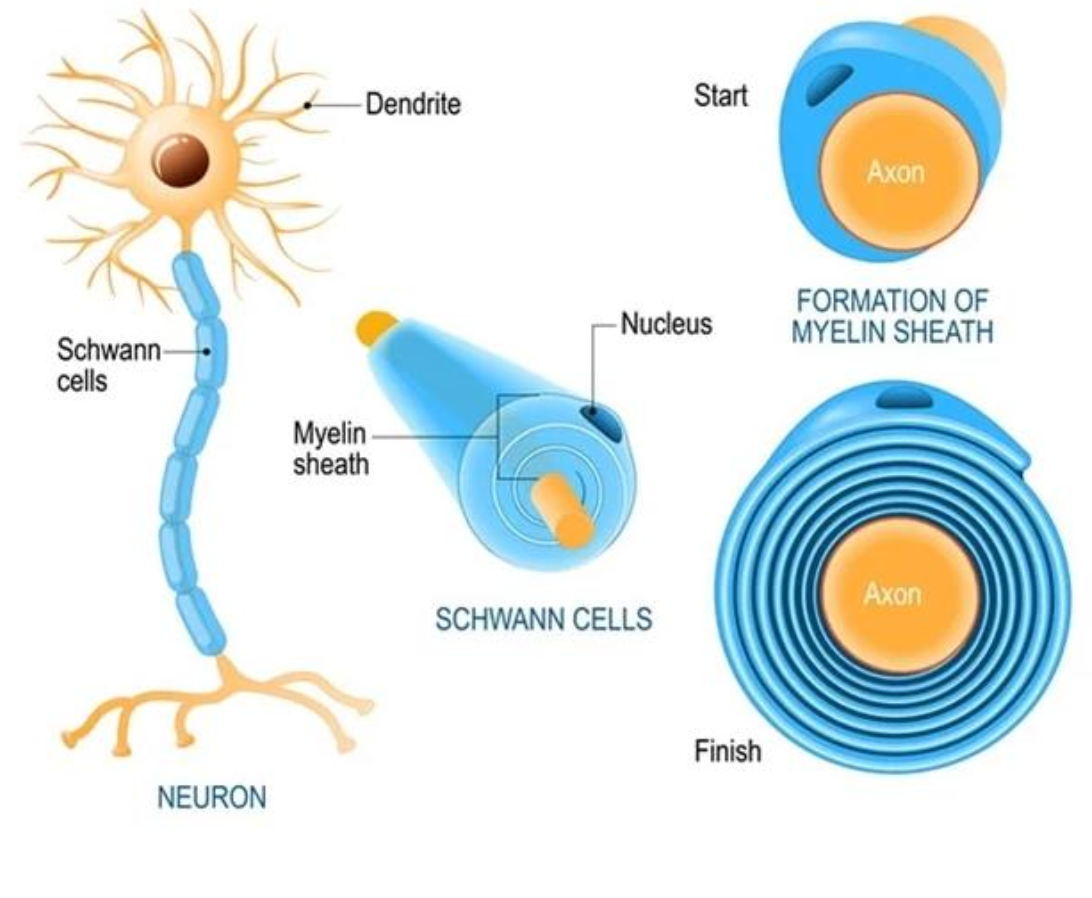
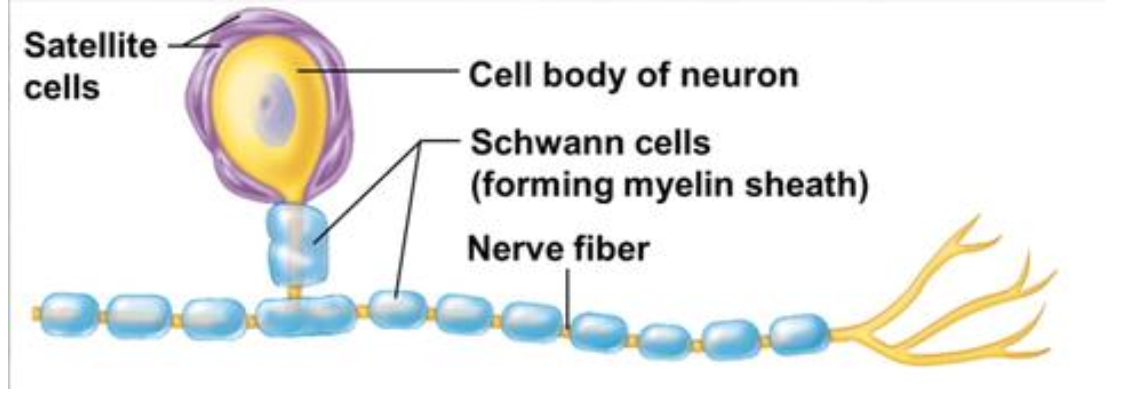
Schwann cells
lia cell that creates ONE myelin sheath (1mm) around a neuron axon
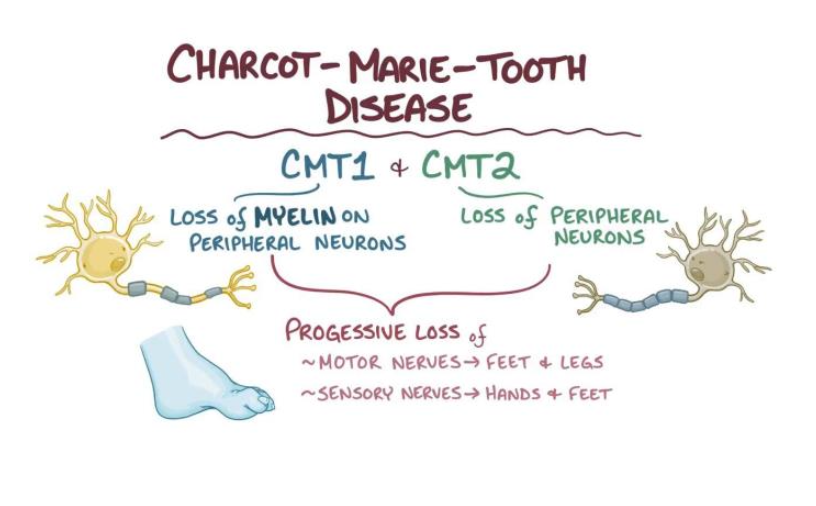
Charcot-Marie-Tooh disease
Neurological disorders that affect the myelin sheath of the motor neurons
Loss of muscle tissue & touch sensation in limbs
Genetic origin, several mutations
Satellite cells
Glial cells that wrap around nerve cell bodies located in ganglia, forming a capsule.
Support role, probably regulating the microenvironment, but not fully understood
Neuroglia is found in
CNS
PNS
Glia in found PSN
Satellite cells
Schwann cells
Glia found in CNS
Microglia
Oligodendrocytes
Astrocytes
Ependymal cells
Satellite glia cells
Surround neuron cell bodies in ganglia
Regulate O₂, CO₂, nutrient, & neurotransmitter levels around neurons in ganglia
Schwann cells
Surround axons in PNS
Are responsible for myelination of peripheral axons
Participate in repair process after injury
Oligodendrocytes
Myelinate CNS axons
Provide structural framework
Astrocytes
Maintain blood-brain barrier
Provide structural support
Regulate ion, nutrient, and dissolved gas concentrations
Absorb & recycle neurotransmitters
Form scar tissue
Microglia
Remove cell debris, wastes, & pathogens by phagocytosis
Ependymal cells
Line ventricles (brain) and central canal (spinal cord)
Assist in producing, circulating, & monitoring of cerebrospinal fluid