Case 1: Hannah Rosen Pt1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
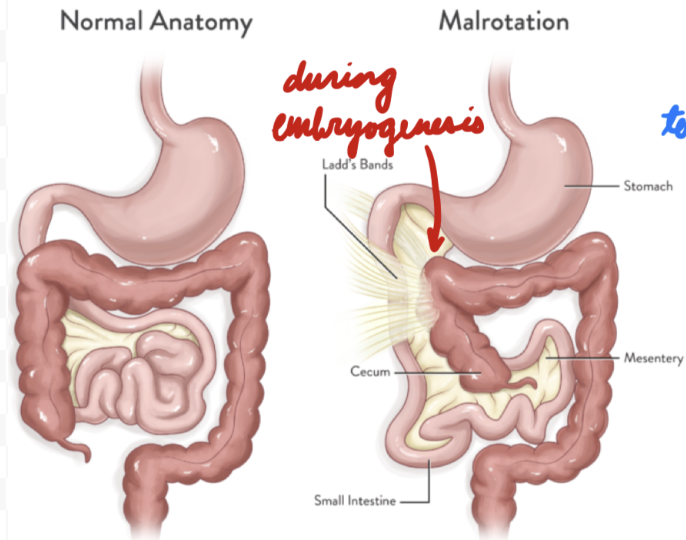
Gut Malrotation
Abnormal midgut rotation during embryogenesis = Improper fixing
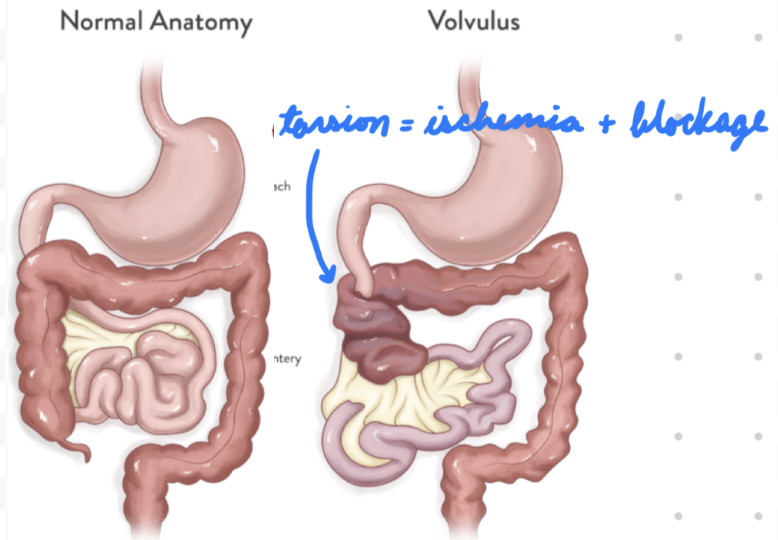
Volvulus
Malrotated midgut torsion → Bowel ischemia + blockage
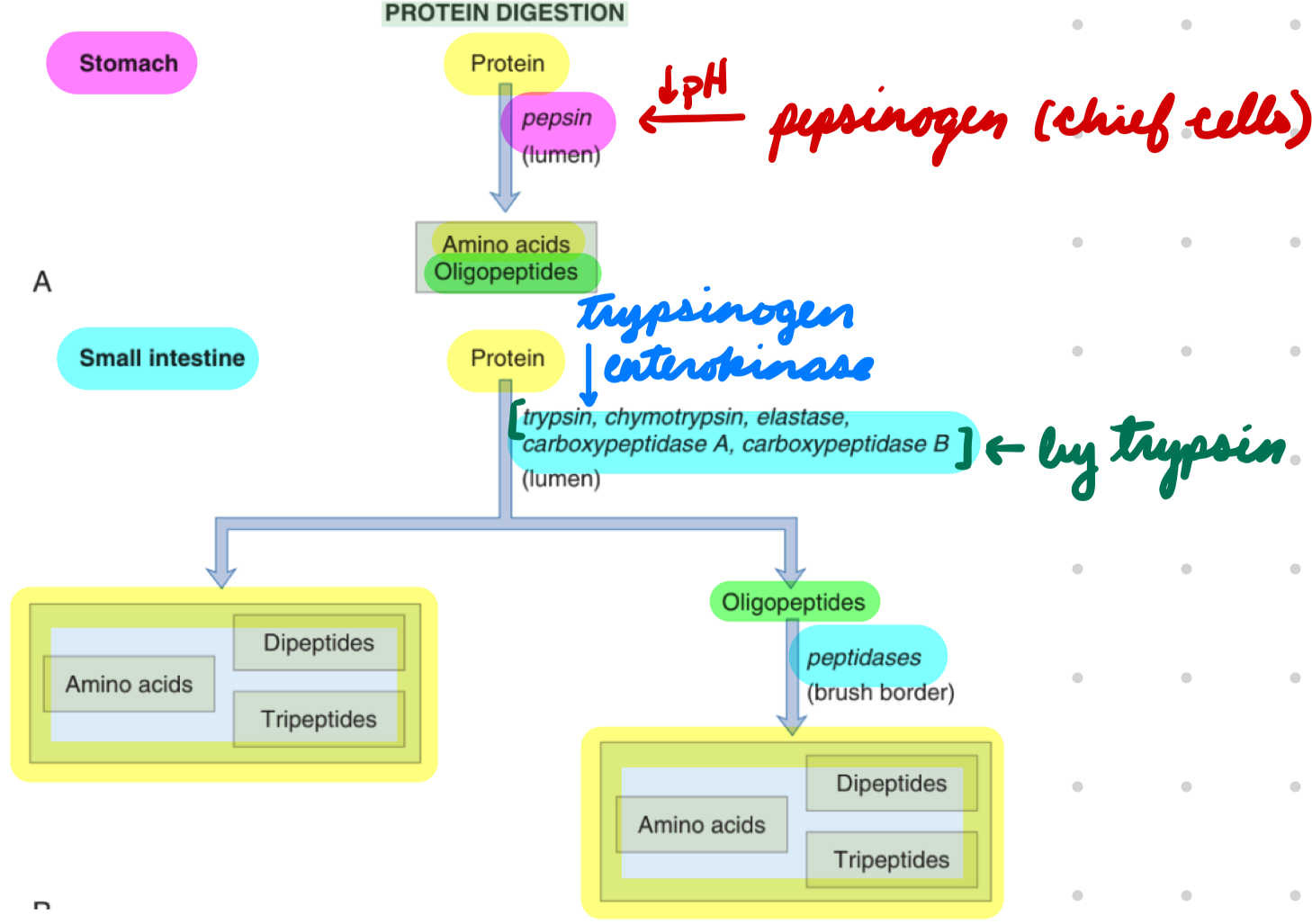
Protein Digestion
Stomach: Pepsin
Small Intestine: Pancreatic and brush-border proteases
Endopeptidases: Hydrolyze peptide bonds
Pepsin
Trypsin
Chymotrypsin
Elastase
Exopeptidases: Hydrolyze amino acids
Carboxypeptidases A/B
Protein Digestion: Pepsin
Chief cells secrete pepsinogen → Pepsin
Activated by low pH from gastric H+
Neutralized in duodenum by high pH
Cleave peptide bonds = Proteins → Polypeptides and amino acids
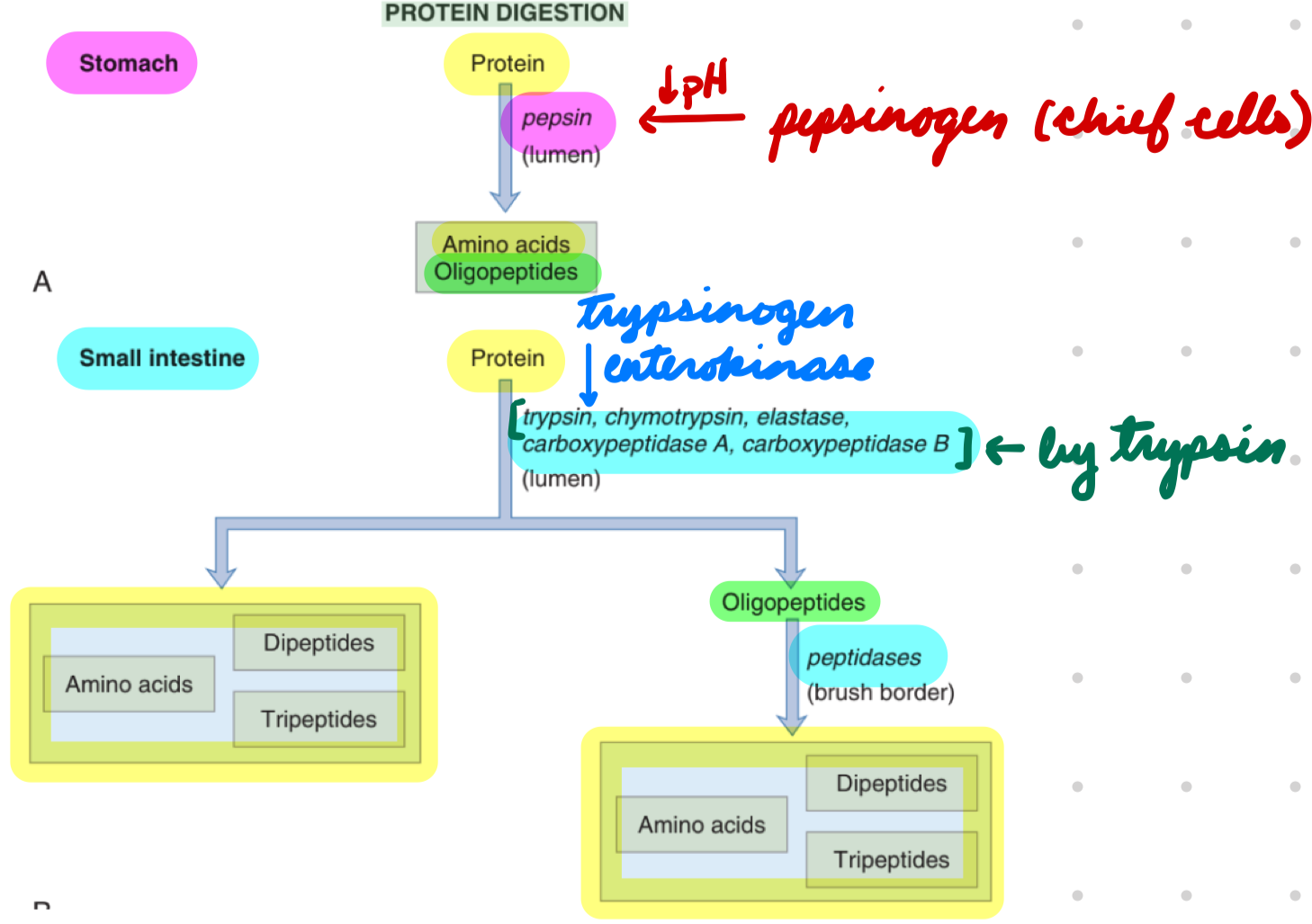
Protein Digestion: Pancreatic + Brush-Border Proteases
Trypsinogen → Trypsin
Enterokinase (brush-border enzyme)
Trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, proelastase, procarboxypeptidase A/B → Trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase, carboxypeptidase A/B
Trypsin
Proteins → Oligopeptides, small peptides, amino acids
Oligopeptides → Small peptides + amino acids
Protein Absorption
As amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides
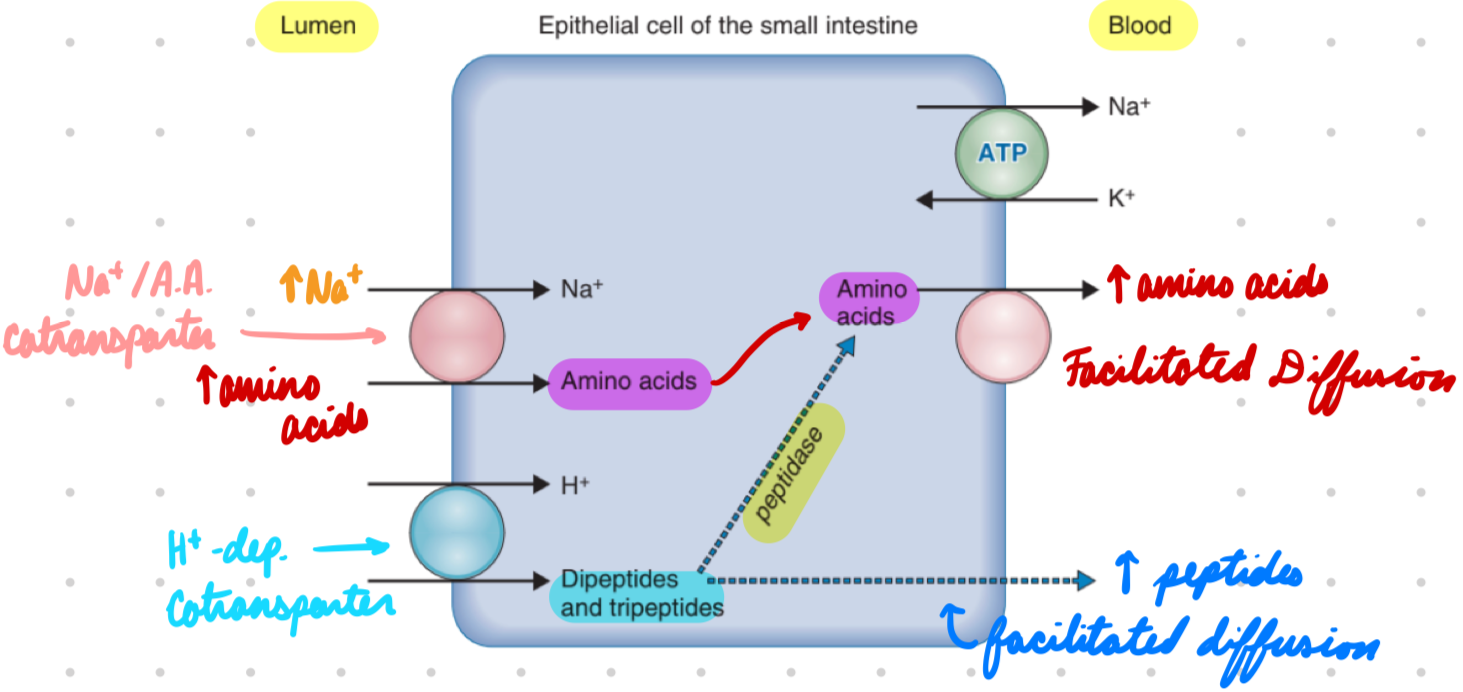
Protein Absorption: Amino Acids
Apical: Na+/amino acid cotransporter
Energy from Na+ gradient
Basolateral: Facilitated diffusion
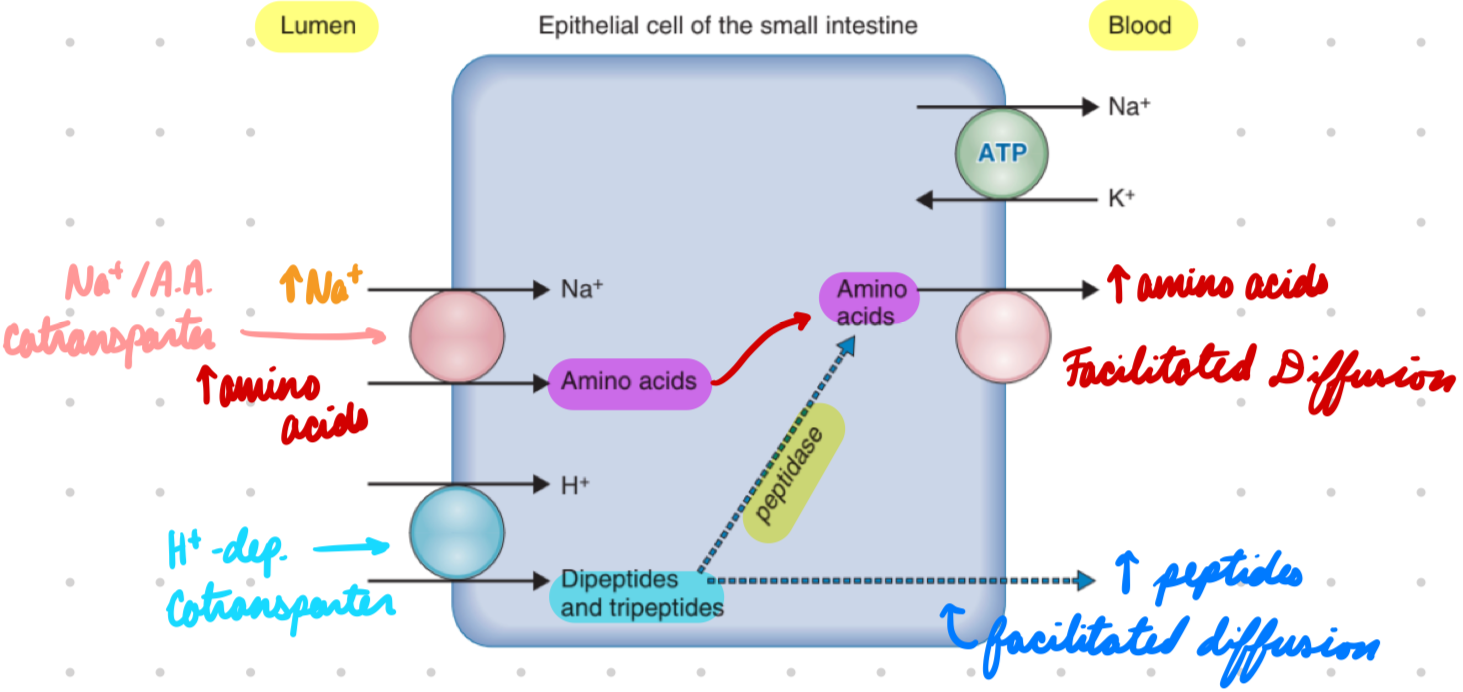
Protein Absorption: Peptides
Apical: H+-dependent cotransporters*
Energy from H+ gradient by Na+/H+ exchanger
In Cell: Some peptides → Amino acids by cytosolic peptidases
Basolateral: Facilitated diffusion
Lipids
Triglycerides (TGA)
Cholesterol
Phospholipids
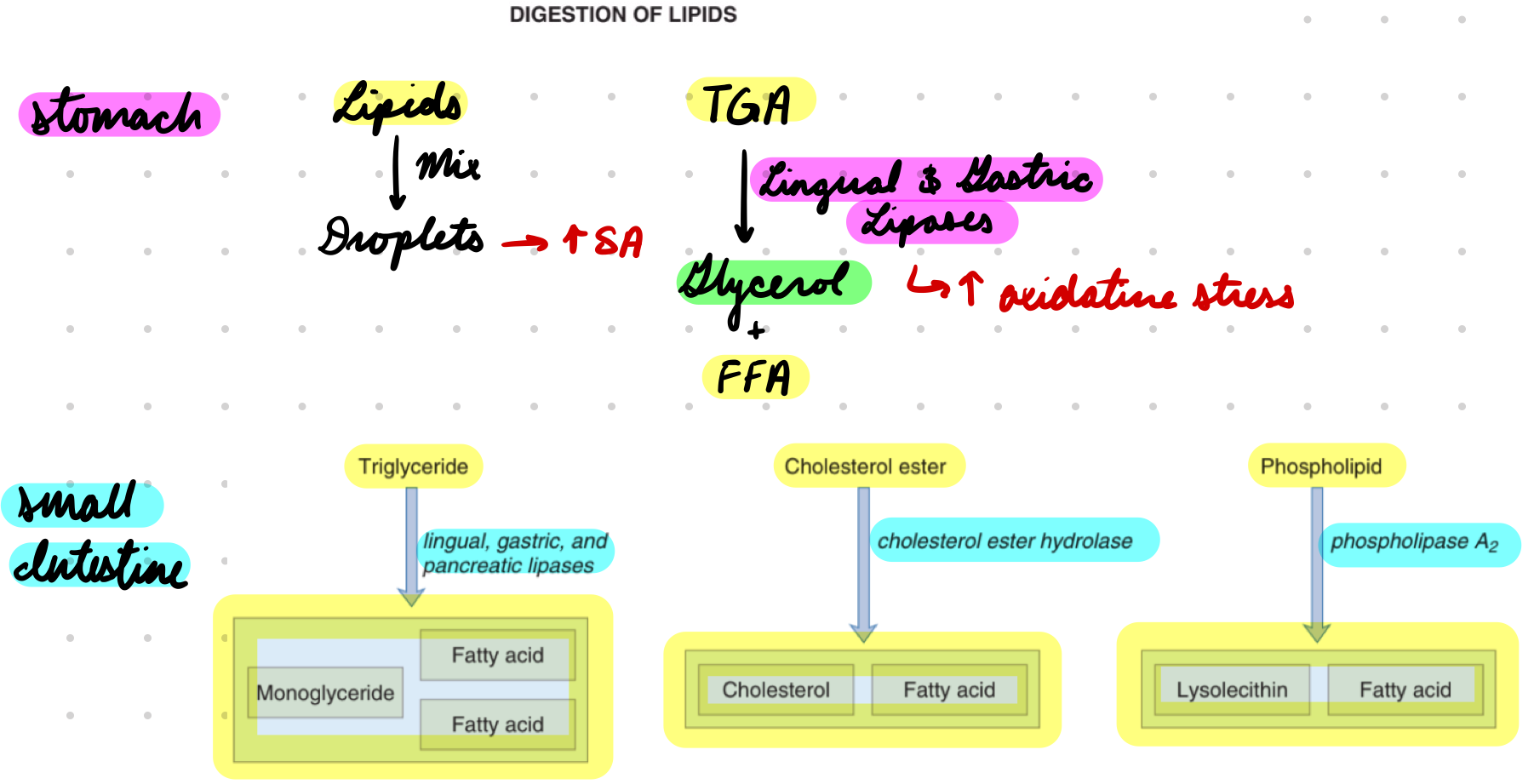
Lipid Digestion
Stomach: Lingual and gastric lipases
Small Intestine: Bile salts*** + pancreatic enzymes
Pancreatic lipase
Cholesterol ester hydrolase
Phospholipase A2
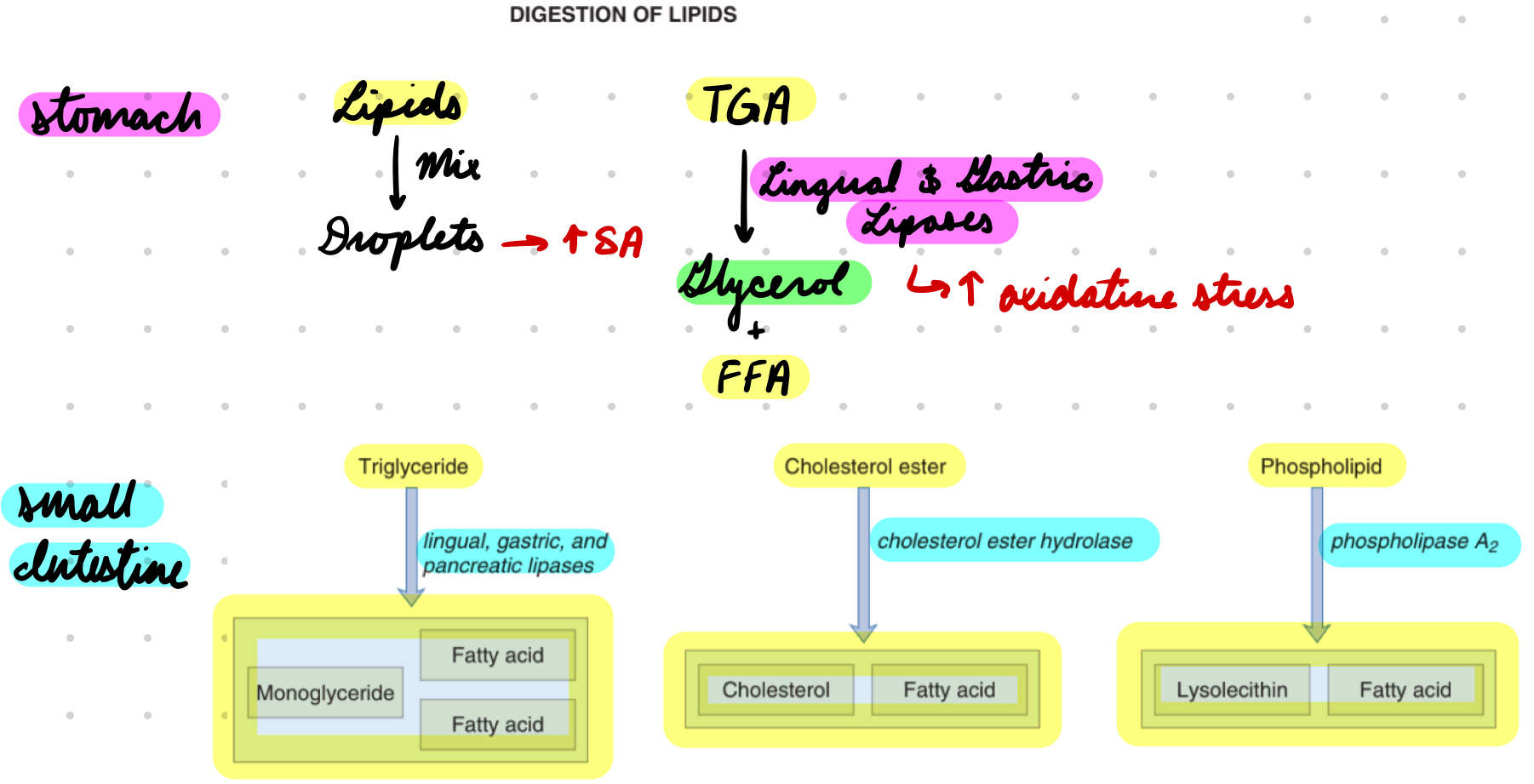
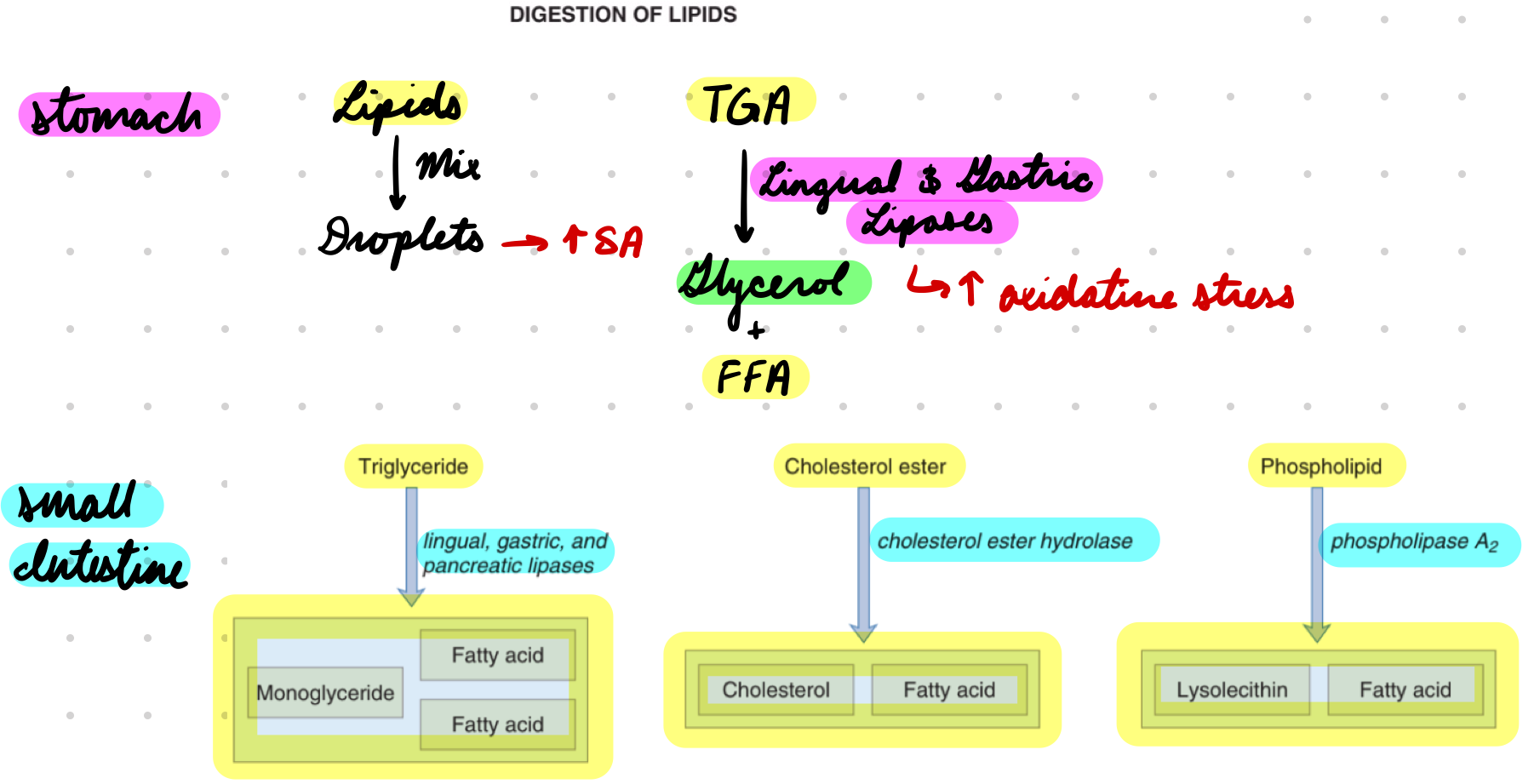
Lipid Digestion: Lingual and Gastric Lipases
Mix lipids into droplets = Increase SA for enzymes
Lipases hydrolyze TGA → Glycerol + FFA
Increased oxidative stress
Lipid Digestion: Bile Salts
Emulsify lipids in droplets = Increase SA
Lipid Digestion: Pancreatic Enzymes
Pancreatic Lipase: TGA → Monoglyceride + FFA
Colipase prevent bile salts breaking down lipase
Cholesterol Ester Hydrolase: Cholesterol → Free cholesterol + FFA
Phospholipase A2: Phospholipids → Lysoleithin + FFA
Activated by trypsin
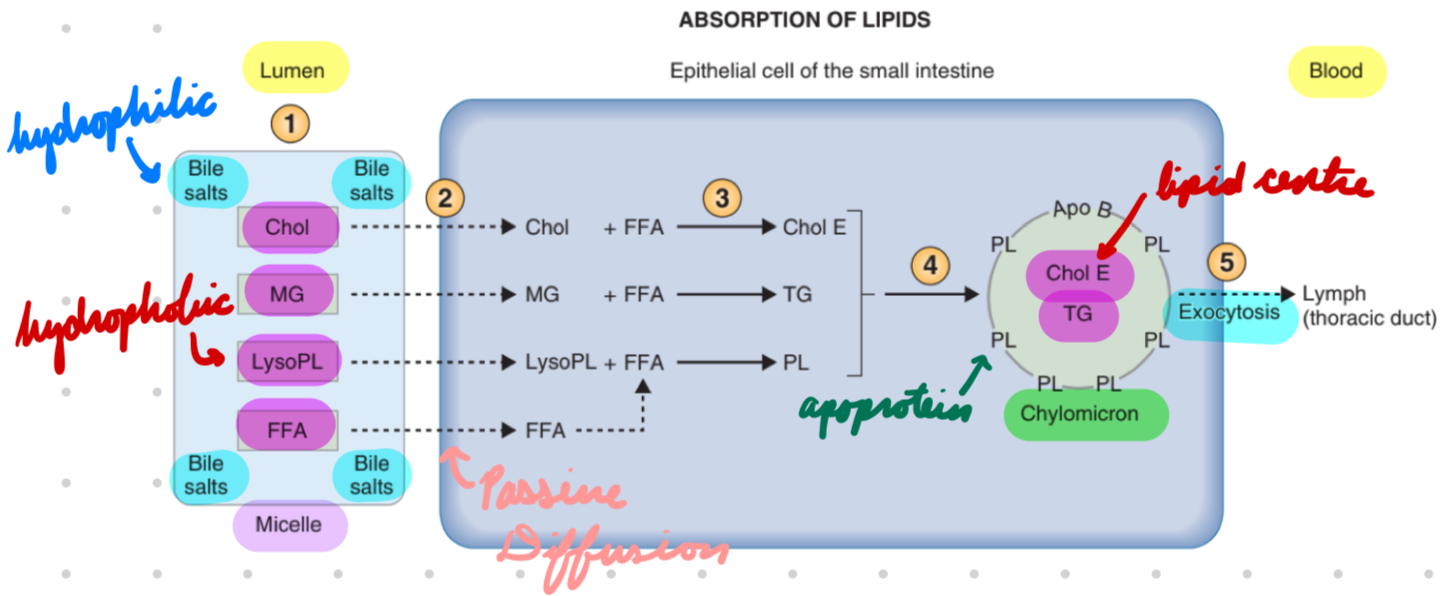
Lipid Absorption
As monoglycerides, cholesterol, lysoleithin, FFA
Lipid Absorption: Process
Lumen: Lipid products → Micelles
Hydrophobic centre (lipid products)
Hydrophilic outer (bile salts)
Apical Membrane: Micelle transport lipid products
Passive diffusion lipids → Cell
In Cell: Lipids packaged → Chylomicrons → Secretory vesicles
Chylomicrons: Lipid centre + apoprotein outer
Basolateral Membrane: Secretory vesicles transport lipids
Exocytosis
Carbs
Polysaccharides
Disaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose, trehalose)
Monosaccharides (glucose, fructose)
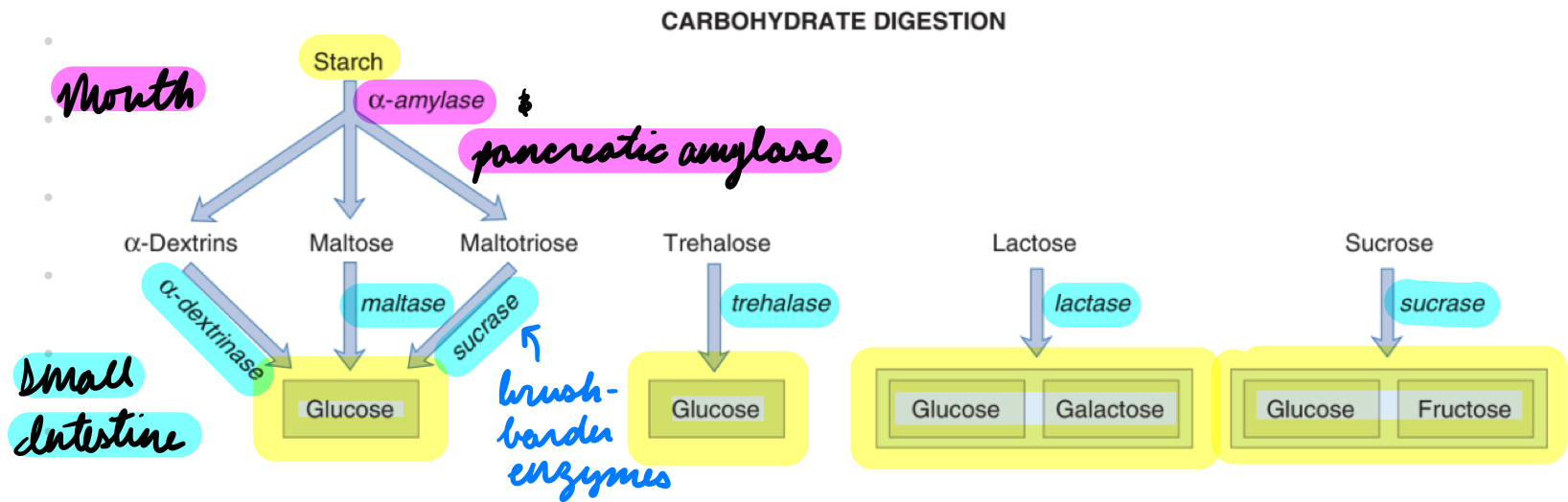
Carb Digestion
Mouth: a-amylase
Small Intestine: Pancreatic and brush-border enzymes
Carb Digestion: a-Amylase
Start starch digestion
Inactivated in stomach (low pH)
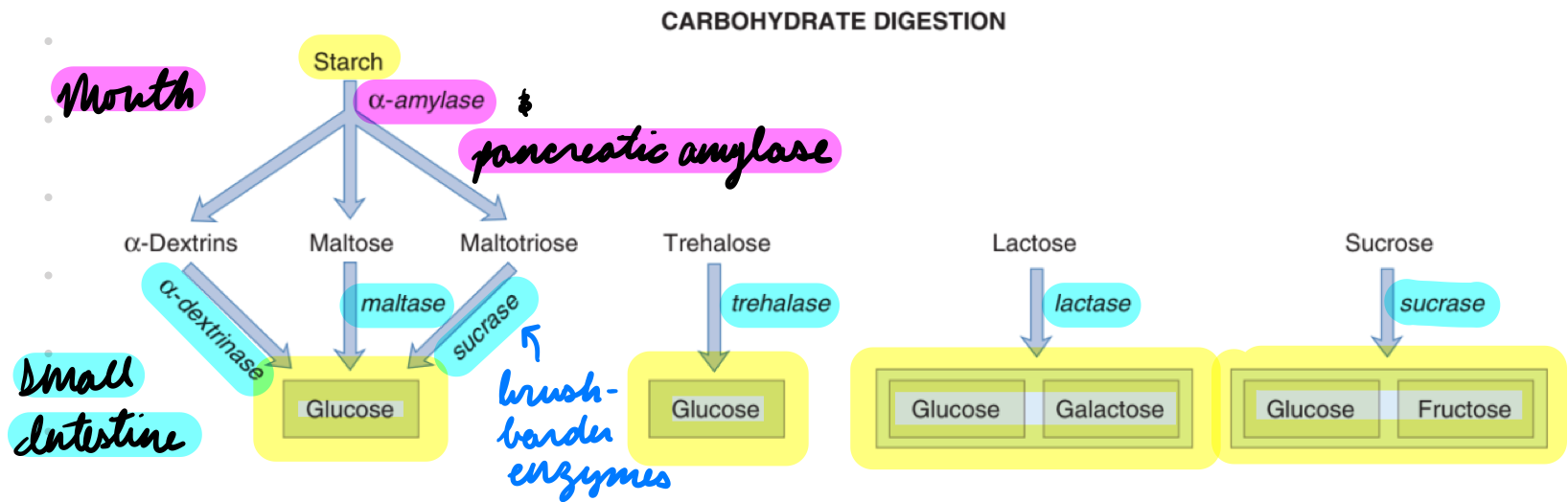
Carb Digestion: Pancreatic and Brush-Border Enzymes
Pancreatic Amylase: Starch → Disaccharides
Brush-Border Enzymes: a-Dextrinase, Maltase, Sucrase
Disaccharides → Monosaccharides (glucose, galactose, fructose)
Carb Absorption
As monosaccharides (glucose, galactose, fructose)
Carb Absorption: Glucose + Galactose
Apical: Na+-glucose cotransporter (SGLT1)
Energy from Na+ gradient by Na+/K+ ATPase
Basolateral: Facilitated diffusion (GLUT2)
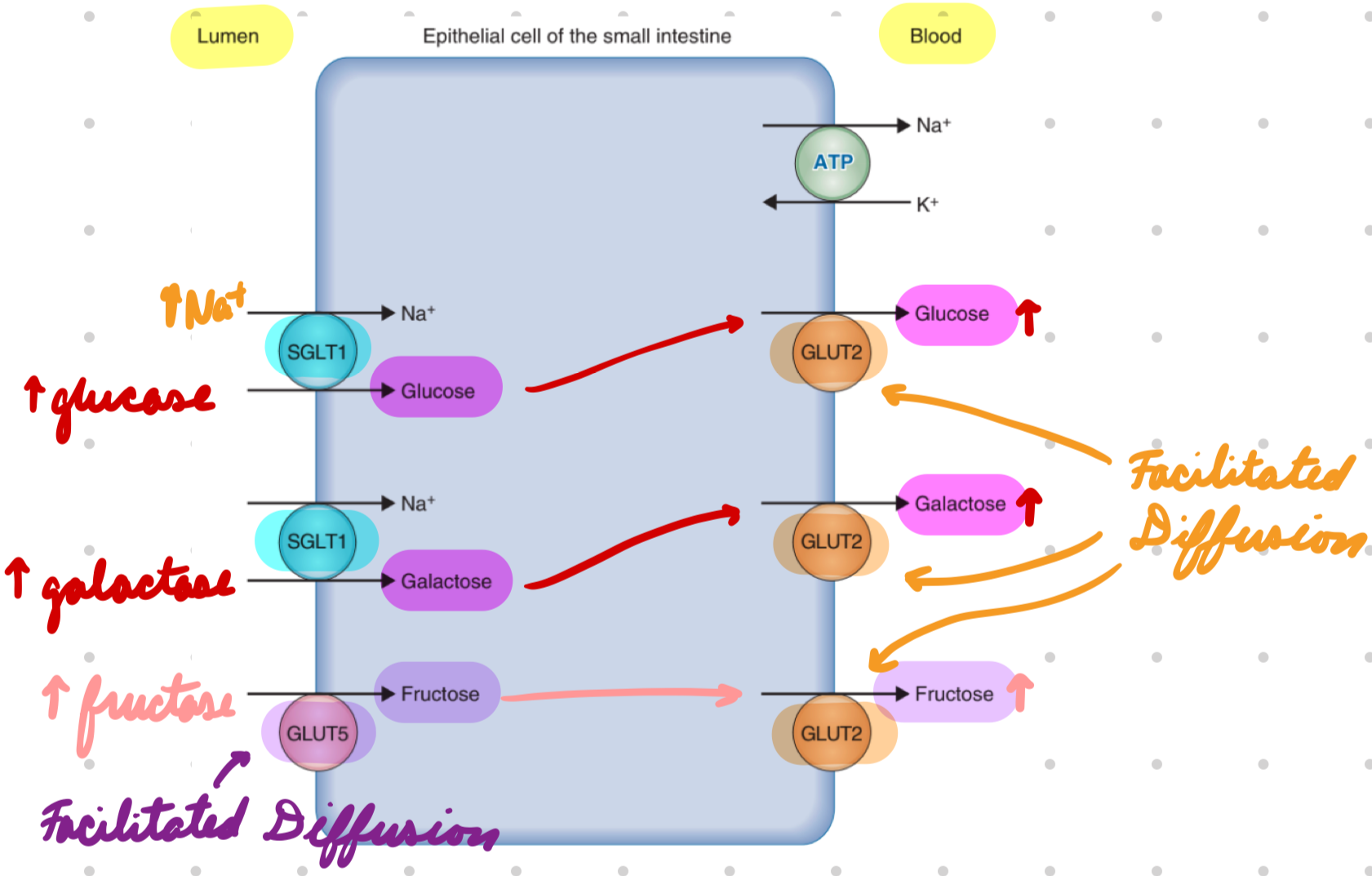
Carb Absorption: Fructose
Facilitated diffusion
Apical: GLUT5
Basolateral: GLUT2
Water Absorption
Everywhere
Mostly in large intestines
Vit B12 Absorption
Terminal ileum
Nutrient Requirements: < 6 Months
Breast milk
Contains:
Proteins
Lactose + oligosaccharides
Fats
Minerals
Trace elements (Fe, Cu, Zn, I, Se, S)
Vitamins
Fe-fortified formula supplementation
Nutrient Requirements: 6-11 Months
Breast milk/Fe-fortified formula
Introduce complementary foods
Common allergens
NO honey
Water
Nutrient Requirements: 12 Months
Breast milk (until ≥ 2 years)
NO formula
Whole milk
Water
Growth
Physical measurement of size, weight, height, length
Development
Measurement of functional ability
Growth Charts
Height and weight on gender-specific chart
Compare to…
Expected growth percentiles
Mid-parental height (estimated adult height from parental height)
Growth Chart: Normal Growth
Follows percentile curve
Height within 2 SD of mid-parental height
Growth Chart: Abnormal Growth
Crossing ≥ 2 percentile lines
> 2-3 years
< 3% or > 97% percentile
> 10cm from mid-parental height
Growth Relation to Feeding: Too High
High calorie intake
Overfeeding
Early complementary food intro (< 4 months)
Growth Relation to Feeding: Too Low
Low calorie intake
Underfeeding
Increased requirements (malignancy)
Decrease absorption
Celiac
IBD
Allergies + intolerances
CF
Decreased energy utilization
Metabolism errors
Genetic conditions
Wasting
Low weight for height
Acute malnutrition
Stunting
Low height for age
Chronic malnutrition
Autosomal Recessive: Pathogenic Mutation
Known to cause disease
Confirm diagnosis and guide management
Autosomal Recessive: Variant of Uncertain Significance (VUS)
Unknown if mutation is disease-causing or benign
No diagnostic confirmation
Autosomal Recessive: Risk to Relatives
Pathogenic Mutation: Increased risk
Follow autosomal recessive inheritance pattern
VUS: Unknown risk
Cannot conduct risk assessment
Cystic Fibrosis (CF): Description
Autosomal recessive disease impairing mucus hydration and clearance
CF: Epidemiology
Most prevalent in White people
Risk Factors:
2 carrier parents of transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) mutation
Siblings with CF
CF: Etiology
CFTR mutation
Most common: ΔF508 phenylalanine deletion
> 2000 mutations
300 confirmed pathogenic
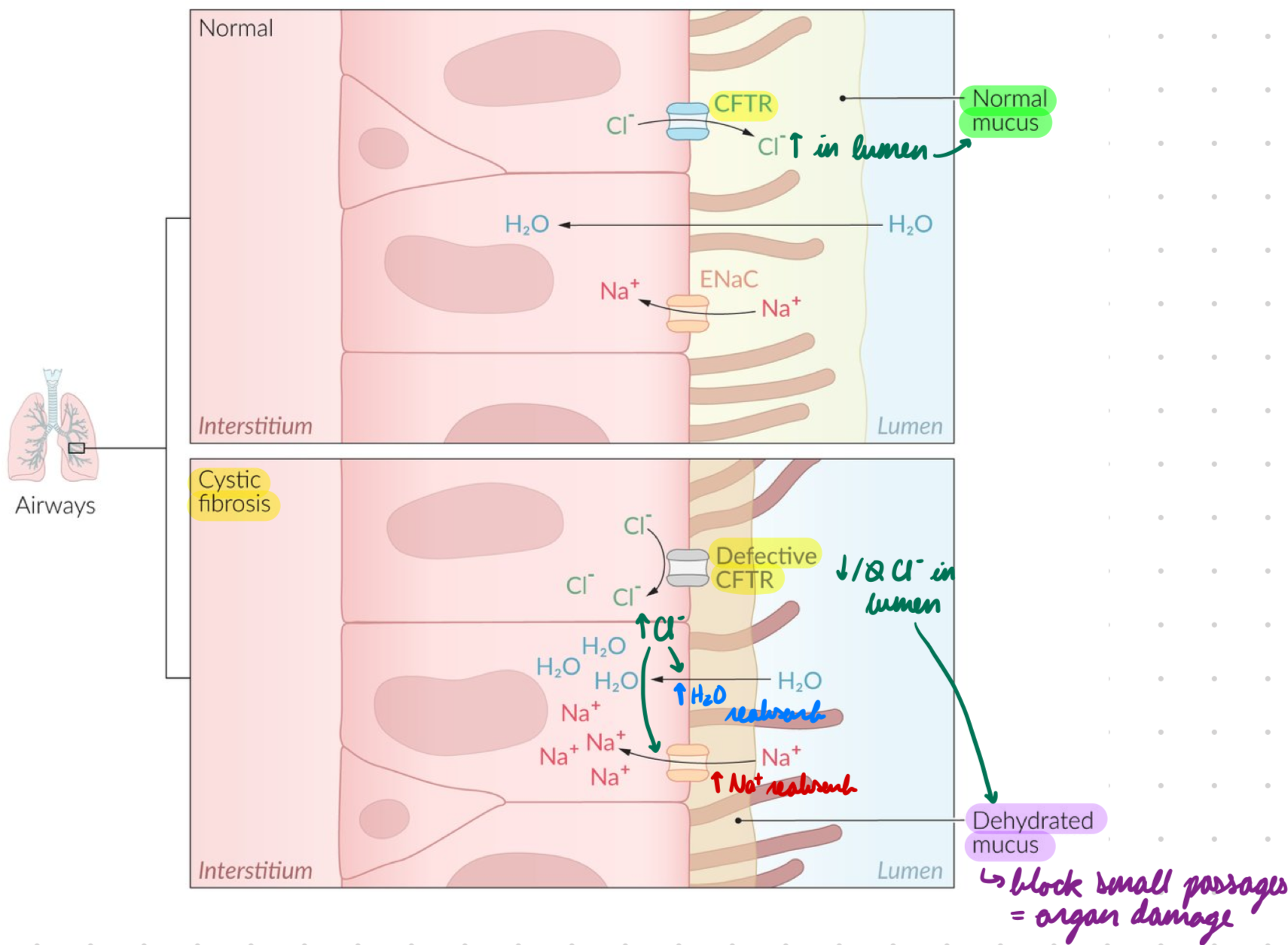
CF: Pathophysiology
CFTR gene mutation = Misfolded CFTR protein
Required for ATP-gated Cl- channel
Low/No functioning ATP-gated Cl- channels in epithelial cell membranes
Sweat Glands: Low Cl- reabsorption = Low Na+ and water reabsorption = High NaCl in sweat
Endocrine Glands: Low Cl- and water secretion into lumen = High Na+ and water reabsorption = Hyperviscous mucus in lumen
Mucus blocks small passages → Organ damage
Lungs
Liver
Pancreas
Intestines
Increase infection risk
CF: Clinical Presentation
Salty sweat
GI:
Meconium ileus**
Low mucous = No meconium (first stool) passing = Intestinal obstruction
Rectal prolapse
Malabsorption → Failure to thrive
Stunting and wasting
Resp:
Recurrent infections
COPD with bronchiectasis (bronchial dilation)
Wheezing
Dyspnea
CF: Investigations
NBS
Confirmatory tests
PFTs*
CXR and CT
CF: NBS
Positive → Confirmatory test
CF: Confirmatory Tests
Sweat Test
Collect sweat + measure Cl-
Positive: ≥ 60 mmol/L
Borderline → Genetic test
Genetic Test
Screen for carriers
Determine targeted therapy
CF: PFT
Spirometry
Low FEV1:FVC
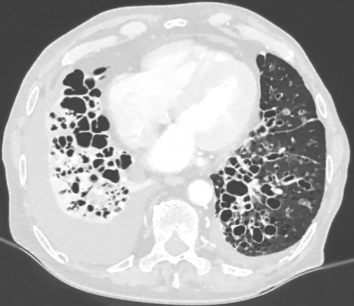
CF: CXR and CT
Air trapping and hyperinflation
Bronchiectasis
CF: Treatment
Antibiotics
Prevent/suppress infections
High-energy diet
Increase nutrition, NaCl, fat-soluble vitamins (ADEK)
Pancreatic enzyme supplements
CFTR modulators
Depend on mutation
CF Treatment: Preserve Lung Function
Pharmacological:
Ibuprofen
Bronchodilators (SABA, LABA)
Mucolytics
Nonpharmacological:
Conventional chest physiotherapy (CPT): Drain mucus
Exercise
CF: Complications
Meconium ileus
Macronutrient malabsorption
Meconium Ileus
Clinical Presentation:
Bilious vomiting
Abdominal distension
Investigation: X-ray with contrast
Dilated small bowel loops (inspissated meconium)
Microcolon (small/narrow colon)
Treatment:
Contrast enema (water-soluble)
Break down stool
Surgery
Macronutrient Malabsorption
Pancreatic duct obstruction = Pancreatic enzyme deficiency (lipase, amylase, protease)