Greenhouse Production 1-4 test
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Romans
Invented the first known greenhouses
Roman greenhouses materials
Stone walls covered with mica
Roman greenhouse heating
Fires burned outside walls to provide warmth
Glass tax repeal
Repeal of the glass tax in 1851 made greenhouses affordable in England
Light consideration
Proper sun exposure increases plant growth and greenhouse success
Natural shading
Trees provide shade in summer to prevent overheating
Orientation
Direction a greenhouse faces affects light and heat efficiency
Foundation
Level and well drained ground supports greenhouse stability
Accessibility
Easy access to water power and pathways improves greenhouse use
Italians
Built the first modern glass greenhouses
Greenhouse
Structure covered with transparent material for growing plants
Range
Two or more greenhouses placed together or connected
Bay
Section of plants with a walkway
House
Short term for greenhouse
Glazing
Material that covers a greenhouse
Attached greenhouse
Connected to another building and usually non commercial
Freestanding greenhouse
Separate structure with its own walls and roof
Connected greenhouse
Multiple greenhouses joined at the gutters
Greenhouse framing materials
Galvanized steel aluminum wood and PVC
Most common large greenhouse framing
Galvanized steel
Best light transmitting glazing
Glass
Least expensive glazing
Polyethylene
Poly lifespan
Usually lasts up to three years
Poly
Short name for polyethylene
Cold frame vs hot bed
Hot beds use extra heat while cold frames rely on sunlight
End wall
Short wall at front or back that supports structure
Side wall
Long wall along sides often used for ventilation
Louvers
Slatted openings that increase airflow
Vents
Roof openings that release heat and moisture
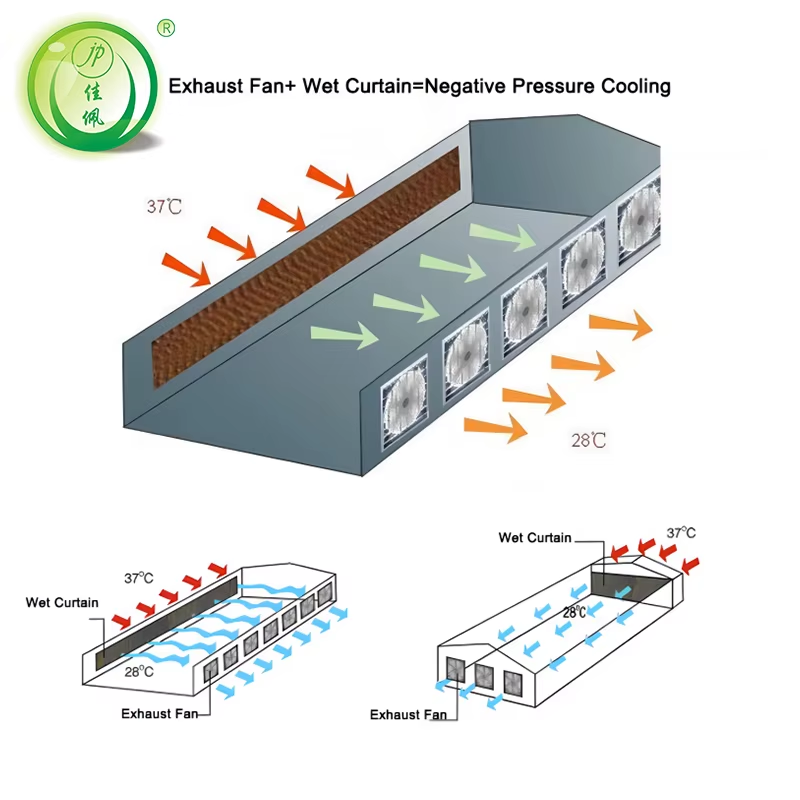
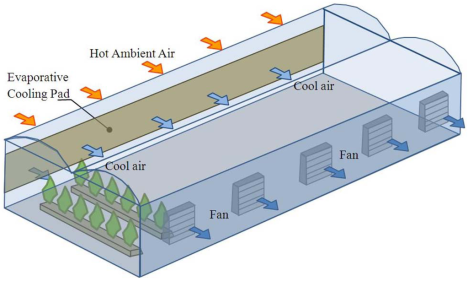
Evaporative cooling system
Fans pull hot air through wet pads to cool the greenhouse
Greenhouse heating systems
Hot water steam forced hot air and infrared
Hot water heating
Heated water circulates through pipes to warm plants
Steam heating
Pressurized steam releases heat through pipes
Forced hot air heating
Heaters blow warm air through the greenhouse
Infrared heating
Radiant heat warms objects instead of air
Exhaust fans
Remove hot humid air from greenhouse
Circulation fans
Mix air evenly inside the greenhouse
Greenhouse flooring types
Concrete porous concrete landscape cloth and gravel
Hand watering
Plants watered manually with hose or can
Overhead sprinklers
Sprinklers above plants that mimic rainfall
Drip irrigation
Water delivered directly to plant roots
Boom irrigation
Moving system that sprays plants evenly
Automated watering
Controlled by timers or sensors
Water trays and saucers
Hold excess water and keep soil moisture steady
Subirrigation types
Capillary mat trough ebb and flow and flood floors
Capillary mat system
Plants absorb water from a wet mat
Trough system
Nutrient solution flows through sloped channels
Ebb and flow system
Benches flood and drain to water plants
Flood floors
Floors flood evenly then drain for irrigation
Thermometer
Tool that shows current temperature
Thermostat
Device that controls heating or cooling systems
Supplemental lighting types
LED HID halide fluorescent induction and incandescent
LED lighting
Energy efficient lights with adjustable plant wavelengths
HID lighting
Very bright lights used for plant growth
Metal halide lighting
Blue light that supports vegetative growth
Fluorescent lighting
Cool lights used for seedlings
Induction lighting
Long lasting efficient full spectrum lights
Incandescent lighting
Inefficient lights that produce excess heat
Photocell benefit
Automatically controls lights to save energy
Photocell
Sensor that responds to light levels
Shade cloth uses
Reduces heat and prevents plant damage
Type II glazing
Fiberglass reinforced polycarbonate or acrylic
Type II glazing cons
Loses light over time and is highly flammable
BTU
Unit that measures heat energy
BTU formula
Thermal resistance times temperature difference
Subirrigation
Watering plants from the root zone
Type III glazing
Glass
Greenhouse fan types
Exhaust fans and circulation fans
Negative pressure system
Exhaust fans pull air in through cooling pads
Igloo

Lean-to

Shade house
Gothic
Ridge and furrow

A-frame
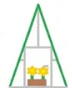
Uneven

Skillion

Sawtooth
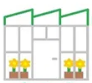
Tri-penta
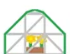
Dome

Tunnel

Flat arch
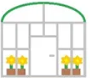
Gable

Uneven span
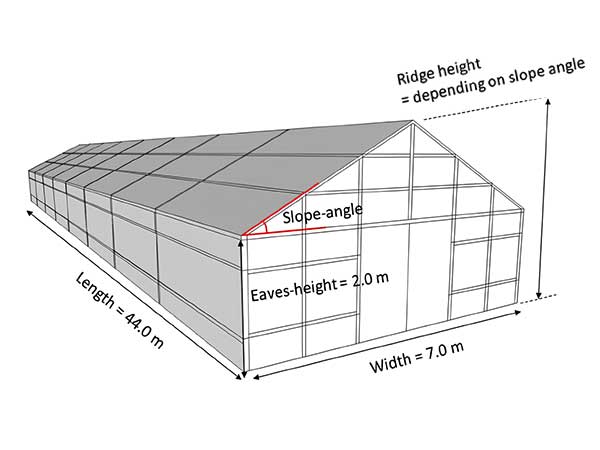
Even span

Quonset
