Biochemistry Test
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Hydroxyl
ex. In Alcohol - EN 1.4

Aldehyde
ex. In Fragrences - EN 0.9
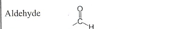
Ketone
ex. In low-carb diets - EN 1.4
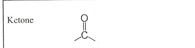
Carboxyl
ex. Acid - EN 1
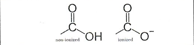
Amino
ex. Amino Acids- EN 0.8
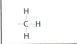
Sulfhydryl
ex. Protein hemoglobin- EN 0.4
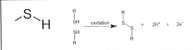
Phosphate
ex. Genetic Material of DNA- EN 1.3
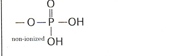
Methyl
ex. Methanol- EN 0.4
Carbohydrates
Stores energy for cellular work, Elements - CHO, Monomer - Monosaccharides, Polymer - Polysaccharides
Lipids
Store energy in protective cell walls, Elements - CHO
Proteins
Functions - Structure, defense, movement, transport, storage, regulation, Elements - CHNO, Monomers - Alpha carbon, amino groups, carboxyl, R groups, Polymer - Polypeptide
Nucleic Acids
DNA stores hereditary information and the body proteins + RNA carriers DNA for protein synthesis, Elements - CHONP, Monomer - Nucleotides, Polymer - DNA, RNA
Cohesion
the sticking together of particles of the same substance
Adhesion
the sticking together of particles of different substances
Polar covalent bond
a chemical bond where electrons are shared unequally between two atoms, creating a partial negative charge on the atom that attracts electrons more strongly and a partial positive charge on the atom that attracts them less
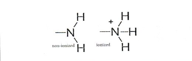
Ionic bond
When an electron transfers from one atom to another, making one of them negative and the other positive, which makes them have a strong attraction to each other
Electronegativity
the strength of attraction an element has to electrons, ED>0.4 it is a polar covalent bond, ED>2 it is an ionic bond, if ED<0.4 it is a nonpolar covalent bond
Electronegativity difference
the difference in electronegativity between two atoms which determines if they have a nonpolar covalent bond, polar covalent bond, or ionic bond
Non-polar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the shared electrons are shared equally
Surface tension
the "skin-like" film on the surface of a liquid caused by cohesive forces holding it together, and the adhesive forces holding it up
Capillary action
the movement of liquid against gravity, due to adhesion and cohesion
Hydrogen bond
the charged regions of water molecules create weak attractions to other molecules