[LEC] CHAPTER 1 PART 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review of Important Concepts
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
1
New cards
RX
alkyl halide
2
New cards
ROH
alcohol
3
New cards
ROR’
ether
4
New cards
RCHO
aldehyde
5
New cards
RCOR’
ketone
6
New cards
RCOOH
carboxylic acid
7
New cards
RCOOR’
ester
8
New cards
RCOOCOR’
acid anhydride
9
New cards
RCOX
acyl chloride
10
New cards
RSO3H
sulphonic acid
11
New cards
RNO2
nitro alkane
12
New cards
RNH2
amine
13
New cards
RCONH2
amide
14
New cards
open-chain
linear structure or not cyclic
15
New cards
cyclic
ring structure
16
New cards
mono, bi, tricyclo
classified based on number of rings
17
New cards
homocyclic and heterocyclic
classified based on ring atoms
18
New cards
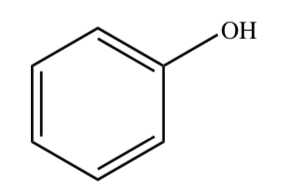
PHENOL
19
New cards
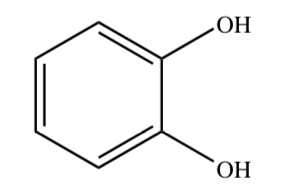
CATECHOL
20
New cards
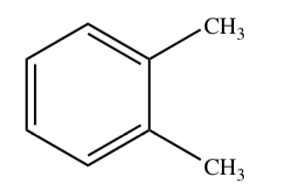
XYLENE (O, M, P)
21
New cards
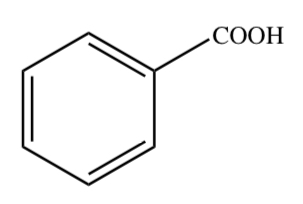
BENZOIC ACID
22
New cards
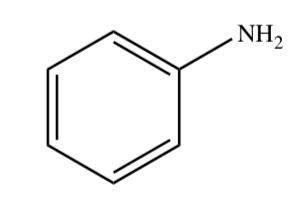
ANILINE
23
New cards
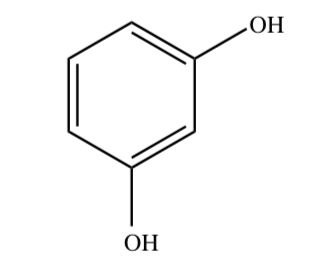
RESORCINOL
24
New cards
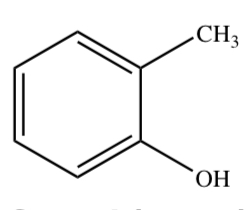
CRESOL (O, M, P)
25
New cards
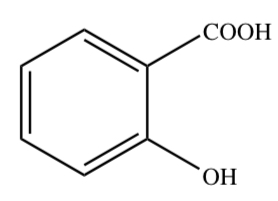
SALICYLIC ACID
26
New cards
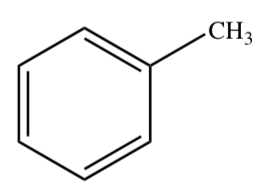
TOLUENE
27
New cards
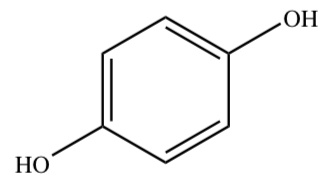
HYDROQUINONE
28
New cards
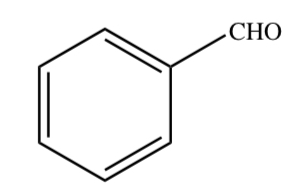
BENZALDEHYDE
29
New cards
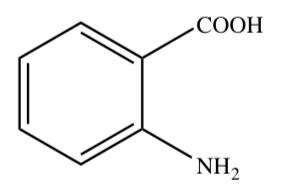
ANTHRANILIC ACID
30
New cards
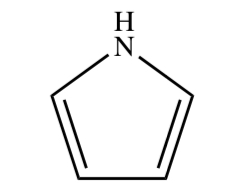
PYRROLE
31
New cards
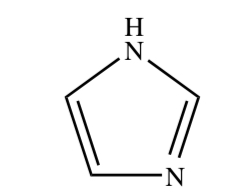
IMIDAZOLE
32
New cards
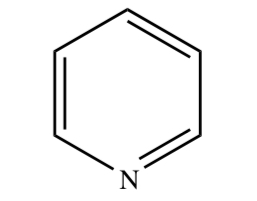
PYRIDINE
33
New cards
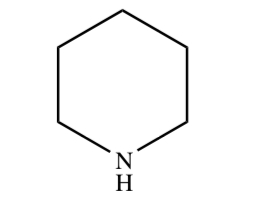
PIPERIDINE
34
New cards
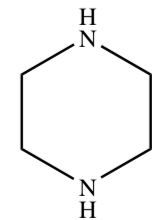
PIPERAZINE
35
New cards
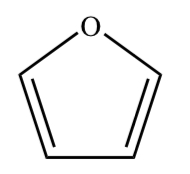
FURAN
36
New cards
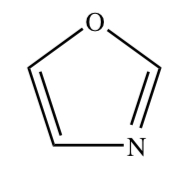
OXAZOLE
37
New cards
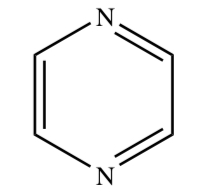
PYRAZINE
38
New cards
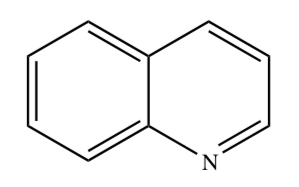
QUINOLINE
39
New cards
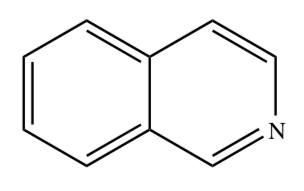
ISOQUINOLINE
40
New cards
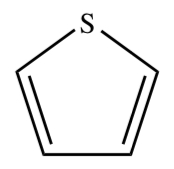
THIOPHENE
41
New cards
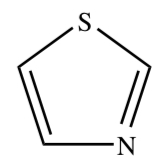
THIAZOLE
42
New cards
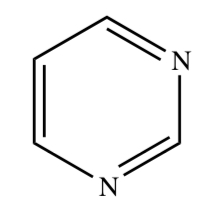
PYRIMIDINE
43
New cards
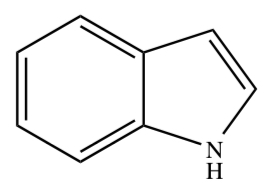
INDOLE
44
New cards
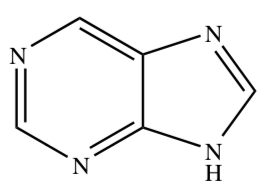
PURINE
45
New cards
CONJUGATED
2 or more c-c double bonds separated by single bonds (alternating)
46
New cards
SATURATED
contains c-c bonds which are purely single bonds
47
New cards
UNSATURATED
at least 1 c-c double or triple bond
48
New cards
ALPHA CARBON
carbon attached to a functional group
49
New cards
VINYLIC/OLEFINIC CARBON
carbon directly holding a double bond
50
New cards
ALLYLIC CARBON
carbon positioned next to a vinylic carbon
51
New cards
BENZYLIC CARBON
carbon positioned next to a benzene
52
New cards
ORTHO
1, 2 placement around a benzene ring
53
New cards
META
1, 3 placement around a benzene ring
54
New cards
PARA
1, 4 placement around a benzene ring
55
New cards
POLAR
water-soluble
56
New cards
NON-POLAR
lipid-soluble
57
New cards
S-IBUPROFEN
isomer A, more potent
58
New cards
RR-IBUPROFEN
isomer B, less potent
59
New cards
one is more potent
s-ibuprofen and r-ibuprofen
60
New cards
both have different uses
quinine and quinidine
61
New cards
QUININE
isomer A, antimalarial
62
New cards
QUINIDINE
isomer B, anti-arrhythmic
63
New cards
one has activity and one has none
cisplatin and transplatin
64
New cards
CISPLATIN
isomer A, active
65
New cards
TRANSPLATIN
isomer B, inactive
66
New cards
one has activity and one is toxic
r-thalidomide and s-thalidomide
67
New cards
R-THALIDOMIDE
isomer A, antiemetic
68
New cards
S-THALIDOMIDE
isomer B, causes birth defects
69
New cards
ABSORPTION
entry of drug from site of administration to the bloodstream